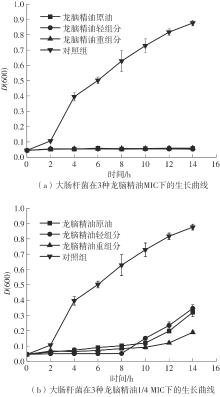
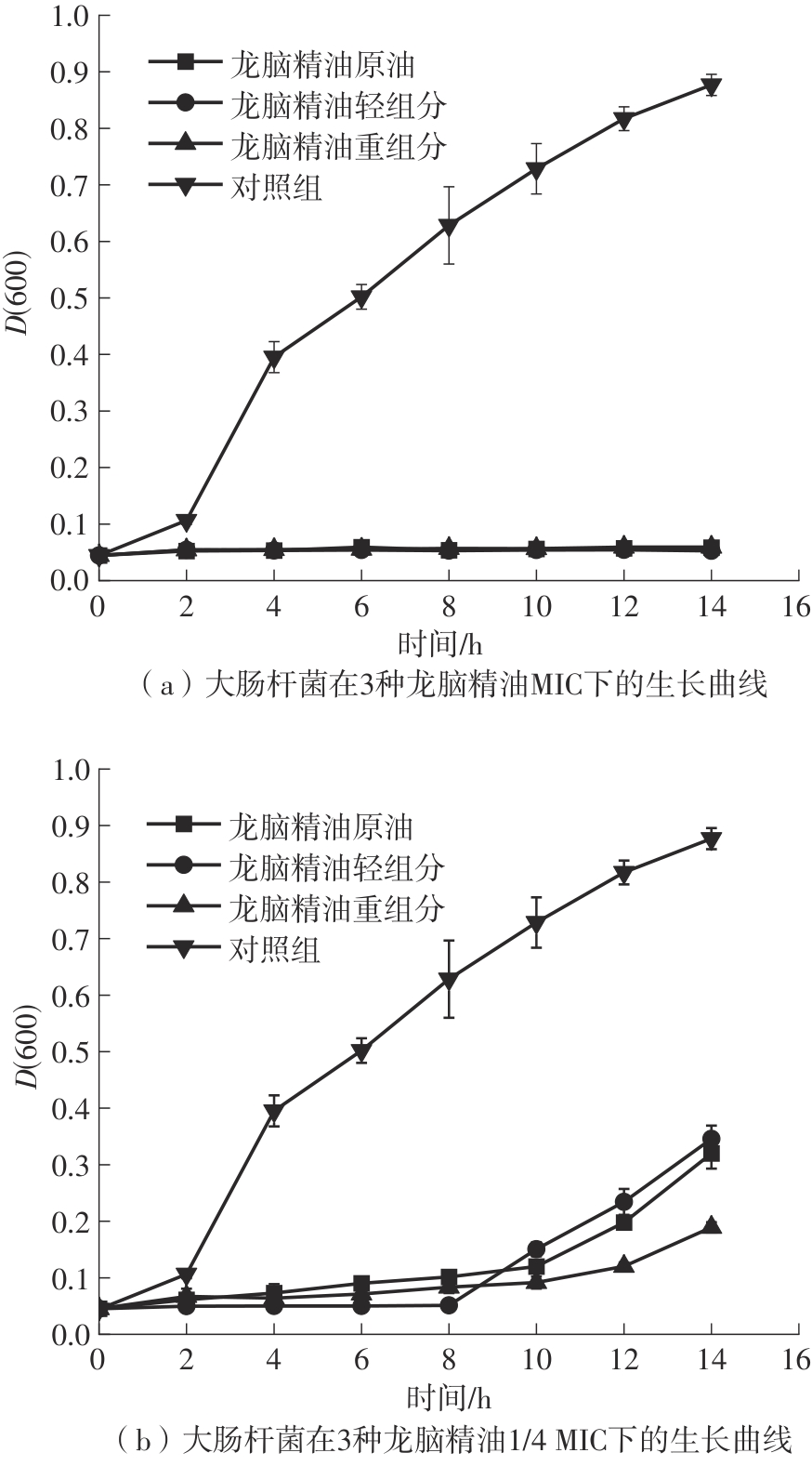
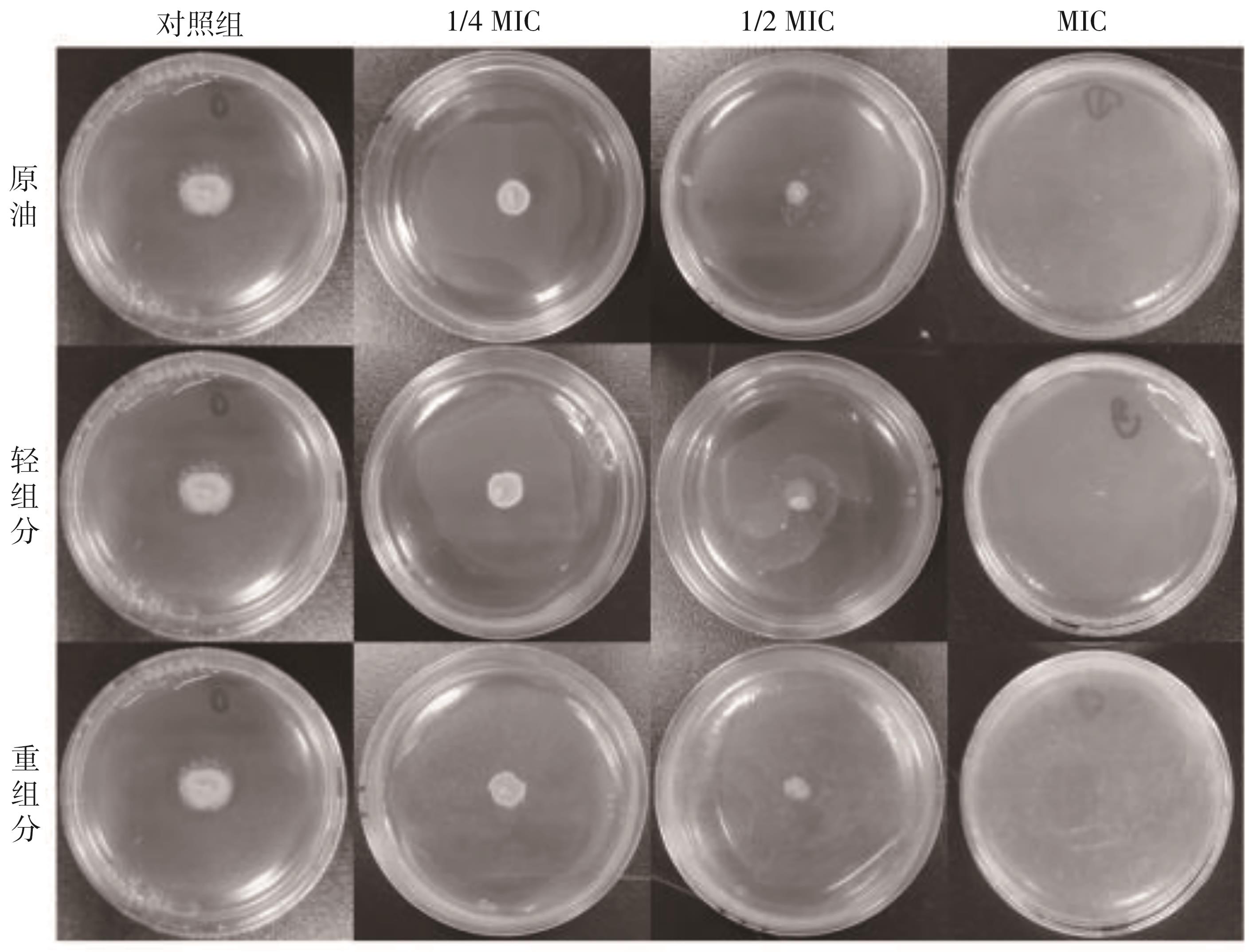
| 1 |
朱琪琪,张继瑜,王承业,等 .河北地区动物源大肠杆菌多重耐药性与流行性分析[J].中国畜牧兽医,2023,50(3):1081-1092.
|
|
ZHU Qiqi, ZHANG Jiyu, WANG Chengye,et al .Analysis of multidrug resistance and prevalence of animal-derived Escherichia coli in Hebei[J].China Animal Husbandry & Veterinary Medicine,2023,50(3):1081-1092.
|
| 2 |
KONG Q, YANG Y .Recent advances in antibacterial agents[J].Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters,2021,35(1):127799/1-8.
|
| 3 |
SADAF M, MOHAMMADREZA P, NARJES A,et al .Stability and antibacterial activity of Thymus daenensis L.essential oil nanoemulsion in mayonnaise[J].Journal of the Science of Food and Agriculture,2020,101(9):3880-3888.
|
| 4 |
LAI T, SUN Y, LIU Y,et al .Cinnamon oil inhibits Penicillium expansum growth by disturbing the carbohydrate metabolic process[J].Journal of Fungi,2021,7(2):123/1-17.
|
| 5 |
袁康,胡振阳,陈可欣,等 .紫苏精油抑制灰绿曲霉的活性与机理[J].食品科学,2020,41(23):63-69.
|
|
YUAN Kang, HU Zhenyang, CHEN Kexin,et al .Acti-vity and mechanism of perilla essential oil in inhibiting Aspergillus glaucus [J].Food Science,2020,41(23):63-69.
|
| 6 |
CUI H Y, ZHANG C H, LI C Z,et al .Antibacterial mechanism of oregano essential oil[J].Industrial Crops and Products,2019,139(8):111498/1-9.
|
| 7 |
KIM Y G, LEE J H, KIM S I,et al .Cinnamon bark oil and its components inhibit biofilm formation and toxin production[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2015,195:30-39.
|
| 8 |
BURT S A, van DER ZEE R, KOETS A P,et al .Carvacrol induces heat shock protein 60 and inhibits synthesis of flagellin in Escherichia coli O157:H7[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2007,73(14):4484-4490.
|
| 9 |
JU J, XIE Y, GUO Y,et al .The inhibitory effect of plant essential oils on foodborne pathogenic bacteria in food[J].Critical Reviews in Food Science and Nutrition,2019,59(20):3281-3292.
|
| 10 |
吴少云,苏健裕,石磊,等 .梅片树叶挥发油和天然右旋龙脑的抑菌性能研究[J].食品工业科技,2012,33(7):85-87.
|
|
WU Shao-yun, SU Jian-yu, SHI Lei,et al .Study on antibacterial activity of essential oil and D-borneol from leaves of Cinnamomun burmannii B1[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry,2012,33(7):85-87.
|
| 11 |
胡珊,梁卫驱,黄皓,等 .不同化学型樟树精油的化学成分和抑菌效果研究[J].安徽农业科学,2022,50(22):193-197.
|
|
HU Shan, LIANG Wei-qu, HUANG Hao,et al .Study on chemical composition and antifungal effect of different chemical types Cinnamomum camphora essential oils[J].Journal of Anhui Agricultural Sciences,2022,50(22):193-197.
|
| 12 |
石冬雪,韩格,刘骞,等 .植物精油结合非热杀菌技术在肉品中应用的研究进展[J].肉类研究,2023,37(1):46-52.
|
|
SHI Dongxue, HAN Ge, LIU Qian,et al .Progress in the application of plant essential oil combined with non-thermal sterilization techniques in the preservation of meat products[J].Meat Research,2023,37(1):46-52.
|
| 13 |
WANG L, LIANG Q, LIN A,et al .Borneol alleviates brain injury in sepsis mice by blocking neuronal effect of endotoxin[J].Life Sciences,2019,232(23):116647/1-10.
|
| 14 |
唐寅,吕晓帆,王莹,等 .龙脑樟精油的化学成分、抗氧化活性和认知改善作用研究[J].日用化学工业,2021,51(11):1095-1101.
|
|
TANG Yin, LV Xiaofan, WANG Ying,et al .Study on chemical components,antioxidant activity and cognitive improvement of borneol essential oil[J].China Surfactant Detergent & Cosmetics,2021,51(11):1095-1101.
|
| 15 |
杨永胜 .植物精油的主要提取技术、应用及研究进展[J].当代化工研究,2021,81(4):153-154.
|
|
YANG Yongsheng .Main extraction technology,application and research progress of plant essential oil[J].Modern Chemical Research,2021,81(4):153-154.
|
| 16 |
何凤平,雷朝云,范建新,等 .植物精油提取方法、组成成分及功能特性研究进展[J].食品工业科技,2019,40(3):307-312,320.
|
|
HE Feng-ping, LEI Chao-yun, FAN Jian-xin,et al .Research progess of extraction methods,components and functional characteristics in essential oil[J].Science and Technology of Food Industry,2019,40(3):307-312,320.
|
| 17 |
王芳,岳朝敏, ANDREEA David,等 .结合GC-MS的分子蒸馏富集柚皮精油抗氧化成分的研究[J].中国粮油学报,2018,33(7):65-71.
|
|
WANG Fang, YUE Chaomin, ANDREEA David,et al .Enrichment of antioxidant components of pomelo[Citrus Grandis (L.)Osbeck]essential oil using molecular distillation combined with GC-MS determination[J].Journal of the Chinese Cereals and Oils Association,2018,33(7):65-71.
|
| 18 |
徐秀娟,鲁平,史清照,等 .雪茄烟叶精油主要成分分析及作用评价[J].烟草科技,2021,54(11):59-68,83.
|
|
XU Xiujuan, LU Ping, SHI Qingzhao,et al .Chemical analysis and sensory evaluation of main components in essential oil of cigar tobacco[J].Tobacco Science & Technology,2021,54(11):59-68,83.
|
| 19 |
申艳红,李志祥,赵占强,等 .亚临界萃取与分子蒸馏结合提取艾叶精油及其成分分析[J].河南师范大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(1):91-97.
|
|
SHEN Yanhong, LI Zhixiang, ZHAO Zhanqiang,et al .Essential oil extraction from Artemisia argyi by subcritical extraction combined with molecular distillation and analysis of its components[J].Journal of Henan Normal University(Natural Science Edition),2022,50(1):91-97.
|
| 20 |
叶征美 .千层金精油的提取、成分分析、抗氧化及抗菌活性的研究[D].福州:福建农林大学,2014.
|
| 21 |
蒋东丽,蒋志芳,陈政声,等 .简单醇热法制备ZnO纳米棒及其抗菌性能研究[J].化工新型材料,2013,41(7):63-65.
|
|
JIANG Dongli, JIANG Zhifang, CHEN Zhengsheng,et al .Antibacterial properties of ZnO nanorods prepared by simple alcohol thermal method[J].New Chemical Materials,2013,41(7):63-65.
|
| 22 |
郑艳晶 .恶臭假单胞菌MnB1生物膜对环境因素Mn(Ⅱ)和H2O2的响应及其机制研究[D].南京:南京大学,2017.
|
| 23 |
余生玲,申光辉,黄廷,等 .藤椒精油对腐败解淀粉芽孢杆菌DY1a生物被膜的抑制作用[J].微生物学通报,2022,49(6):2135-2151.
|
|
YU Shengling, SHEN Guanghui, HUANG Ting,et al .Antibiofilm effect of Zanthoxylum armatum DC.essential oil against spoilage Bacillus amyloliquefaciens DY1a[J].Microbiology China,2022,49(6):2135-2151.
|
| 24 |
虞秀芳 .关于亚抑制浓度庆大霉素可通过抑制大肠杆菌丛动性降低细菌毒力的研究[D].石河子:石河子大学,2019.
|
| 25 |
张瑶 .裂解酶P26ly对金黄色葡萄球菌、大肠杆菌生物被膜清除作用的研究[D].昆明:昆明理工大学,2021.
|
| 26 |
SHI N, GAO Y, YIN D,et al .The effect of the sub-minimal inhibitory concentration and the concentrations within resistant mutation window of ciprofloxacin on MIC,swimming motility and biofilm formation of Pseudomonas aeruginosa [J].Microbial Pathogenesis,2019,137:103765/1-8.
|
| 27 |
UNLU M, ERGENE E, UNLU G V,et al .Composition,antimicrobial activity and in vitro cytotoxicity of essential oil from Cinnamomum zeylanicum Blume (Lauraceae)[J].Food & Chemical Toxicology,2010,48(11):3274-3280.
|
| 28 |
YEH R Y, SHIU Y L, SHEI S C,et al .Evaluation of the antibacterial activity of leaf and twig extracts of stout camphor tree,Cinnamomum kanehirae,and the effects on immunity and disease resistance of white shrimp,Litopenaeus vannamei [J].Fish & Shellfish Immuno-logy,2009,27(1):26-32.
|
| 29 |
SRIVASTAVA B, SINGH P, SHUKLA R,et al .A novel combination of the essential oils of Cinnamomum camphora and Alpinia galanga in checking aflatoxin B1 production by a toxigenic strain of Aspergillus flavus [J].World Journal of Microbiology & Biotechnology,2008,24(5):693-697.
|
| 30 |
STURBELLE R T, de AVILA L F D, ROOS T B,et al .The role of quorum sensing in Escherichia coli(ETEC) virulence factors[J].Veterinary Microbiology,2015,180(3):245-252.
|
| 31 |
杨姗姗,马丽,孙柏欣,等 .细菌趋化性研究进展[J].中国农学通报,2015,31(6):121-127.
|
|
YANG Shanshan, MA Li, SUN Baixin,et al .Pro-gress in bacterial chemotaxis[J].Chinese Agricultural Science Bulletin,2015,31(6):121-127.
|
| 32 |
MAIER B, WONG G C L .How bacteria use type Ⅳ Pili machinery on surfaces[J].Trends in Microbiology,2015,23(12):775-788.
|
| 33 |
吴浪涛 .浓香型白酒窖泥梭菌的趋化性与代谢特性研究[D].无锡:江南大学,2022.
|
| 34 |
BHATTACHARYA M, WOZNIAK D J, STOODLEY P,et al .Prevention and treatment of Staphylococcus aureus biofilms[J].Expert Review of Anti-Infective Therapy,2015,13(12):1499-1516.
|
| 35 |
FANG K, PARK O J, HONG S H .Controlling biofilms using synthetic biology approaches[J].Biotechnology Advances,2020,40:107518/1-12.
|
| 36 |
韩乔,刘悦,潘路路 .食源性致病菌生物被膜的形成及危害研究进展[J].食品安全导刊,2023,378(13):133-135.
|
|
HAN Qiao, LIU Yue, PAN Lulu .Research advances in the formation and hazard of biofilms formed by foodborne pathogens[J].China Food Safety Magazine,2023,378(13):133-135.
|