Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (11): 62-73.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210715
Special Issue: 2022年生物工程
• Biological Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Effects of Vitamin D Supplement on Gut Microbiota in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients
HAN Yuanping1 XU Siya1 JIAN Xile2
- 1.College of Life Sciences,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610065,Sichuan,China
2.West China Hospital,Sichuan University,Chengdu 610041,Sichuan,China
-
Received:2021-11-12Online:2022-11-25Published:2022-02-11 -
Contact:徐思雅(1995-),女,硕士研究生,主要从事肠道菌群、非酒精性脂肪肝病研究。 E-mail:408204850@qq.com -
About author:韩源平(1959-),男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事组织损伤修复、纤维化、肝硬化等研究.Email:hanyp@scu.edu.cn. -
Supported by:the Science and Technology Program of Sichuan Province(20ZDYF0122)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
HAN Yuanping, XU Siya, JIAN Xile . Effects of Vitamin D Supplement on Gut Microbiota in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Patients[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(11): 62-73.
share this article
Table 1
Mean serum 25(OH)D levels in NAFLD patients during the clinical treatment"
| 试验对象 | 第0天 | 第0天均值 | 第30天 | 第30天均值 | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 组别 | 患者编号 | ||||
| 对照组 | 患者1 | 59.00 | 46.26 ± 4.15 | 46.23 | 48.31 ± 5.02A |
| 患者2 | 28.38 | 36.13 | |||
| 患者3 | 56.11 | 50.29 | |||
| 患者4 | 70.00 | 52.96 | |||
| 患者5 | 44.61 | 63.79 | |||
| 患者6 | 49.70 | 67.75 | |||
| 患者7 | 58.79 | 51.34 | |||
| 患者8 | 41.64 | 30.38 | |||
| 患者9 | 42.44 | 29.61 | |||
| 患者10 | 25.25 | 24.07 | |||
| 患者11 | 21.19 | 22.89 | |||
| 患者12 | 34.64 | 43.95 | |||
| 患者13 | 32.31 | 38.57 | |||
| 患者14 | 67.12 | 71.20 | |||
| 患者15 | 55.86 | 63.33 | |||
| VD组 | 患者1 | 38.63 | 54.20 ± 4.92a | 61.27 | 70.78 ± 5.25Bb |
| 患者2 | 25.31 | 55.47 | |||
| 患者3 | 59.74 | 96.43 | |||
| 患者4 | 91.13 | 76.30 | |||
| 患者5 | 37.14 | 65.61 | |||
| 患者6 | 48.61 | 80.19 | |||
| 患者7 | 46.78 | 63.89 | |||
| 患者8 | 64.30 | 65.20 | |||
| 患者9 | 47.96 | 111.60 | |||
| 患者10 | 64.94 | 77.58 | |||
| 患者11 | 65.20 | 81.85 | |||
| 患者12 | 24.64 | 36.45 | |||
| 患者13 | 70.47 | 77.12 | |||
| 患者14 | 56.78 | 77.19 | |||
Table 2
Variation of mean biochemistry index in NAFLD patients during the clinical treatment"
| 指标 | 对照组 (n=15) | VD组 (n=14) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第0天 | 第30天 | 第0天 | 第30天 | |
| ALT/ (U·L-1) | 113.60 ± 12.42 | 87.60 ± 17.53 | 132.10 ± 13.66a | 75.50 ± 7.07b |
| AST/ (U·L-1) | 66.33 ± 7.99 | 55.47 ± 9.82 | 75.36 ± 8.82 | 60.14 ± 7.73 |
| ALP/ (U·L-1) | 110.10 ± 10.52 | 108.90 ± 9.20 | 99.50 ± 5.75 | 107.10 ± 6.92 |
| GGT/ (U·L-1) | 119.80 ± 39.02 | 71.00 ± 16.01 | 76.00 ± 20.67 | 59.64 ± 12.85 |
| TP/ (g·L-1) | 74.71 ± 2.00 | 77.84 ± 1.41 | 73.83 ± 1.40a | 77.30 ± 1.41b |
| ALB/ (g·L-1) | 45.13 ± 1.58 | 45.64 ± 0.812A | 46.77 ± 1.07a | 48.75 ± 1.18Bb |
| GLO/ (g·L-1) | 29.78 ± 1.11a | 32.37 ± 1.33b | 27.37 ± 1.00 | 28.73 ± 1.24 |
| TBIL/ (μmol·L-1) | 18.98 ± 4.00 | 15.90 ± 2.38 | 15.15 ± 2.31 | 13.47 ± 1.92 |
| DBIL/ (μmol·L-1) | 6.68 ± 2.27 | 5.78 ± 1.31 | 5.14 ± 1.17 | 4.35 ± 0.85 |
| IBIL/ (μmol·L-1) | 12.30 ± 1.83 | 10.98 ± 1.42 | 9.84 ± 1.29 | 9.12 ± 1.25 |
| TBA/ (μmol·L-1) | 20.36 ± 9.32 | 9.04 ± 2.76 | 7.22 ± 1.35 | 6.54 ± 1.06 |
| UREA/ (mmol·L-1) | 4.07 ± 0.28 | 4.02 ± 0.26A | 4.52 ± 0.24 | 4.96 ± 0.31B |
| CR/ (μmol·L-1) | 65.87 ± 3.37 | 66.41 ± 2.99 | 67.21 ± 3.09 | 68.93 ± 3.56 |
| UA/ (μmol·L-1) | 381.60 ± 20.33 | 387.80 ± 21.47 | 409.90 ± 25.22 | 405.70 ± 22.74 |
| CA/ (mmol·L-1) | 2.39 ± 0.04 | 2.40±0.03 | 2.41 ± 0.03a | 2.47 ± 0.03b |
| P/ (mmol·L-1) | 1.07± 0.04a | 0.94 ± 0.04b | 0.90 ± 0.05 | 0.95 ± 0.05 |
| GLU/ (mmol·L-1) | 7.86 ± 2.82 | 5.19 ± 0.13 | 5.16 ± 0.14 | 5.00 ± 0.21 |
| INS/ (μlu·mL-1) | 11.78 ± 1.19 | 11.65 ± 1.61 | 16.51 ± 2.85 | 12.28 ± 1.07 |
| CHOL/ (mmol·L-1) | 4.69 ± 0.24 | 4.45 ± 0.22 | 4.53± 0.18 | 4.41 ± 0.22 |
| TG/ (mmol·L-1) | 1.68 ± 0.18 | 1.51 ± 0.11 | 2.26 ± 0.45 | 1.69 ± 0.19 |
| HDL-C/ (mmol·L-1) | 1.24 ± 0.05 | 1.25 ± 0.06A | 1.06 ± 0.05 | 1.03 ± 0.05B |
| LDL-C/ (mmol·L-1) | 2.98 ± 0.26 | 2.93 ± 0.23 | 2.87 ± 0.15 | 2.99 ± 0.26 |
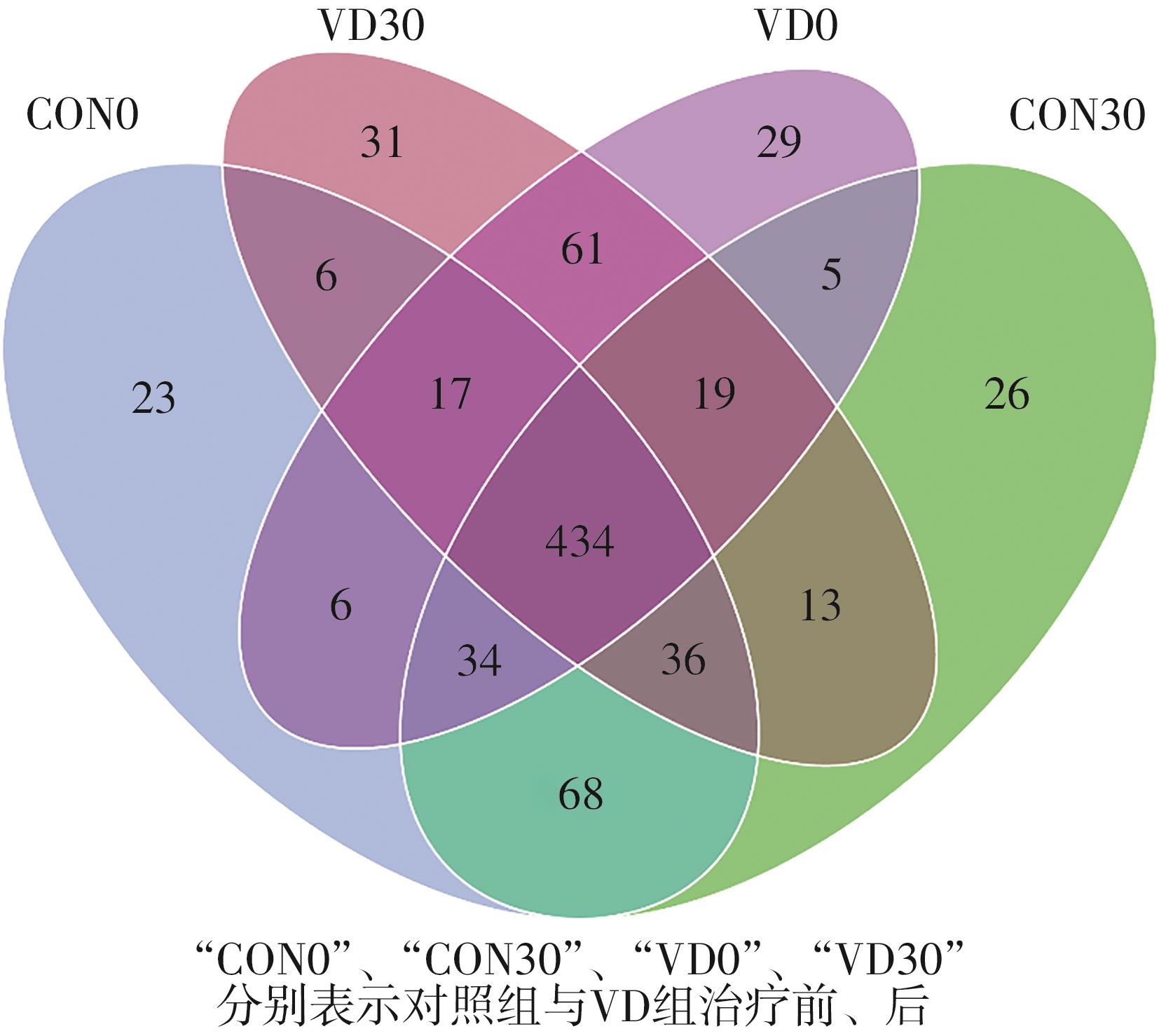
Table 4
Top 10 abundant taxa at family levels of gut microbiota in NAFLD patients"
| 分类群 | 对照组(n=15) | VD组(n=14) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第0天 | 第30天 | 第0天 | 第30天 | |
| F_Bacteroidaceae | 29.98 ± 5.214 | 31.47 ± 5.355 | 42.68 ± 6.255 | 36.80 ± 5.992 |
| F_Prevotellaceae | 16.98 ± 5.743 | 12.33 ± 4.565 | 14.73 ± 5.633 | 17.08 ± 6.033 |
| F_Lachnospiraceae | 18.69 ± 1.989 | 21.26 ± 3.276A | 17.62 ± 2.459a | 16.68 ± 2.467Bb |
| F_Ruminococcaceae | 12.44 ± 2.032 | 15.00 ± 3.237 | 6.891 ± 1.608 | 10.68 ± 2.633 |
| F_Veillonellaceae | 4.991 ± 1.630 | 5.097 ± 1.877 | 6.462 ± 2.121 | 5.657 ± 2.252 |
| F_Rikenellaceae | 4.155 ± 1.315 | 3.272 ± 0.655 | 1.322 ± 0.572 | 2.043 ± 0.818 |
