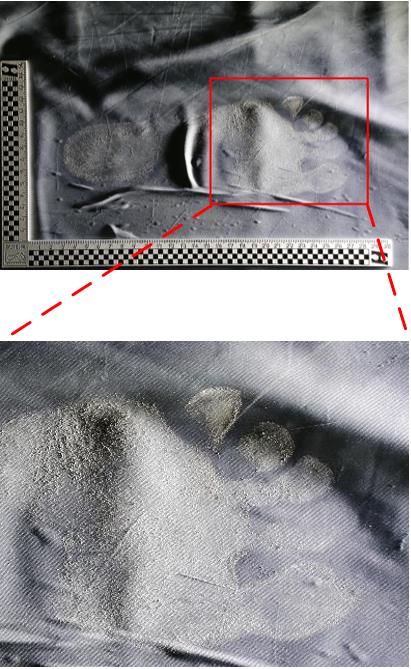
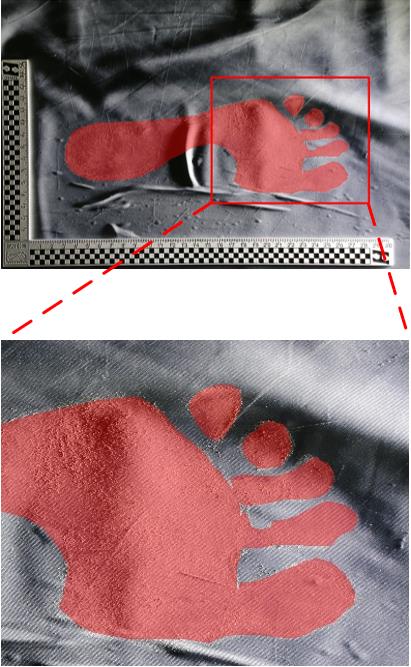
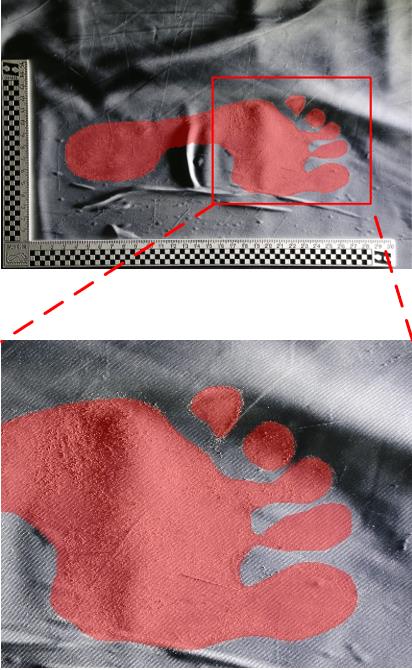
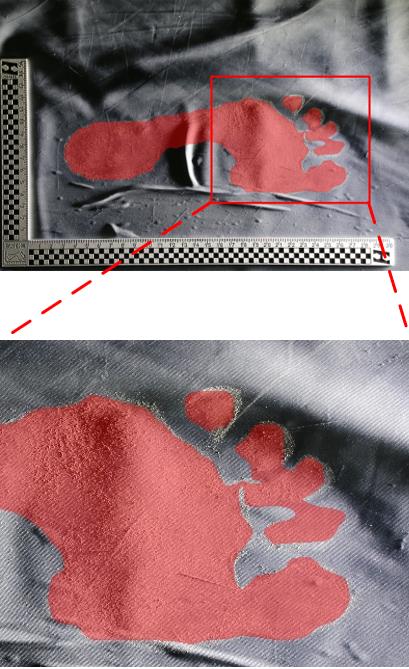
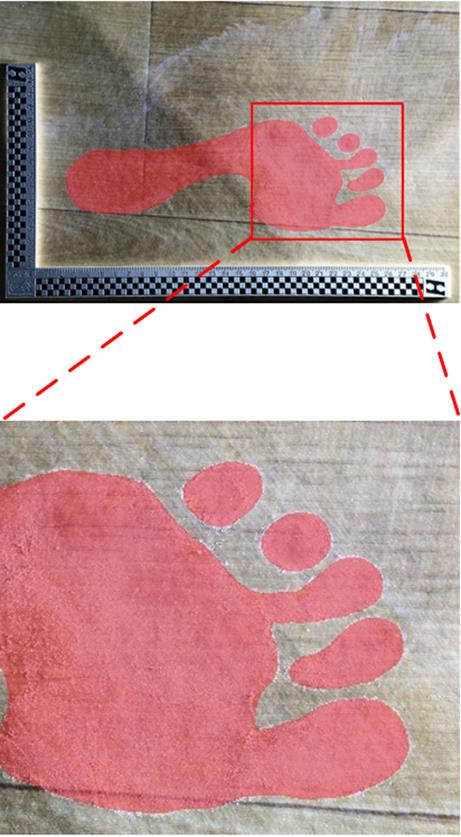
| 1 |
吴一全,朱丽,吴诗婳 .基于二维Arimoto灰度熵的图像阈值分割快速迭代算法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2016,44(5):48-57.
|
|
WU Yi-quan, ZHU Li, WU Shi-hua .Fast iterative algorithm for image threshold segmentation based on two-dimensional Arimoto gray entropy [J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2016,44(5):48-57.
|
| 2 |
TREMEAU A, BOREL N .A region growing and mer-ging algorithm to color segmentation[J].Pattern Recognition,1997,30(7):1191-1203.
|
| 3 |
王卫星,吴林春 .基于分数阶积分谷底边界检测的路面裂缝提取[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2014,42(1):117-122.
|
|
WANG Wei-xing, WU Lin-chun .Extraction of pavement cracks based on valley edge detection of fractional integral[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2014,42(1):117-122.
|
| 4 |
徐曼 .基于改进快速分水岭算法的图像分割技术研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2010.
|
| 5 |
LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T .Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence, 2017,39(4):640-651.
|
| 6 |
BADRINARAYANAN V, KENDALL A, CIPOLLA R .SegNet:a deep convolutional encoder-decoder architecture for image segmentation[J].IEEE Transactions Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,39(12):2481-2495.
|
| 7 |
RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T .U-Net:convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Munich:Springer,2015:234-241.
|
| 8 |
CHAURASIA A, CULURCIELLO E .LinkNet:exploi-ting encoder representations for efficient semantic segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Visual Communications and Image Processing.St.Petersburg:IEEE,2017:1-4.
|
| 9 |
XIA X, KULIS B .W-Net:a deep model for fully unsuper-vised image segmentation[EB/OL].(2017-11-22) [2024-04-25]..
|
| 10 |
YUAN Y, CHEN X, WANG J .Object-contextual re-presentations for semantic segmentation[C]∥ Procee-dings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:173-190.
|
| 11 |
ZHAO H, SHI J, QI X,et al .Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:6230-6239.
|
| 12 |
CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, KOKKINOS I,et al .DeepLab:semantic image segmentation with deep convolutional nets,atrous convolution,and fully connected CRFs[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2017,40(4):834-848.
|
| 13 |
CHEN L C, PAPANDREOU G, SCHROFF F,et al .Rethinking atrous convolution for semantic image segmentation[EB/OL]. (2017-06-17)[2024-04-25]..
|
| 14 |
LI H, XIONG P, AN J, et al .Pyramid attention network for semantic segmentation [EB/OL].(2018-05-25)[2024-04-25]..
|
| 15 |
PUNN N S, AGARWAL S .Modality specific U-Net variants for biomedical image segmentation:a survey [J].Artificial Intelligence Review,2022,55(7):5845-5889.
|
| 16 |
杨晋生,陈洪鹏,关欣,等 .一种多尺度轻量级脑胶质瘤图像分割网络[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(12):132-141.
|
|
YANG Jinsheng, CHEN Hongpeng, GUAN Xin,et al .A multi-scale lightweight brain glioma image segmentation network[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(12):132-141.
|
| 17 |
XU J, XIONG Z, BHATTACHARYYA S P .PIDNet:a real-time semantic segmentation network inspired by PID controllers[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vancouver:IEEE,2023:19529-19539.
|
| 18 |
CARION N, MASSA F, SYNNAEVE G,et al .End-to-end object detection with transformers[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:213-229.
|
| 19 |
DOSOVITSKIY A, BEYER L, KOLESNIKOV A,et al .An image is worth 16×16 words:transformers for image recognition at scale[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Ninth International Conference on Learning Representations.[S.l.]: OpenReview.net,2021:1-21.
|
| 20 |
ZHENG S, LU J, ZHAO H,et al .Rethinking semantic segmentation from a sequence-to-sequence perspective with transformers[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Nashville:IEEE,2021:6877-6886.
|
| 21 |
STRUDEL R, GARCIA R, LAPTEV I,et al .Segmenter:transformer for semantic segmentation[C] ∥Proceedings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Confe-rence on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:7242-7252.
|
| 22 |
XIE E, WANG W, YU Z,et al .SegFormer:simple and efficient design for semantic segmentation with transformers [C] ∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 34:35th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.San Diego:Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation,Inc.,2021:12077-12090.
|
| 23 |
RANFTL R, BOCHKOVSKIY A, KOLTUN V .Vision transformers for dense prediction[C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2021:12159-12168.
|
| 24 |
CHEN Y, DAI X, CHEN D,et al .Mobile-Former:bridging MobileNet and transformer[C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:5260-5269.
|
| 25 |
MEHTA S, RASTEGARI M .MobileVit:light-weight,general-purpose,and mobile-friendly vision transformer[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Tenth International Confe-rence on Learning Representations.[S.l.]:OpenReview.net,2022:1-26.
|
| 26 |
ZHANG W, HUANG Z, LUO G,et al .TopFormer:token pyramid transformer for mobile semantic segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Confe-rence on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:12073-12083.
|
| 27 |
LI Y, YUAN G, WEN Y,et al .EfficientFormer: vision transformers at MobileNet speed[C] ∥ Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems 35:36th Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.San Diego:Neural Information Processing Systems Foundation,Inc.,2022:1-16.
|
| 28 |
WAN Q, HUANG Z, LU J,et al .SeaFormer: squeeze-enhanced axial transformer for mobile semantic segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the Eleventh International Conference on Learning Representations.[S.l.]:OpenReview.net,2023:1-19..
|
| 29 |
LIN T Y, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R,et al .Feature pyramid networks for object detection [C] ∥ Procee-dings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:936-944.
|
| 30 |
GU J, KWON H, WANG D,et al .Multi-scale high- resolution vision transformer for semantic segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:12084-12093.
|
| 31 |
HUANG H, LIN L, TONG R,et al .UNet 3+:a full-scale connected UNet for medical image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE International Confe-rence on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing.Barcelona:IEEE,2020:1055-1059.
|
| 32 |
CHEN L C, ZHU Y, PAPANDREOU G,et al . Encoder-decoder with atrous separable convolution for semantic image segmentation[C] ∥ Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich:Springer,2018:833-851.
|
| 33 |
YUAN Y, HUANG L, GUO J,et al .OCNet:object context for semantic segmentation[J].International Journal of Computer Vision,2021,129:2375-2398.
|
| 34 |
FU J, LIU J, TIAN H,et al .Dual attention network for scene segmentation [C] ∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:3141-3149.
|