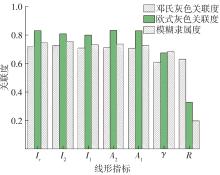
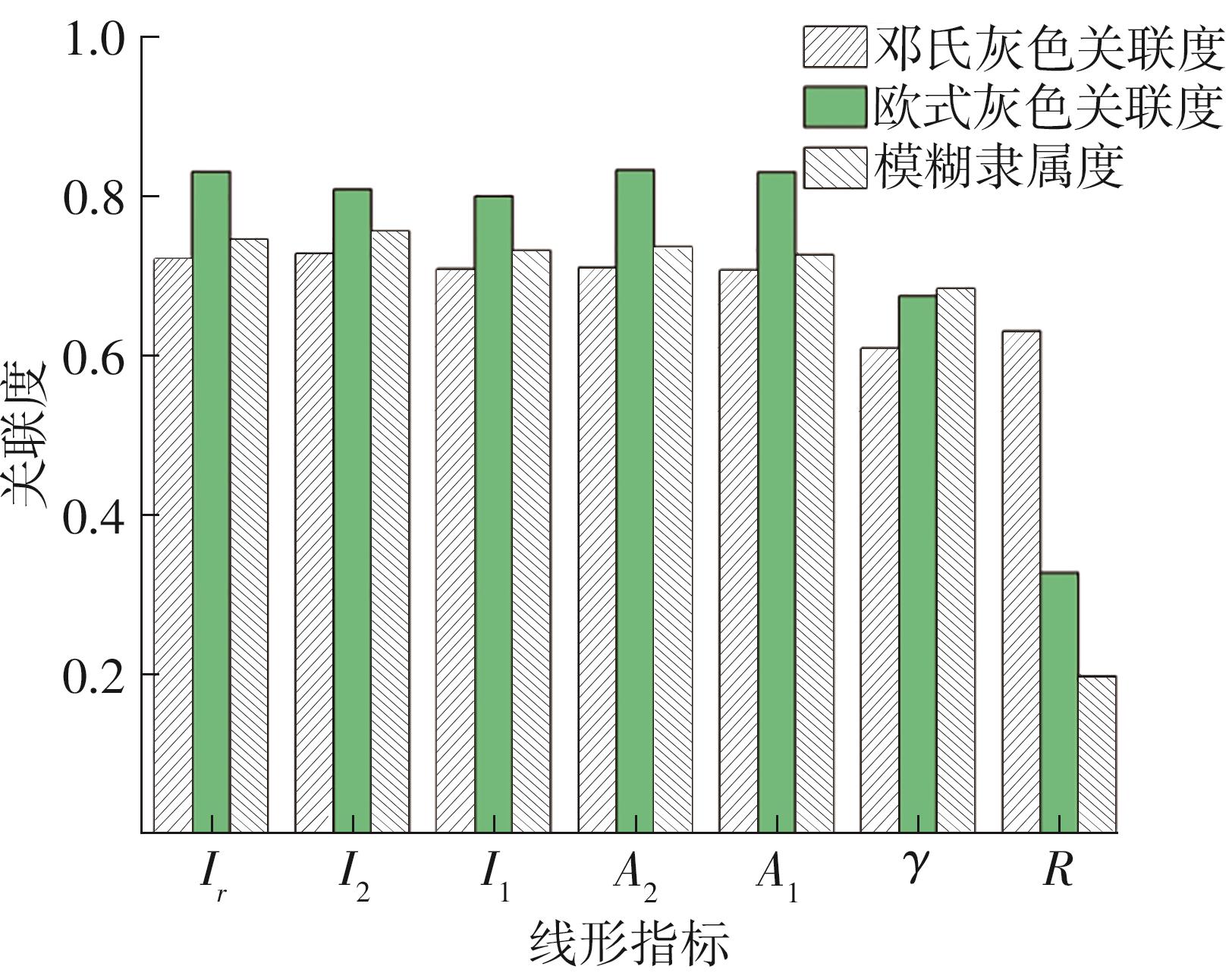
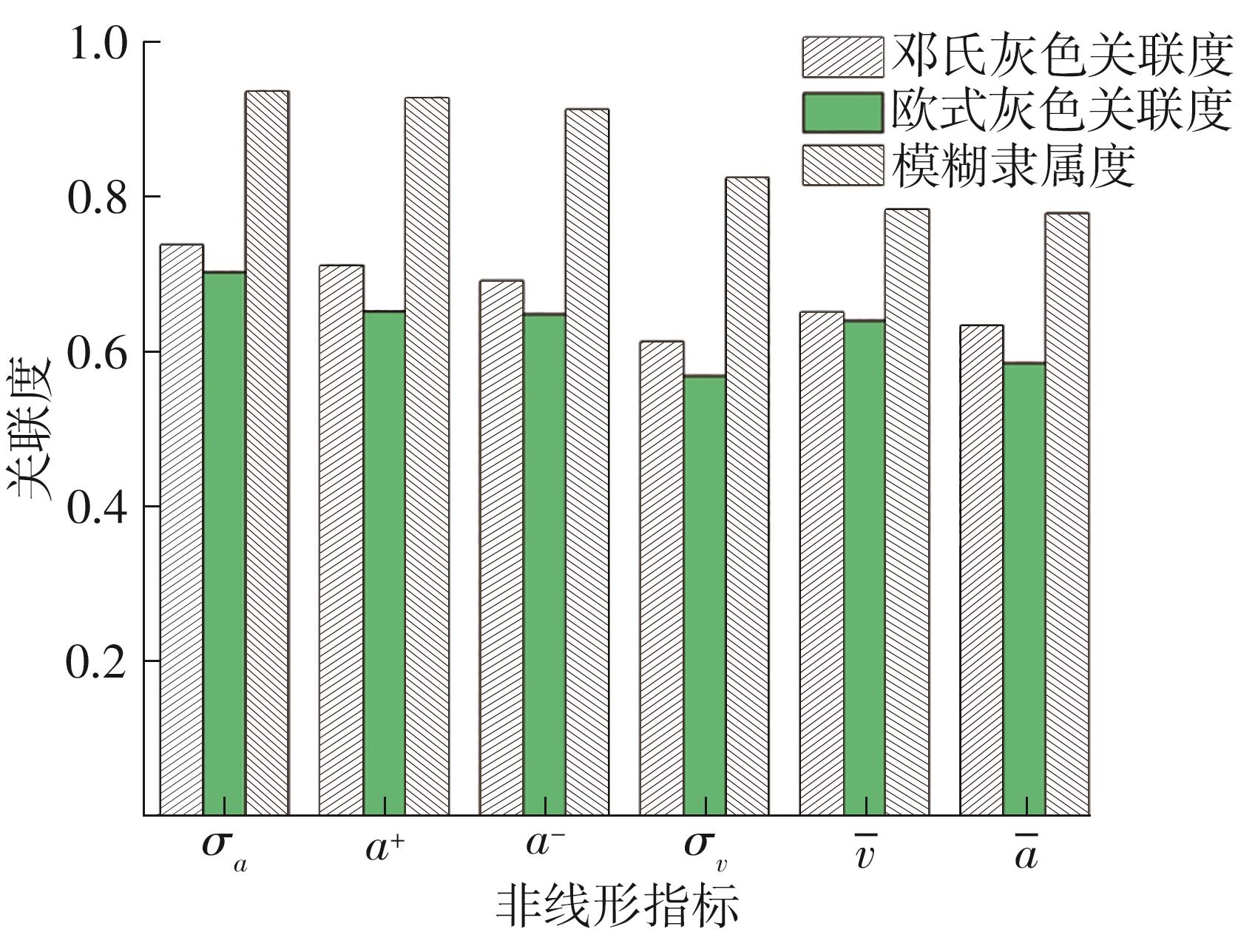
| 1 |
国资委 .推动央企绿色低碳发展扎实有序做好“碳达峰、碳中和”工作[J].新能源科技,2022,24(6):7-8.
|
|
The State-Owned Assets Supervision and Administration Commission of the State Council .Promote the green and low-carbon development of central enterprises to do a solid and orderly work of“carbon peak and carbon neutrality”[J].New Energy Technology,2022,24(6):7-8.
|
| 2 |
刘吉毅,黄福友,陈斌 .交通运输业碳排放影响因素及减排策略研究[J].公路,2023,68(5): 252-259.
|
|
LIU Jiyi, HUANG Fuyou, CHEN Bin .Research on influencing factors and emission reduction strategies of carbon emission in transportation industry[J].Highway,2023,68(5):252-259.
|
| 3 |
熊阳欣, 秦之湄, 胡秋萍,等 .城市汽车年检碳排放数据挖掘及其应用研究[J].环境科学学报,2021,41(12):5083-5092.
|
|
XIONG Yangxin, QIN Zhimei, HU Qiuping,et al .Research on carbon emission data mining and application in urban vehicle emission inspection[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2021,41(12):5083-5092.
|
| 4 |
陈正委,熊文磊,高升,等 .轻型高速公路代表性车型与纵断面设计指标研究[J].公路,2023,68(9):1-11.
|
|
CHEN Zhengwei, XIONG Wenlei, GAO Sheng,et al .Research on typical vehicle types and vertical section indicators of light expressway[J].Highway,2023,68(9):1-11.
|
| 5 |
林学东 .发动机原理[M].第2版.北京:机械工业出版社,2014.
|
| 6 |
刘真 .道路线形指标对车辆尾气排放及燃油经济的影响研究[D].南京:东南大学,2017.
|
| 7 |
HU J, FREY H C .Comparison of real world light-duty gasoline vehicle emissions for high altitude mountainous versus low altitude piedmont study areas[C]∥Procee-dings of the Annual Conference and Exhibition,Air & Waste Management Association. Pittsburgh:Tavlor and Francis Ltd,2017:1-25.
|
| 8 |
吴胜利,邢文婷,邵毅明,等 .基于重庆道路试验的车辆行驶工况影响因素分析[J].交通运输工程学报,2021,21 (2):150-158.
|
|
WU Shengli, XING Wenting, SHAO Yiming,et al .Analysis of factors affecting vehicle driving condition based on road test in Chongqing[J].Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2021,21(2):150-158.
|
| 9 |
ZHANG L, HU X, QIU R,et al .Comparison of real-world emissions of LDGVs of different vehicle emission standards on both mountainous and level roads in China[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2019,69:24-39.
|
| 10 |
LLOPIS-CASTELLÓ D, PÉREZ-ZURIAGA M A, CAMACHO-TORREGROSA J F,et al .Impact of horizontal geometric design of two-lane rural roads on vehicle CO2 emissions [J].Transportation Research Part D,2018,59:46-57.
|
| 11 |
许金良,景立竹,韩跃杰,等 .基于MOVES的小半径圆曲线路段载重柴油车碳排放预测模型[J].公路交通科技,2018,35 (12):124-131,158.
|
|
XU Jinliang, JING Lizhu, HAN Yuejie,et al .A carbon emission prediction model for heavy-duty diesel trucks in small-radius curves based on MOVES[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2018,35 (12):124-131,158.
|
| 12 |
DEMIR E, BEKTA T, LAPORTE G .A comparative analysis of several vehicle emission models for road freight transportation[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2011,16(5):347-357.
|
| 13 |
孙文圃,许金良,景立竹,等 .基于MOVES的高速公路纵坡段载重柴油车辆碳排放预测模型的研究 [J].公路交通科技,2015,32(12):144-150.
|
|
SUN Wen-pu, XU Jin-liang, JING Li-zhu,et al .Study on carbon emission prediction model of heavy-duty diesel vehicle in expressway longitudinal slope sections based on MOVES[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2015,32(12):144-150.
|
| 14 |
T L KIM-NGOC, NGUYENTHIHONG D, VOVAN T .Fuzzy cluster analysis algorithm for image data based on the extracted feature intervals[J].Granular Compu-ting,2023,8(6):2067-2081.
|
| 15 |
HUANG Y, SHEN L, LIU H .Grey relational analysis,principal component analysis and forecasting of carbon emissions based on long short-term memory in China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2019,209:415-423.
|
| 16 |
邓长城,程雪利,李辉,等 .基于灰色关联度的轴承温度影响因素分析[J].轴承,2024(3):52-57.
|
|
DENG Changcheng, CHENG Xueli, LI Hui,et al .Analysis of bearing temperature based on grey relational method[J].Bearing,2024(3):52-57.
|
| 17 |
曾亮 .改进的灰色多变量GM(1,N)模型及其应用[J].西南大学学报(自然科学版),2019,41(9):68-76.
|
|
ZENG Liang .An improved grey multivariable GM(1,N)model and its application[J].Journal of Southwest University (Natural Science Edition),2019,41(9):68-76.
|
| 18 |
张志清,李晨,贺成林 .双车道公路小半径曲线段行车速度与行车轨迹关系研究[J].道路交通与安全,2016,16(5):22-26.
|
|
ZHANG Zhiqing, LI Chen, HE Chenglin .Research on the relationships between driving speed and driving track path on small radius curves of two-lane highways [J].Road Traffic and Safety,2016,16(5):22-26.
|
| 19 |
LUQUE R, CASTRO M .Highway geometric design consistency:speed models and local or global assessment[J].International Journal of Civil Engineering,2016,14(6):1-9.
|
| 20 |
NAVIN F .Some factors in the design of rural highway curves [C]∥Proceeding of the 94th Annual Meeting of the Transportation Research Board.Washington DC:Transportation Research Board,2015: 1-14.
|
| 21 |
刘明,何超,李加强,等 .基于比功率与发动机功率的重型柴油车实际道路排特性[J].科学技术与工程,2018,18(34):64-70.
|
|
LIU Ming, HE Chao, LI Jiaqiang,et al .Actual road emission characteristics of heavy-duty diesel vehicle based on vehicle specific power and engine power[J].Science Technology and Engineering,2018,18(34):64-70.
|
| 22 |
孙凤 .面向交通排放测算的轻重型车比功率分布特性与模型研究[D].北京:北京交通大学,2012.
|