华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (6): 56-65.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240396
考虑空调系统的燃料电池汽车能量管理策略
赵又群1( ), 徐周1, 虞志浩1, 林棻1, 何鲲鹏1,2, 尤庆伸2
), 徐周1, 虞志浩1, 林棻1, 何鲲鹏1,2, 尤庆伸2
- 1.南京航空航天大学 能源与动力学院,江苏 南京 210016
2.奇瑞新能源汽车股份有限公司,安徽 芜湖 241002
Energy Management Strategies for Fuel Cell Vehicle Considering Air Conditioning Systems
ZHAO Youqun1( ), XU Zhou1, YU Zhihao1, LIN Fen1, HE Kunpeng1,2, YOU Qingshen2
), XU Zhou1, YU Zhihao1, LIN Fen1, HE Kunpeng1,2, YOU Qingshen2
- 1.School of Energy and Power,Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,Nanjing 210016,Jiangsu,China
2.Chery New Energy Vehicle Co. ,Ltd. ,Wuhu 241002,Anhui,China
摘要:
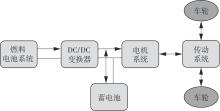
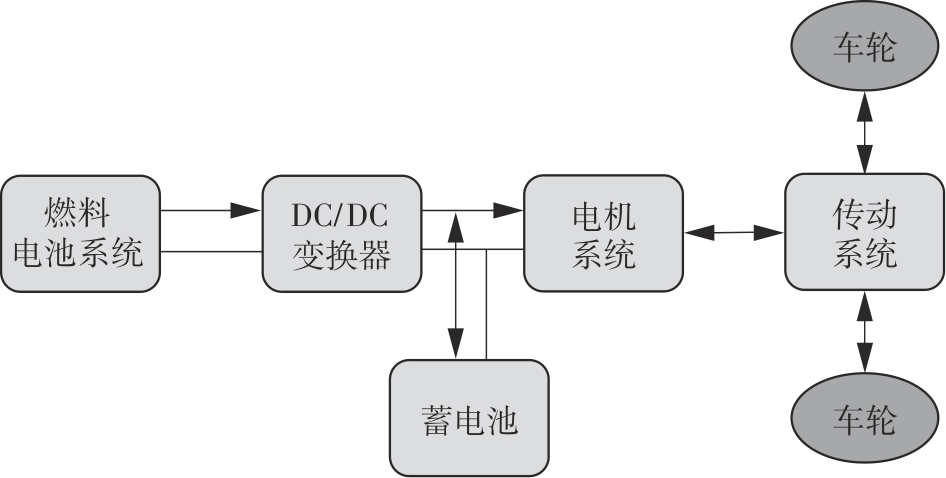
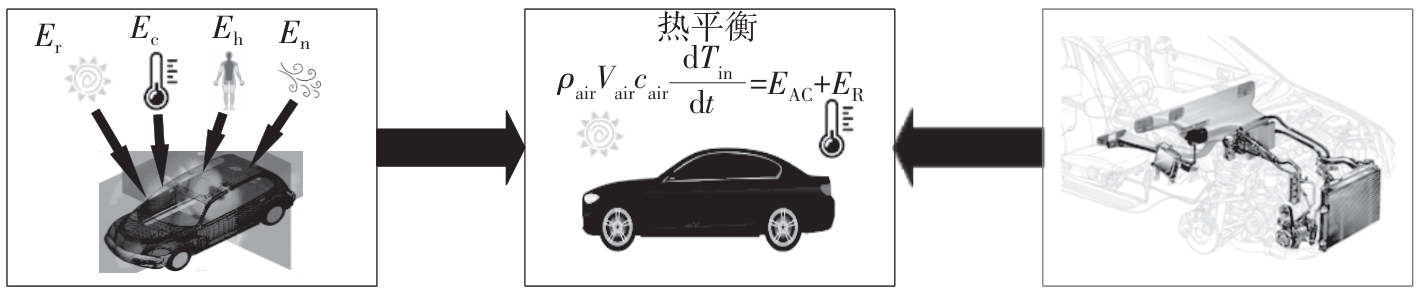
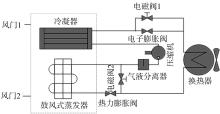
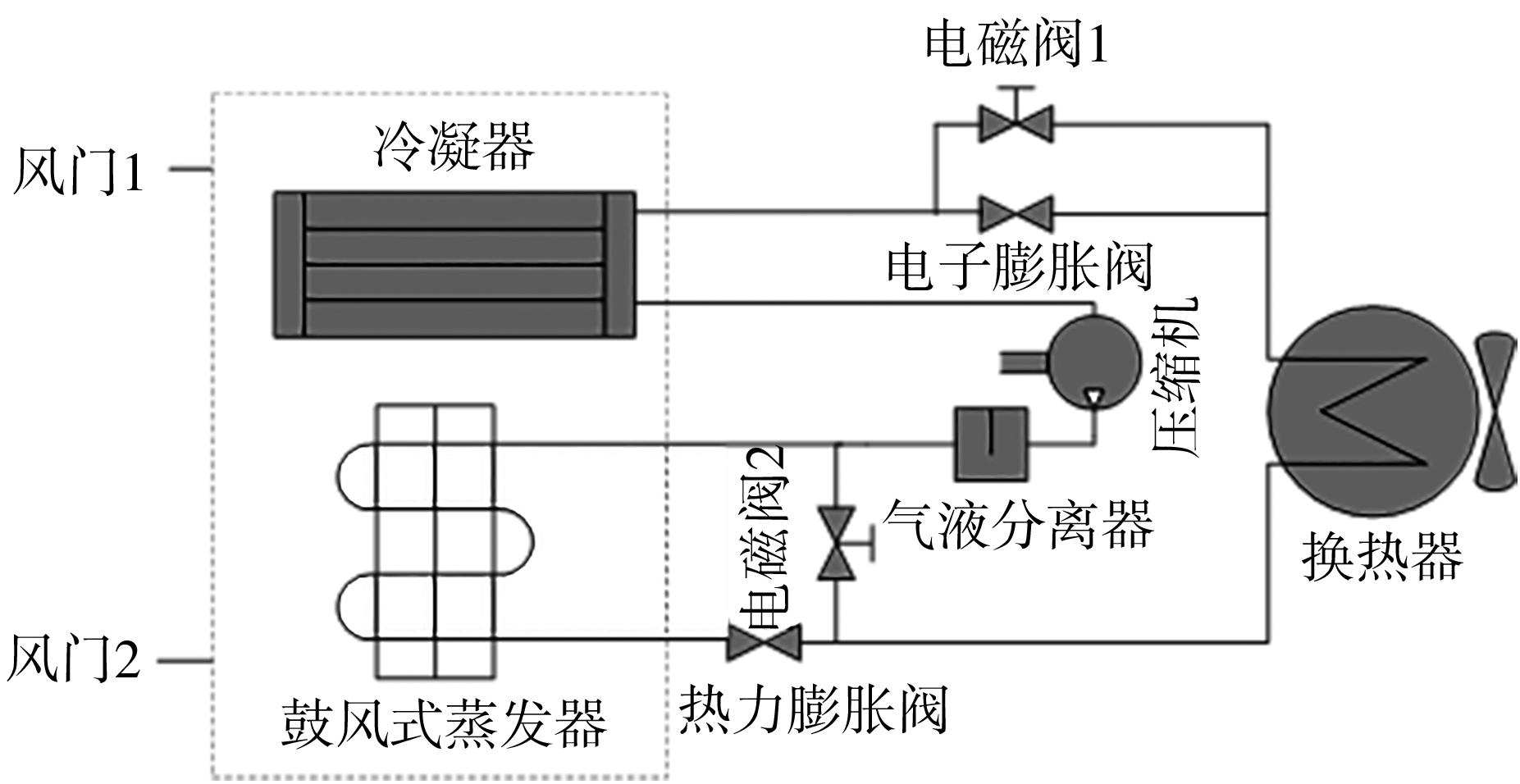
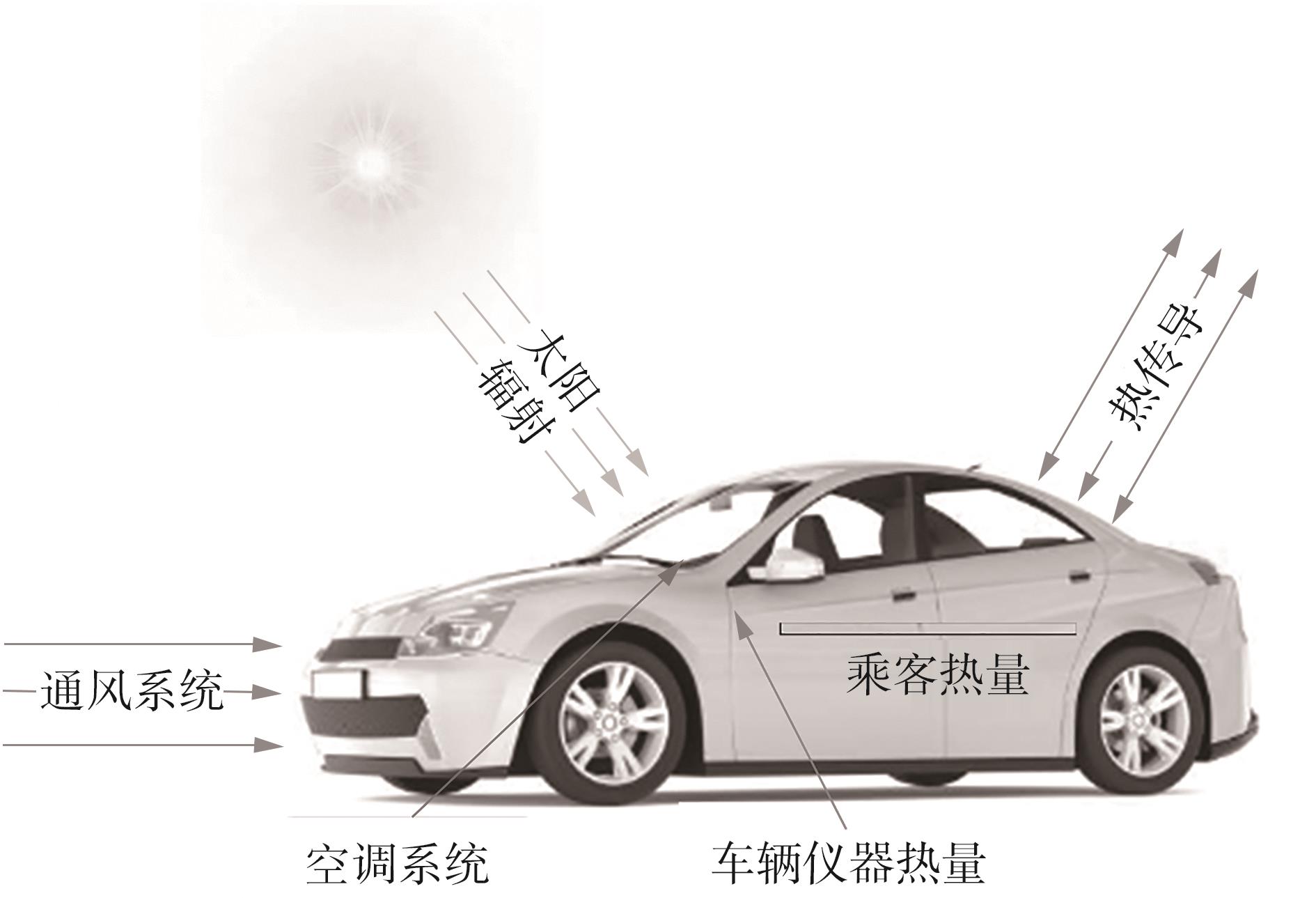
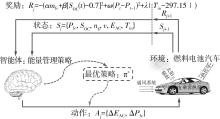
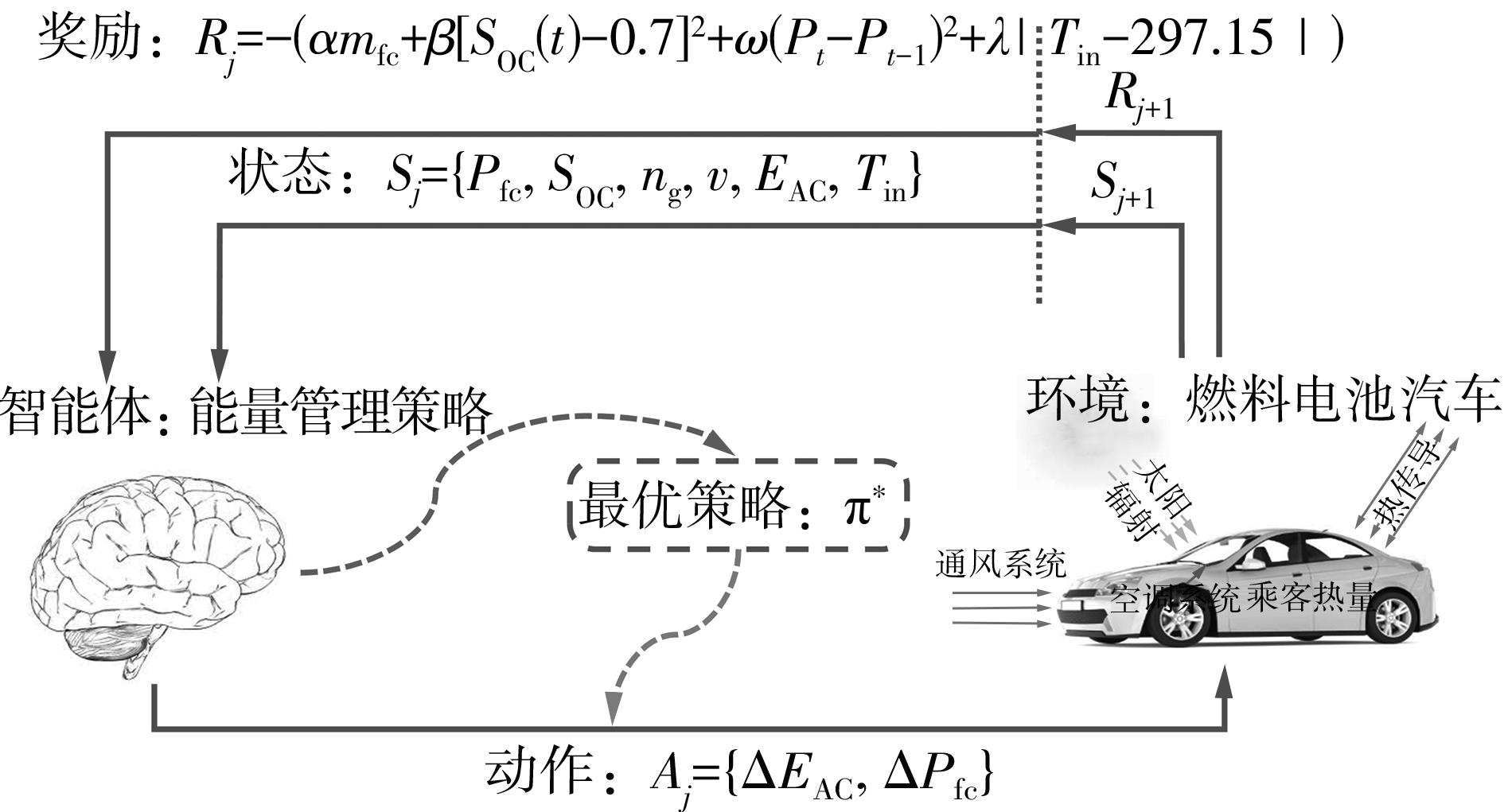
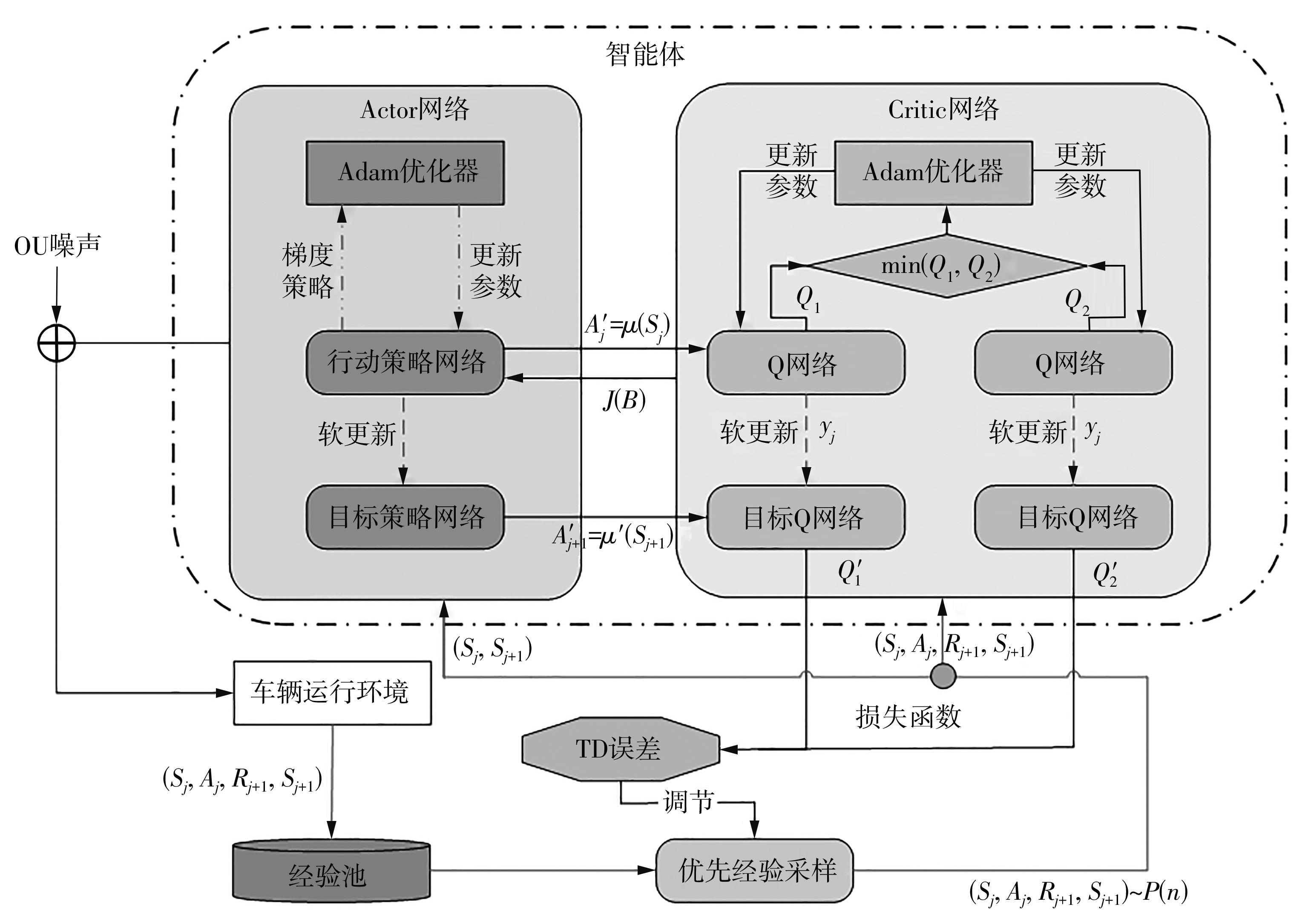
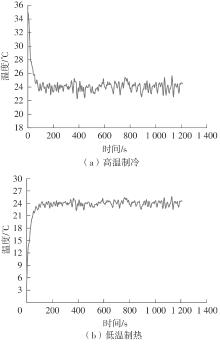
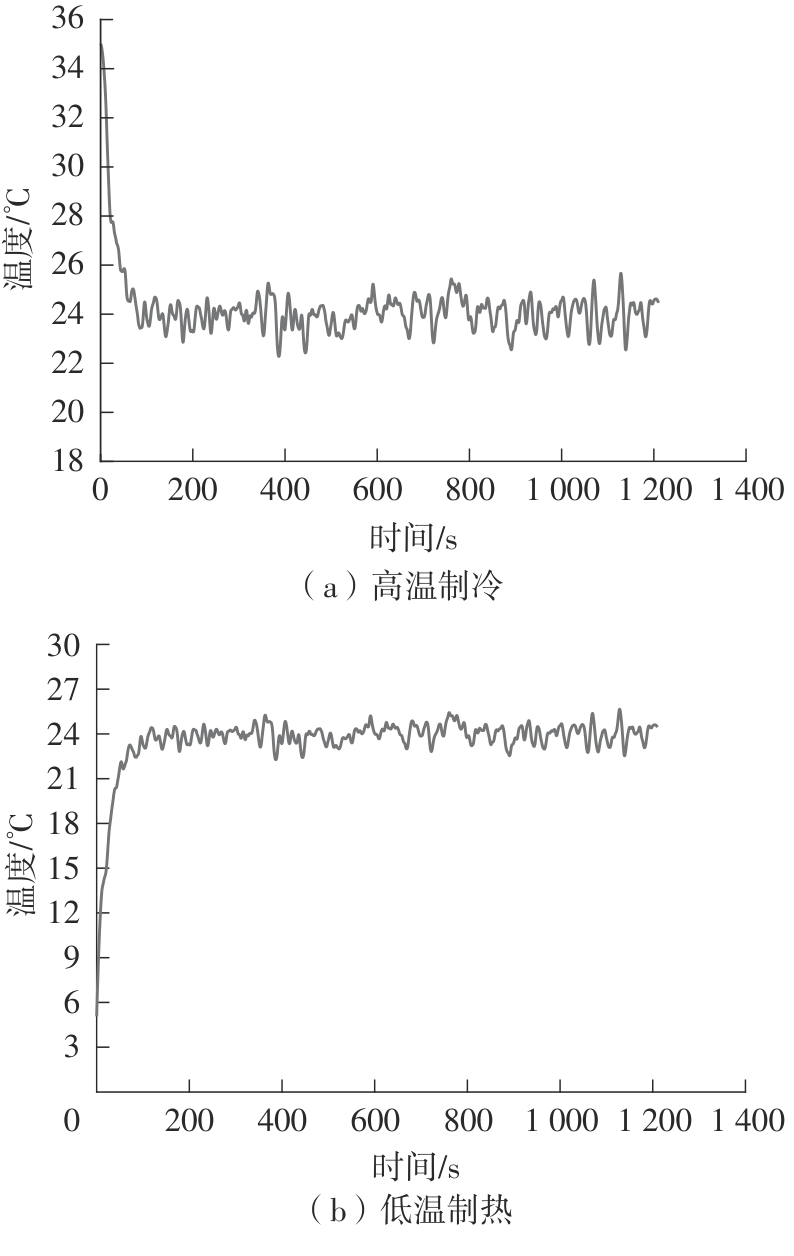
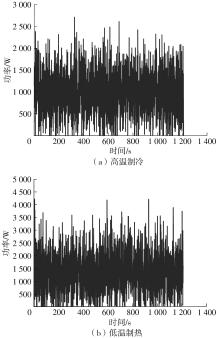
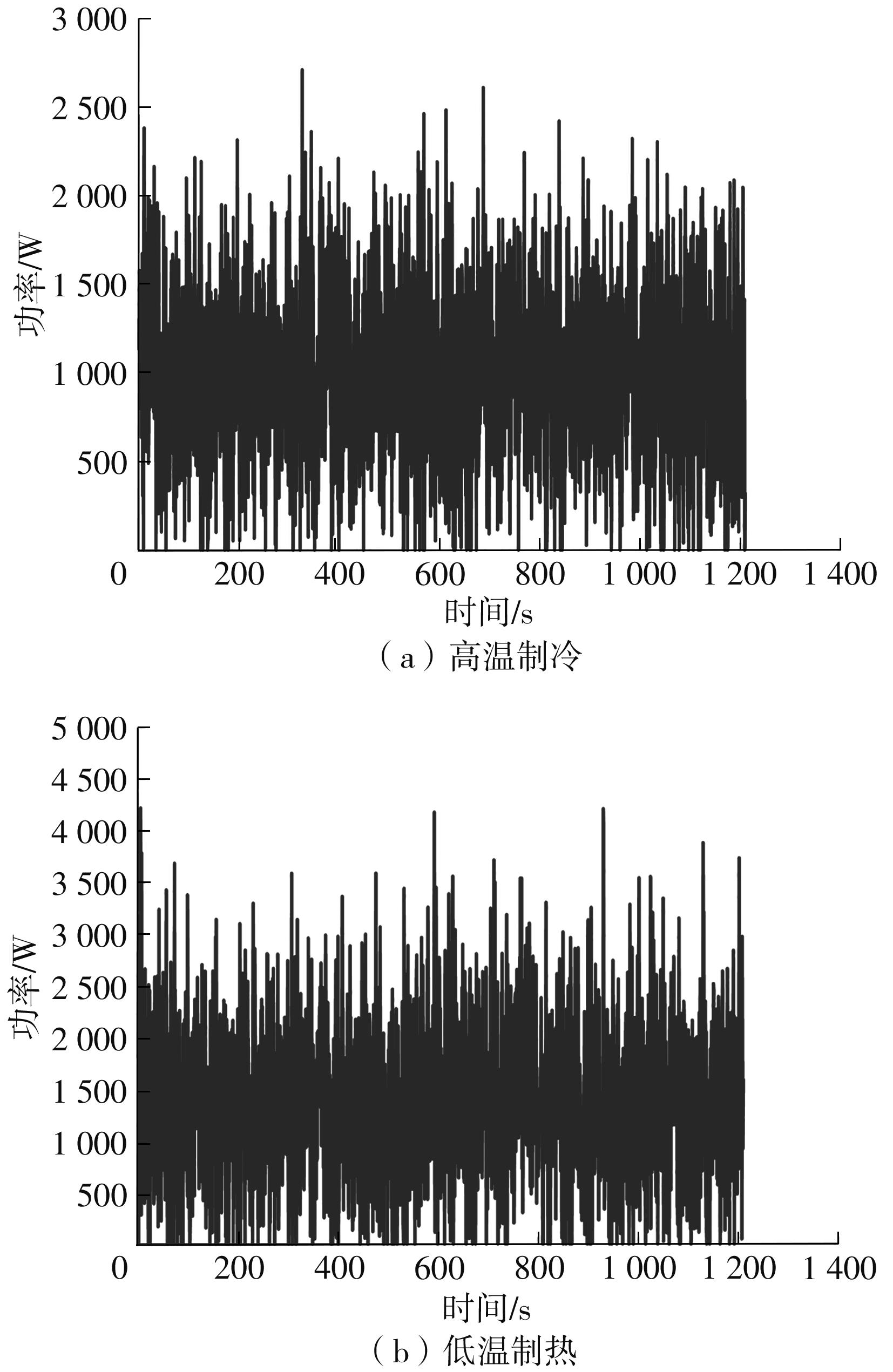
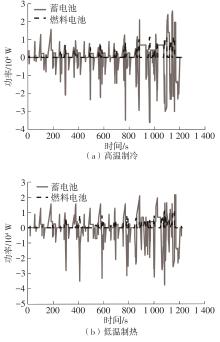
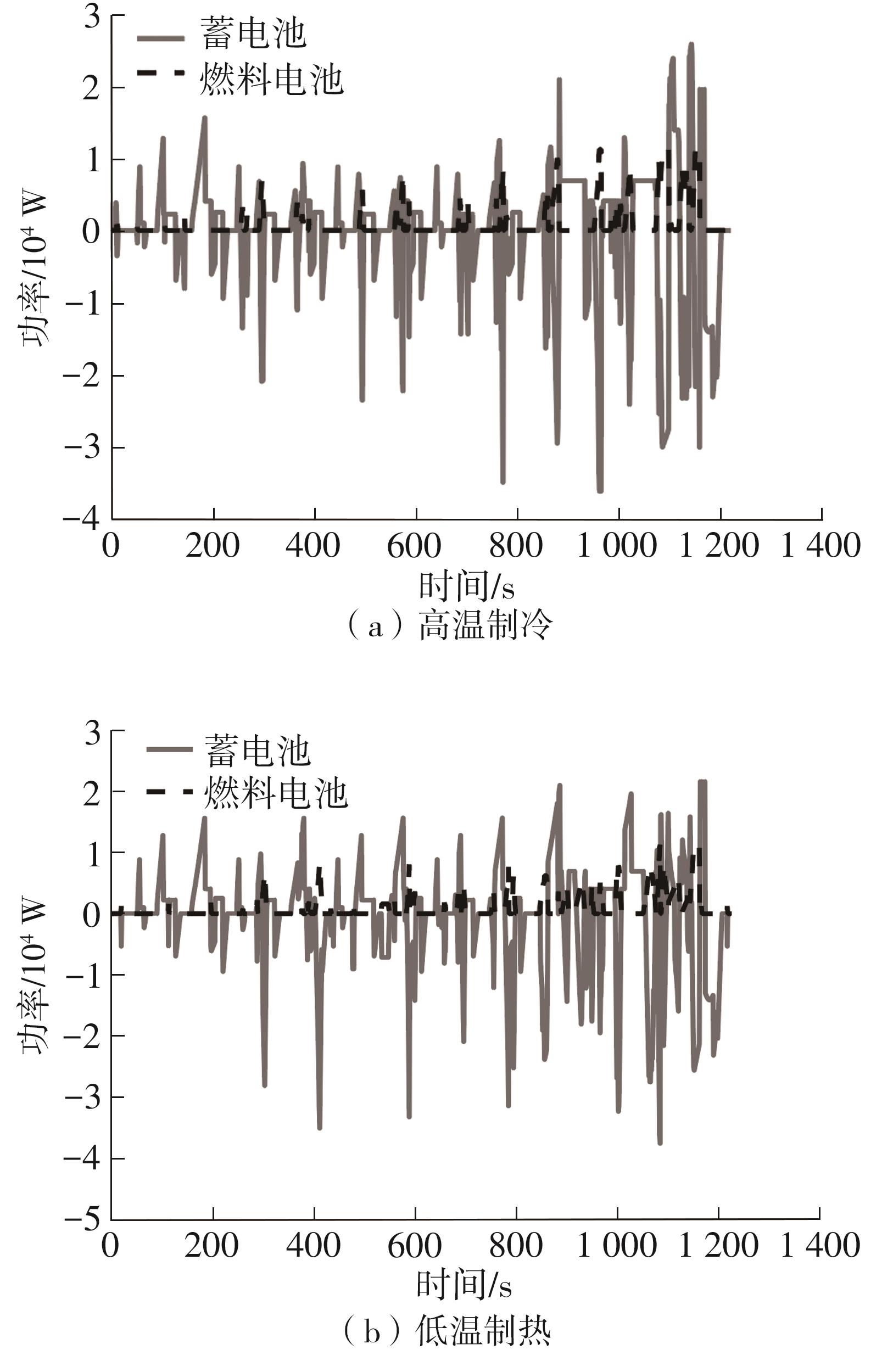
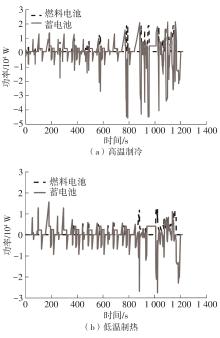
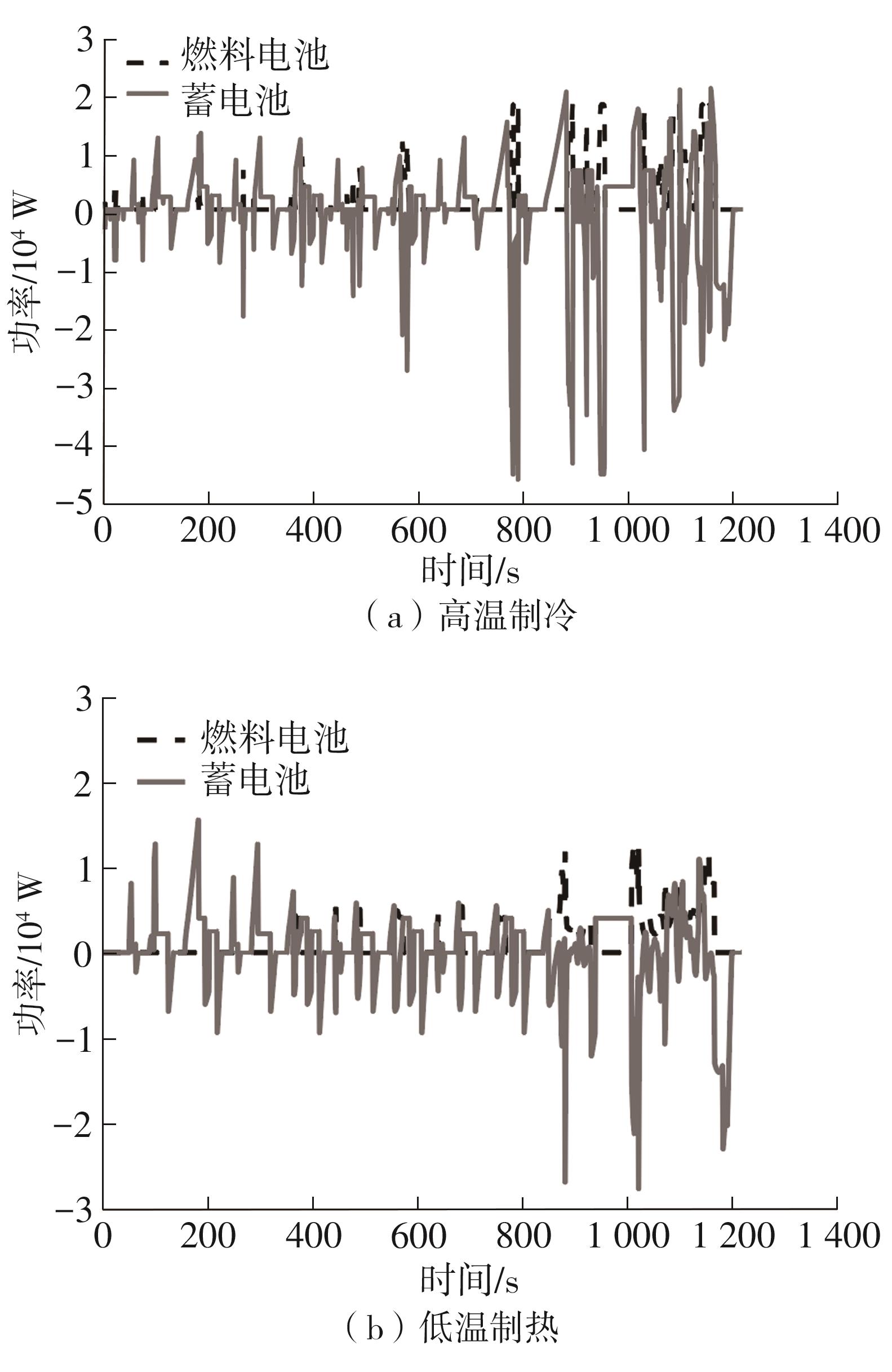
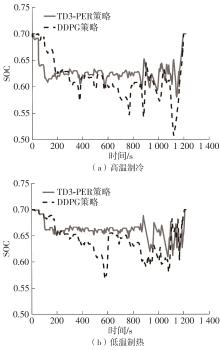
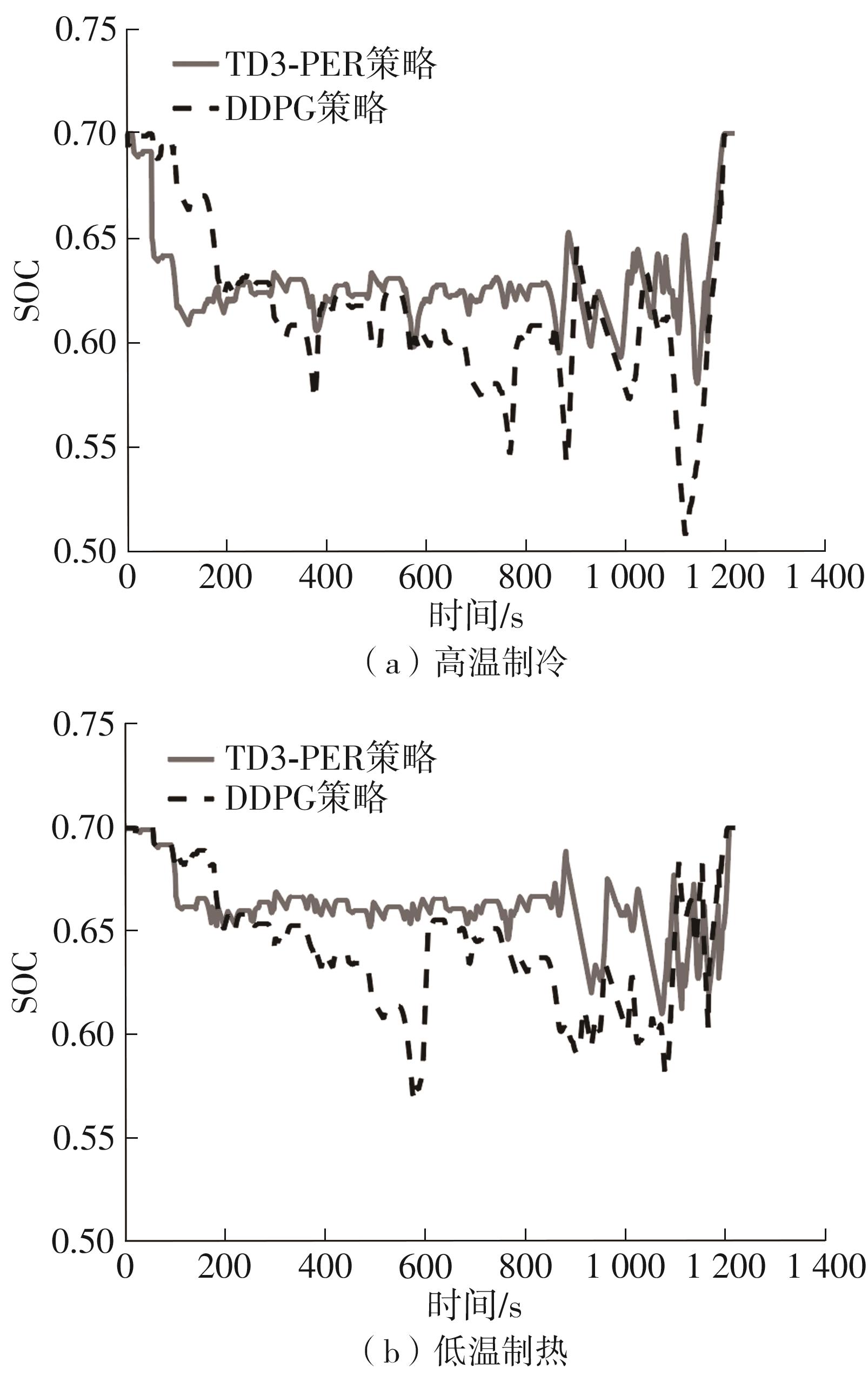
在燃料电池混合动力汽车的实际运行中,空调系统为驾驶员和乘客提供舒适的环境,然而空调系统的运行效果与汽车实际运行的能量分配相互影响,因此需要将空调系统考虑进能量管理策略,设计出在满足舱内温度舒适性要求的情况下,兼顾整车氢耗经济性的能量管理策略。首先在建立整车动力学模型的基础上,利用热平衡方程建立热泵空调系统模型和热负荷模型;然后采用结合了双Q网络和深度确定性策略梯度的优先经验采样的双延迟深度确定性策略梯度(TD3-PER)算法,建立考虑空调系统能耗与车辆运行需求的能量管理策略。在NEDC典型工况下进行仿真得出:TD3-PER能量管理策略下的空调系统能够使舱温在100 s内迅速达到并维持在22~26 ℃的舒适范围内,满足制冷/制热的同时又保证车舱温度舒适,验证了考虑空调系统时TD3-PER能量管理策略的可行性;在空调系统制冷/制热时,相比传统的深度确定性策略梯度(DDPG)算法策略,基于TD3-PER算法策略的功率分配情况能够延长燃料电池和蓄电池使用寿命,且在制冷/制热时根据氢耗量分别可提高2.59和3.58个百分点的经济性,验证了基于TD3-PER算法能量管理策略在降低氢耗量、提高整车经济性方面相较于传统算法更具优势。
中图分类号: