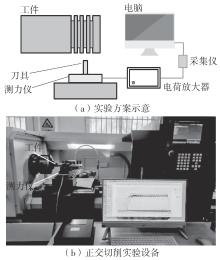
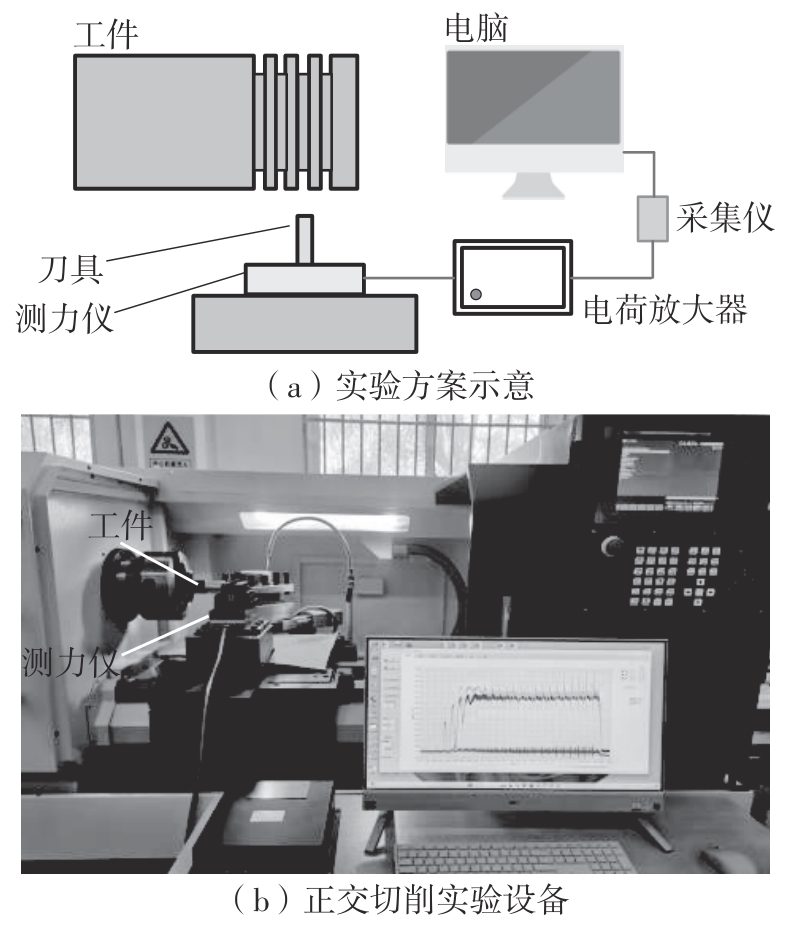
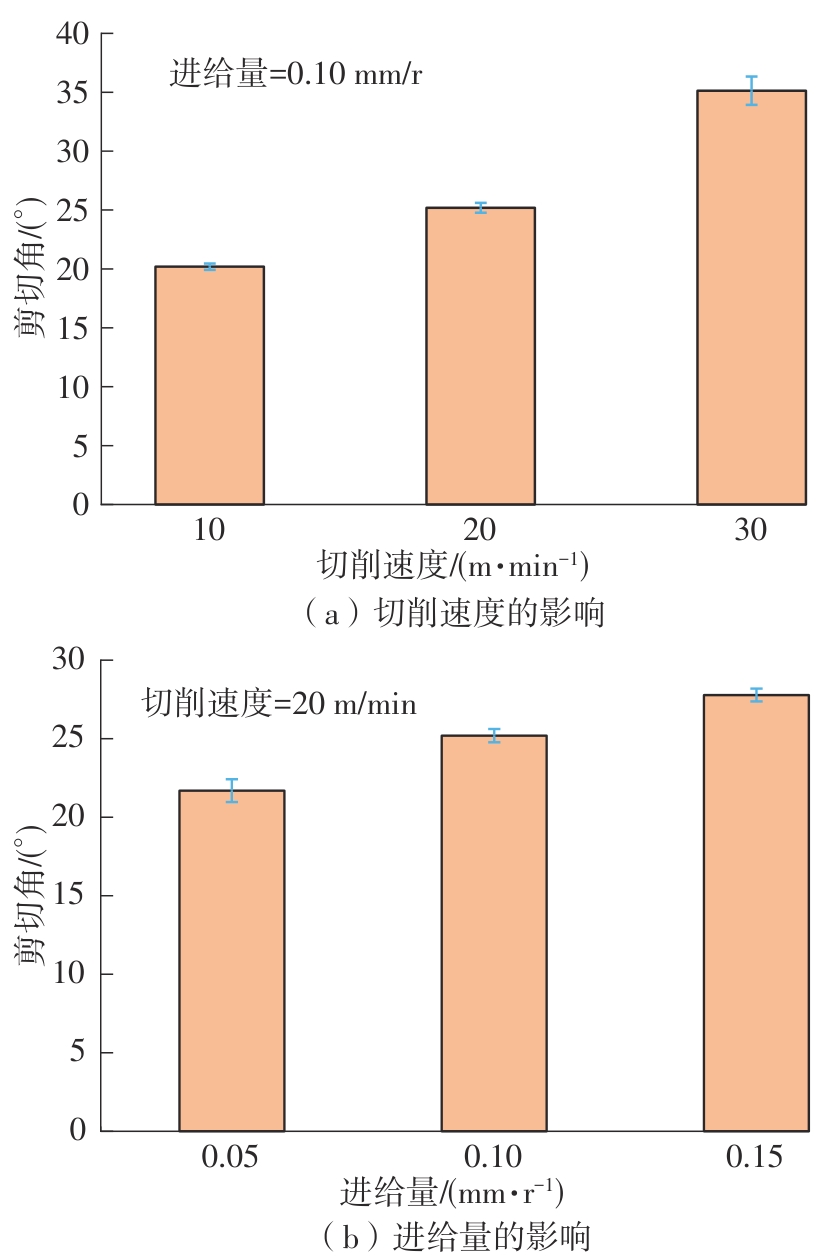
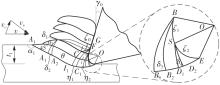
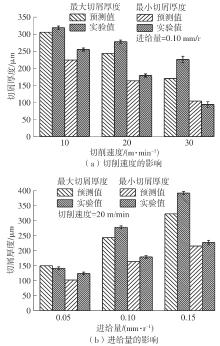
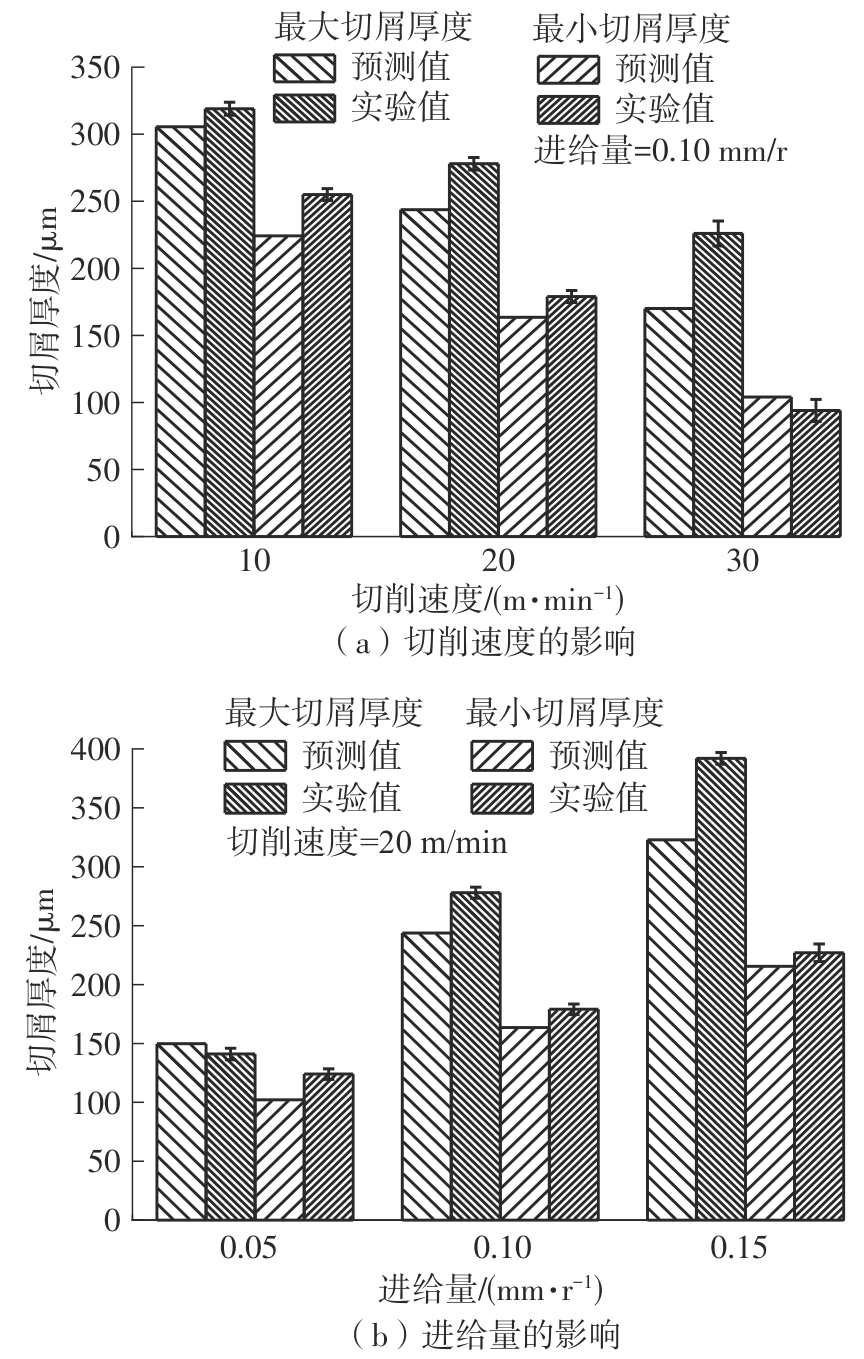
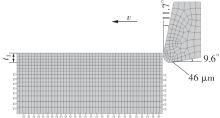
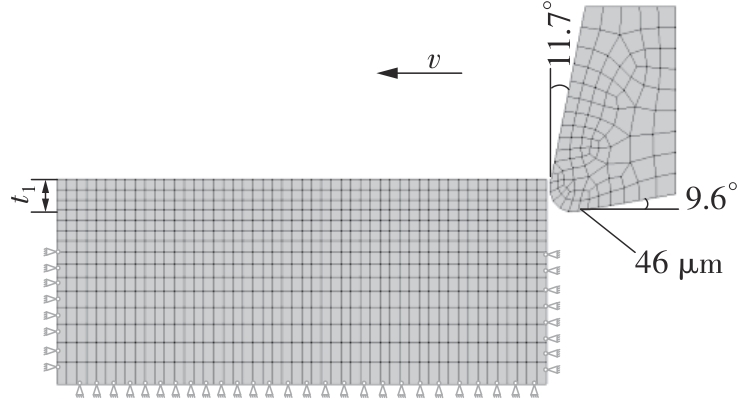
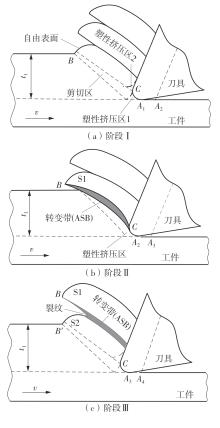
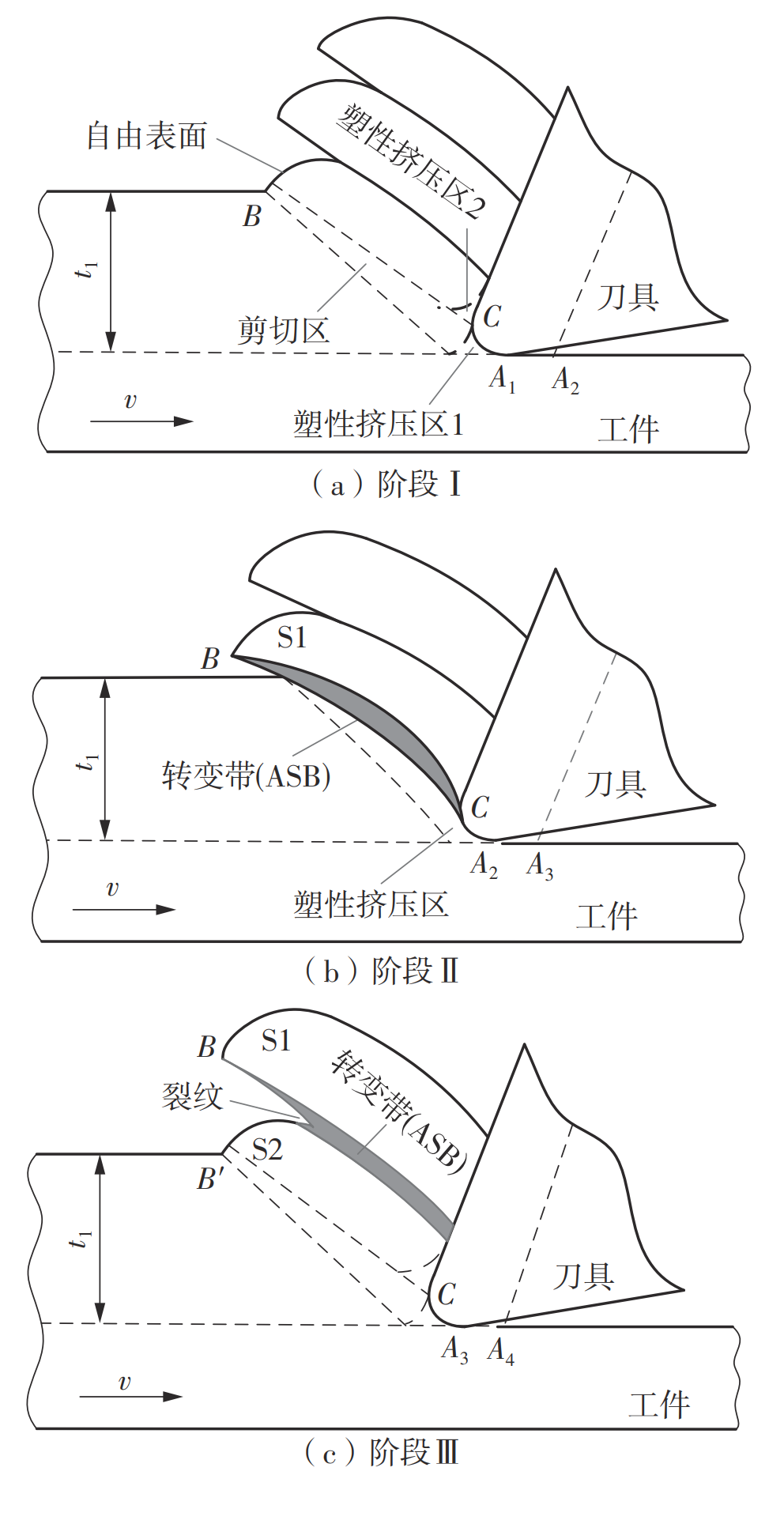
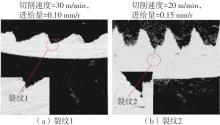
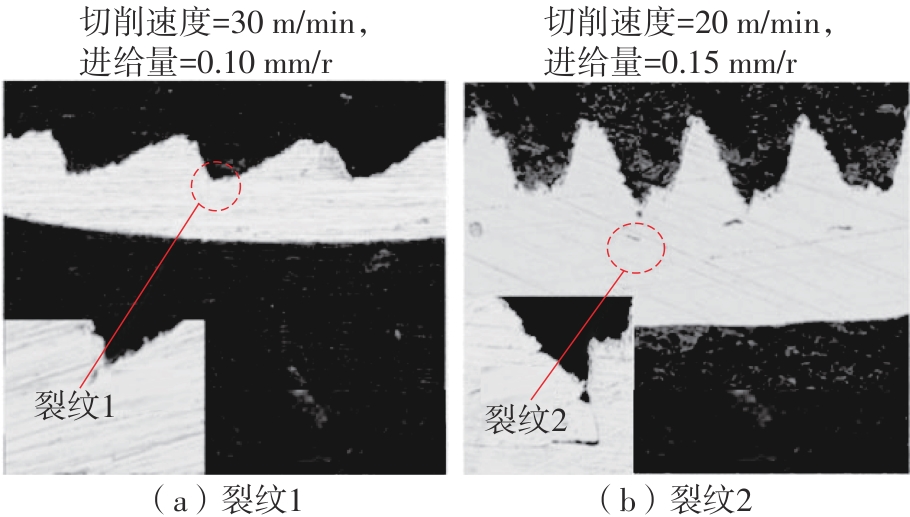
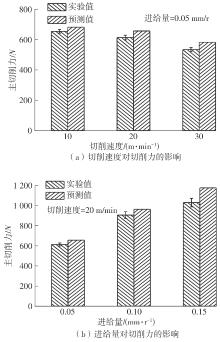
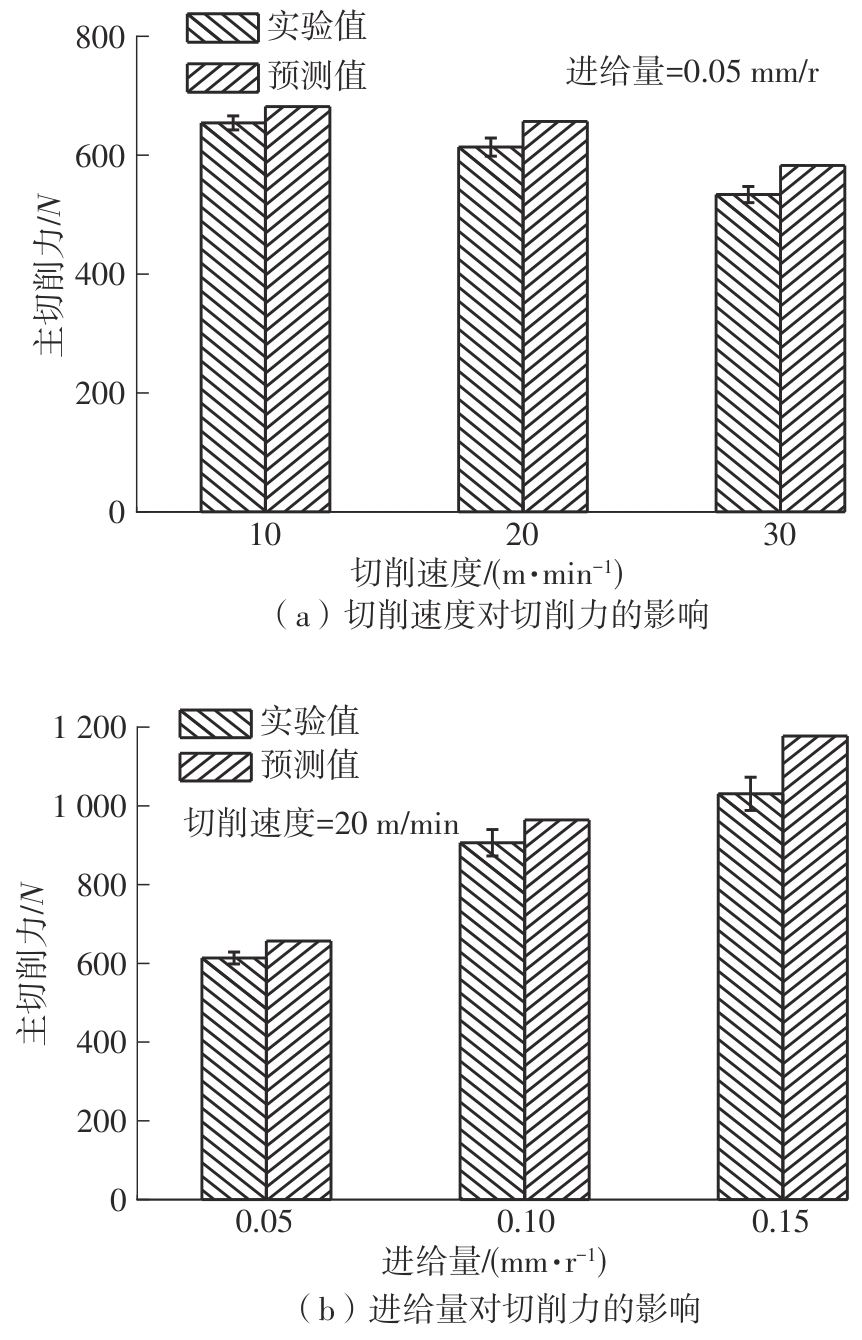
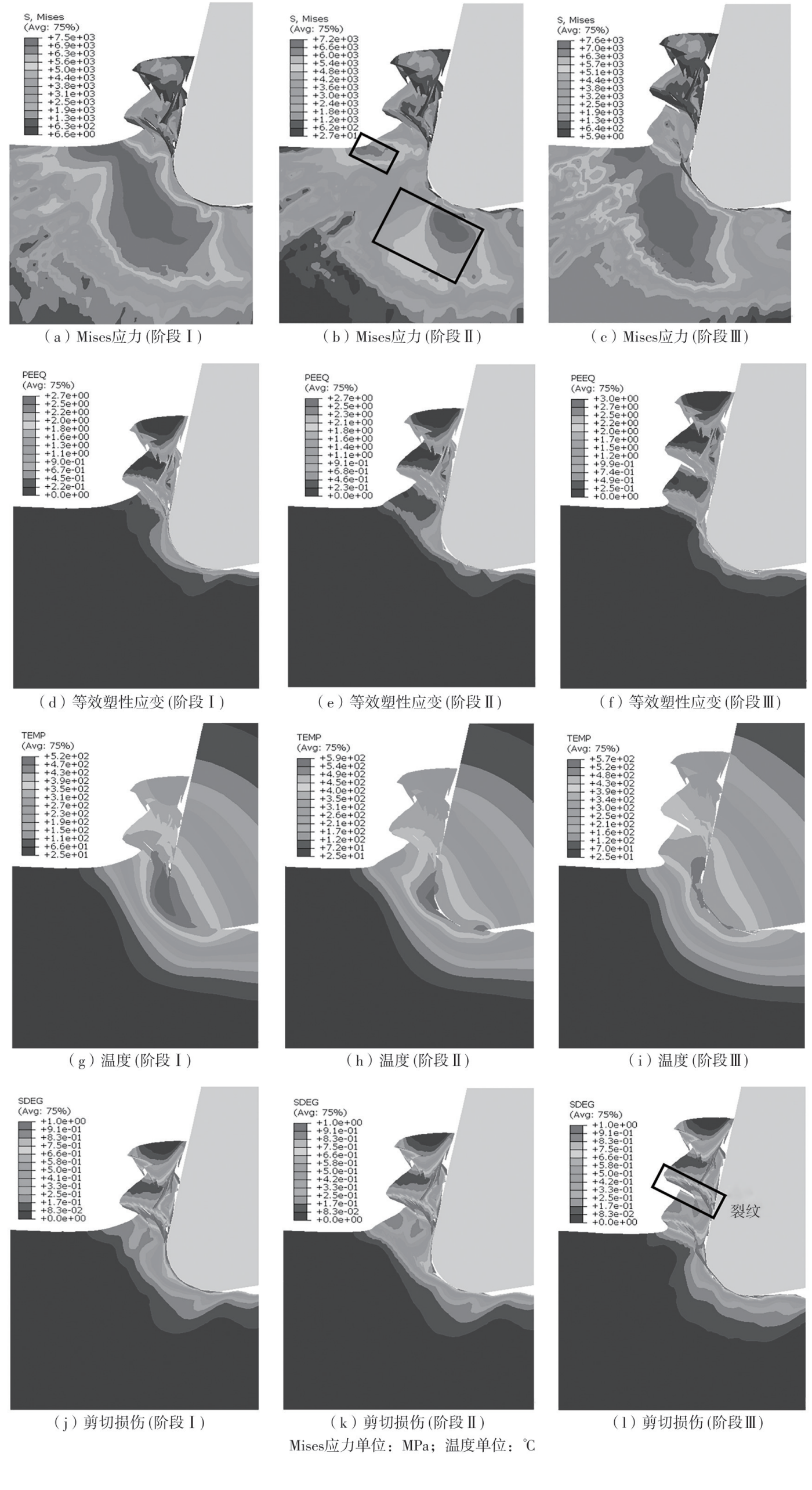
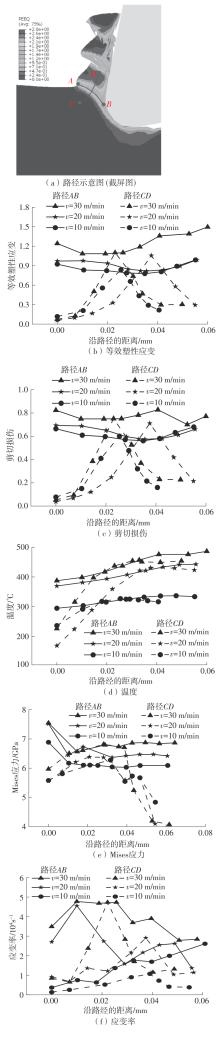
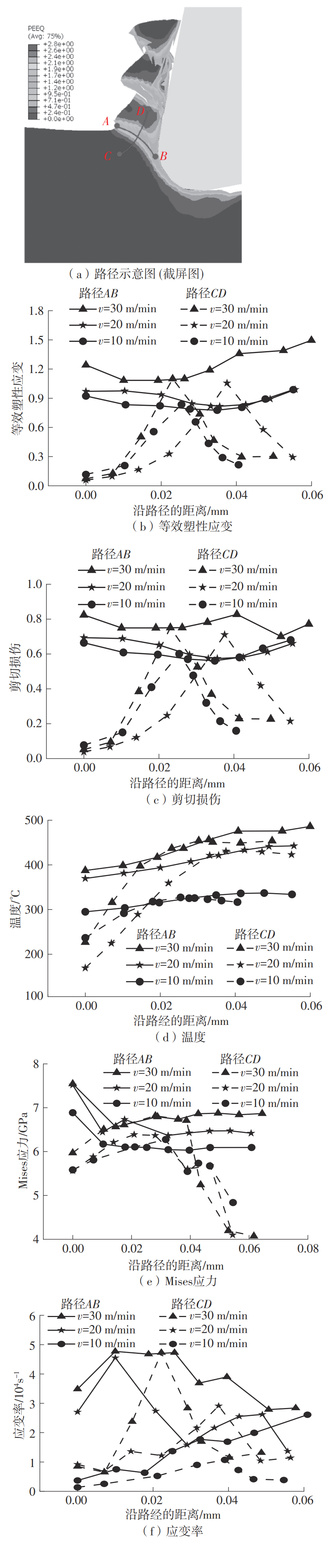
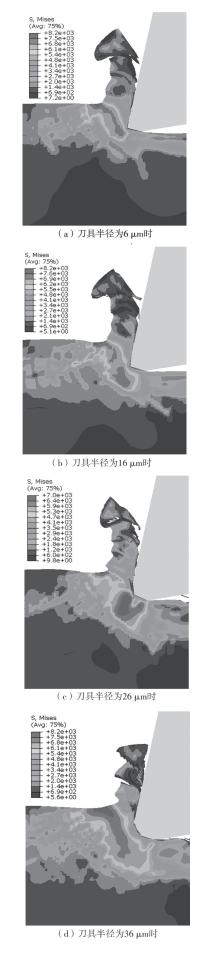
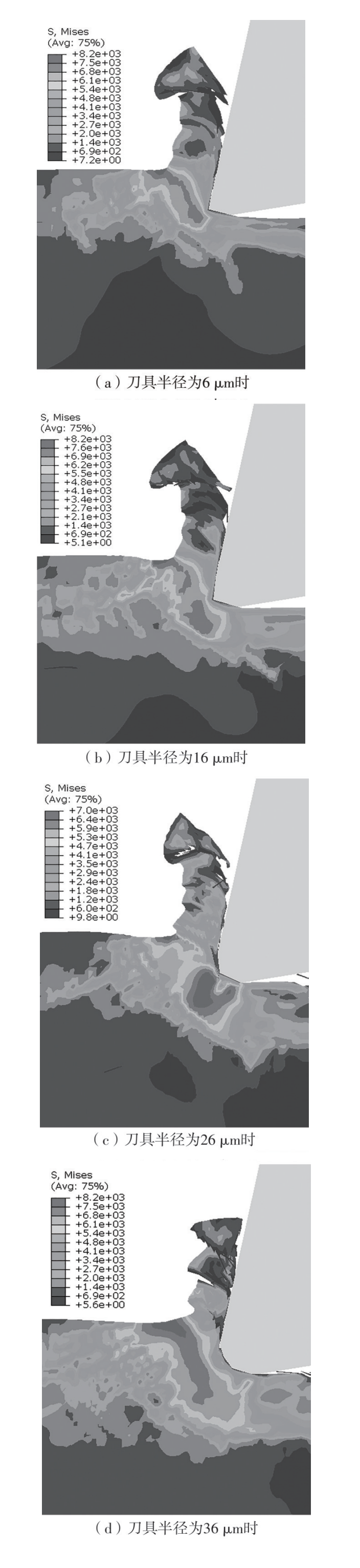
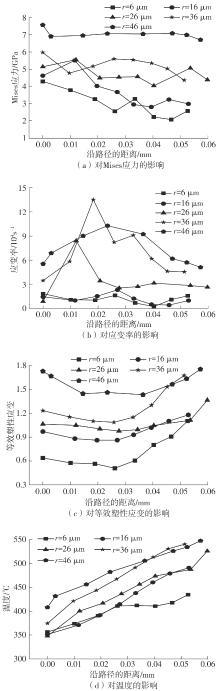
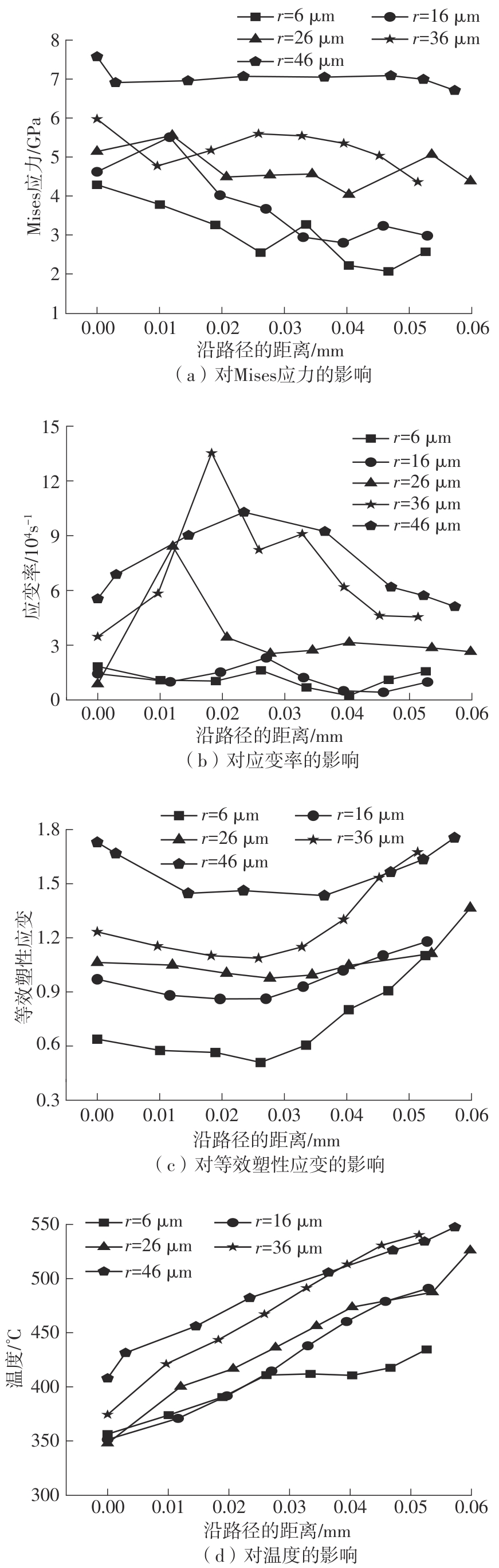
| 1 |
李福林,谭海兵,孟令超,等 .新型铸&锻GH4198合金组织特征及偏析行为[J].稀有金属,2020,44(8):807-815.
|
|
LI Fulin, TAN Haibing, MENG Lingchao,et al .Microstructural characteristics and segregation behavior of a newly developed cast & wrought superalloy GH4198[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2020,44(8):807-815.
|
| 2 |
谷月峰,崔传勇,袁勇,等 .一种高性能航空涡轮盘用铸锻合金的研究进展[J].金属学报,2015,51(10):1191-1206.
|
|
GU Yuefeng, CUI Chuanyong, YUAN Yong,et al .Research progress in a high performance cast & wrought superalloy for turbine disc applications[J].Acta Metall Sinica,2015,51(10):1191-1206.
|
| 3 |
LIU C, WAN M, ZHANG W,et al .Chip formation mechanism of Inconel 718:a review of models and approaches[J].Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2021,34(1):1-16.
|
| 4 |
LIU D, NI C, WANG Y,et al .Review of serrated chip characteristics and formation mechanism from conventional to additively manufactured titanium alloys[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2024,970:172573.
|
| 5 |
VYAS A, SHAW M C .Mechanics of saw-tooth chip formation in metal cutting[J].1999,121(2):163-172.
|
| 6 |
史红艳,赵先锋,姜雪婷 .滑移线场理论在正交切削过程中的研究现状[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(1):14-31.
|
|
SHI Hongyan, ZHAO Xianfeng, JIANG Xueting .Current research on the application of slip line field theory in the orthogonal cutting process[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2019,47(1):14-31.
|
| 7 |
CHEN X, TANG J, DING H,et al .A new geometric model of serrated chip formation in high-speed machining[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,62:632-645.
|
| 8 |
PANG L, HOSSEINI A, HUSSEIN H M,et al .Application of a new thick zone model to the cutting mechanics during end-milling[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2015,96:91-100.
|
| 9 |
FANG N .Slip-line modeling of machining with a rounded-edge tool—Part I:new model and theory[J].Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,2003,51(4):715-742.
|
| 10 |
UYSAL A, JAWAHIR I S .Analysis of slip-line model for serrated chip formation in orthogonal machining of AISI 304 stainless steel under various cooling/lubricating conditions[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,67:447-460.
|
| 11 |
王敏杰,王阳,魏兆成,等 .切削过程绝热剪切带的滑移线场研究[J].机械工程学报,2022,58(7):284-294.
|
|
WANG Minjie, WANG Yang, WEI Zhaocheng,et al .Slip line field of adiabatic shear band in cutting process[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2022,58(7):284-294.
|
| 12 |
CHEN X, TANG J, Ding H,et al .A new geometric model of serrated chip formation in high-speed machining[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2021,62:632-645.
|
| 13 |
LI B, ZHANG S, ZHANG Q,et al .Simulated and experimental analysis on serrated chip formation for hard milling process[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2019,44:337-348.
|
| 14 |
JOMAA W, MACHRI O, LEVESQUE J,et al .Finite element simulation and analysis of serrated chip formation during high-speed machining of AA7075-T651 alloy[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2017,26:446-458.
|
| 15 |
WANG B, LIU Z .Investigations on the chip formation mechanism and shear localization sensitivity of high-speed machining Ti6Al4V[J].The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2014,75(5/6/7/8):1065-1076.
|
| 16 |
付秀丽,艾兴,刘战强,等 .高速切削加工航空铝合金7050-T7451剪切角模型研究[J].中国机械工程,2007,18(2):220-224.
|
|
FU Xiuli, AI Xing, LIU Zhanqiang,et al .Study on shear angle model of aluminum alloy 7050-T7451 in high speed machining[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2007,18(2):220-224.
|
| 17 |
HILL R .On the limits set by plastic yielding to the intensity of singularities of stress[J].Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids,1954,2(4):278-285.
|
| 18 |
刘龙飞,胡少华,卢立伟 .切削速度对AZ31镁合金高速切削切屑形成的影响[J].稀有金属,2016,40(7):654-659.
|
|
LIU Longfei, HU Shaohua, LU Liwei .Sawtooth chip of AZ31 magnesium alloy under high-speed cutting and different cutting velocities[J].Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2016,40(7):654-659.
|
| 19 |
XIONG Y, WANG W, JIANG R,et al .Mechanisms and FEM simulation of chip formation in orthogonal cutting in-situ TiB2/7050Al MMC[J].Materials,2018,11(4):606/1-19.
|
| 20 |
王兵 .高速切削材料变形及断裂行为对切屑形成的影响机理研究[D].济南:山东大学,2016.
|
| 21 |
ZHEN-BIN H, KOMANDURI R .On a thermomechanical model of shear instability in machining[J].CIRP Annals,1995,44(1):69-73.
|
| 22 |
殷继花,林有希,孟鑫鑫,等 .航空铝合金7075-T651高速铣削锯齿形切屑的形成机理研究[J].表面技术,2019,48(5):275-285.
|
|
YIN Ji-hua, LIN You-xi, MENG Xin-xin,et al .Formation mechanism of sawtooth chip in high speed milling of aeronautical aluminum alloy 7075-T651[J].Surface Technology,2019,48(5):275-285.
|
| 23 |
杨奇彪 .高速切削锯齿形切屑的形成机理及表征[D].济南:山东大学,2012.
|
| 24 |
谷丽瑶,王敏杰,孙传俊 .高速切削过程绝热剪切局部化断裂的特性试验[J].机械工程学报,2014,50(15):166-171.
|
|
GU Liyao, WANG Minjie, SUN Chuanjun .Experimental study on characteristics of adiabatic shear loca-lization fracture in high speed machining[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2014,50(15):166-171.
|
| 25 |
ZHU X, SHI J, LIU Y,et al .Study on formation mechanism of serrated chip of Ti-6Al-4V titanium alloy based on shear slip theory[J].The International Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Technology,2022,122(3/4):1353-1365.
|