华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (5): 45-55.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240397
轨道用中空薄壁大小幅铝型材的挤压规律分析
刘国勇, 高士泽, 朱冬梅
- 北京科技大学 机械工程学院,北京 100083
Analysis of Extrusion Law of Large-Scale and Small-Scale Aluminum Profiles with Hollow Thin Wall for Rails
LIU Guoyong, GAO Shize, ZHU Dongmei
- School of Mechanical Engineering,University of Science and Technology Beijing,Beijing 100083,China
摘要:
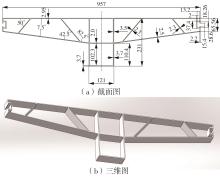
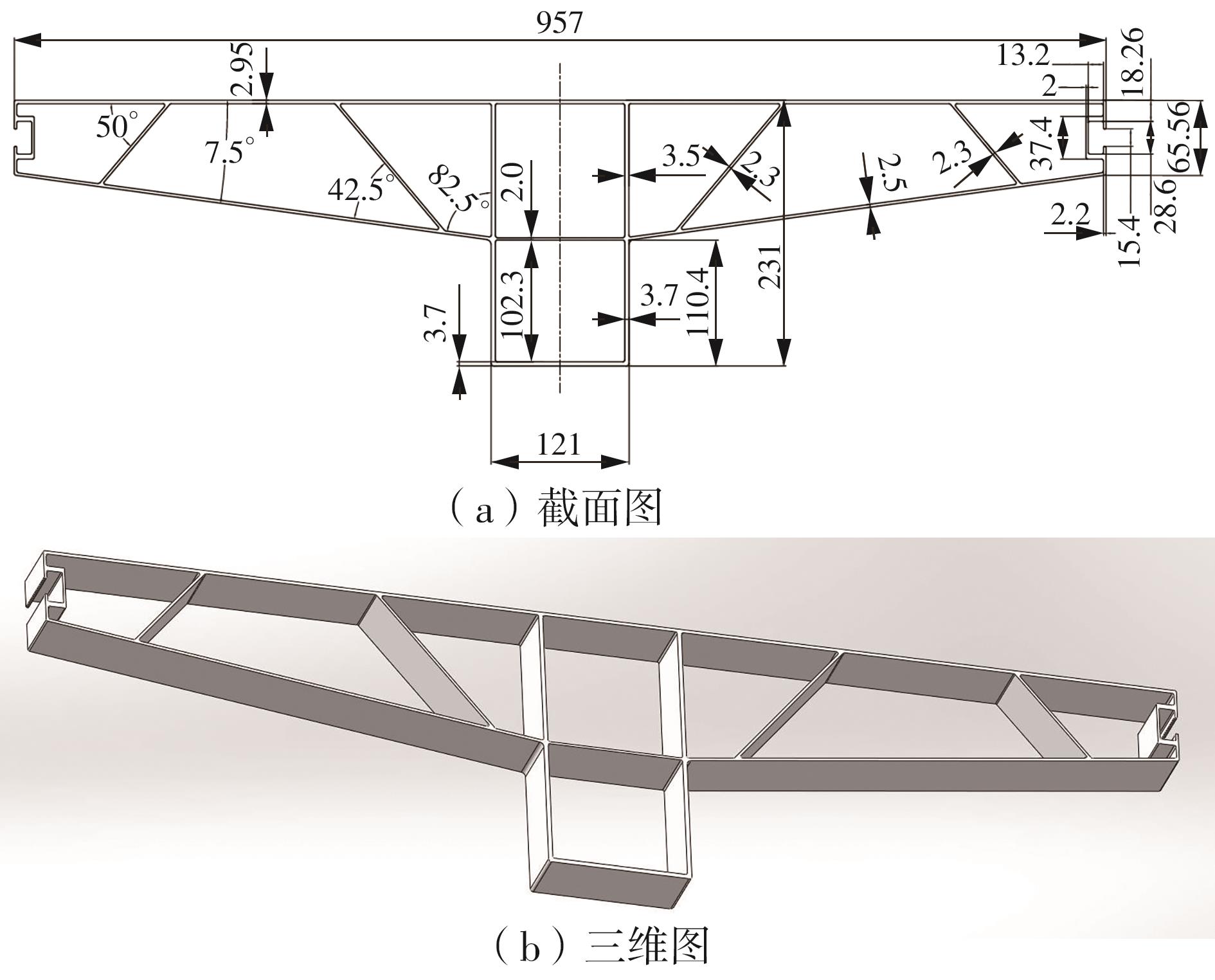
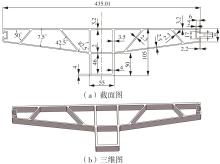
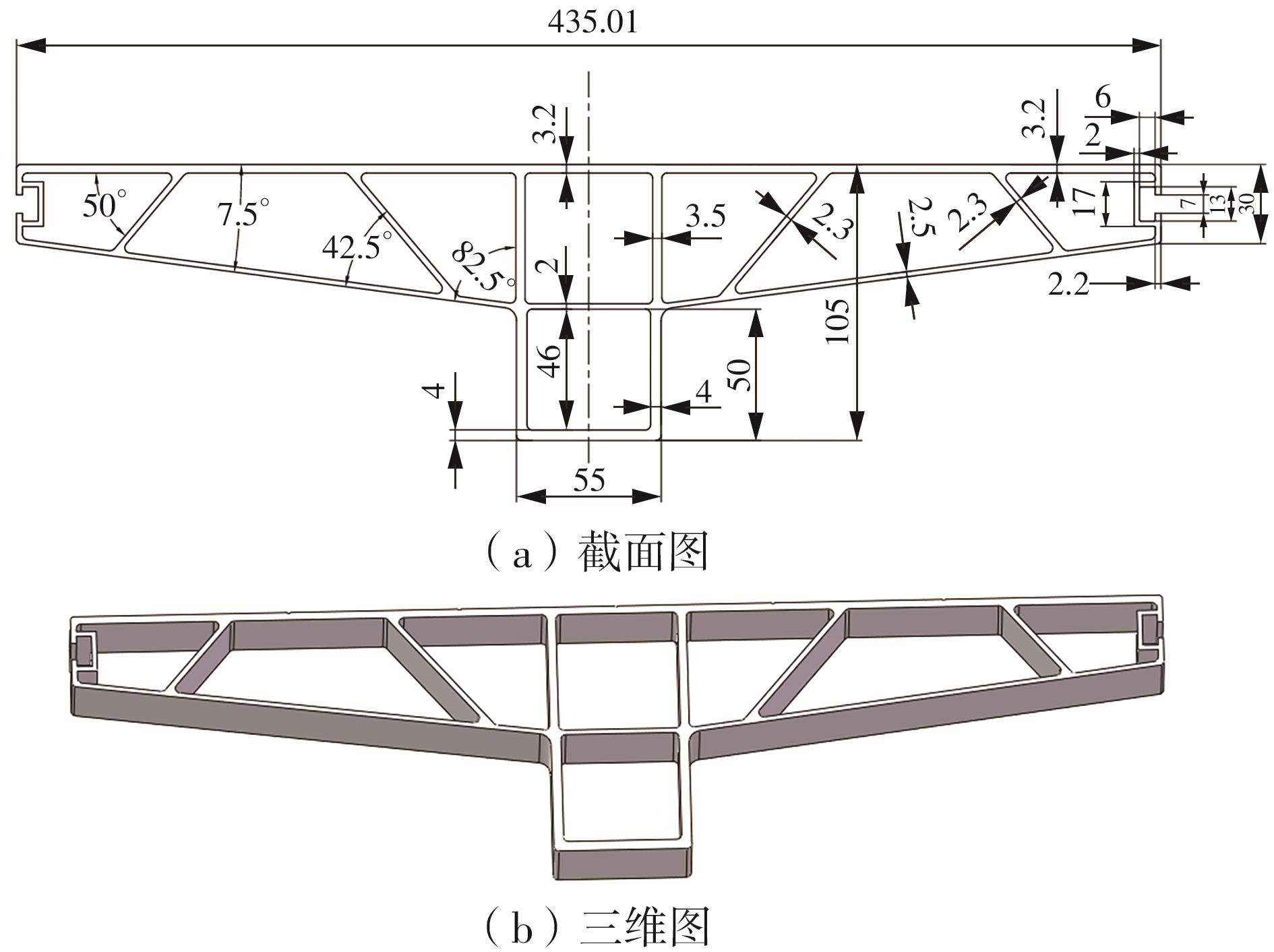
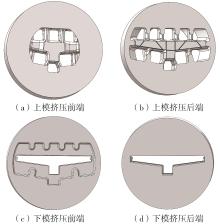
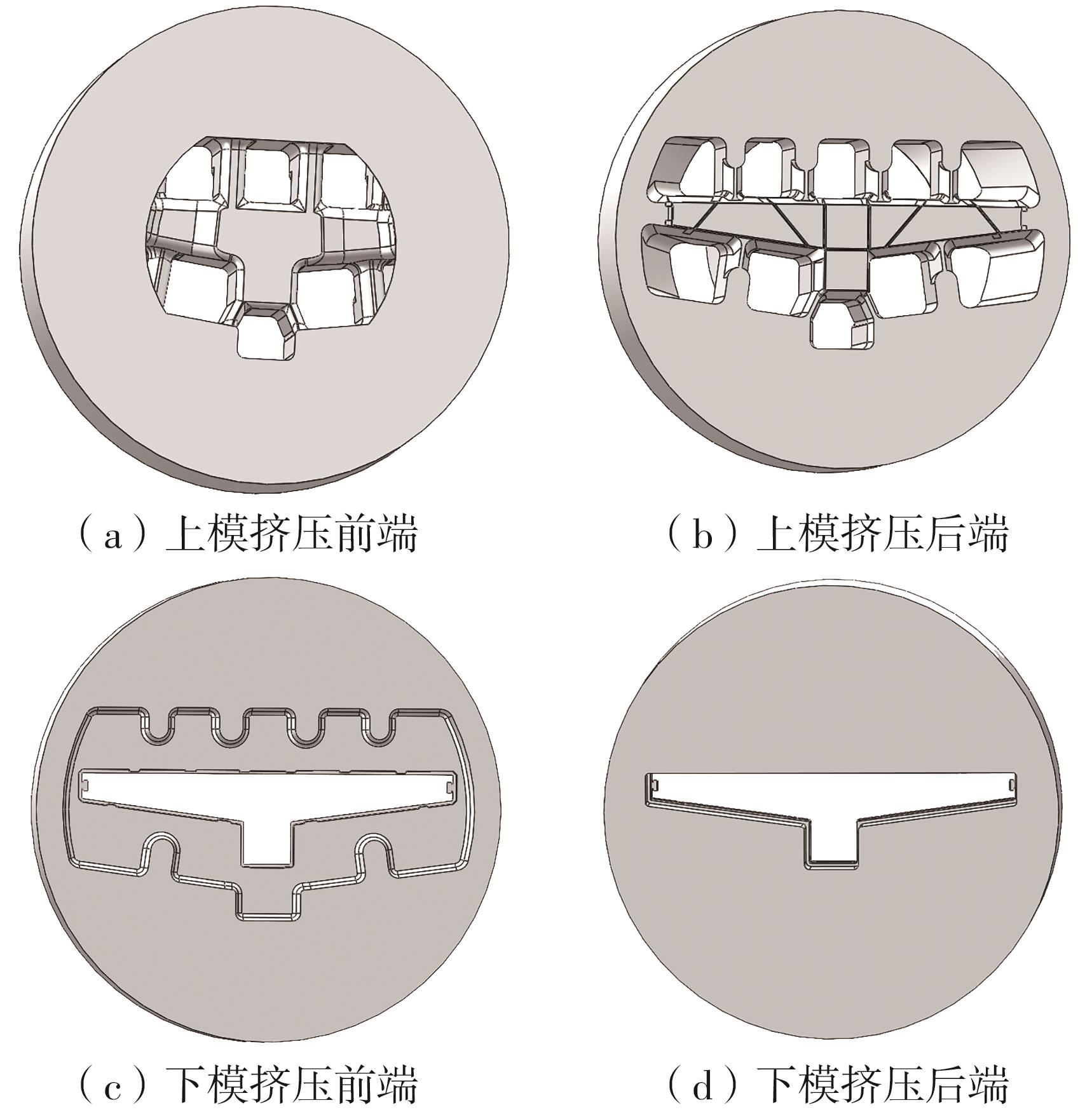
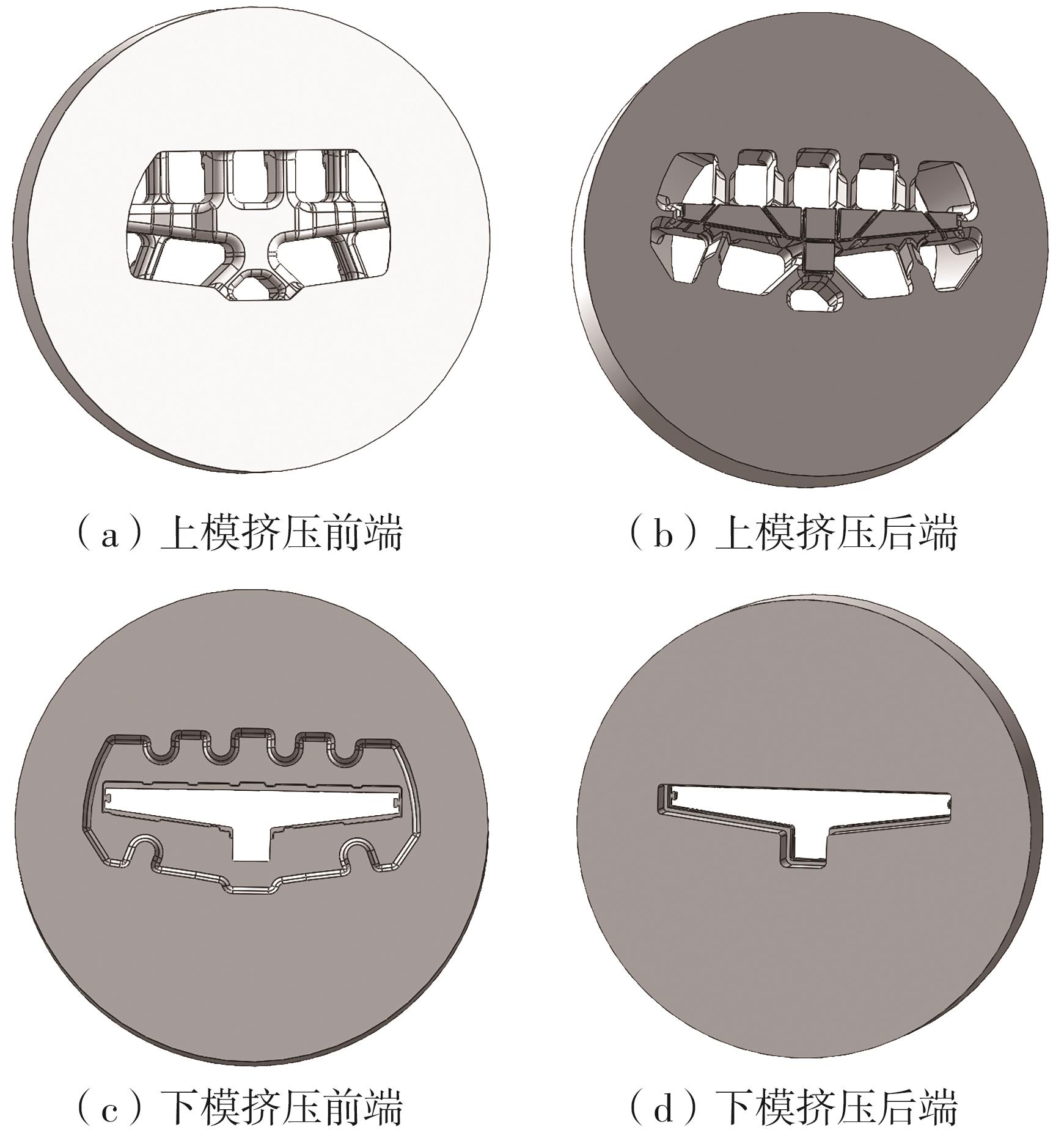
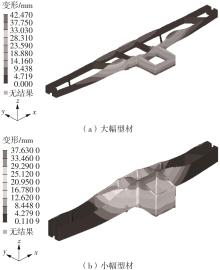
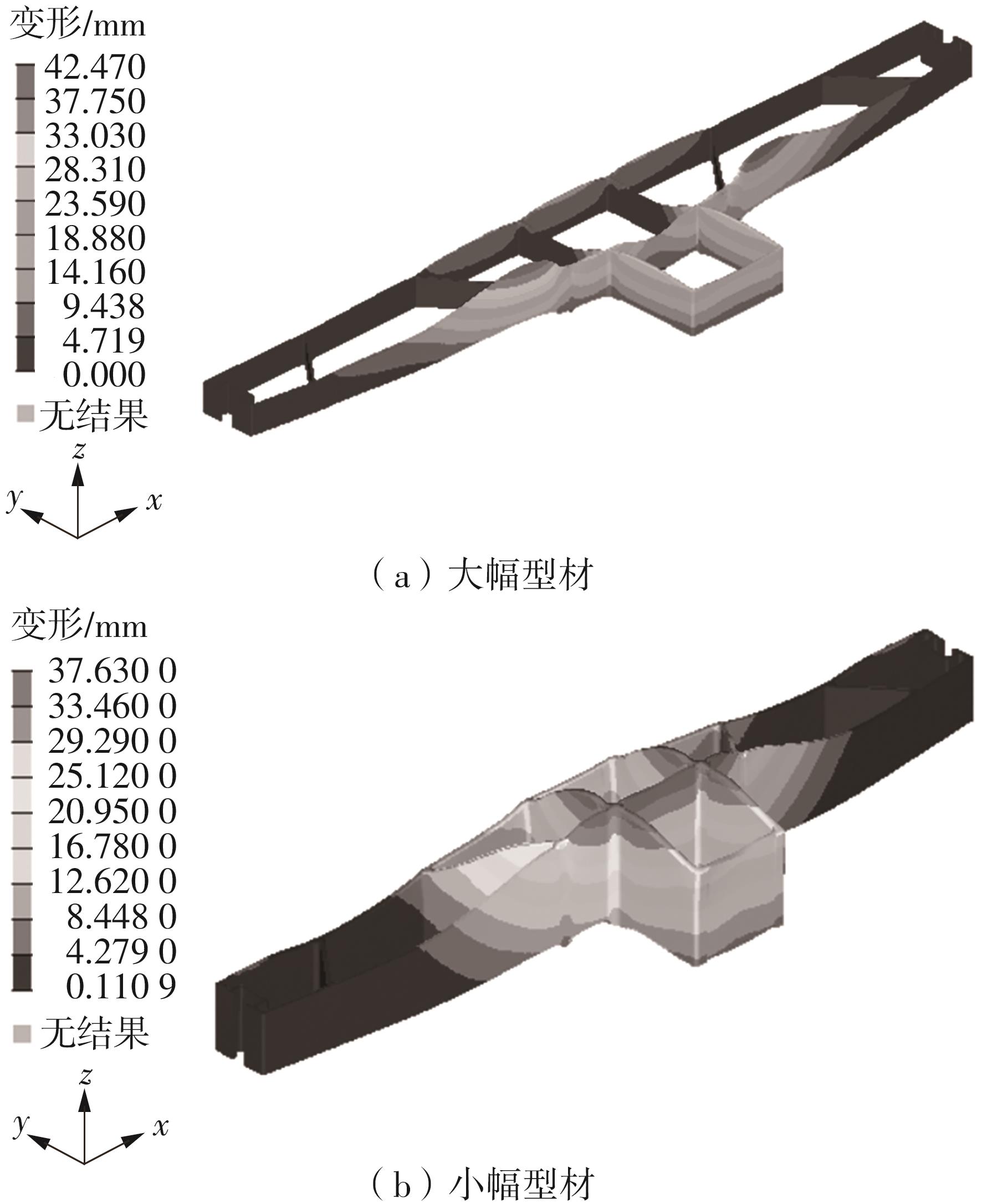
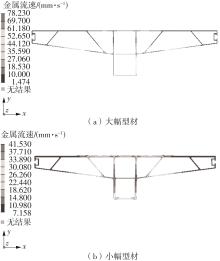
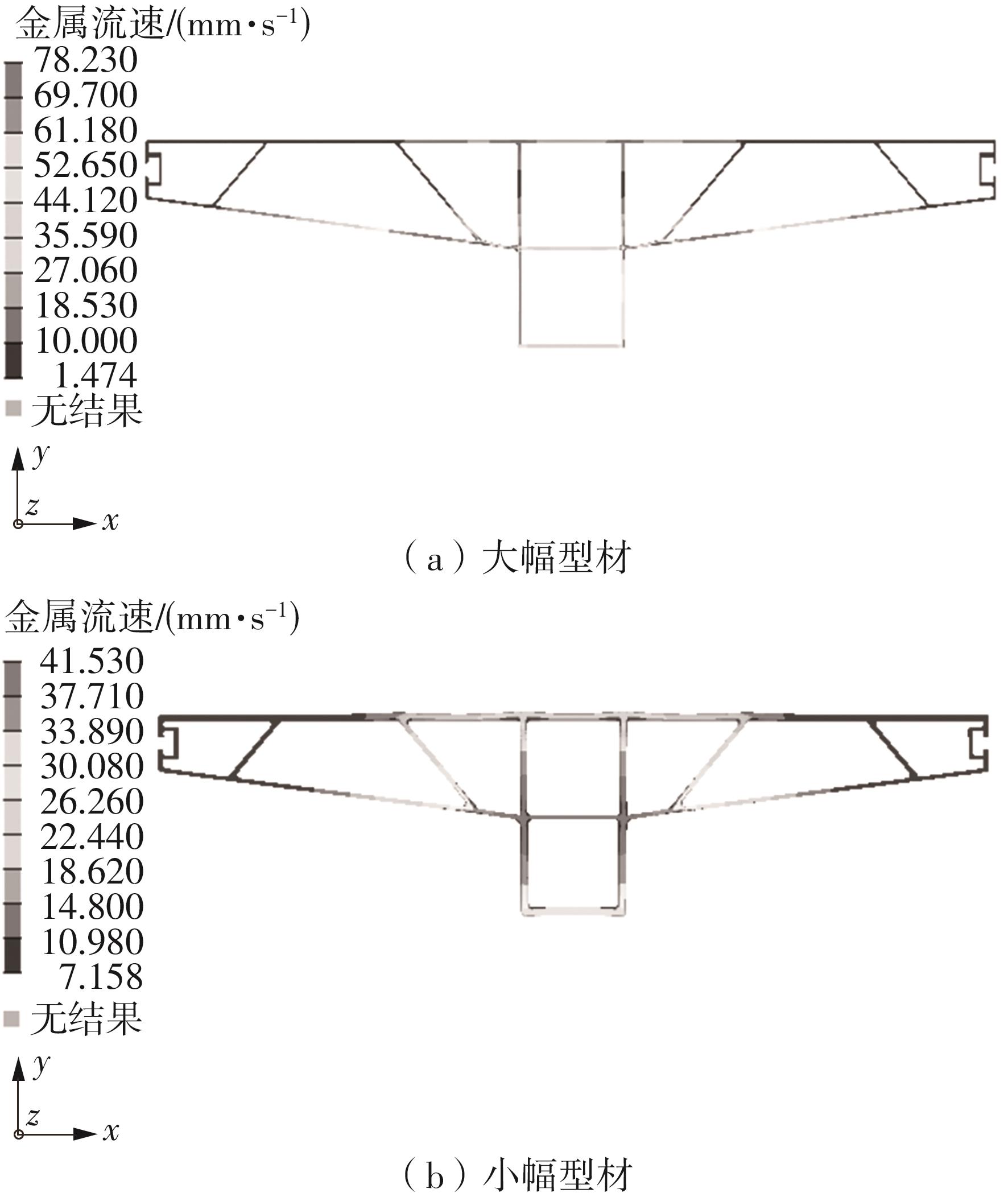
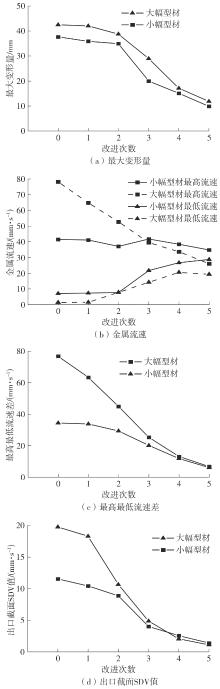
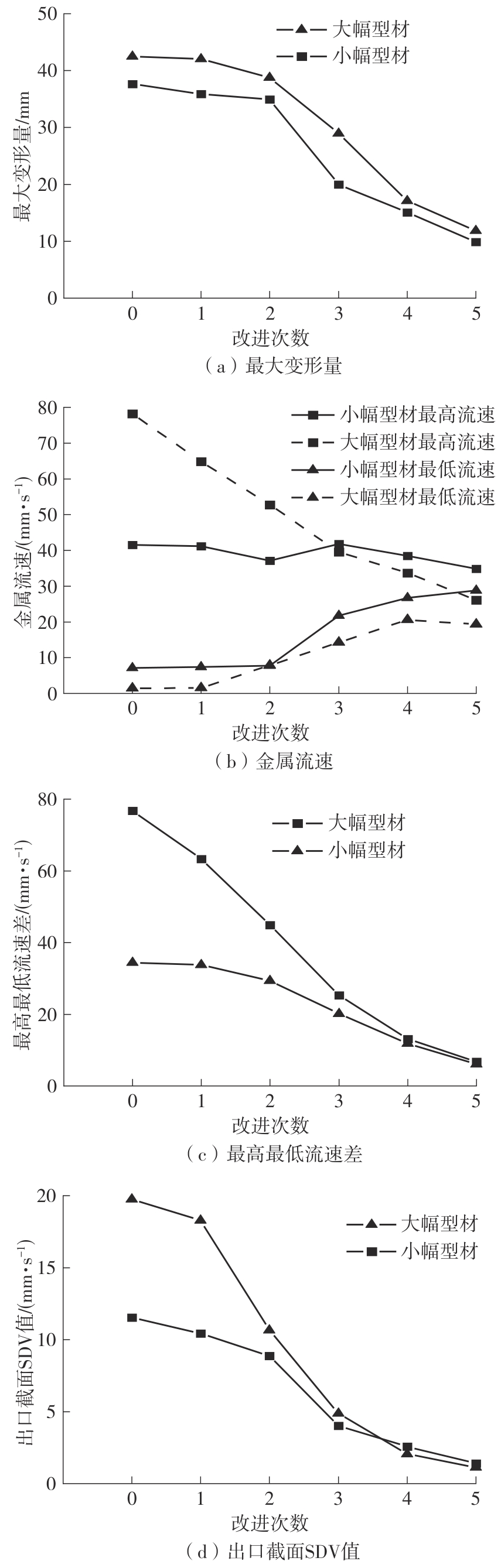
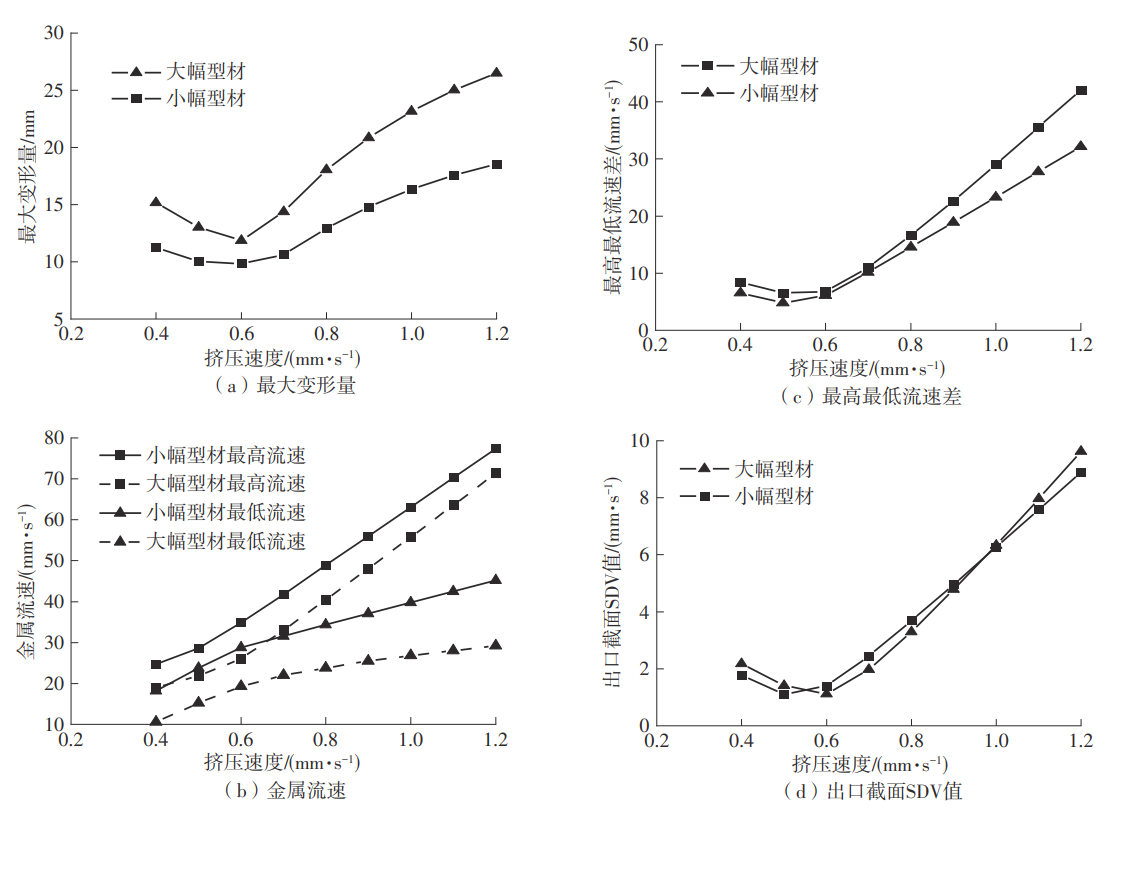
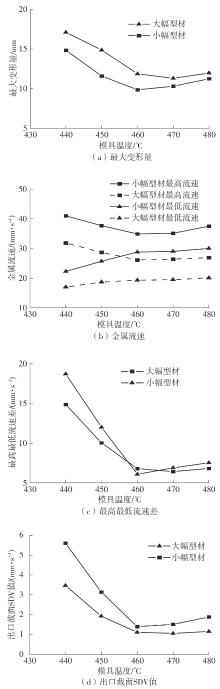
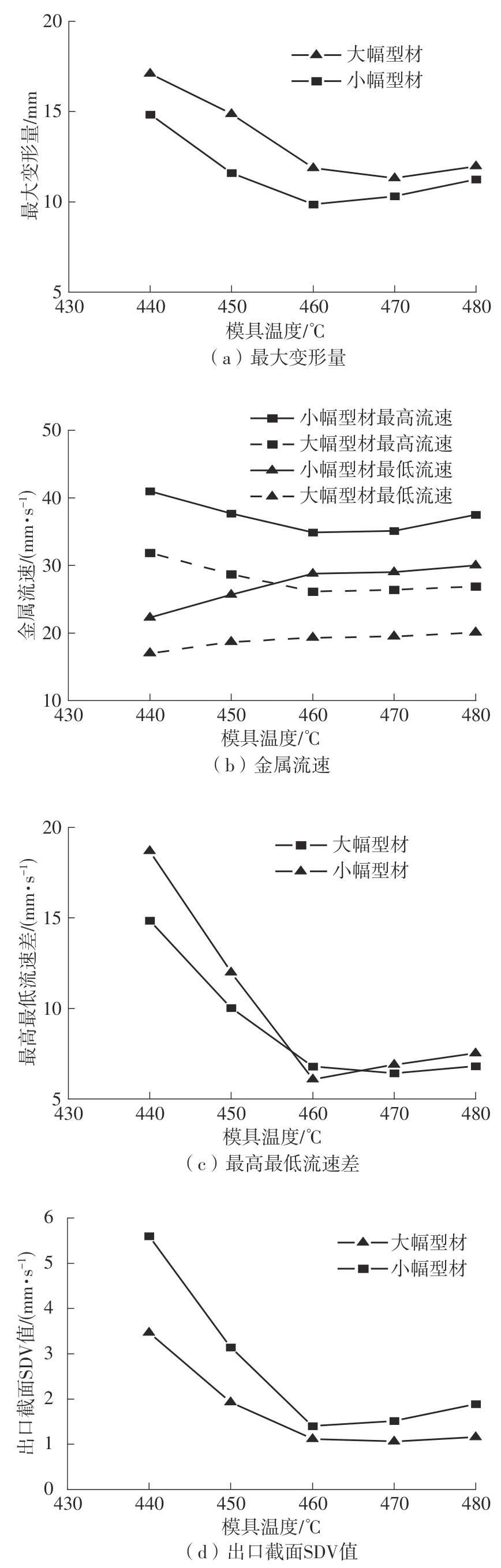
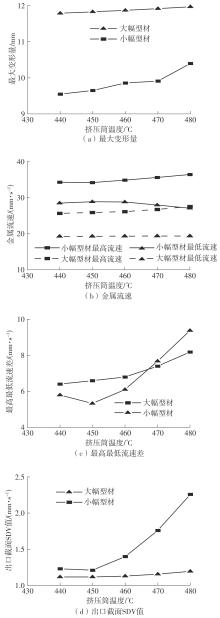
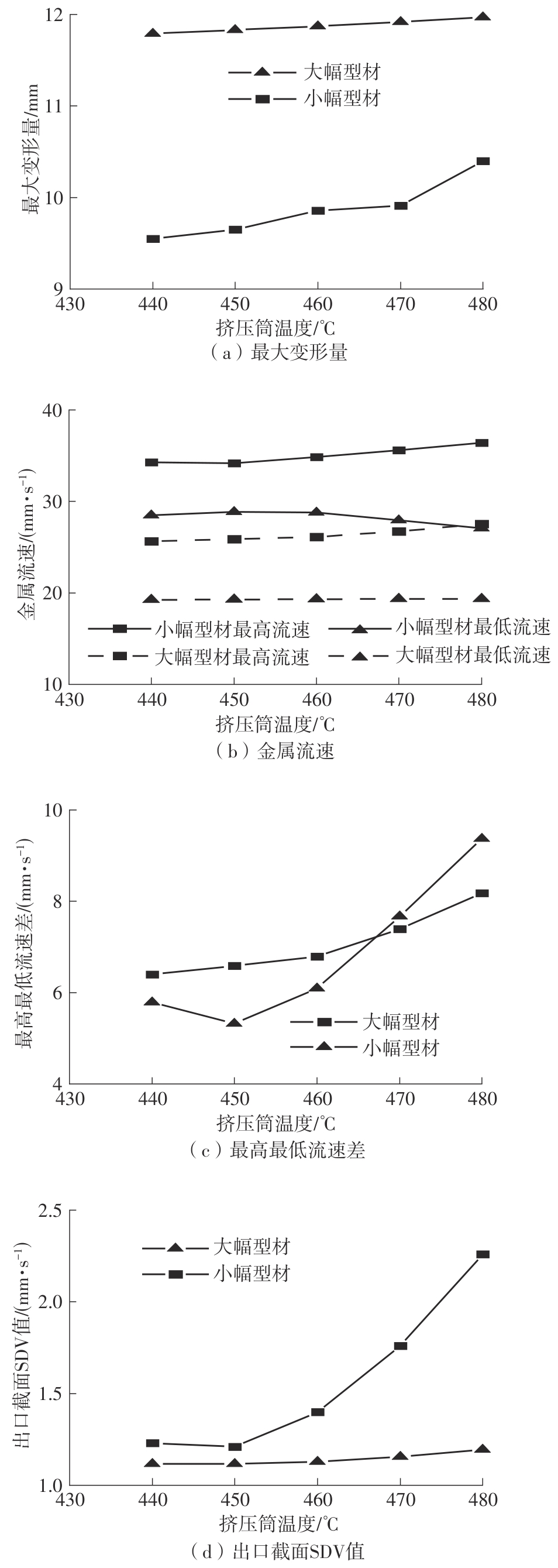
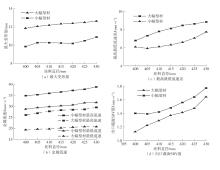
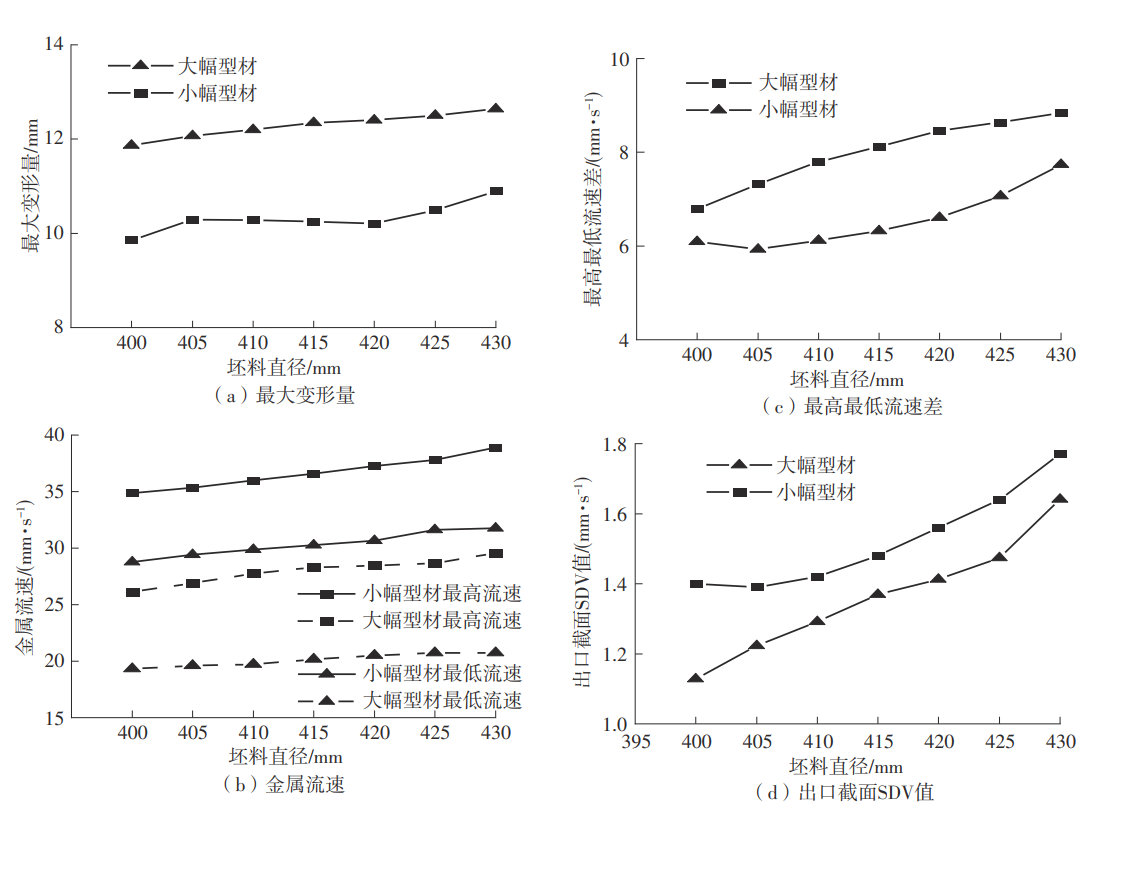
为探究轨道用中空薄壁大小幅铝型材的挤压规律,采用HyperXtrude仿真软件对型材的挤压过程进行了详细的数值模拟,分析模具结构和工艺参数的影响,并对比了2个形状相似的大幅型材和小幅型材的成型规律。结果表明:在模具结构方面,焊合室与引流槽对大小幅型材的影响最为明显,其中焊合室的变化对小幅型材的最大变形量有更明显的降低效果,降幅达42.82%,而大幅型材的降幅为25.34%;引流槽的变化则表现出不同的影响趋势,引流槽变化后,大幅型材的最大变形量降幅为40.88%,而小幅型材的为24.72%,其原因是小幅型材的引流槽较短,大幅型材引流槽的修改则更为复杂,故引流槽变化对大幅型材的影响更为显著。在工艺参数方面,分析了不同条件下型材金属变形量、金属流速和型材出口截面流速均方差的变化,发现挤压速度和模具温度对大幅型材的影响更为显著,而坯料直径对小幅型材的影响更为显著。该文研究结果为优化铝型材的挤压工艺提供了理论依据。
中图分类号: