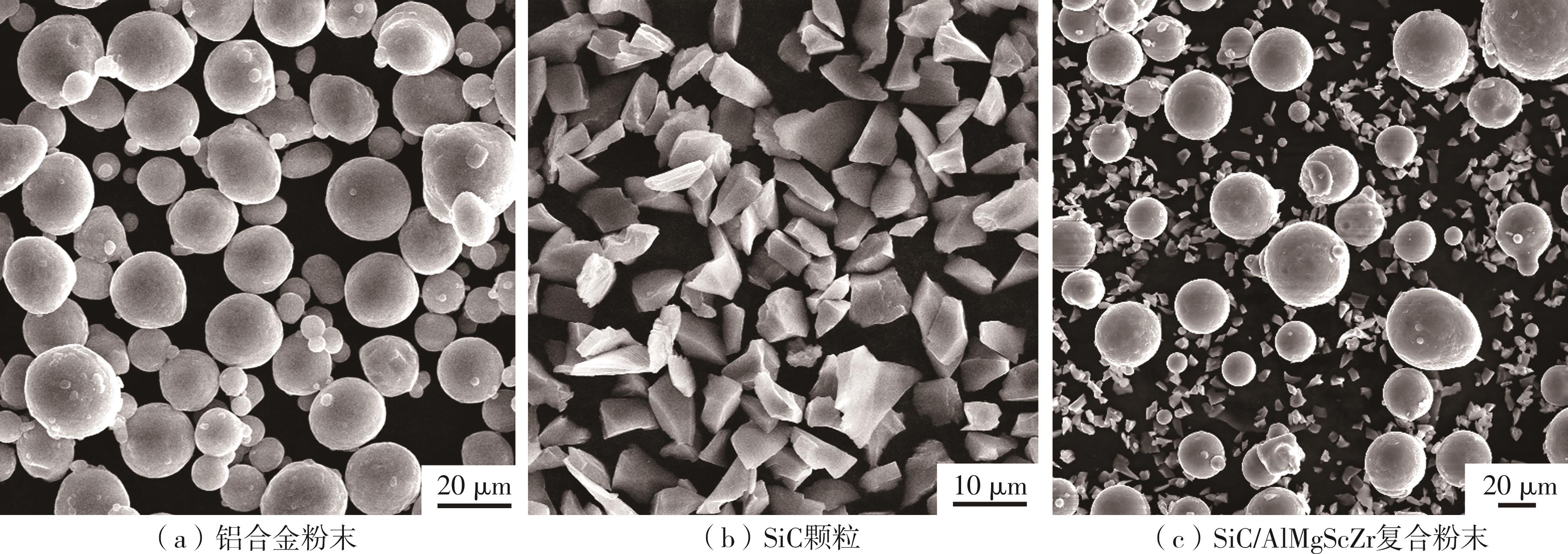
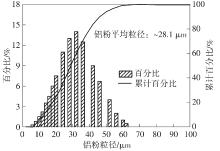
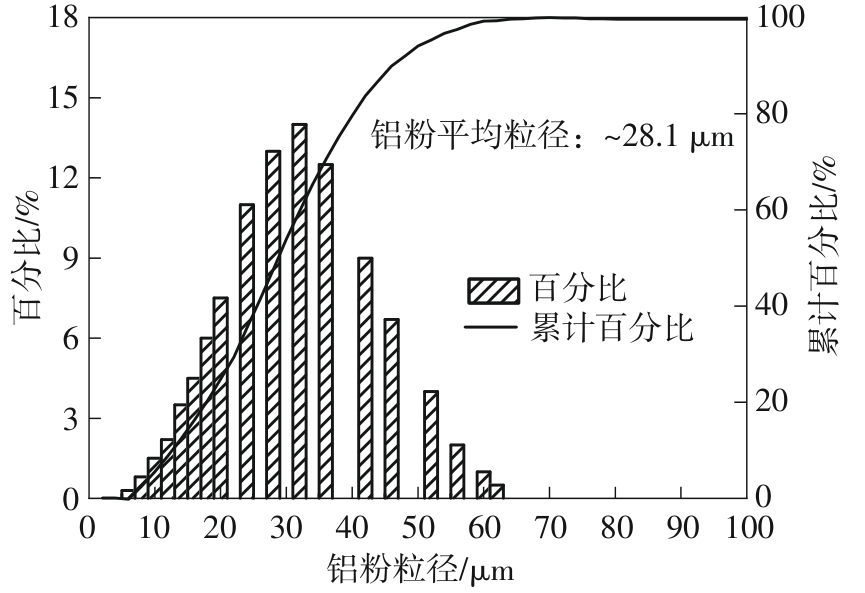
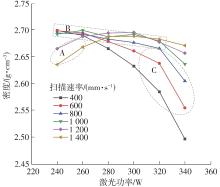
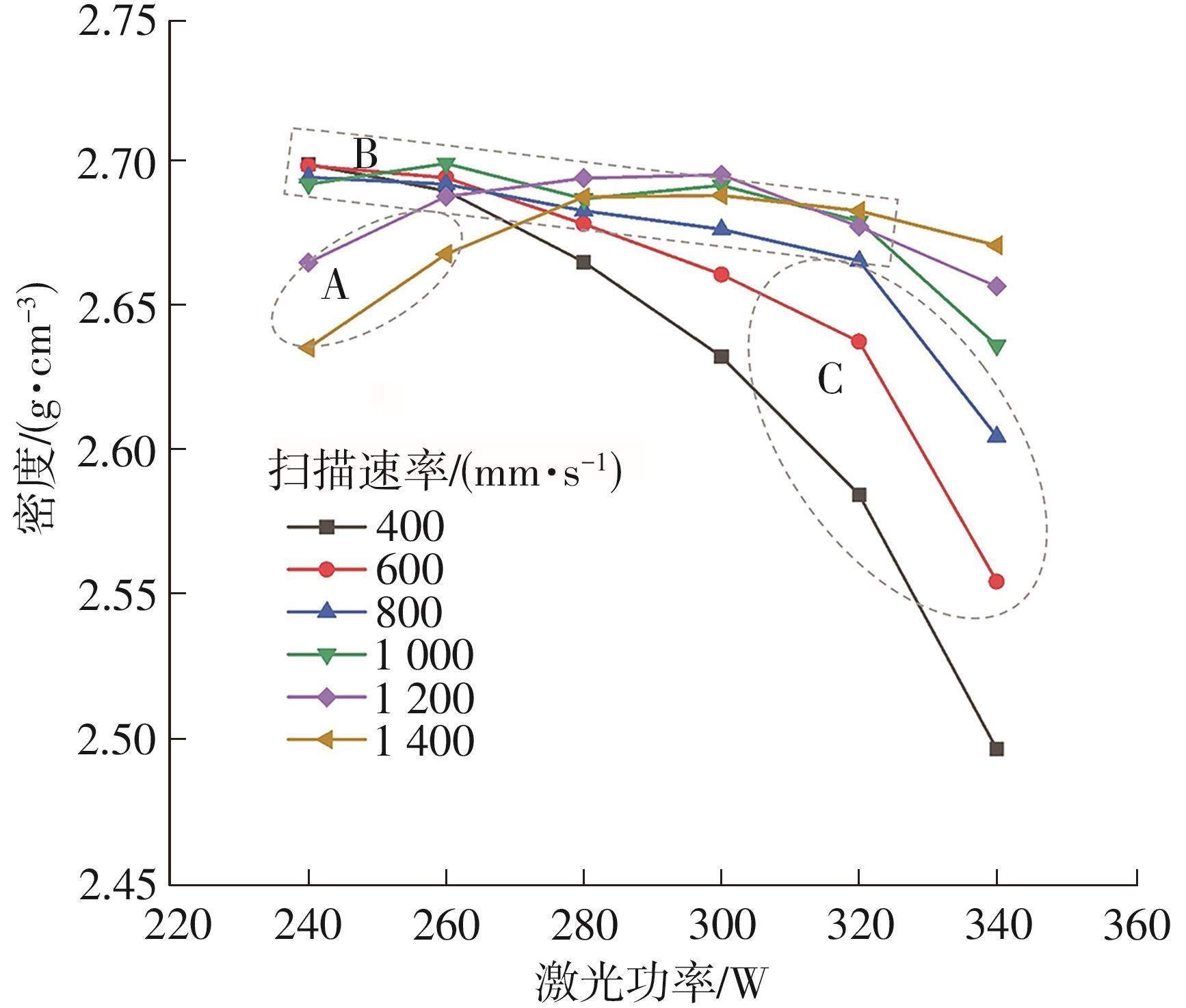
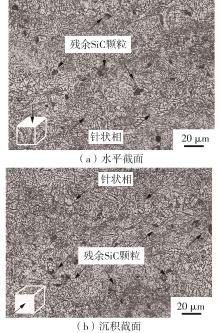
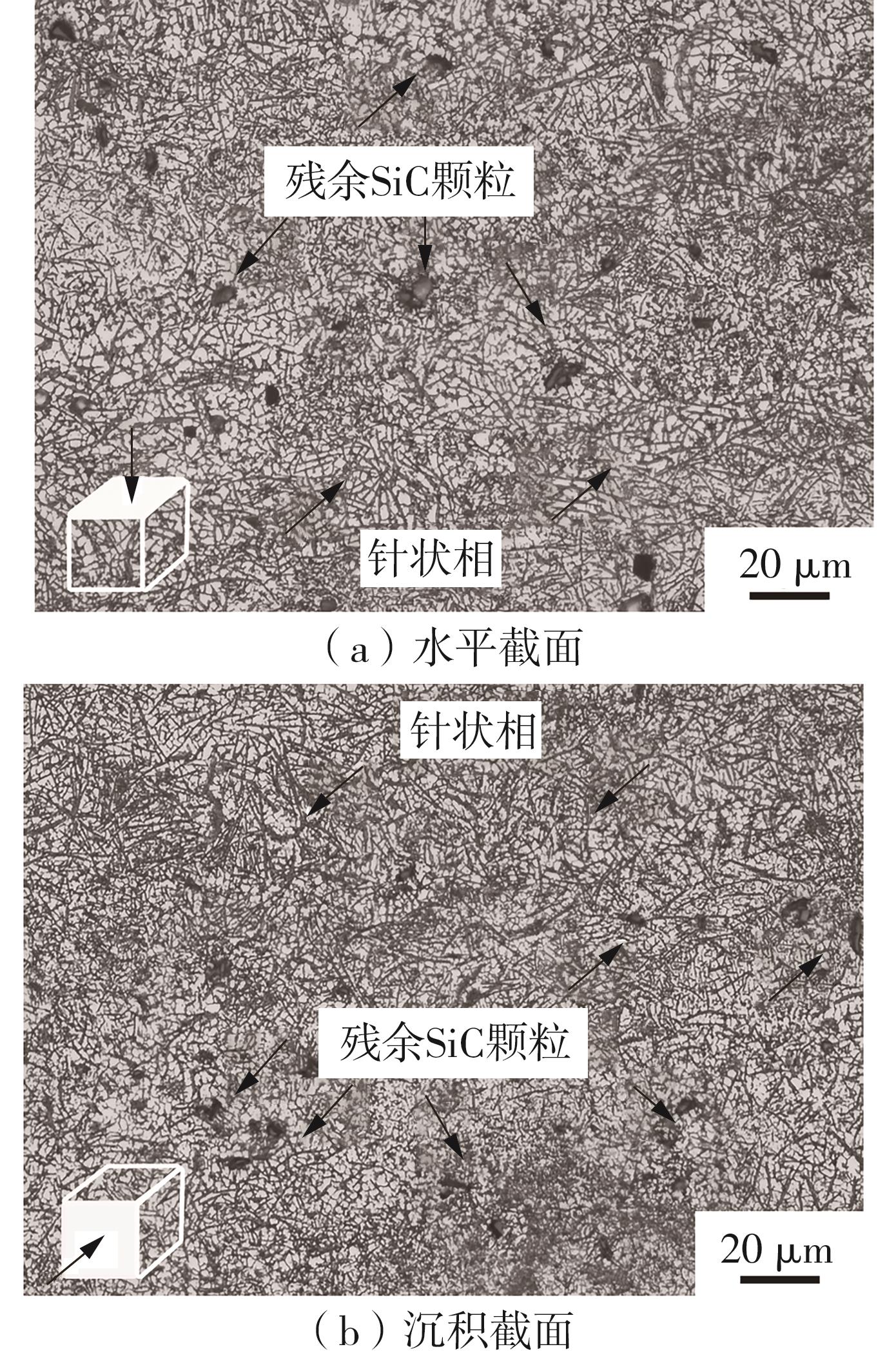
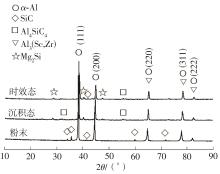
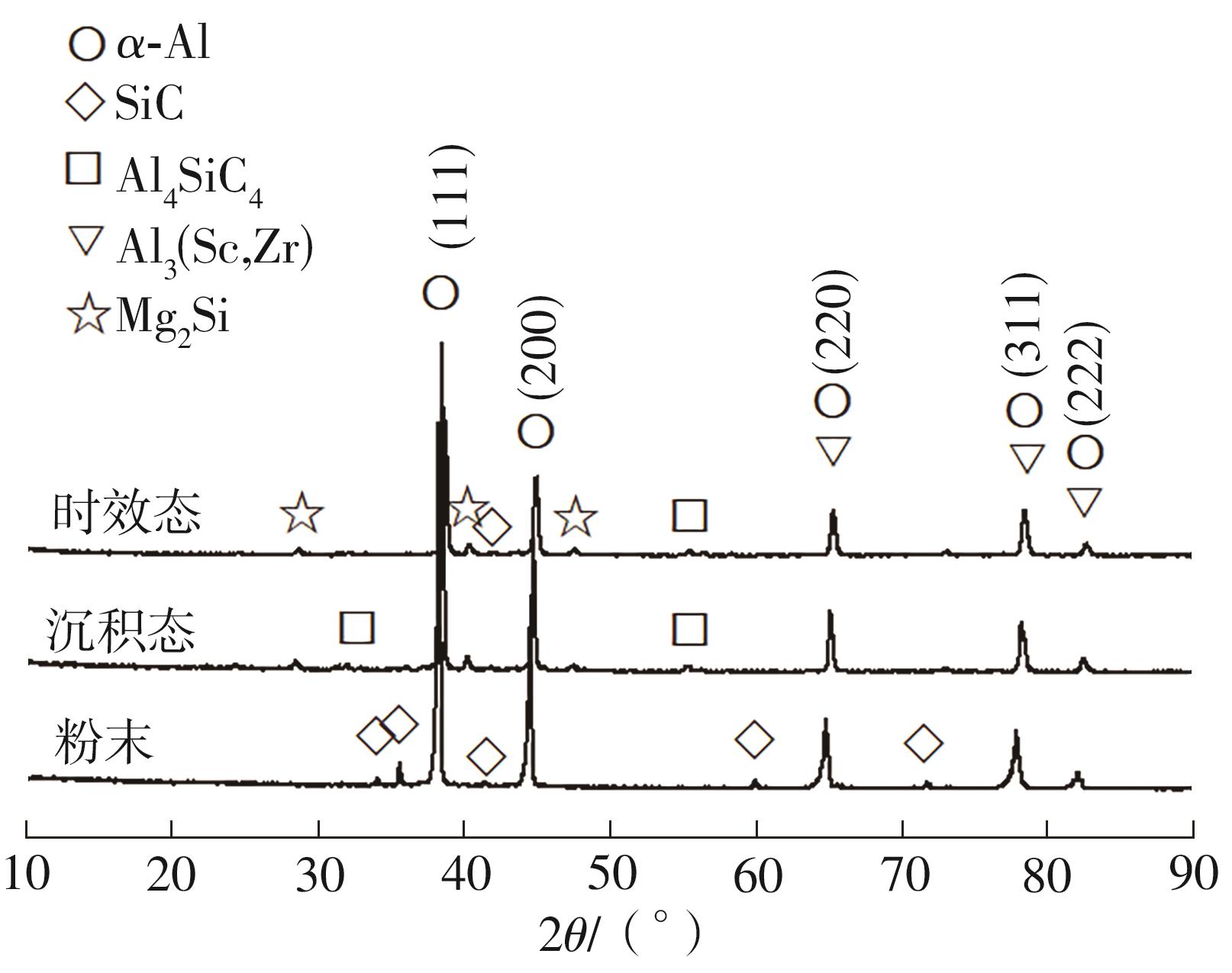
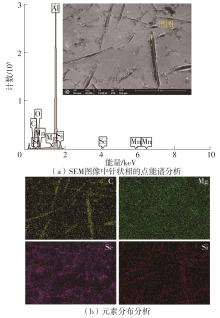
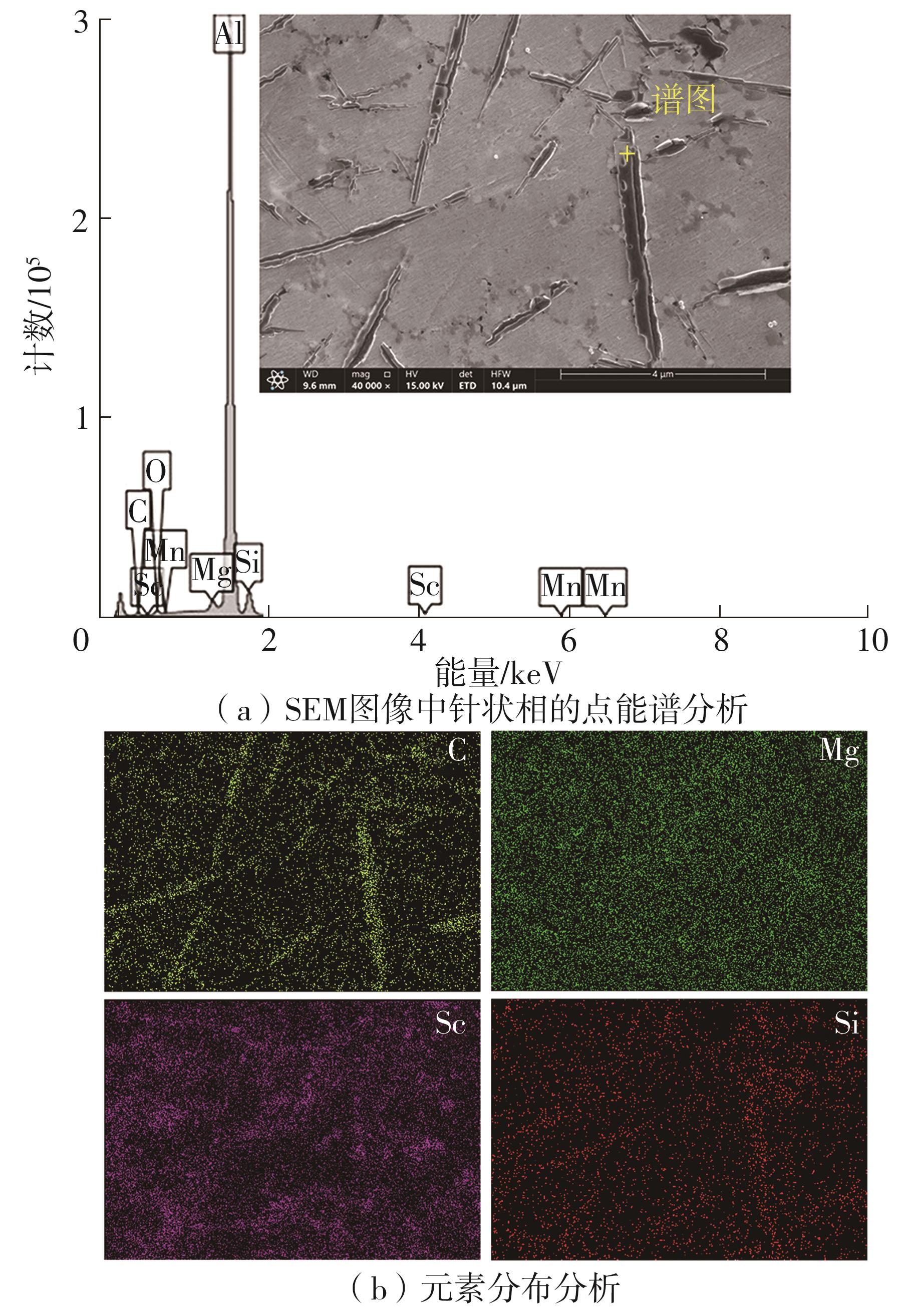
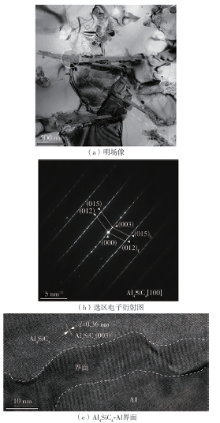
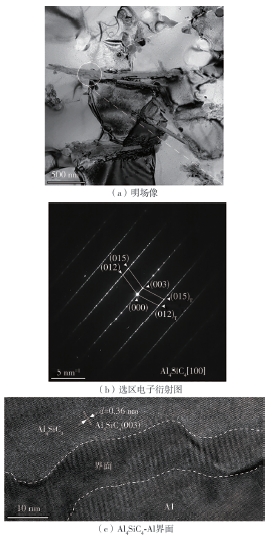
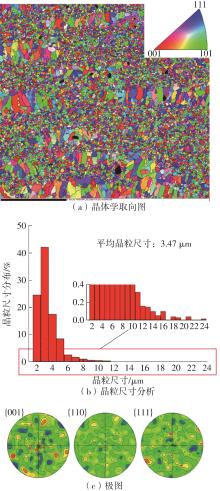
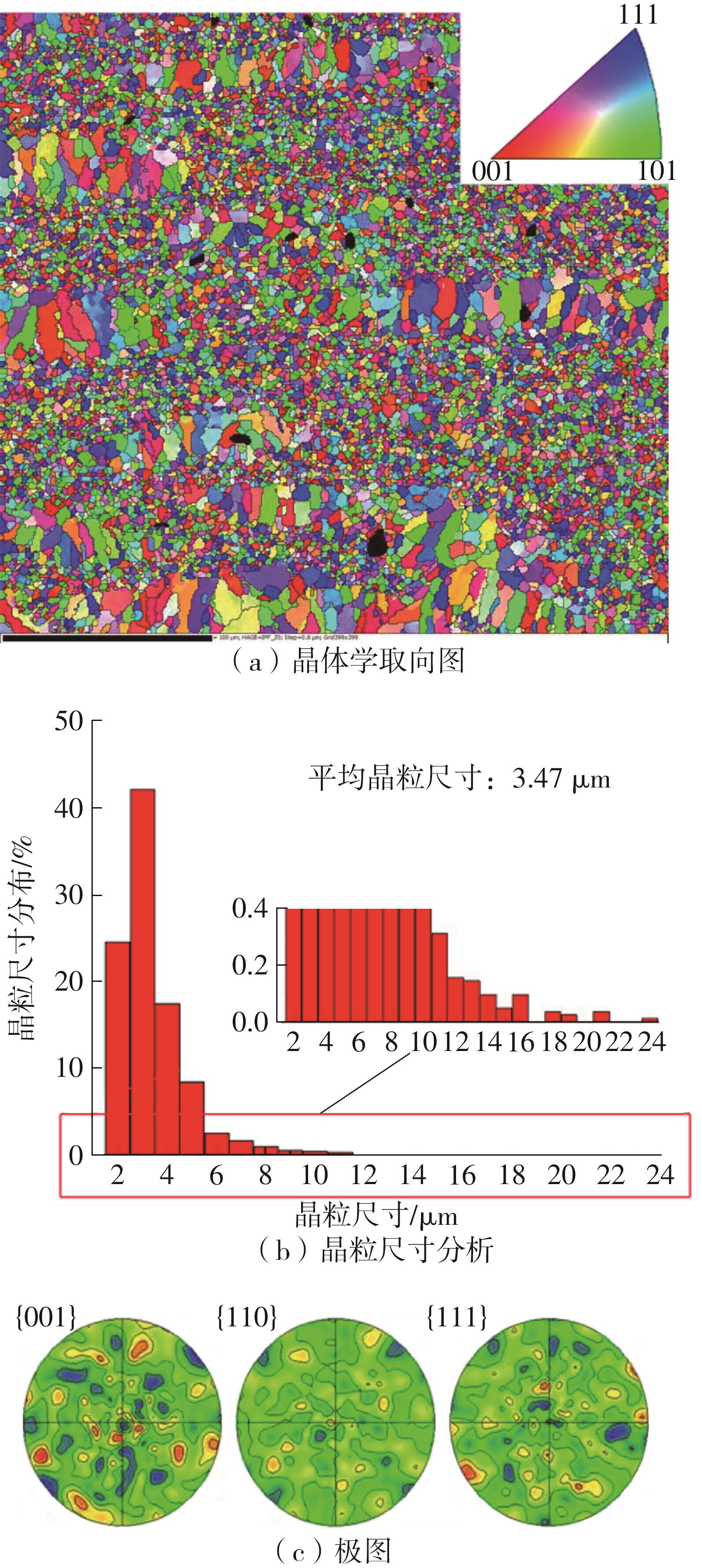
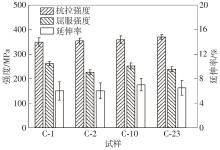
| 1 |
DEBROY T, WEI H L, ZUBACK J,et al .Additive manufacturing of metallic components-process,structure and properties[J].Progress in Materials Science,2018,92:112-224.
|
| 2 |
ZHANG J L, GAO J B, SONG B,et al .A novel crack-free Ti-modified Al-Cu-Mg alloy designed for selective laser melting[J].Additive Manufacturing,2020,38:101829/1-12.
|
| 3 |
WEIDMANN J, GROßMANN A, MITTELSTEDT C .Laser powder bed fusion manufacturing of aluminum honeycomb structures:theory and testing[J].International Journal of Mechanical Sciences,2020,180:105639/1-18.
|
| 4 |
OLAKANMI E O, COCHRANE R F, DALGARNO K W .A review on selective laser sintering/melting (SLS/SLM) of aluminium alloy powders:processing,microstructure,and properties[J].Progress in Materials Science,2015,74:401-477.
|
| 5 |
王悦,王继杰,张昊,等 .热处理对激光选区熔化AlSi10Mg合金显微组织及力学性能的影响[J].金属学报,2021,57(5):613-622.
|
|
WANG Yue, WANG Jijie, ZHANG Hao,et al .Effects of heat treatments on microstructure and mechanical properties of AlSi10Mg alloy produced by selective laser melting[J].Acta Metallurgica Sinica,2021,57(5):613-622.
|
| 6 |
GU D D, YANG Y, XI L X,et al .Laser absorption behavior of randomly packed powder-bed during selective laser melting of SiC and TiB2 reinforced Al matrix composites[J].Optics and Laser Technology,2019,119:105600/1-9.
|
| 7 |
LI X P, JI G, CHEN Z,et al .Selective laser melting of nano-TiB2 decorated AlSi10Mg alloy with high fracture strength and ductility[J].Acta Materialia,2017,29:183-193.
|
| 8 |
XI L, GU D D, GUO S,et al .Grain refinement in laser manufactured Al-based composites with TiB2 ceramic[J].Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2020,9(3):2611-2622.
|
| 9 |
GAO C, XIAO Z, LIU Z,et al .Selective laser melting of nano-TiN modified AlSi10Mg composite powder with low laser reflectivity[J].Materials Letters,2019,236:362-365.
|
| 10 |
DAI D H, GU D D .Influence of thermodynamics within molten pool on migration and distribution state of reinforcement during selective laser melting of AlN/AlSi10Mg composites[J].International Journal of Machine Tools and Manufacture,2016,100:14-24.
|
| 11 |
XI L X, ZHANG H, WANG P,et al .Comparative investigation of microstructure,mechanical properties and strengthening mechanisms of Al-12Si/TiB2 fabricated by selective laser melting and hot pressing[J].Ceramics International,2018,44(15):17635-17642.
|
| 12 |
XI L X, DING K, ZHANG H,et al .In-situ synthesis of aluminum matrix nanocomposites by selective laser melting of carbon nanotubes modified Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloys[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,891:162047/1-9.
|
| 13 |
WANG J H, LIU T, LUO L S,et al .Selective laser melting of high-strength TiB2/AlMgScZr composites:microstructure,tensile deformation behavior,and mechanical properties[J].Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2022,16:786-800.
|
| 14 |
ZHAO X, GU D D, MA C L,et al .Microstructure characteristics and its formation mechanism of selective laser melting SiC reinforced Al-based composites[J].Vacuum,2019,160:189-196.
|
| 15 |
马国楠,樊子煜,杨鹏伟,等 .选区激光熔化TiC/AlMgScZr复合材料的成形工艺研究[J].兵器材料科学与工程,2023,46(3):41-47.
|
|
MA Guonan, FAN Ziyu, YANG Pengwei,et al .Forming process of TiC/AlMgScZr composites by selective laser melting[J].Ordnance Material Science and Engineering,2023,46(3):41-47.
|
| 16 |
MA R L, PENG C Q, CAI Z Y,et al .Manipulating the microstructure and tensile properties of selective laser melted Al-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy through heat treatment[J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,831:154773/1-10.
|
| 17 |
ZHAO J H, XUE X, WANG B B,et al .Selective laser melting Al-3.4Mg-0.5Mn-0.8Sc-0.4Zr alloys:from melting pool to the microstructure and mechanical pro-perties[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A,2021,825:141889/1-10.
|
| 18 |
BAYOUMY D, SCHLIEPHAKE D, DIETRICH S,et al .Intensive processing optimization for achieving strong and ductile Al-Mn-Mg-Sc-Zr alloy produced by selective laser melting[J].Materials & Design,2021,198:109317/1-15.
|
| 19 |
ARUNACHALAM R, KRISHNAN P K, MURALIRAJA R .A review on the production of metal matrix composites through stir casting-furnace design,properties,challenges,and research opportunities[J].Journal of Manufacturing Processes,2019,42:213-245.
|
| 20 |
TJONG S C, MA Z Y .Microstructural and mechanical characteristics of in situ metal matrix composites[J].Materials Science & Engineering R-Reports,2000,29(3/4):49-113.
|
| 21 |
VIALA J C, FORTIER P, BOUIX J .Stable and metastable phase equilibria in the chemical interaction between aluminium and silicon carbide[J].Journal of Materials Science,1990,25:1842-1850.
|
| 22 |
GU D D, CHANG F, DAI D H .Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of novel aluminum based composites with multiple reinforcing phases[J].Journal of Manufacturing Science and Engineering,2015,137:021010-1-021010-11.
|
| 23 |
ZHOU S Y, SU Y, WANG H,et al .Selective laser melting additive manufacturing of 7xxx series Al-Zn-Mg-Cu alloy:cracking elimination by co-incorporation of Si and TiB2 [J].Additive Manufacturing,2020,36:101458/1-12.
|
| 24 |
TAN Q Y, FAN Z Q, TANG X Q,et al .A novel strategy to additively manufacture 7075 aluminium alloy with selective laser melting[J].Materials Science and Engineering:A,2021,821:141638/1-15.
|
| 25 |
ANANDKUMAR R, ALMEIDA A, COLAÇO R,et al .Microstructure and wear studies of laser clad Al-Si/SiC(p) composite coatings[J].Surface and Coatings Technology,2007,201(24):9497-9505.
|
| 26 |
SPIERINGS A B, DAWSON K, KERN K,et al .SLM-processed Sc- and Zr-modified Al-Mg alloy:mechanical properties and microstructural effects of heat treatment[J].Materials Science and Engineering A,2017,701:264-273.
|