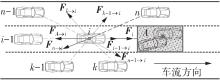
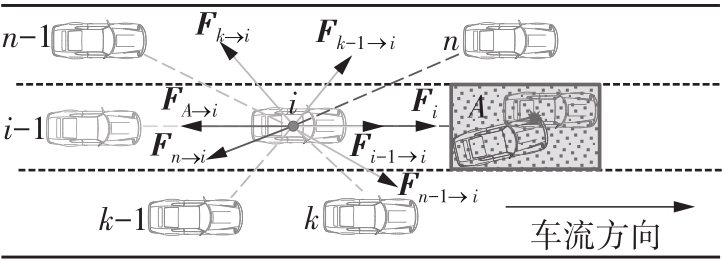
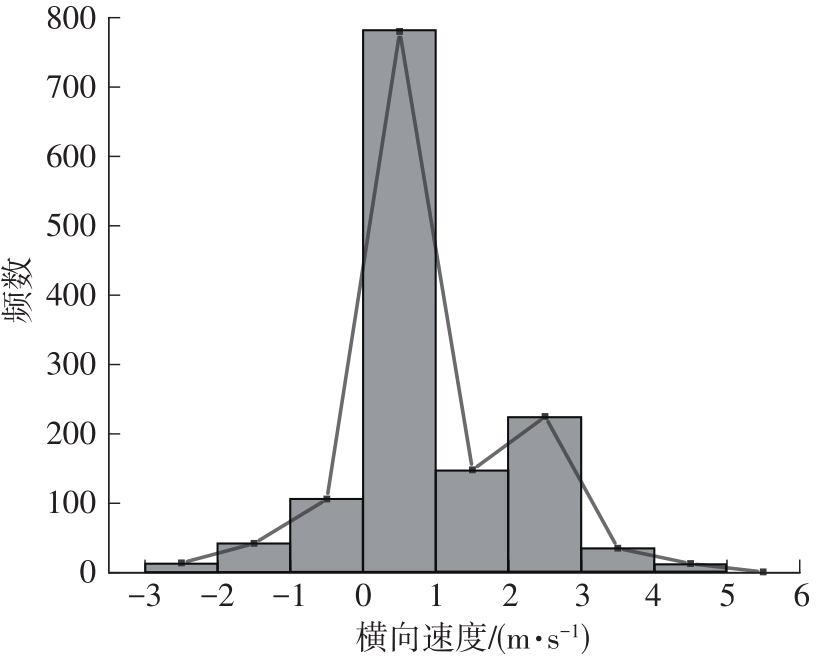
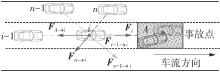
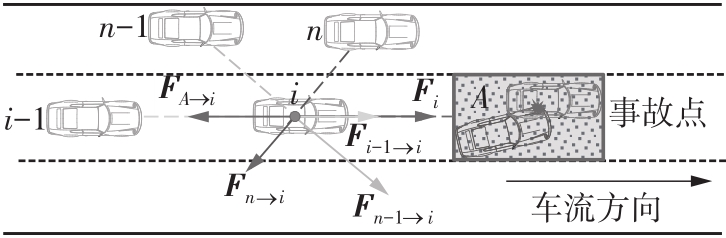
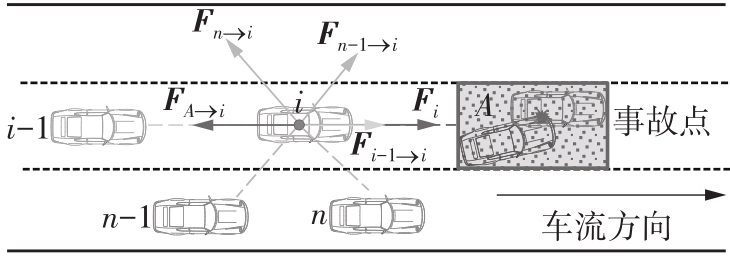
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (7): 66-75.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210787
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Cooperative Lane Change Decision-Making Model of Bottleneck Emergency Section in Weaving Area Based on Social Force
QIN Yaqin1 QIAN Zhengfu1 XIE Jiming1 LIU Bing2 ZHAO Rongda2 WANG Yueran3 HUANG Lei3
- 1.Faculty of Transportation Engineering,Kunming University of Science and Technology,Kunming 650500,Yunnan,China
2.Yunnan Communications Investment & Construction Group Co. ,Ltd. ,Kunming 650103,Yunnan,China
3.Yunnan Science Research Institute of Communication Co. ,Ltd. ,Kunming 650011,Yunnan,China
-
Received:2021-12-10Online:2022-07-25Published:2022-04-22 -
Contact:谢济铭(1994-),男,博士,主要从事城市干道交通状态识别与演变研究。 E-mail:xiejiming@stu.kust.edu.cn -
About author:秦雅琴(1972-),女,博士,教授,主要从事交通系统安全与仿真研究。E-mail:qinyaqin@kust.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(71861016);the National Key Research and Development Program of China(2018YFB1600500)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
QIN Yaqin, QIAN Zhengfu, XIE Jiming, et al. Cooperative Lane Change Decision-Making Model of Bottleneck Emergency Section in Weaving Area Based on Social Force[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(7): 66-75.
share this article
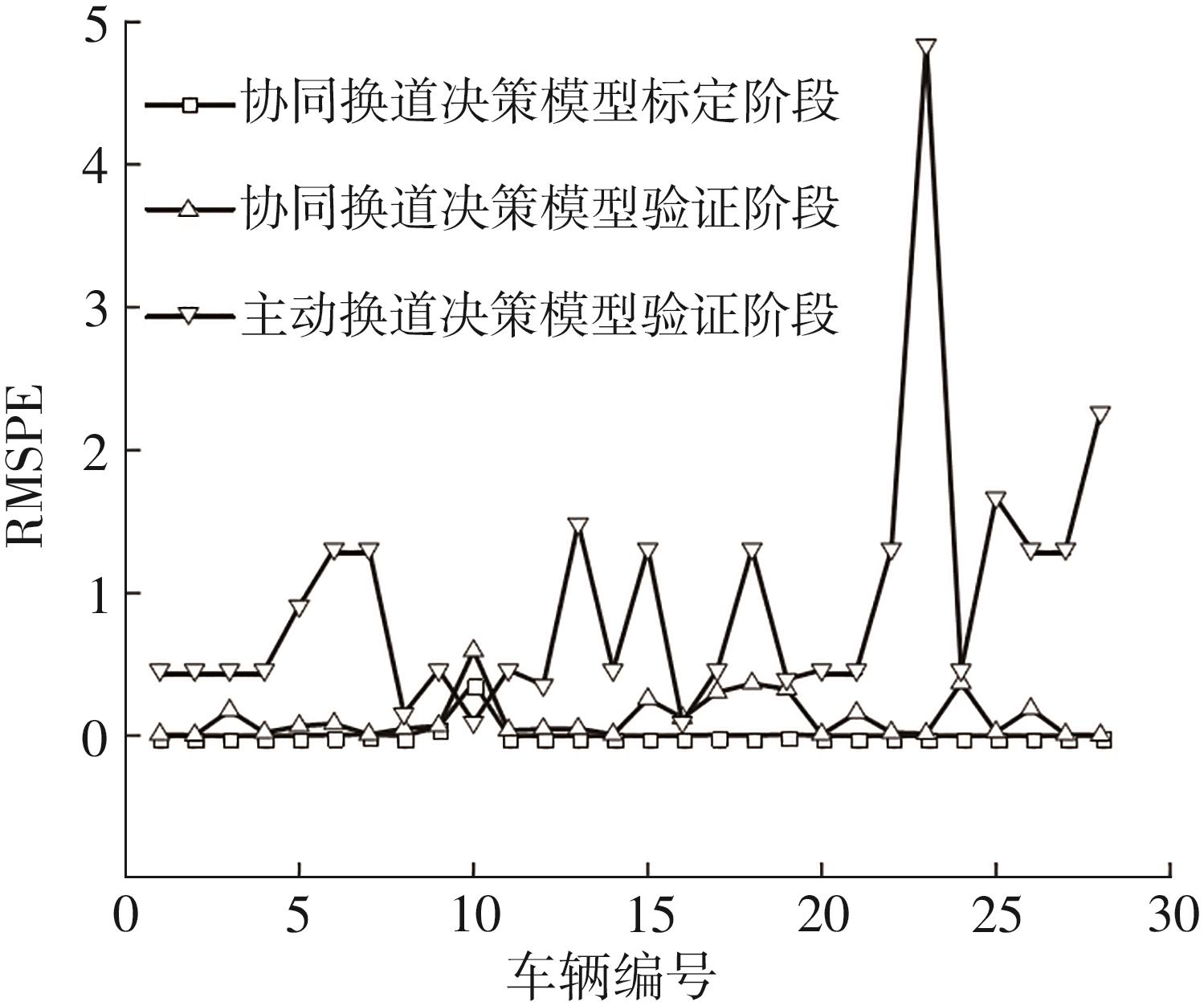
Table 2
Calibrated parameters of model"
| 参数 | 参数描述 | 参数范围 | 平均值 | 标准差 | 5% 分位数 | 95% 分位数 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| α | 期望速度修正系数 | [-10.09,12.13] | 1.612 | 10.892 | 2.918 | 3.465 |
| β | 从众系数 | [-13.52,24.84] | 1.279 | 9.502 | 2.194 | 4.974 |
| χ | 对后车的排斥强度 | [0.17,38.42] | 6.658 | 8.069 | 0.766 | 22.179 |
| δ | 对后车排斥力的作用范围 | [2.63,76.76] | 18.558 | 17.128 | 5.538 | 45.270 |
| ε | 对相邻车道前后车辆的排斥强度 | [1.02,66.22] | 13.339 | 12.228 | 5.093 | 36.456 |
| ? | 受相邻车道车辆排斥力的作用范围 | [7.77,97.43] | 26.356 | 22.517 | 11.623 | 68.838 |
| φ | 对事故车辆(障碍物)的排斥强度 | [4.13,99.51] | 27.020 | 19.334 | 12.653 | 71.623 |
| γ | 受事故车辆(障碍物)排斥力的作用范围 | [3.15,100] | 31.462 | 26.190 | 12.344 | 85.709 |
|
| [1] | QIU Yudong, WANG Zhan, XIE Zhishen. Optimization for Steel Frames with Semirigid Connections Based on Hybrid Algorithms [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 72-77. |
| [2] | WENG Jiancheng, WANG Maolin, LIN Pengfei, et al. Cross-line Combined Bus Scheduling Optimization Method Based on Passenger Flow Characteristic Identification [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 39-48. |
| [3] | ZHENG Yajing, LI Yaohui, JIN Wenzhou. Connection Scheme Optimization of Last Trains of Urban Mass Transit Network Based on Considering the Transfer Passengers [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(5): 32-39,72. |
| [4] | XIA Qinxiang, LI Kai, MA Jun, et al. Die Electrode Scheduling Problem Solution Based on Genetic Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 80-87. |
| [5] | ZHOU Zhong, DENG Zhuoxiang, CHEN Yun, et al. Strength Prediction of Foam Light Soil Based on GA-BP Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(11): 125-132. |
| [6] | LIU Xuan, WANG Zihang, ZHANG Tongrui, et al. Optimal Control Strategy for Lateral Stability of Port Heavy-Duty AGV [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(8): 113-121. |
| [7] | LI Jing WANG Chen ZHANG Jiaxu. Vehicle Speed Estimation Based on UniTire Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(5): 47-55. |
| [8] | LUO Yutao, ZHOU Tianyang, XU Xiaotong. Time-Varying LQR Control of Four-Wheel Steer /Drive Vehicle Based on Genetic Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(3): 114-122. |
| [9] | JIN Gang HE Zhihao WANG Yingjun. 5G Frequency Selection Surface Shape Optimization Method Based on Genetic Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(11): 95-105. |
| [10] | WEN Huiying, LIN Yifeng, WU Haoshu, et al. Extended Co-evolutionary Algorithm for Path Planning Based on the Urban Traffic Environment Evolution [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(10): 1-10. |
| [11] | LI Jiale LIU Zhenbo WANG Xuefei. Distribution Path Optimization of Electric Vehicles Considering Charging and Discharging Strategy in Smart Grid [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(10): 31-40. |
| [12] | JIN Wenzhou, HU Weiyang, DENG Jiayi, et al. Flexible Scheduling Model of Demand Response Transit Based on Hybrid Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(1): 123-133. |
| [13] | LIU Gang, GUO Deming, ZHENG Wencheng, et al. Axial Thermal Circuit Model-Based Calculation of Contact Resistance of Contact Surface Between the Overhead Ground Wire and Armor Rod [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(7): 9-19. |
| [14] | LI Haijian, ZHAO Guoqiang, YANG Yanfang, et al. Characteristics of Vehicle Spatiotemporal Diagram Under the Emergency Braking Warning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(7): 76-84. |
| [15] | ZHAO Xing JI Kang LIN Hao XU Peng. Resource Allocation Model Based on Multi-objective Path Planning in Emergency Management [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(4): 76-82. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||