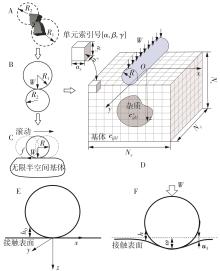
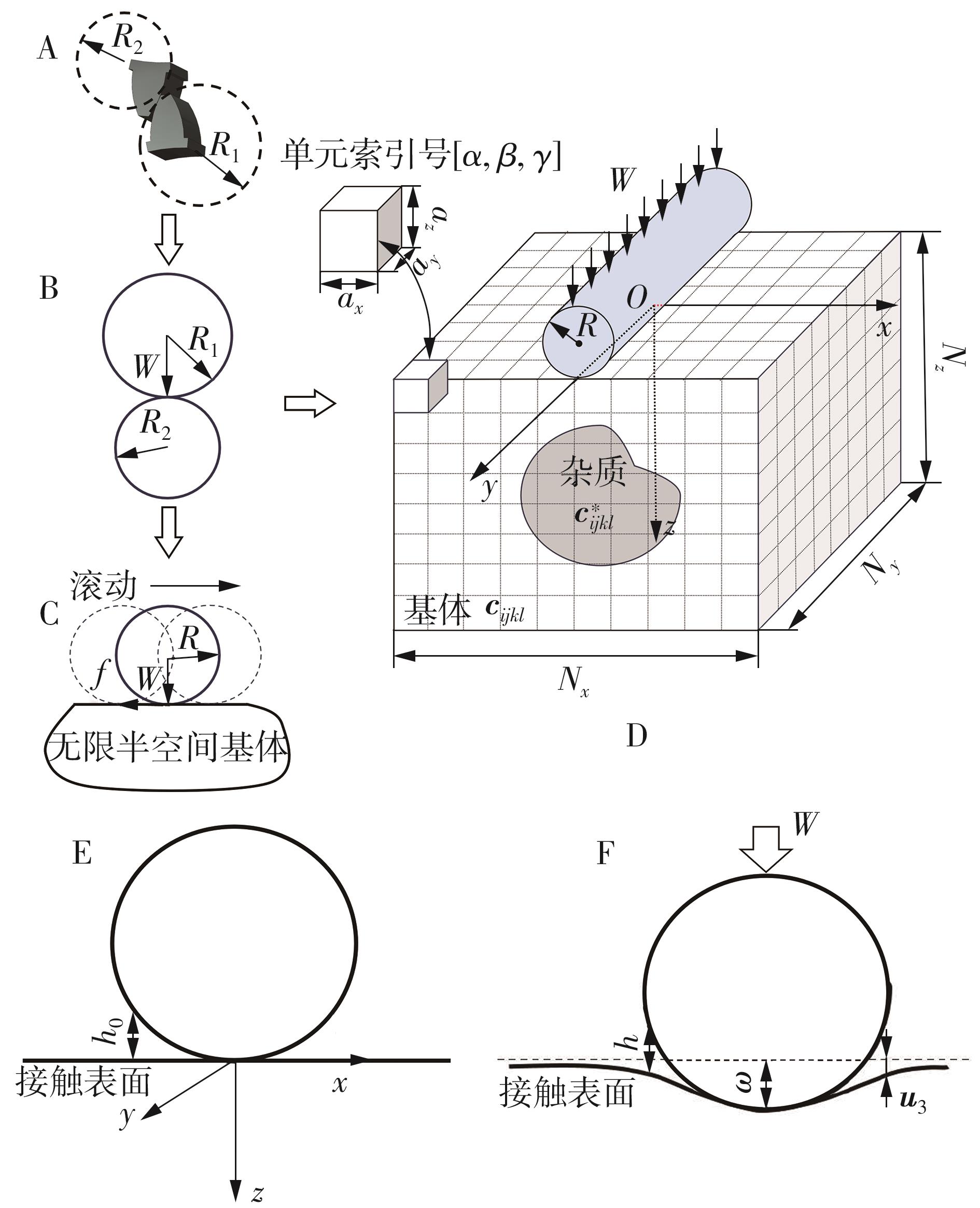
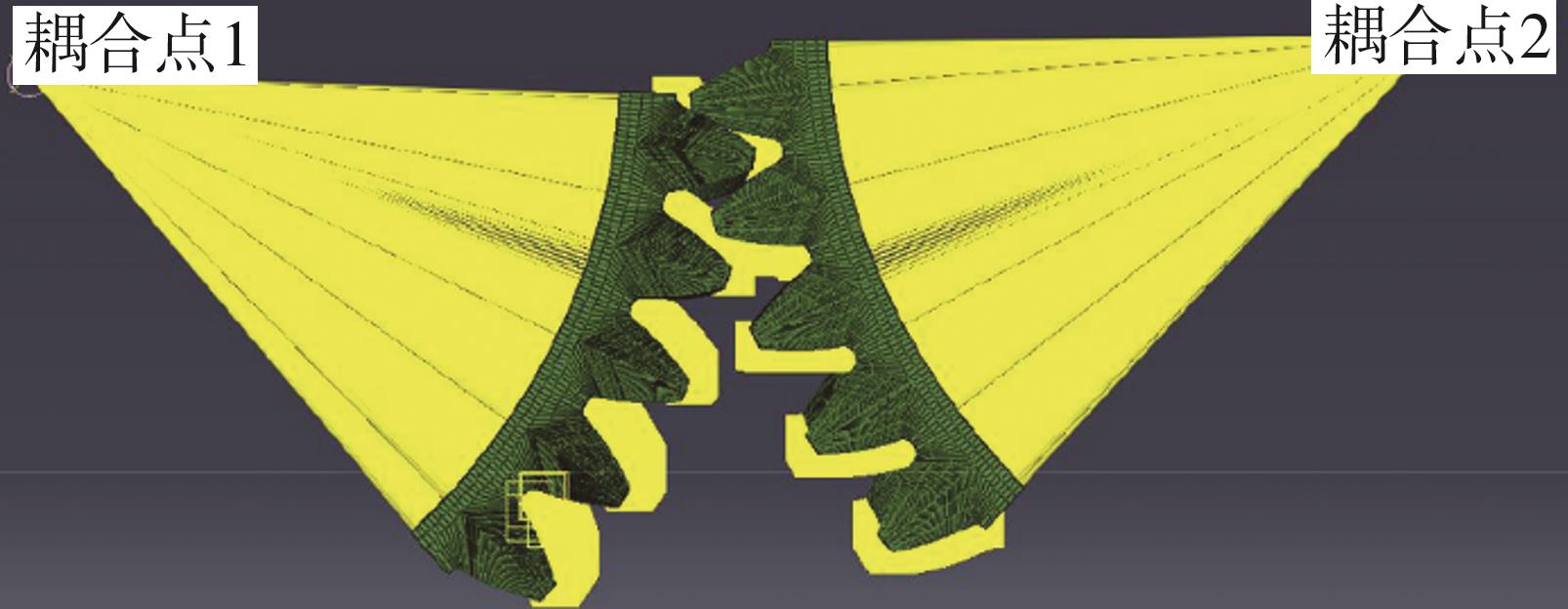
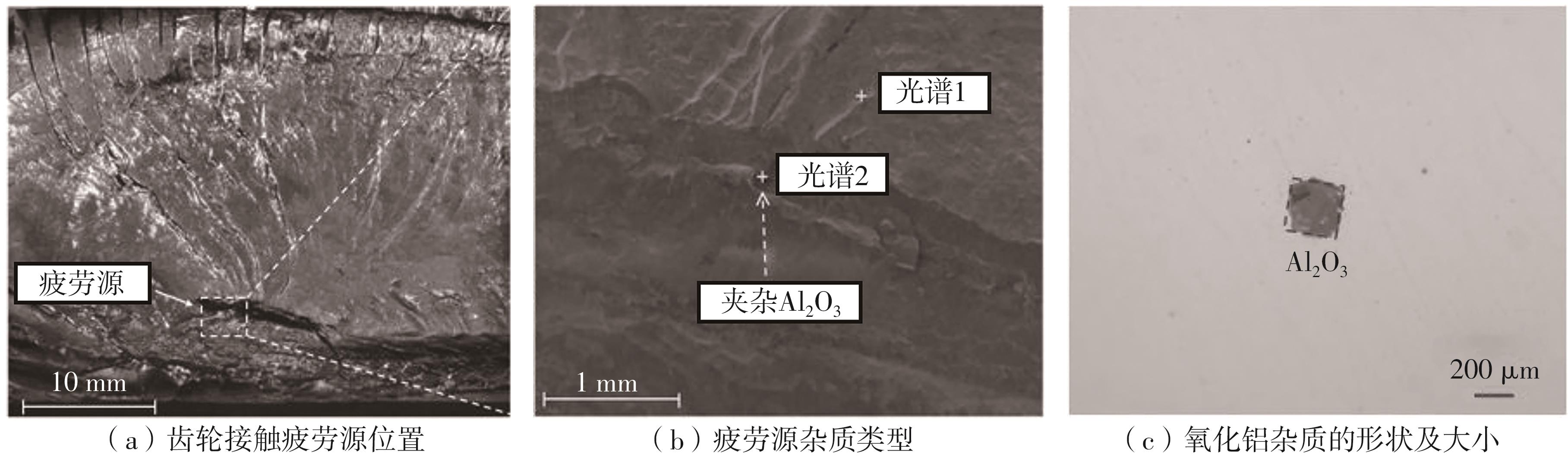
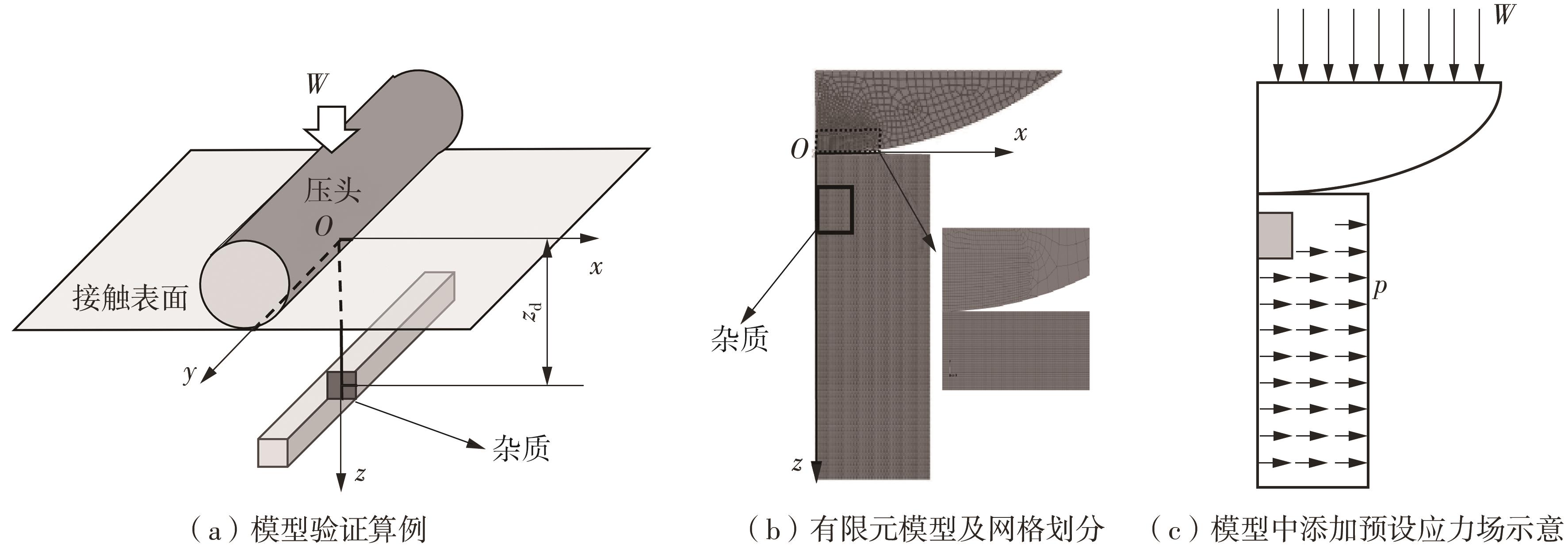
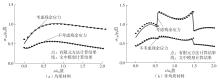
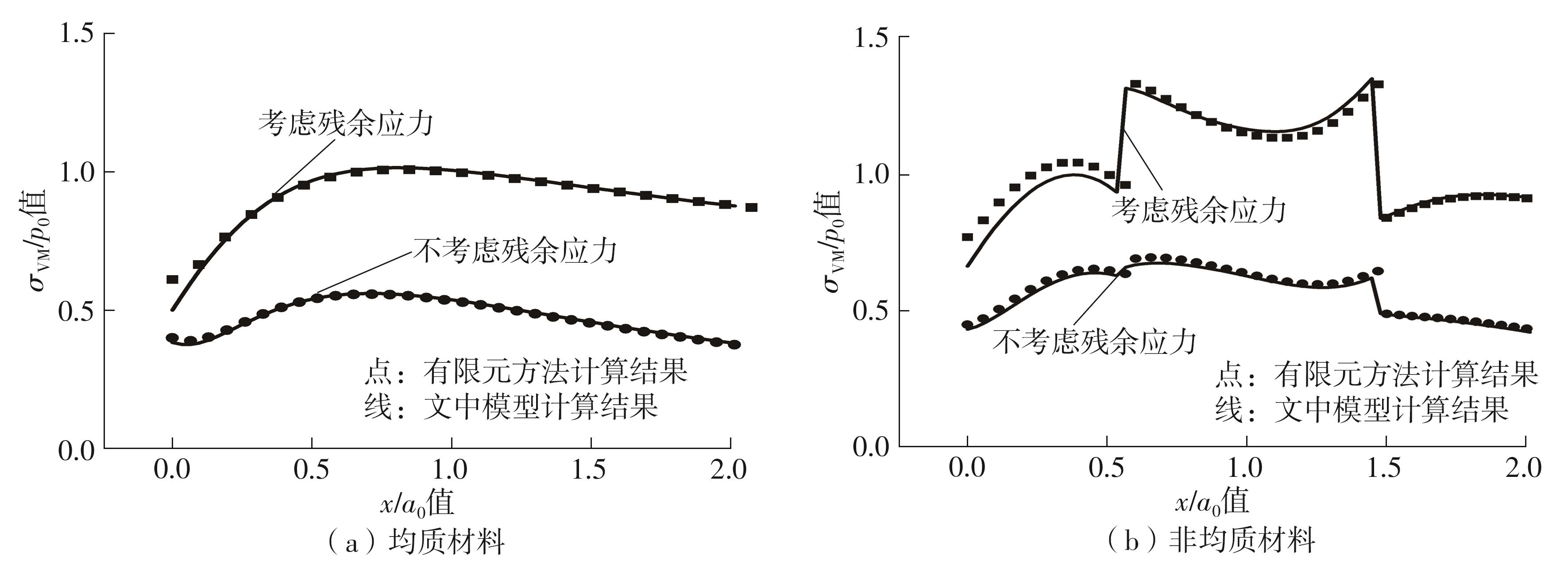
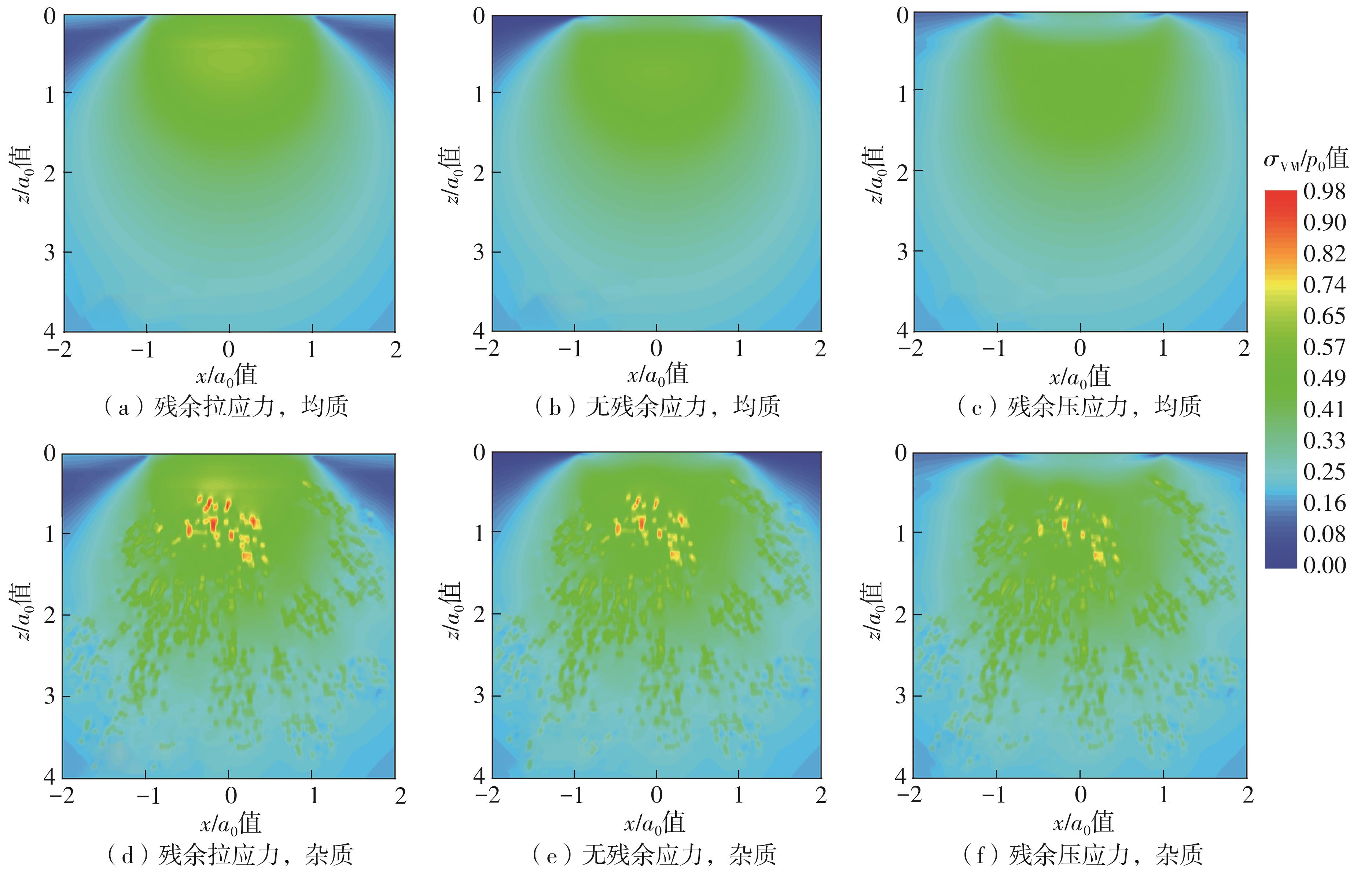
| [1] |
BURRELL N .Improved gear life through controlled shot peening[J].Gear Technology,1986(9/10):12-18,64.
|
| [2] |
WANG Y, ZHANG W, LIU Y .Analysis model for surface residual stress distribution of spiral bevel gear by generating grinding[J].Mechanism and Machine Theory,2018,130:477-490.
|
| [3] |
WANG G, ZHU D, ZOU S,et al .Simulation and experimental esearch on electrical control anti-backlash based on a novel type of variable tooth thickness involute gear pair[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2022,2:126-140.
|
| [4] |
WANG C, ZHANG H, XIONG X,et al .Changes in surface integrity of cemented tungsten carbide with shot peening treatment[J].Surface and Coatings Technology,2021,425:127710/1-10.
|
| [5] |
DALY J .Problems related to stress corrosion cracking reduced by controlled shot peening[J].Industrial Heating,1998,65(5):65-70.
|
| [6] |
GU Y .Corrosion behavior and residual stress of microarc oxidation coated AZ31 magnesium alloy for biomedical applications[D].Fairbanks:University of Alaska Fairbanks,2012.
|
| [7] |
THORNTON P A .The influence of nonmetallic inclusions on the mechanical properties of steel:a review[J].Journal of Materials Science,1971,6:347-356.
|
| [8] |
LIU J, ZHANG M, JIANG F,et al .Numerical simulation for elasto-plastic contact of novel Ti-(SiCf/Al3Ti)- laminated composite with double-layered SiC fiber reinforcements[J].Metals,2019,9(2):165-193.
|
| [9] |
LEROUX J, FULLERINGER B, NELIAS D .Contact analysis in presence of spherical inhomogeneities within a half-space[J].International Journal of Solids and Structures,2010,47(22/23):3034-3049.
|
| [10] |
WANG W, LIU H, ZHU C,et al .Evaluation of rolling contact fatigue of a carburized wind turbine gear considering the residual stress and hardness gradient[J].Journal of Tribology,2018,140(6):14-26.
|
| [11] |
WANG W, LIU H, ZHU C,et al .Effect of the residual stress on contact fatigue of a wind turbine carburized gear with multiaxial fatigue criteria[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2018,151:263-273.
|
| [12] |
YOU S, TANG J, ZHOU W,et al .Research on calculation of contact fatigue life of rough tooth surface considering residual stress[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2022,140:106459/1-14.
|
| [13] |
CHEN Z, JIANG Y, TONG Z,et al .Residual stress distribution design for gear surfaces based on genetic algorithm optimization[J].Materials,2021,14(2):366/1-17.
|
| [14] |
HASHIMOTO K, FUJIMATSU T, TSUNEKAGE N,et al .Study of rolling contact fatigue of bearing steels in relation to various oxide inclusions[J].Materials & Design,2011,32(3):1605-1611.
|
| [15] |
CERULLO M .Sub-surface fatigue crack growth at alumina inclusions in AISI 52100 roller bearings[J].Procedia Engineering,2014,74:333-338.
|
| [16] |
TIEMENS B L .Performance optimization and computational design of ultra-high strength gear steels[D].Chicago:Northwestern University,2006.
|
| [17] |
张文博,刘怀举,朱才朝,等 .夹杂物对齿轮接触疲劳性能影响的仿真分析[J].机械传动,2020,44(11):14-20,52.
|
|
ZHANG Wenbo, LIU Huaiju, ZHU Caichao,et al .Simulation analysis of the influence of inclusion on contact fatigue performance of gear[J].Mechanical Transmission,2020,44(11):14-20,52.
|
| [18] |
LI Z, FREBORG A M, HANSEN B D,et al .Modeling the effect of carburization and quenching on the development of residual stresses and bending fatigue resistance of steel gears[J].Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance,2013,22:664-672.
|
| [19] |
RAJESH S, MARIMUTHU P, BABU P D,et al .Contact fatigue life estimation for asymmetric helical gear drives[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2022,164:107155/1-11.
|
| [20] |
NAJJARI M, GUILBAULT R .Modeling the edge contact effect of finite contact lines on subsurface stresses[J].Tribology International,2014,77:78-85.
|
| [21] |
NAJJARI M, GUILBAULT R .Edge contact effect on thermal elastohydrodynamic lubrication of finite contact lines[J].Tribology International,2014,71:50-61.
|
| [22] |
JIA X, WANG W, ZHAO Z,et al .A contact fatigue model of helical gear under elastohydrodynamic lubrication[J].Tribology,2014,34(1):8-14.
|
| [23] |
CAZAN S, DĂNILĂ C, CREŢU S .Tooth contact analysis of helical gears using semi-analytical methods in real gearing situations[J].Tribology International,2023,185:108482/1-16.
|
| [24] |
ALLEY E S, NEU R W .Microstructure-sensitive modeling of rolling contact fatigue[J].International Journal of Fatigue,2010,32(5):841-850.
|
| [25] |
WANG Q J, ZHU D .Interfacial mechanics:theories and methods for contact and lubrication[M].[S.l.]:CRC Press,2019:170-190.
|
| [26] |
WANG Q J, SUN L, ZHANG X,et al .FFT-based methods for computational contact mechanics[J].Frontiers in Mechanical Engineering,2020,6:61/1-22.
|
| [27] |
CHEN W W, ZHOU K, KEER L M,et al .Modeling elasto-plastic indentation on layered materials using the equivalent inclusion method[J].International Journal of Solids and Structures,2010,47(20):2841-2854.
|
| [28] |
ESHELBY J D .The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion,and related problems[J].Proceedings of the Royal Society of London,Series A:Mathematical and Physical Sciences,1957,241(1226):376-396.
|
| [29] |
LIU S, JIN X, WANG Z,et al .Analytical solution for elastic fields caused by eigenstrains in a half-space and numerical implementation based on FFT[J].International Journal of Plasticity,2012,35:135-154.
|
| [30] |
ZHANG M, ZHAO N, WANG Z,et al .Efficient numerical method with a dual-grid scheme for contact of inhomogeneous materials and its applications[J].Computational Mechanics,2018,62(5):991-1007.
|
| [31] |
ZHOU Q, JIN X, WANG Z,et al .Numerical implementation of the equivalent inclusion method for 2D arbitrarily shaped inhomogeneities[J].Journal of Elasticity,2015,118:39-61.
|
| [32] |
方宗德 .齿轮轮齿承载接触分析(LTCA)的模型和方法[J].机械传动,1998,22(2):1-3.
|
|
FANG Zongde .Models and methods of load-bearing contact analysis (LTCA) for gear teeth[J].Mechanical Transmission,1998,22(2):1-3.
|
| [33] |
李雁淮,王飞,吕坚,等 .单丸粒喷丸模型和多丸粒喷丸模型的有限元模拟[J].西安交通大学学报,2007,41(3):348-352.
|
|
LI Yanhuai, WANG Fei, Jian LÜ,et al .Finite element simulation of single Sshot peening model and multiple shot peening model[J].Journal of Xi’an Jiaotong University,2007,41(3):348-352.
|
| [34] |
AGHA S R .Fatigue performance of superfinish hard turned surfaces in rolling contact[D].West Lafayette:Purdue University,2000.
|
| [35] |
黄新春,史恺宁 .高温合金磨削残余应力机理及对疲劳寿命的影响研究[J].航空精密制造技术,2021,57(6):1-5.
|
|
HUANG Xin-chun, SHI Kai-ning .Study of residual stress and its influence on fatigue life in grinding superalloy[J].Aeronautical Precision Manufacturing Technology,2021,57(6):1-5.
|
| [36] |
李康 .湿喷丸强化Ti-6Al-4V合金的微动磨损和微动疲劳行为及其机理研究[D].大连:大连理工大学,2016.
|
| [37] |
LI S X .Effects of inclusions on very high cycle fatigue properties of high strength steels[J].International Materials Reviews,2012,57(2):92-114.
|
| [38] |
LIU R, SUN D, HOU J,et al .Fatigue life analysis of wind turbine gear with oxide inclusion[J].Fatigue & Fracture of Engineering Materials & Structures,2021,44(3):776-787.
|
| [39] |
IBRAHIM I A, MOHAMED F A, LAVERNIA E J .Particulate reinforced metal matrix composites-a review[J].Journal of Materials Science,1991,26:1137-1156.
|
| [40] |
DANG-VAN K .Macro-micro approach in high-cycle multiaxial fatigue[M]∥ MCDOWELL D L,ELLIS J R.Advances in Multiaxial Fatigue.[S.l.]:ASTM,1993:120-130.
|
| [41] |
KAROLCZUK A, MACHA E .A review of critical plane orientations in multiaxial fatigue failure criteria of metallic materials[J].International Journal of Fracture,2005,134(3/4):267-304.
|
| [42] |
DANG-VAN K, CAILLETAUD G, FLAVENOT J F,et al .Criterion for high cycle fatigue failure under multiaxial loading[J].Mechanical Engineering Publications,Biaxial and Multiaxial Fatigue,1989:459-478.
|
| [43] |
闻邦椿 .机械设计手册(单行本):疲劳强度与可靠性设计[M].北京:机械工业出版社,2015.
|
| [44] |
HARRIS T A, YU W K .Lundberg-Palmgren fatigue theory:considerations of failure stress and stressed volume[J].Journal of Tribology,1999,121(1):85-89.
|