| F_Streptococcaceae | 0.042 ± 0.009 | 0.080 ± 0.041 | 1.254 ± 1.199 | 0.039 ± 0.015 |
| F_Tannerellaceae | 3.021 ± 0.830 | 2.958 ± 0.791 | 2.604 ± 1.024 | 2.564 ± 0.530 |
| F_Fusobacteriaceae | 0.140 ± 0.073 | 0.280 ± 0.201 | 1.472 ± 0.947 | 0.886 ± 0.351 |
| F_Erysipelotrichaceae | 0.519 ± 0.101 | 0.470 ± 0.091 | 0.380 ± 0.100a | 0.672 ± 0.162b |
Table 5
Top 10 abundant taxa at genus levels of gut microbiota in NAFLD patients"
| 分类群 | 对照组(n=15) | VD组(n=14) | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 第0天 | 第30天 | 第0天 | 第30天 | |
| G_Bacteroides | 29.98 ± 5.214 | 31.47 ± 5.355 | 42.68 ± 6.255 | 36.80 ± 5.992 |
| G_Faecalibacterium | 5.335 ± 1.142 | 7.547 ± 2.167 | 2.993 ± 0.842 | 5.864 ± 2.405 |
| G_Megamonas | 2.825 ± 1.507 | 2.516 ± 1.173 | 4.823 ± 2.106 | 4.503 ± 2.101 |
| G_Lachnospira | 6.916 ± 1.483 | 7.643 ± 1.929 | 5.019 ± 0.943 | 3.916 ± 0.832 |
| G_Roseburia | 2.039 ± 0.561 | 3.851 ± 1.631 | 3.316 ± 0.941 | 2.301 ± 0.720 |
| G_unidentified_Prevotellaceae | 0.149 ± 0.087 | 0.327 ± 0.312 | 1.866 ± 0.957 | 2.774 ± 1.678 |
| G_Alistipes | 4.123 ± 1.316 | 3.256 ± 0.658 | 1.322 ± 0.572 | 2.042 ± 0.818 |
| G_Streptococcus | 0.041 ± 0.008 | 0.079 ± 0.041 | 1.254 ± 1.199 | 0.038 ± 0.015 |
| G_Dialister | 1.686 ± 0.761 | 1.610 ± 1.116 | 1.381 ± 0.884 | 0.949 ± 0.799 |
| G_unidentified_Erysipelotrichaceae | 0.257 ± 0.063 | 0.237 ± 0.056 | 0.181 ± 0.053a | 0.345 ± 0.085b |
| 1 | FRIEDMAN S L, NEUSCHWANDER-TETRI B A, RINELLA M,et al .Mechanisms of NAFLD development and therapeutic strategies [J].Nature Medicine,2018,24(7):908-922. |
| 2 | VERNON G, BARANOVA A, YOUNOSSI Z M .Systematic review:the epidemiology and natural history of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and non-alcoholic steatohepatitis in adults [J].Alimentary Pharmacology and Therapeutics,2011,34(3):274-285. |
| 3 | YOUNOSSI Z M, KOENIG A B, ABDELATIF D,et al .Global epidemiology of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease-meta-analytic assessment of prevalence,incidence,and outcomes [J].Hepatology,2016,64(1):73-84. |
| 4 | ZHOU J, ZHOU F, WANG W,et al .Epidemiological features of NAFLD From 1999 to 2018 in China [J].Hepatology,2020,71(5):1851-1864. |
| 5 | ESTES C, ANSTEE Q M, ARIAS-LOSTE M,et al .Modeling NAFLD disease burden in China,France,Germany,Italy,Japan,Spain,United Kingdom,and United States for the period 2016—2030 [J].Journal of Hepatology,2018,69(4):896-904. |
| 6 | POLYZOS S A, KOUNTOURAS J, MANTZOROS C S .Obesity and nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:from pathophysiology to therapeutics [J].Metabolism,2019,92:82-97. |
| 7 | ISSA D, PATEL V, SANYAL A J .Future therapy for non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J].Liver International,2018,38(S1):56-63. |
| 8 | DAY C P, JAMES O F W .Steatohepatitis:a tale of two "hits"?[J].Gastroenterology,1998,114(4):842-845. |
| 9 | TILG H, MOSCHEN A R .Evolution of inflammation in nonalcoholic fatty liver disease:the multiple parallel hits hypothesis [J].Hepatology,2010,52(5):1836-1846. |
| 10 | CHASSAING B, ETIENNE-MESMIN L, GEWIRTZ A T .Microbiota-liver axis in hepatic disease [J].Hepatology,2014,59(1):328-339. |
| 11 | PENDYALA S, WALKER J M, HOLT P R .A high-fat diet is associated with endotoxemia that originates from the gut [J].Gastroenterology,2012,142(5):1100-1101. |
| 12 | HENAO-MEJIA J, ELINAV E, STROWIG T,et al .Inflammasomes:far beyond inflammation [J].Nature Immunology,2012,13(4):321-324. |
| 13 | SHEN F, ZHENG Rui-Dan, SUN Xing-Qiang,et al .Gut microbiota dysbiosis in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J].Hepatobiliary & Pancreatic Diseases International,2017,16(4):375-381. |
| 14 | SCHWIMMER J B, JOHNSON J S, ANGELES J E,et al .Microbiome signatures associated with steatohepatitis and moderate to severe fibrosis in children with nonalcoholic fatty liver disease [J].Gastroenterology,2019,157(4):1109-1122. |
| 15 | ZHU L, BAKER S S, GILL C,et al .Characterization of gut microbiomes in nonalcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) patients:a connection between endogenous alcohol and NASH [J].Hepatology,2013,57(2):601-609. |
| 16 | PARK D, KWON H, OH S W,et al .Is vitamin D an independent risk factor of nonalcoholic fatty liver disease?:a cross-sectional study of the healthy population [J].Journal of Korean Medical Science,2017,32(1):95-101. |
| 17 | KIM H S, ROTUNDO L, KOTHARI N,et al .Vitamin D is associated with severity and mortality of non-alcoholic fatty liver disease:a US population-based study [J].Journal of Clinical and Translational Hepatology,2017,5(3):185-192. |
| 18 | TARGHER G, BERTOLINI L, SCALA L,et al .Associations between serum 25-hydroxyvitamin D3 concentrations and liver histology in patients with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J].Nutrition,Metabolism and Cardiovascular Diseases,2007,17(7):517-524. |
| 19 | ELIADES M, SPYROU E, AGRAWAL N,et al .Meta-analysis:vitamin D and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease [J].Alimentary Pharmacology & Therapeutics,2013,38(3):246-254. |
| 20 | SU D, NIE Y, ZHU A,et al .Vitamin D signaling through induction of paneth cell defensins maintains gut microbiota and improves metabolic disorders and hepatic steatosis in animal models [J].Frontiers in Physiology,2016,7:498. |
| 21 | LUTHOLD R V, FERNANDES G R, FRANCO-DE-MORAES A C,et al .Gut microbiota interactions with the immunomodulatory role of vitamin D in normal individuals [J].Metabolism,2017,69:76-86. |
| 22 | KANHERE M, HE J, CHASSAING B,et al .Bolus weekly vitamin D3 supplementation impacts gut and airway microbiota in adults with cystic fibrosis:a double-blind,randomized,placebo-controlled clinical trial [J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology & Metabolism,2018,103(2):564-574. |
| 23 | GHALY S, KAAKOUSH N O, LLOYD F,et al .High dose vitamin D supplementation alters faecal microbiome and predisposes mice to more severe colitis [J].Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):11511. |
| 24 | WATERHOUSE M, HOPE B, KRAUSE L,et al .Vitamin D and the gut microbiome:a systematic review of in vivo studies [J].European Journal of Nutrition,2019,58(7):2895-2910. |
| 25 | YUE S, ZHAO D, PENG C,et al .Effects of theabrownin on serum metabolites and gut microbiome in rats with a high-sugar diet [J].Food & Function,2019,10(11):7063-7080. |
| 26 | 廖祥鹏,张增利,张红红,等,维生素D与成年人骨骼健康应用指南(2014年标准版) [J].中国骨质疏松杂志,2014,20(9):1011-1030. |
| LIAO Xiang-peng, ZHANG Zeng-li, ZHANG Hong-hong,et al .Application guideline for vitamin D and bone health in adult Chinese ( 2014 standard edition) [J].Chinese Journal of Osteoporosis,2014,20(9):1011-1030. | |
| 27 | YU S, FANG H, HAN J,et al .The high prevalence of hypovitaminosis D in China:a multicenter vitamin D status survey [J].Medicine,2015,94(8):e585/1-6. |
| 28 | 程义勇 .《中国居民膳食营养素参考摄入量》2013修订版简介 [J].营养学报,2014,36(4):313-317. |
| CHENG Yi-yong,Introduction to the Chinese Dietary Reference Intakes (2013 Revised Edition) [J].Acta Nutrimenta Sinica,2014,36(4):313-317. | |
| 29 | HOLICK M F, BINKLEY N C, BISCHOFF-FERRARI H A,et al .Evaluation,treatment,and prevention of vitamin D deficiency:an endocrine society clinical practice guideline [J].The Journal of Clinical Endocrinology and Metabolism,2011,96(7):1911-1930. |
| 30 | AMIRI H L, AGAH S, AZAR J T,et al .Effect of daily calcitriol supplementation with and without calcium on disease regression in non-alcoholic fatty liver patients following an energy-restricted diet:randomized,controlled,double-blind trial [J].Clinical Nutrition,2017,36(6):1490-1497. |
| 31 | SHARIFI N, AMANI R, HAJIANI E,et al .Does vitamin D improve liver enzymes,oxidative stress,and inflammatory biomarkers in adults with non-alcoholic fatty liver disease?a randomized clinical trial [J].Endocrine,2014,47(1):70-80. |
| 32 | 曾义岚,韩源平,王丽,等,维生素D缺乏与非酒精性脂肪性肝病的关系及机制 [J].中国肝脏病杂志(电子版),2019,11(1):12-16. |
| ZENG Yi-lan, HAN Yuan-ping, WANG Li,et al .Relationship between vitamin D deficiency and non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and its mechanism [J].Chinese Journal of Liver Diseases (Electronic Version),2019,11(1):12-16. | |
| 33 | ZENG Y, LUO M, PAN L,et al .Vitamin D signaling maintains intestinal innate immunity and gut microbiota:potential intervention for metabolic syndrome and NAFLD [J].American Journal of Physiology-Gastrointestinal and Liver Physiology,2020,318(3):G542-G553. |
| 34 | KAMEYAMA K, ITOH K,Intestinal colonization by a Lachnospiraceae bacterium contributes to the development of diabetes in obese mice [J].Microbes and Environments,2014,29(4):427-430. |
| 35 | ZENG H, ISHAQ S L, ZHAO F Q,et al .Colonic inflammation accompanies an increase of beta-catenin signaling and Lachnospiraceae/Streptococcaceae bacteria in the hind gut of high-fat diet-fed mice [J].The Journal of Nutritional Biochemistry,2016,35:30-36. |
| 36 | KISHIDA Y, OKUBO H, OHNO H,et al .Effect of miglitol on the suppression of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis development and improvement of the gut environment in a rodent model [J].Journal of Gastroenterology,2017,52(11):1180-1191. |
| 37 | CAVALLARI J F, POKRAJAC N T, ZLITNI S,et al .NOD2 in hepatocytes engages a liver-gut axis to protect against steatosis,fibrosis,and gut dysbiosis during fatty liver disease in mice [J].American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism,2020,319(2):E305-E314. |
| 38 | BOSMAN E S, ALBERT A Y,LUI H,et al .Skin exposure to narrow band ultraviolet (UVB) light modulates the human intestinal microbiome [J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2019,10:2410. |
| [1] | XU Mingfang LI Ming SHEN Linyan CHEN Gengnan WANG Yangyang. Simultaneous Determination of Ergosterol and VD2 Content in Lentinus edodes Based on LC-MS /MS Method [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(3): 109-118. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||