华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (3): 80-87.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240296
高增益MO-TFT心率信号检测前置放大器研究
吴朝晖, 陈家琳, 赵明剑, 李斌
- 华南理工大学 微电子学院,广东 广州 511442
Research on High-Gain MO-TFT Heart Rate Signal Detection Preamplifier
WU Zhaohui, CHEN Jialin, ZHAO Mingjian, LI Bin
- School of Microelectronics,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 511442,Guangdong,China
摘要:
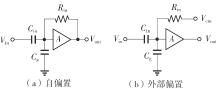
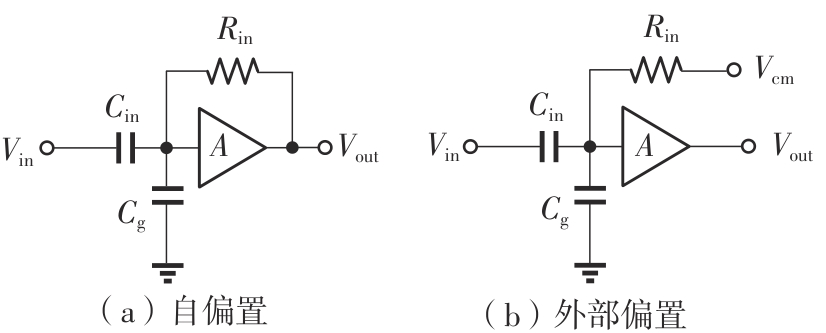
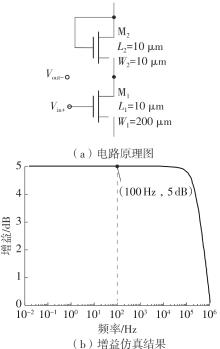
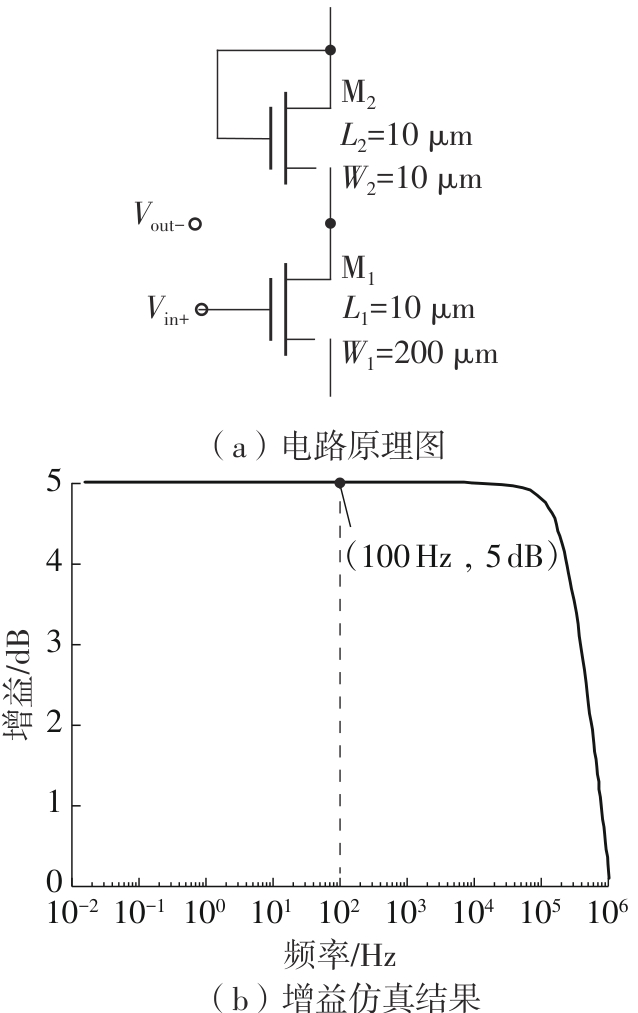
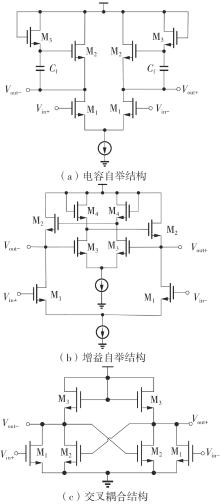
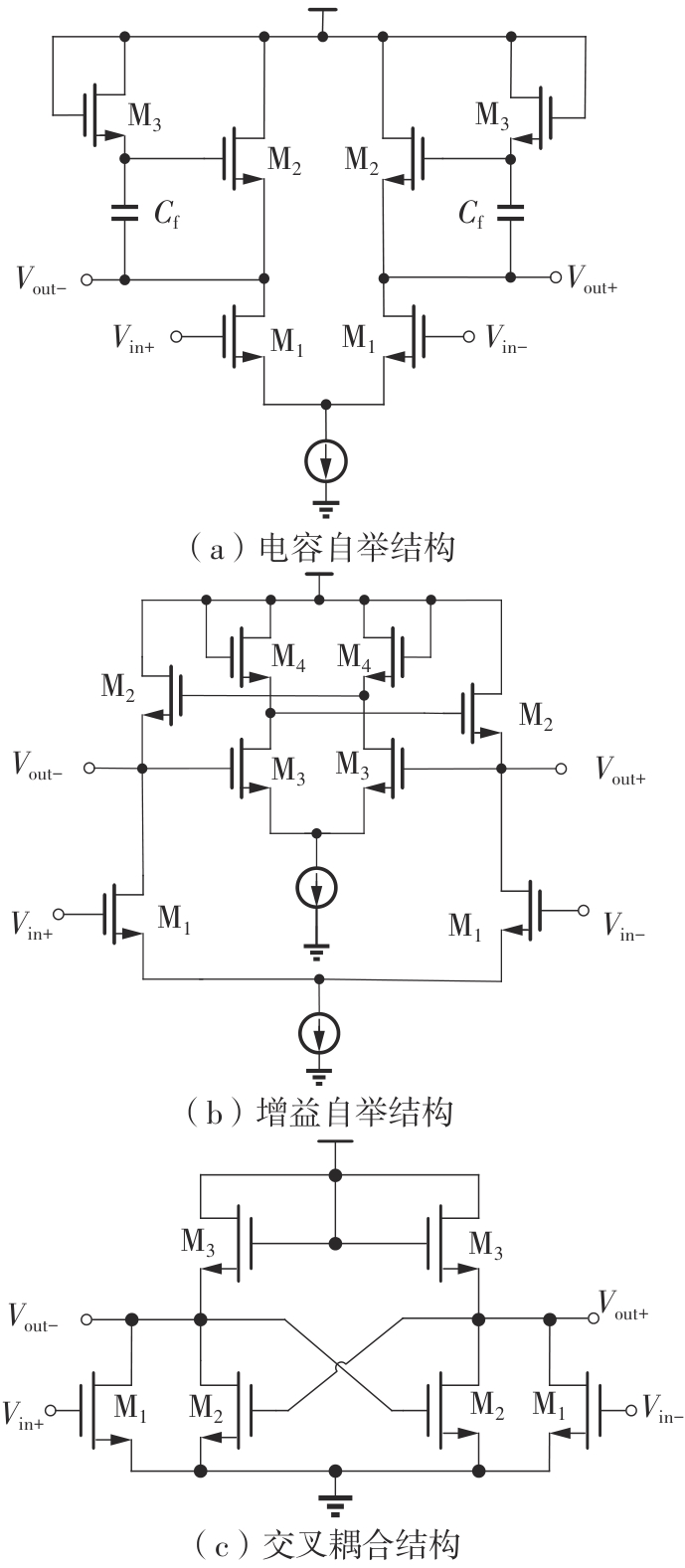
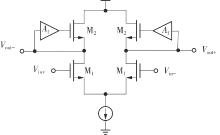
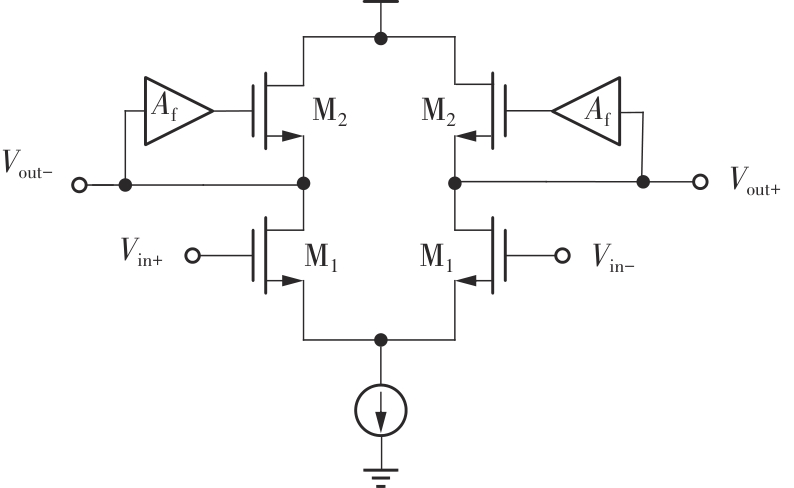
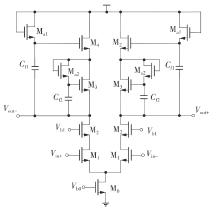
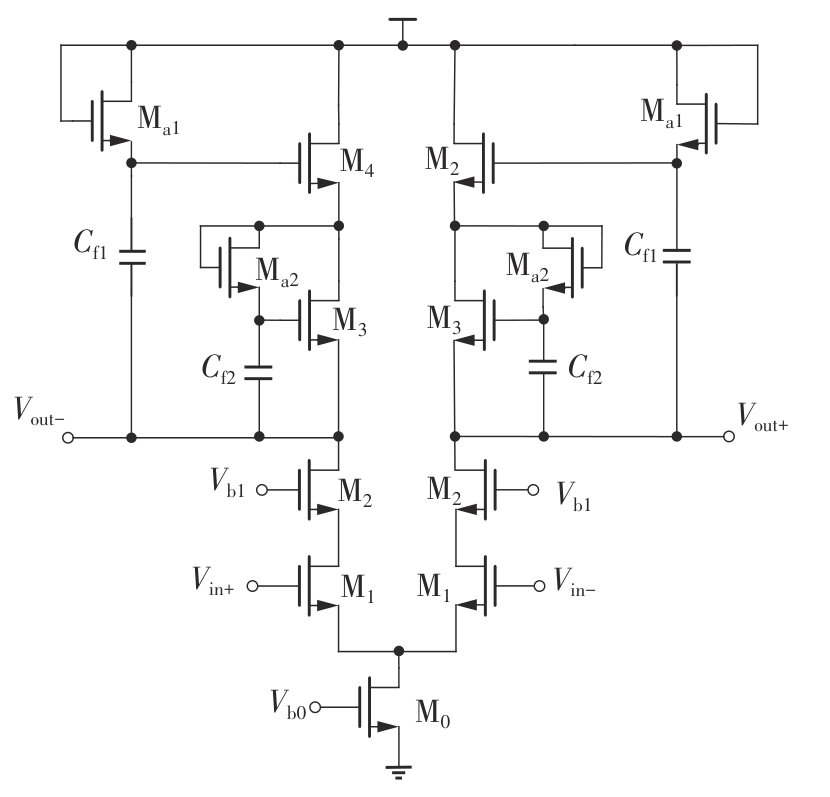
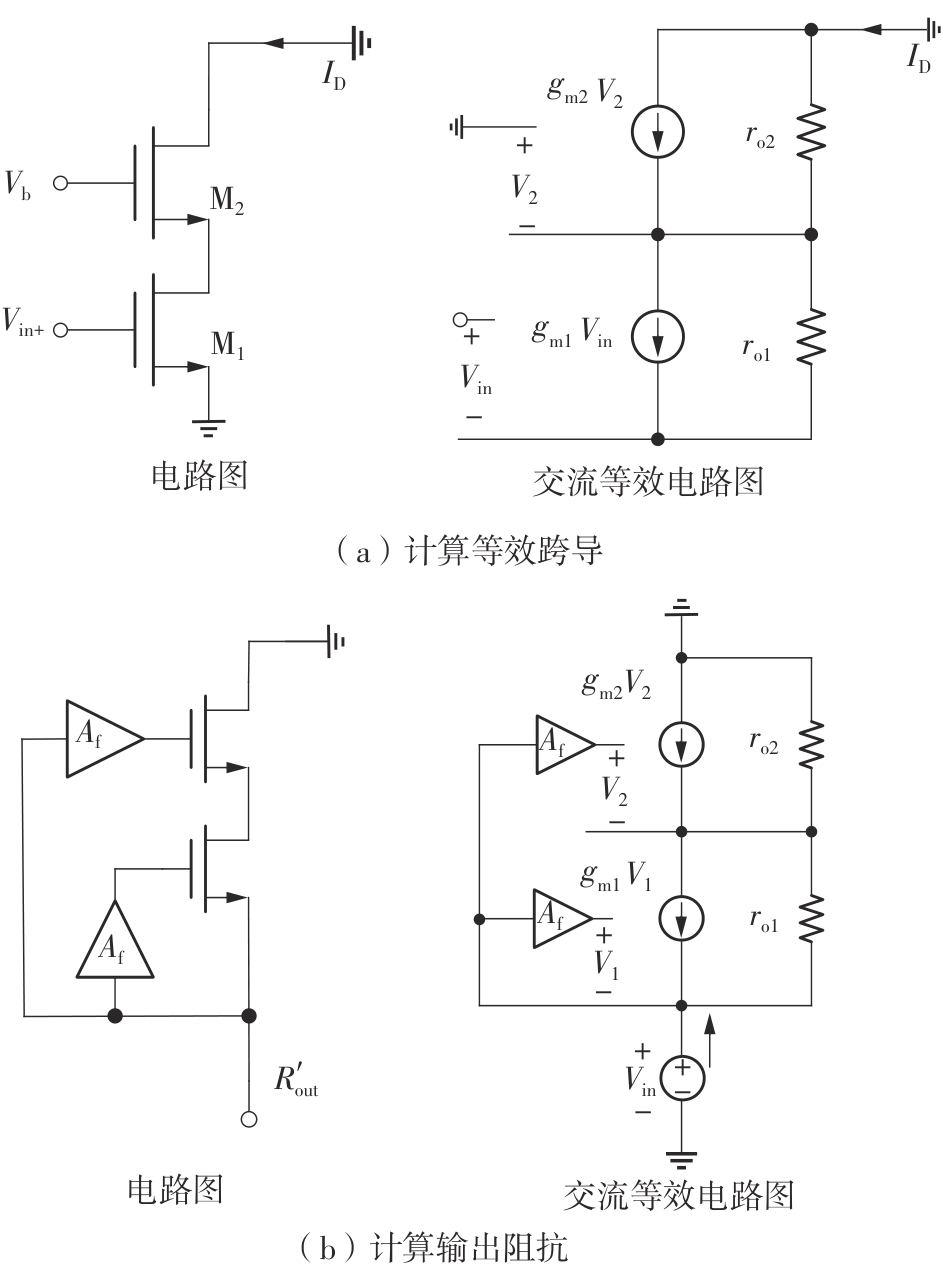
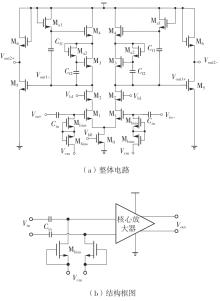
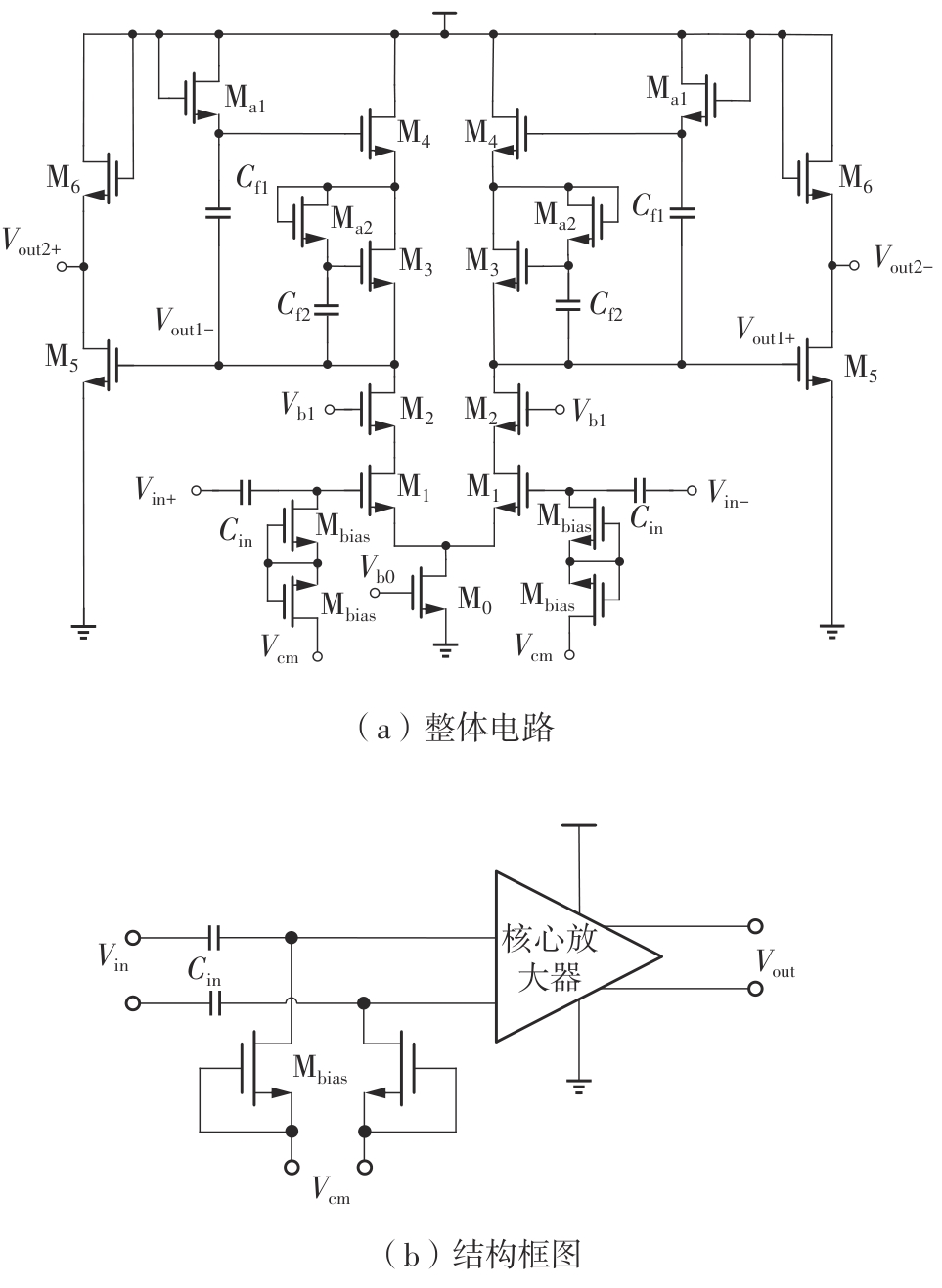
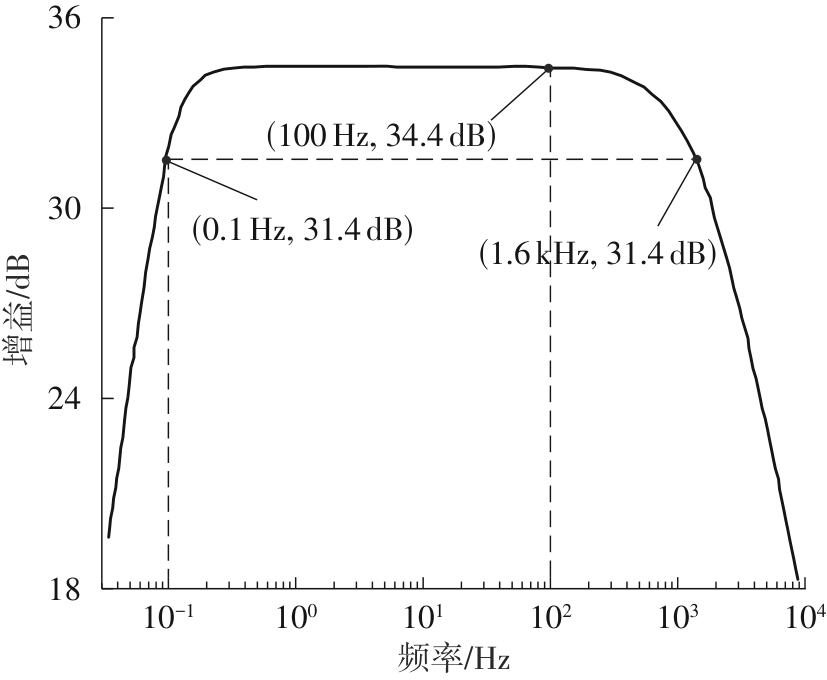
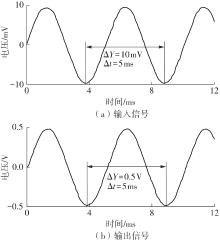
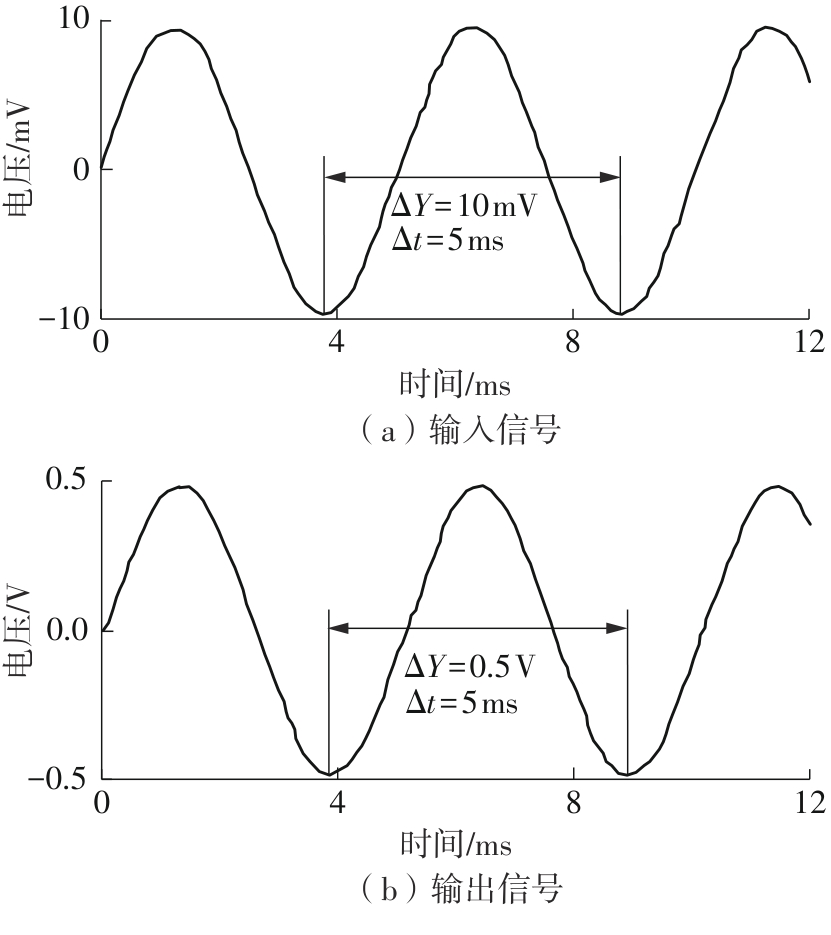
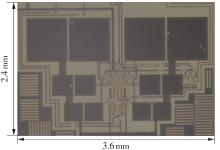
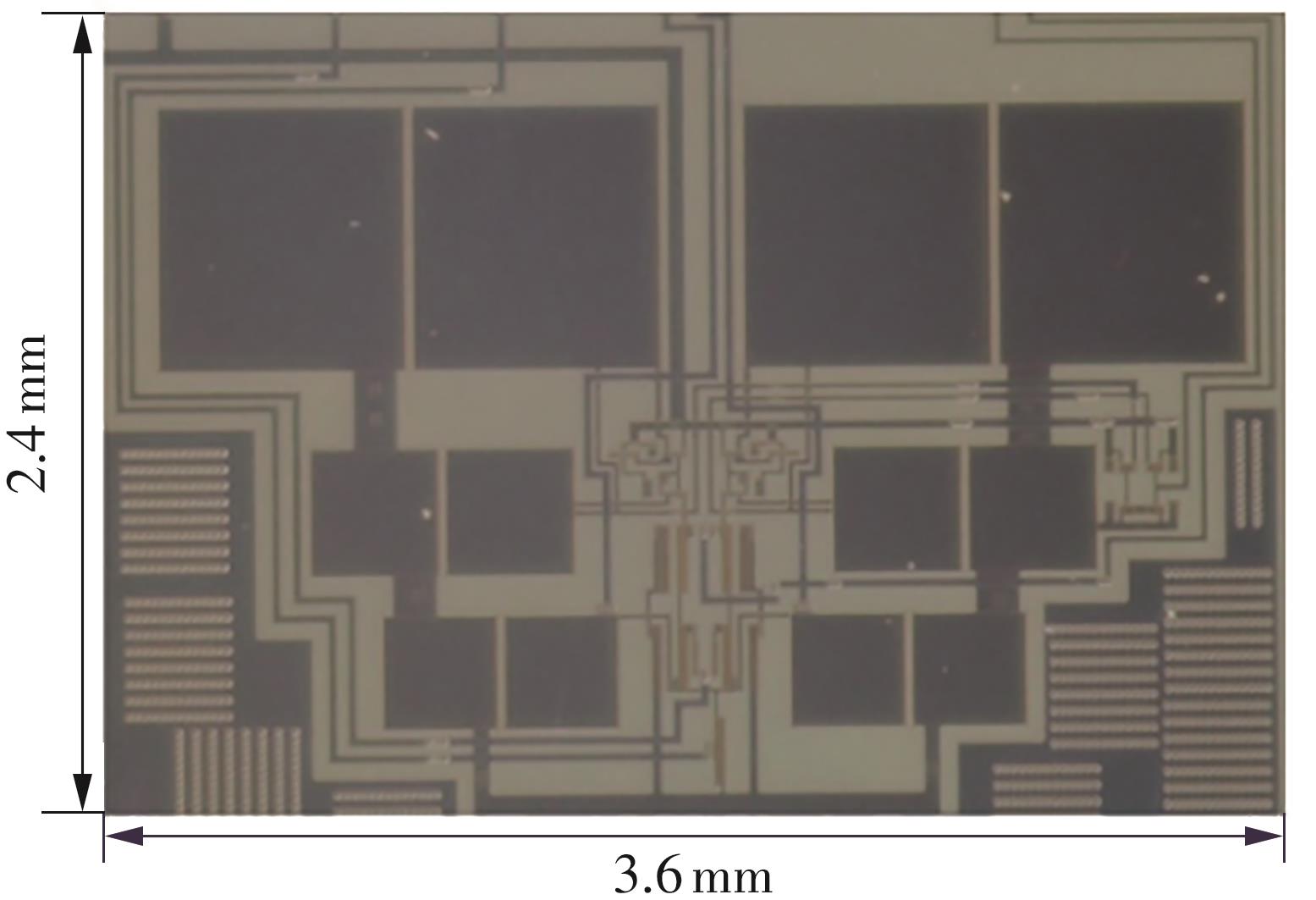
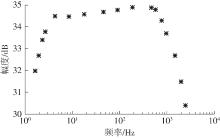
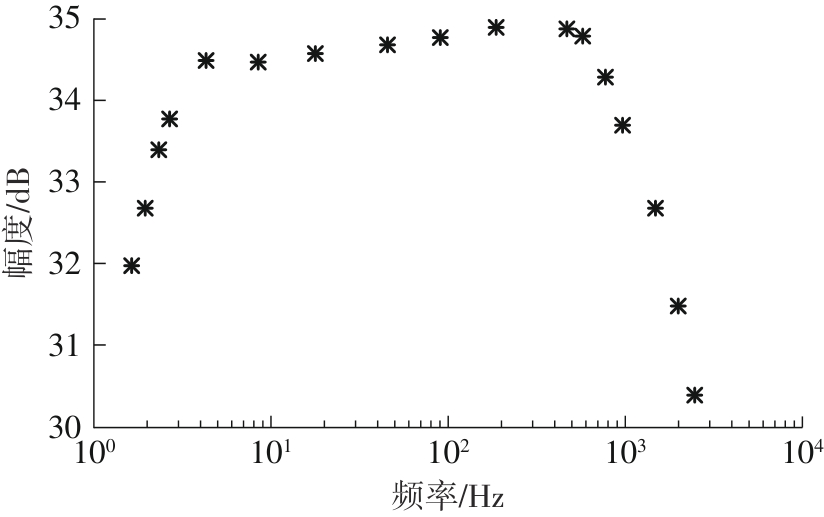
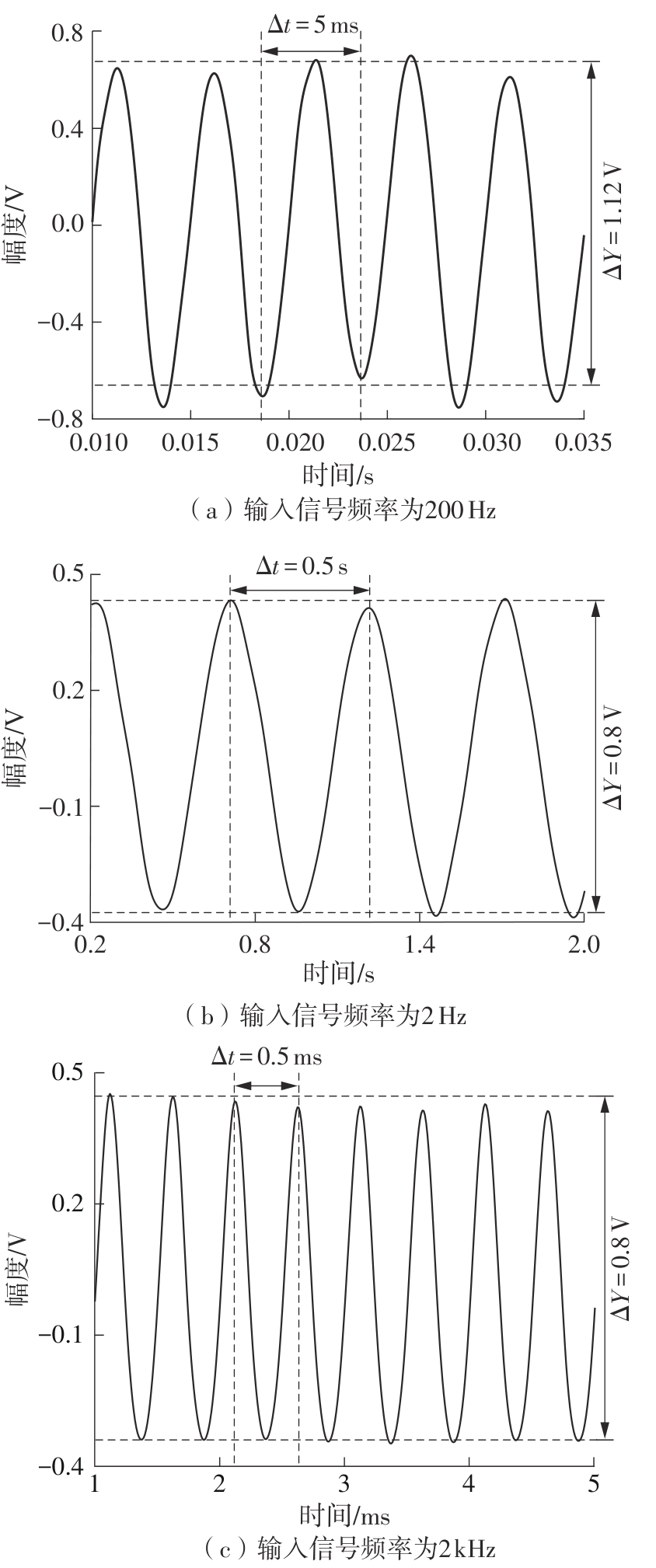
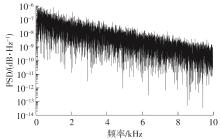
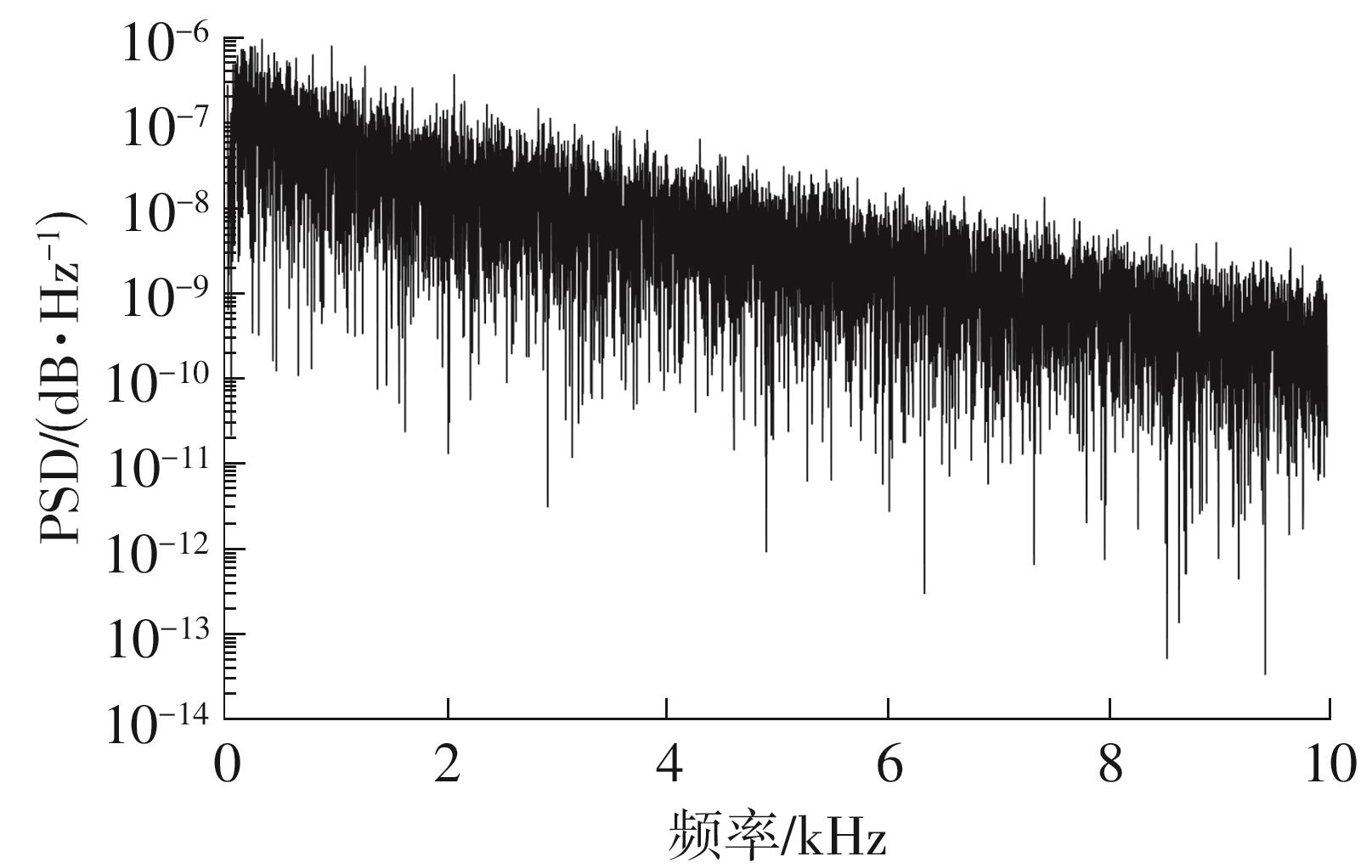
金属氧化物薄膜晶体管(MO-TFT)可以用来实现检测心率信号的柔性可穿戴系统,但MO-TFT缺少高性能互补器件,导致实现的前置放大器增益较小,而且MO-TFT器件的性能较差,给后级模块的设计带来了困难。为提升前置放大器的增益,降低后级电路对器件性能的要求,该文提出了一种共源共栅电容自举结构前置放大器。该前置放大器主要由外部耦合偏置模块和核心放大器模块构成;核心放大器模块使用稳定性好、输出电压摆幅大和功耗低的电容自举技术,并结合了共源共栅结构,以提升电路的整体增益;外部耦合偏置模块使用功耗较低、输入阻抗较大和工作点设置简单的交流耦合外部偏置结构,以满足心率信号检测前置放大器的带通要求。采用10 μm IZO-TFT工艺对所提出的前置放大器进行设计和流片测试,结果表明:在20 V电源电压条件下,该放大器的增益为35 dB,带宽为2 Hz~2 kHz,噪声均方根值为118.2 μV,功耗为0.1 mW,实现的前置放大器满足心率信号检测要求;与现有的MO-TFT心率信号检测前置放大器相比,所设计的前置放大器增益提升了约10 dB,降低了后级模块对器件性能的要求,有利于实现模拟信号的数字化,保持信号的完整性。
中图分类号: