华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (8): 138-145.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230743
细菌纤维素基CNFs/ZnO吸波材料的制备及性能
- 华南理工大学 材料科学与工程学院,广东 广州 510640
Preparation and Properties of Bacterial Cellulose Based CNFs/ZnO Microwave Absorbing Materials
LIU Pingan( ), LIN Baoshun, DING Huiling, XIAO Liang, ZHANG Zhijie
), LIN Baoshun, DING Huiling, XIAO Liang, ZHANG Zhijie
- School of Materials Science and Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
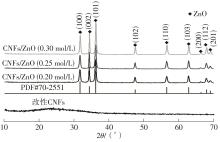
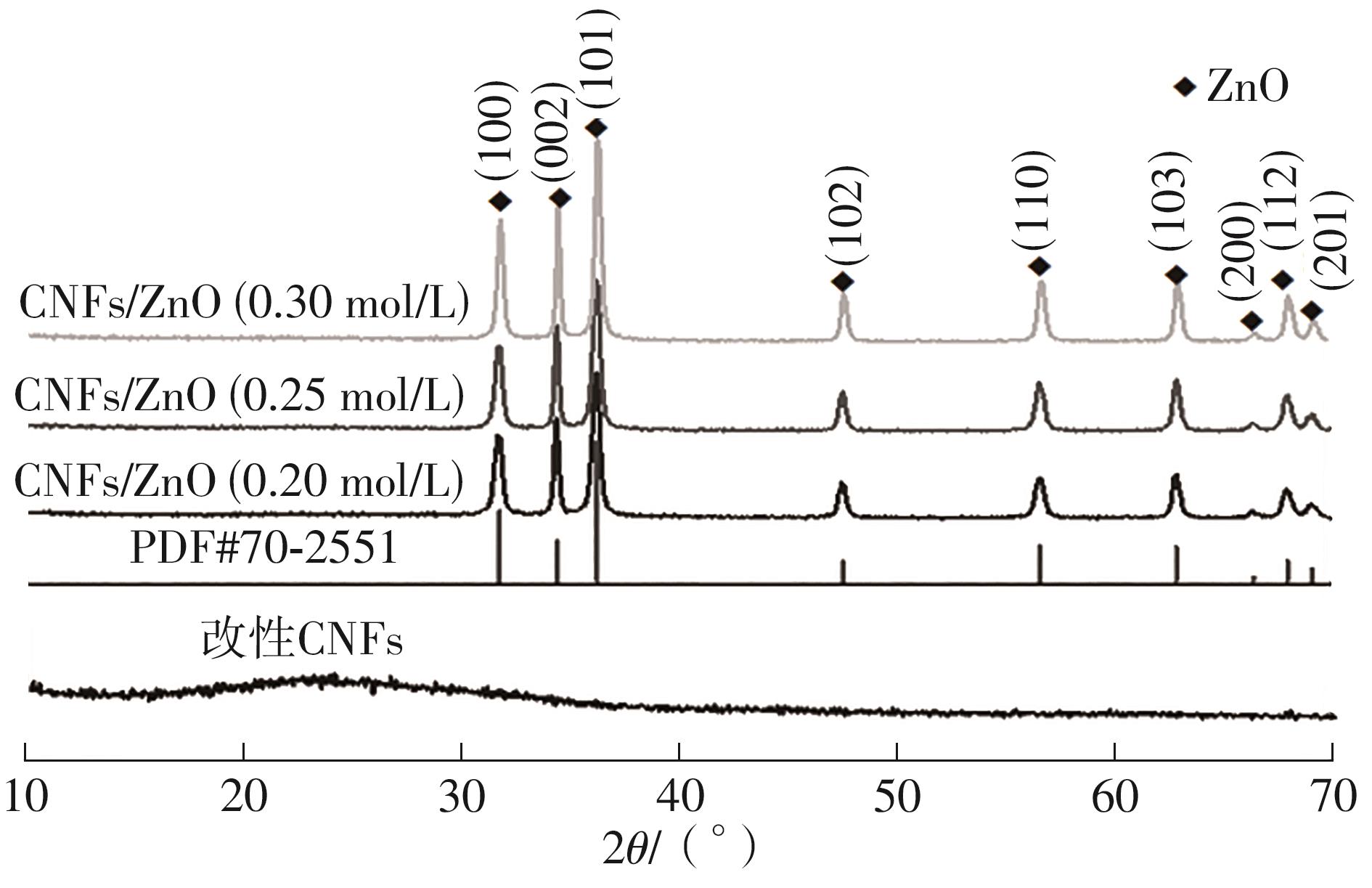
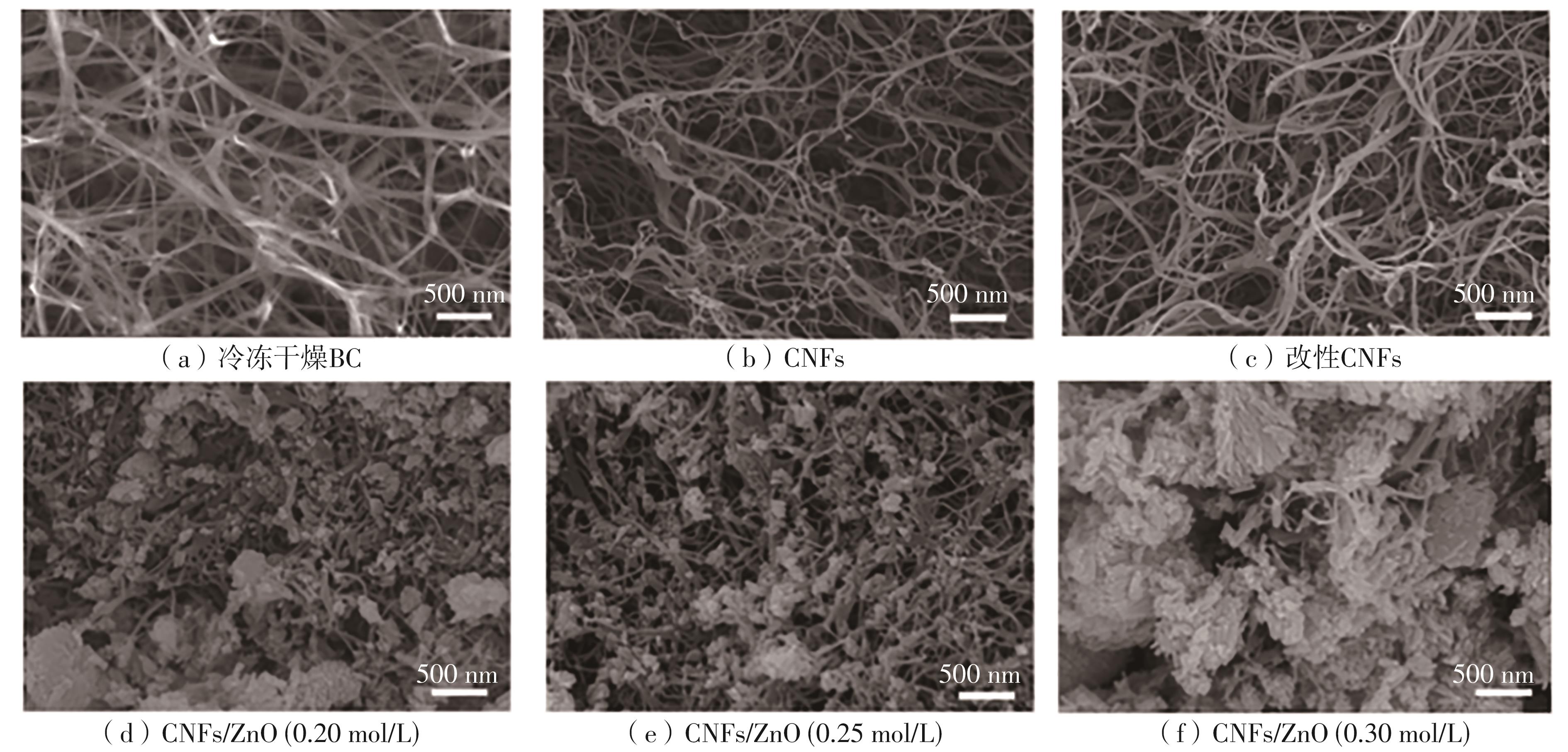
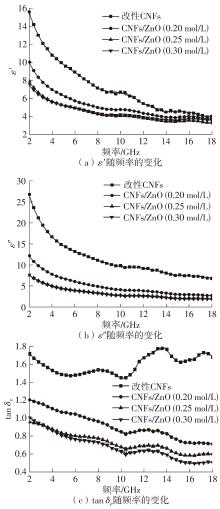
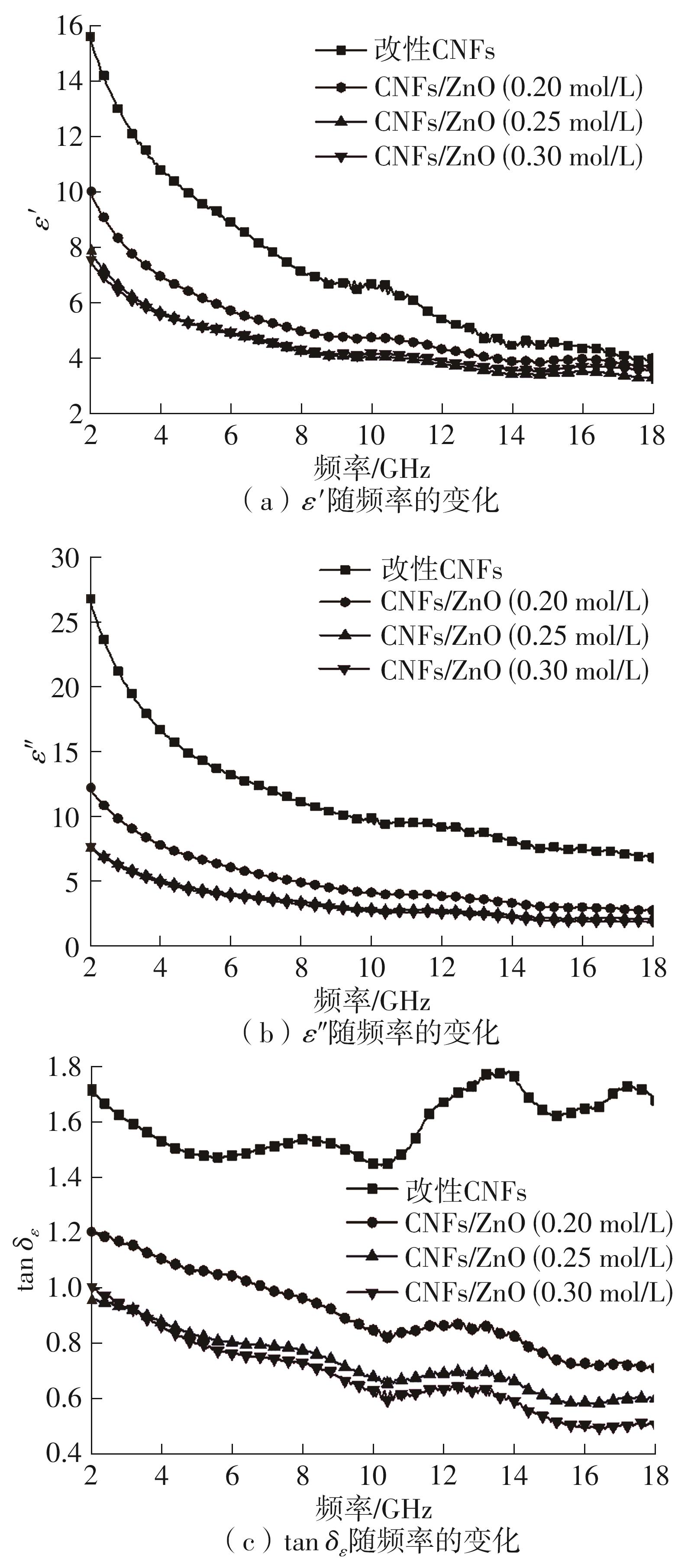
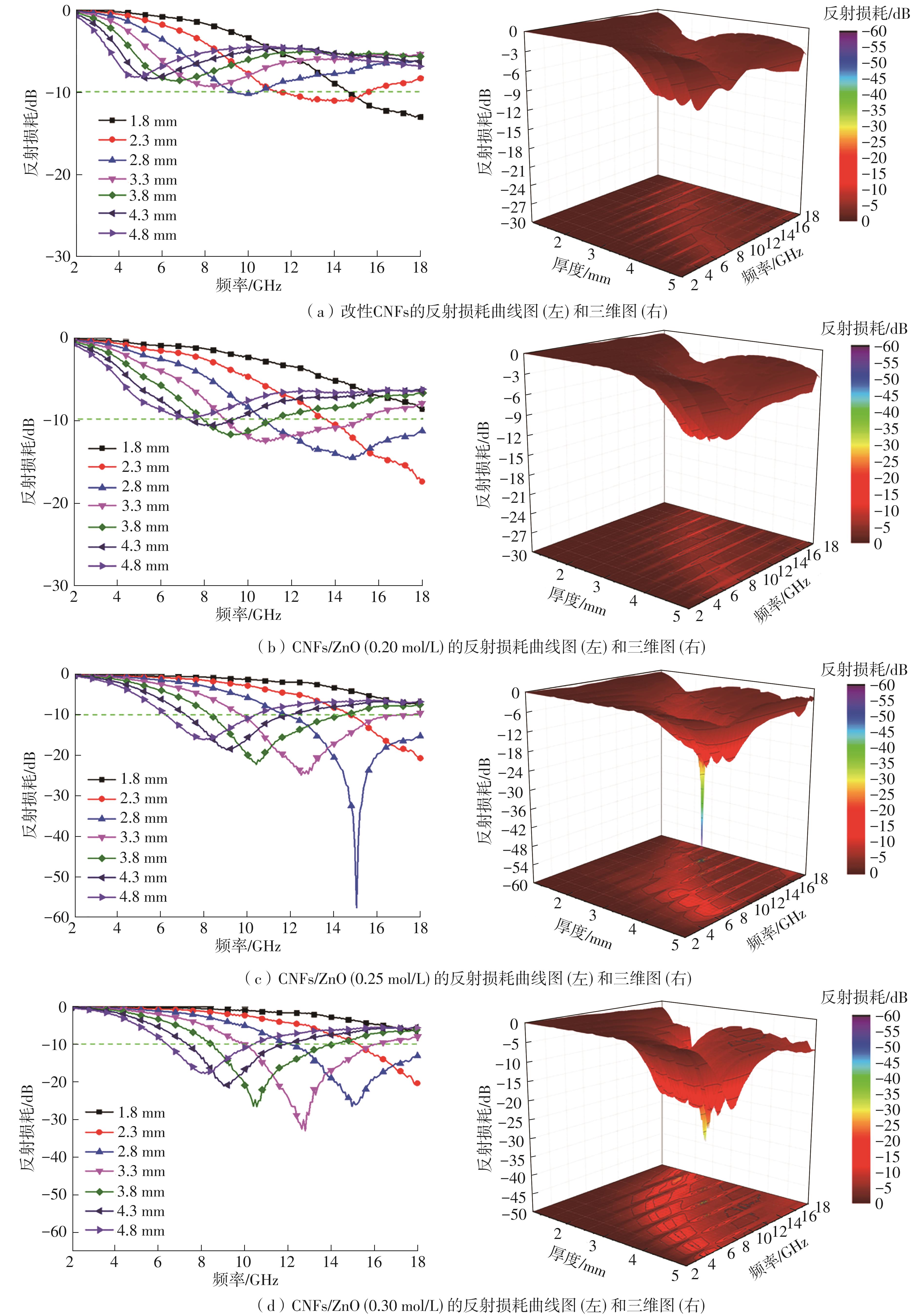
随着电子信息技术的不断发展,电磁污染问题日益严重,高效吸波材料的研究受到越来越多的关注。该文以生物多孔材料细菌纤维素为碳源,采用碳化改性和水热法两步制备了细菌纤维素基CNFs/ZnO复合材料,研究了二水合醋酸锌的浓度对CNFs/ZnO复合材料吸波性能的影响。通过X射线衍射仪(XRD)、冷场发射扫描电子显微镜(FESEM)、矢量网络分析仪(VNA)对复合材料的结构、形貌和吸波性能进行表征。结果表明:CNFs/ZnO复合材料被成功制备,其中碳纳米纤维(CNFs)没有明显的衍射峰,呈无定形状态;碳化和改性CNFs均保持了细菌纤维素三维网络多孔架构的精细纳米纤维微观形貌,但是CNFs变得卷曲且直径明显减小;CNFs/ZnO复合材料中,ZnO被紧密吸引在CNFs表面或随机插入CNFs的空隙中。通过改变二水合醋酸锌的浓度可以控制ZnO在复合材料中的含量,进而调控复合材料的电磁参数,获得良好的阻抗匹配。当二水合醋酸锌的浓度为0.25 mol/L时,ZnO在CNFs上分散得最为均匀,此时CNFs和ZnO的电阻损耗、介电损耗和界面极化等协同作用于三维多孔网络结构上,增加了复合材料对电磁波的多次反射、散射和长程耗散作用。该条件下制备的CNFs/ZnO复合材料,在涂层厚度为2.8 mm、频率为15.1 GHz附近时,其最佳反射损耗为-57.5 dB,有效吸收带宽为7.1 GHz,是一种可靠的复合吸波材料。
中图分类号: