华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 119-134.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230658
所属专题: 2024年土木建筑工程
增设角部阻尼器箍头榫木节点的抗震性能
陈庆军1,2 雷浚2 李冰州2 左志亮2 蔡健1,2
- 1.华南理工大学 亚热带建筑与城市科学全国重点实验室,广东 广州 510640
2.华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广东 广州 510640
3.广东省普通高校工程抗震研究中心,广东 广州 510640
-
收稿日期:2023-10-24出版日期:2024-07-25发布日期:2024-02-29 -
通信作者:左志亮(1982—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事钢-混凝土组合结构、木结构研究。 E-mail:ctzlzuo@scut.edu.cn -
作者简介:陈庆军(1975—),男,博士,教授,主要从事木结构、混凝土结构等研究。E-mail: qjchen@scut.edu.cn -
基金资助:广东省自然科学基金资助项目(2021A1515012603)
Seismic Performance of Hoop Head Tenon Timber Joint with Added Corner Dampers
CHEN Qingjun1,2 LEI Jun2 LI Bingzhou2 ZUO Zhiliang2 CAI Jian1,2
- 1.State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building and Urban Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
3.Engineering Seismic Research Center of Guangdong,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2023-10-24Online:2024-07-25Published:2024-02-29 -
Contact:左志亮(1982—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事钢-混凝土组合结构、木结构研究。 E-mail:ctzlzuo@scut.edu.cn -
About author:陈庆军(1975—),男,博士,教授,主要从事木结构、混凝土结构等研究。E-mail: qjchen@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021A1515012603)
摘要:
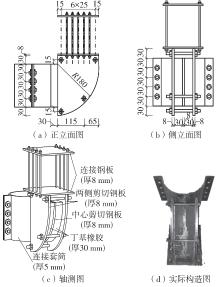
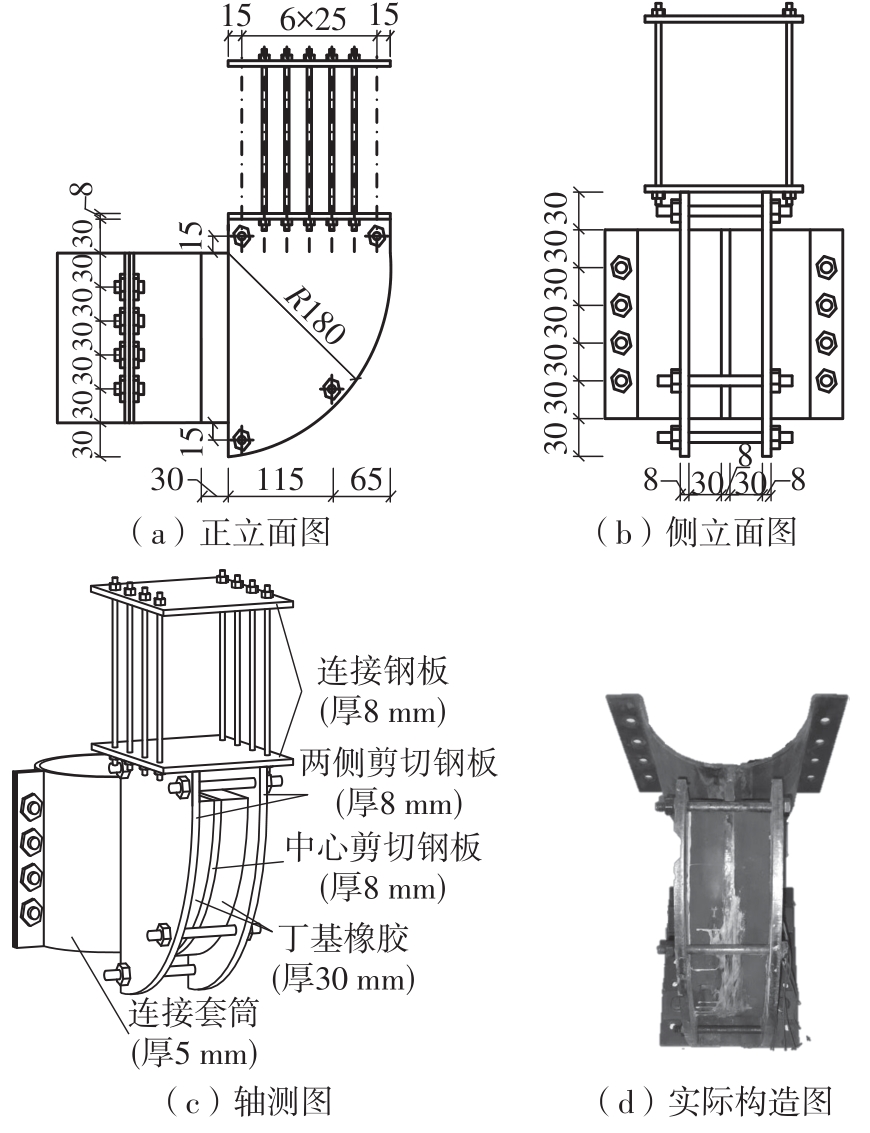
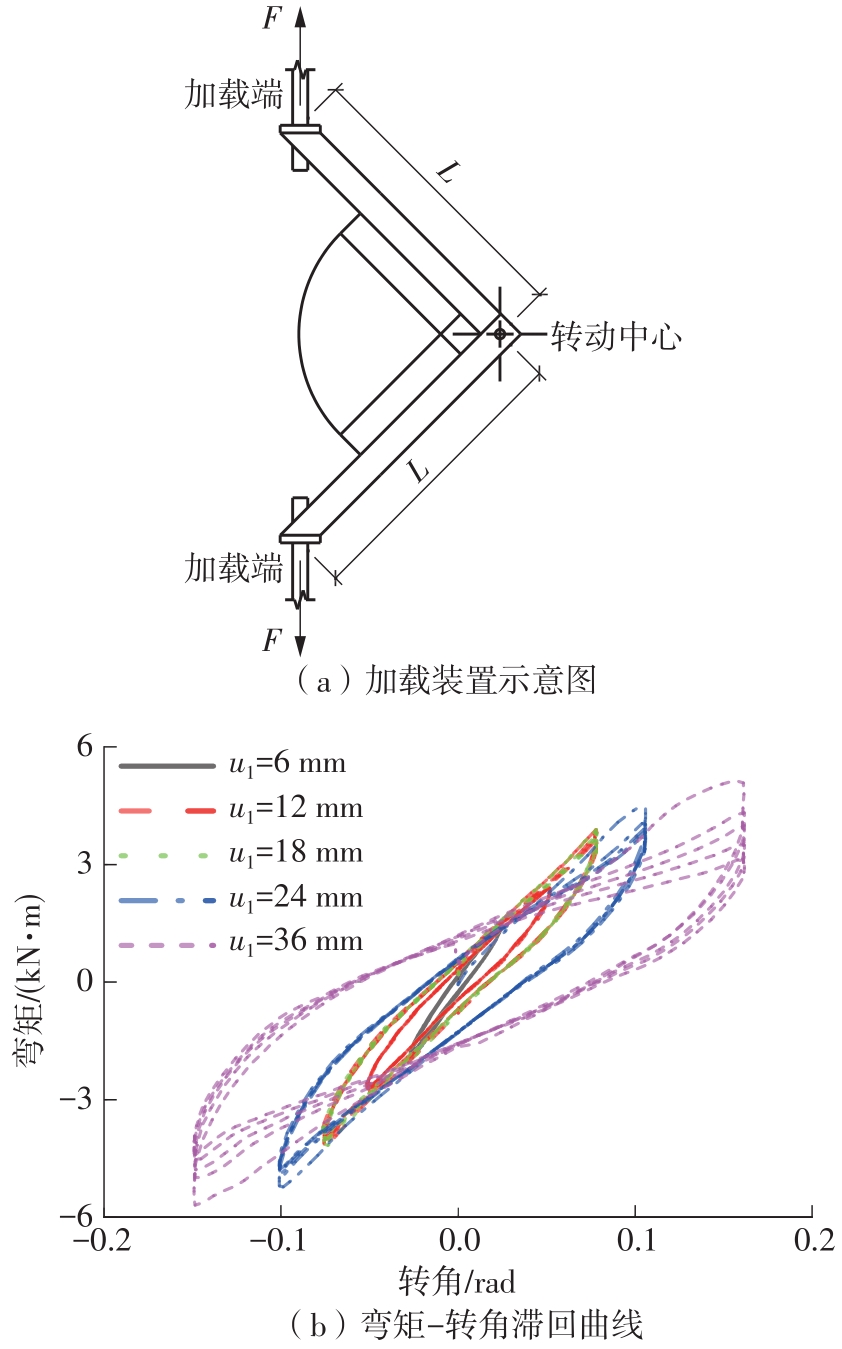
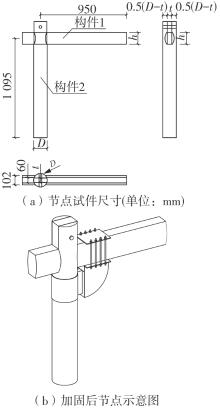
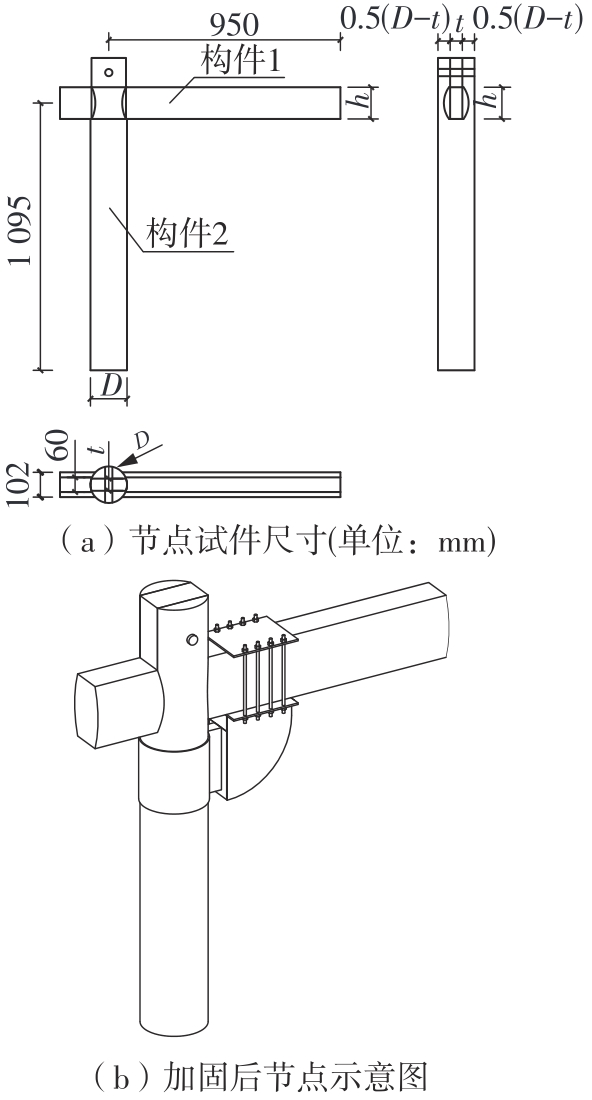
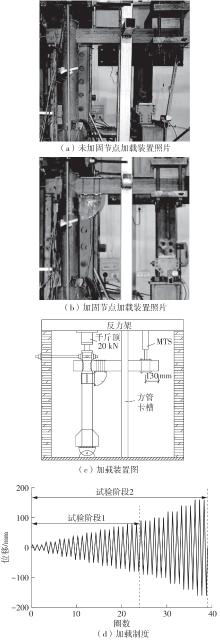
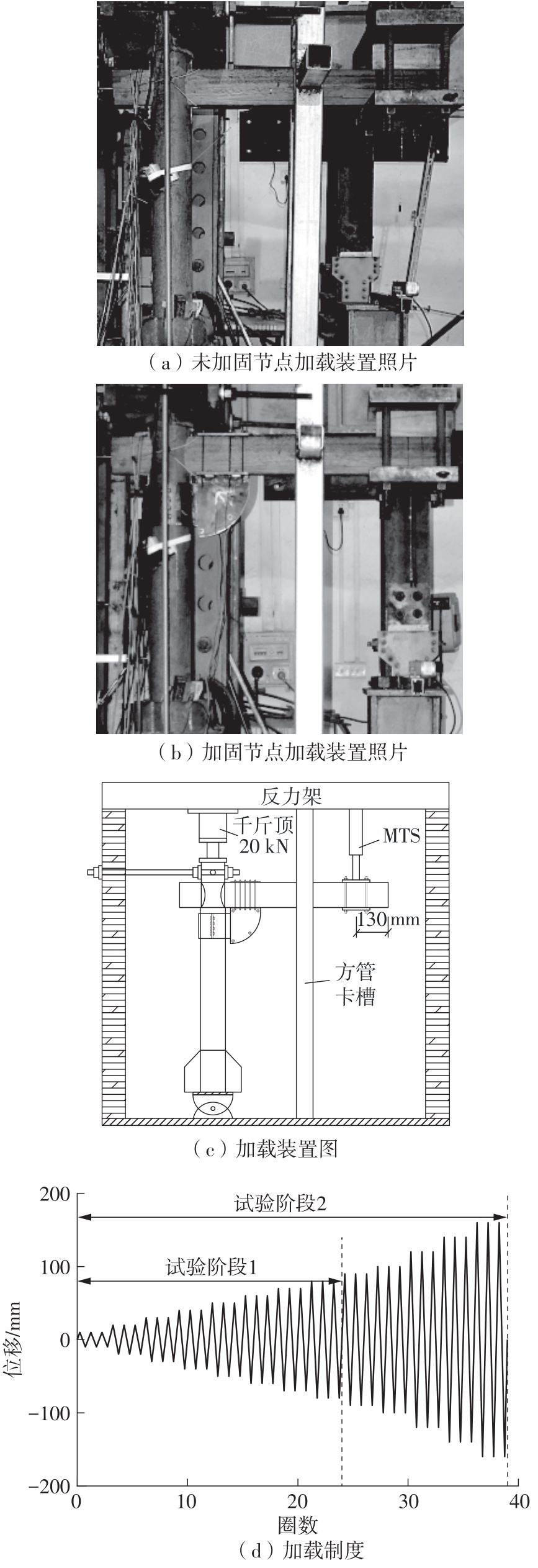
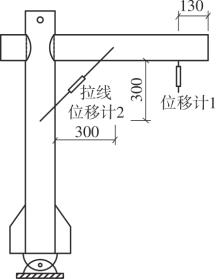
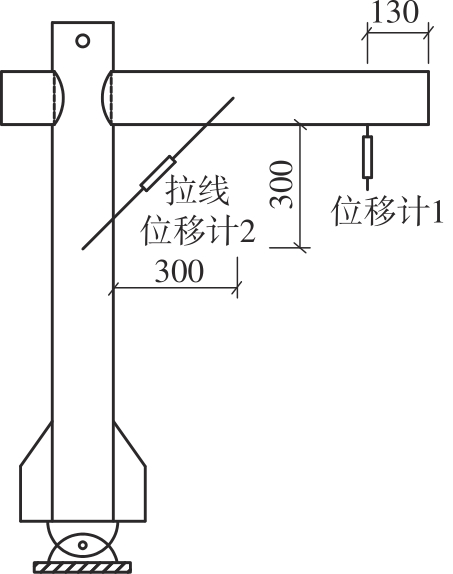
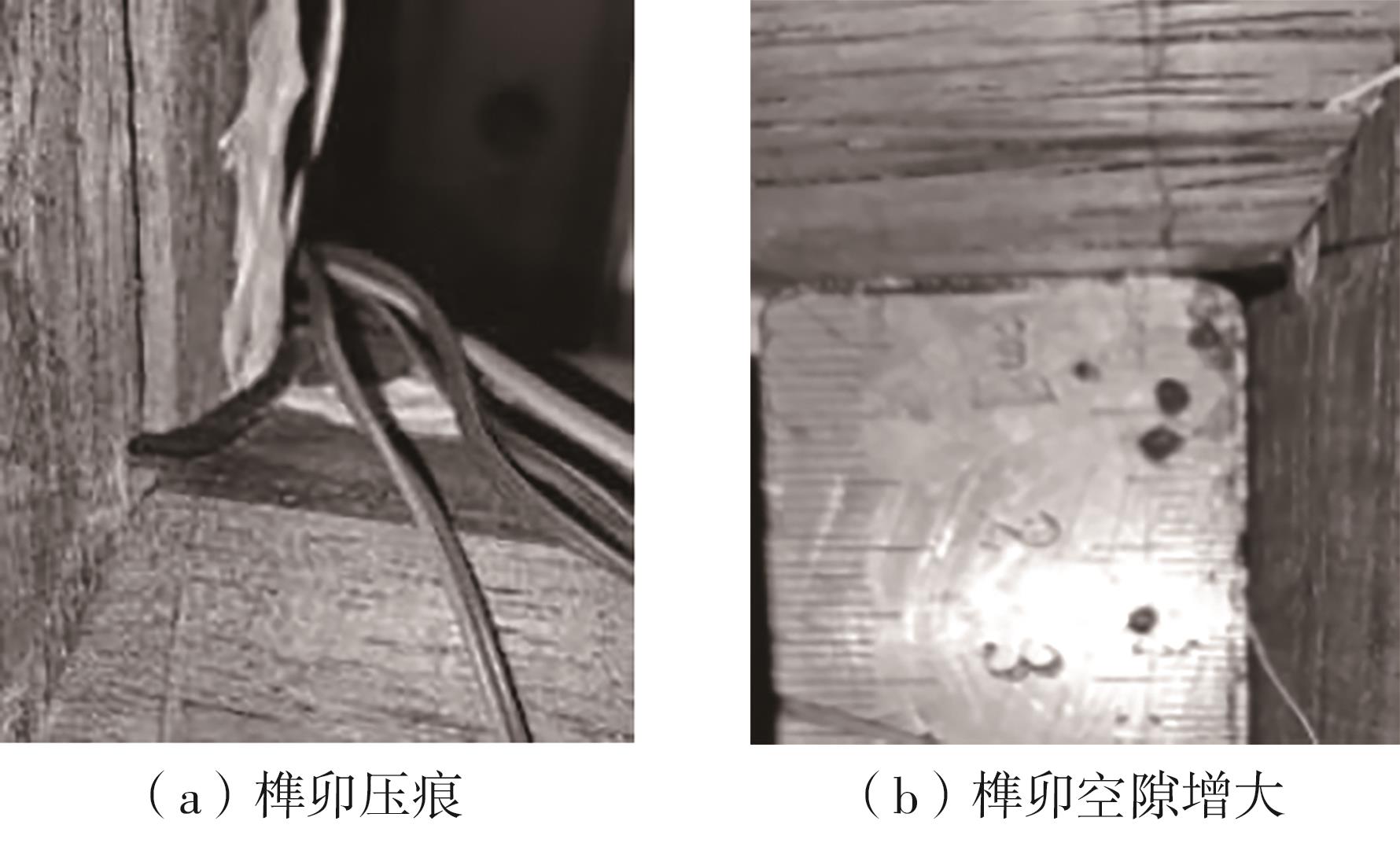
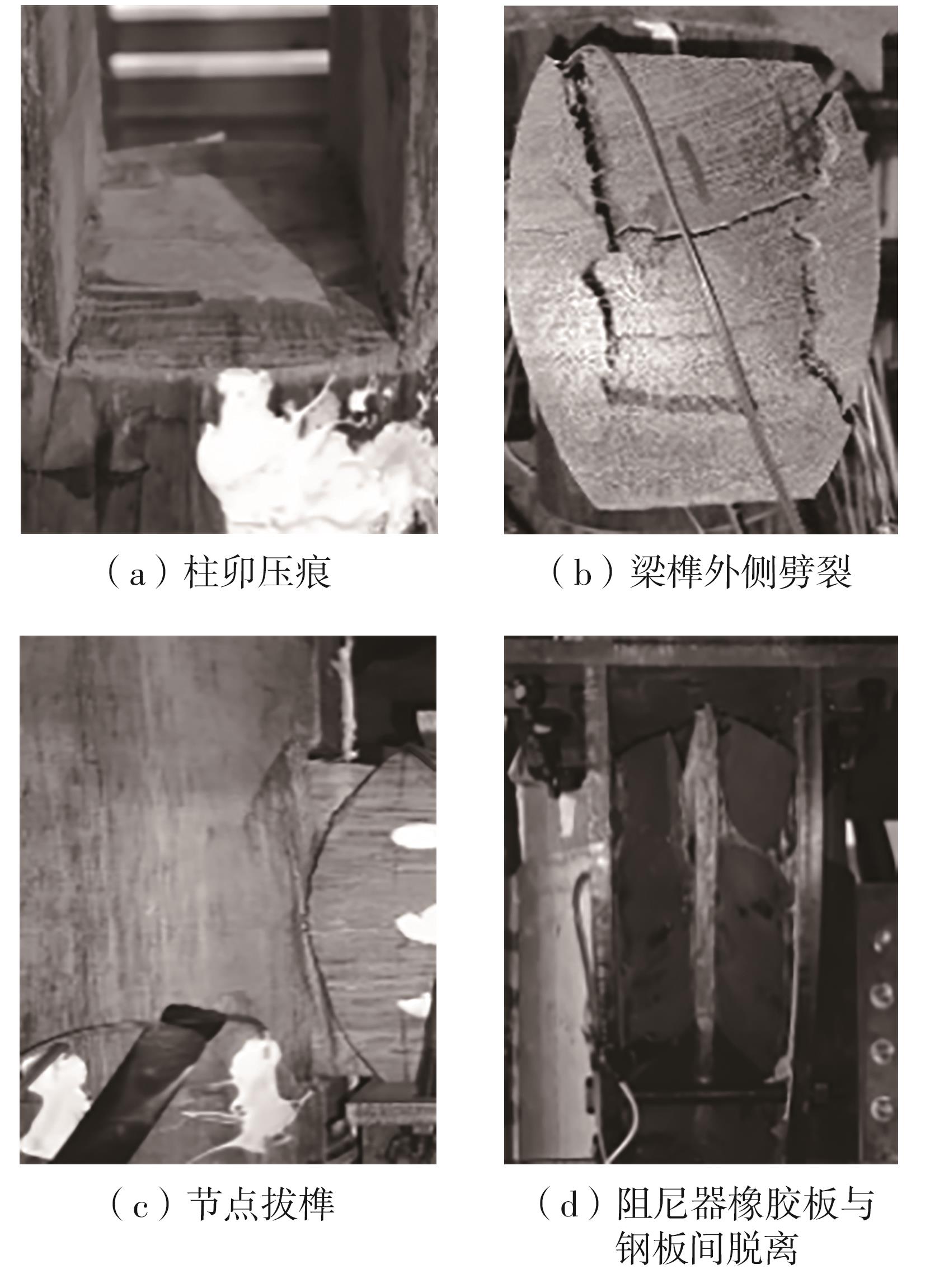
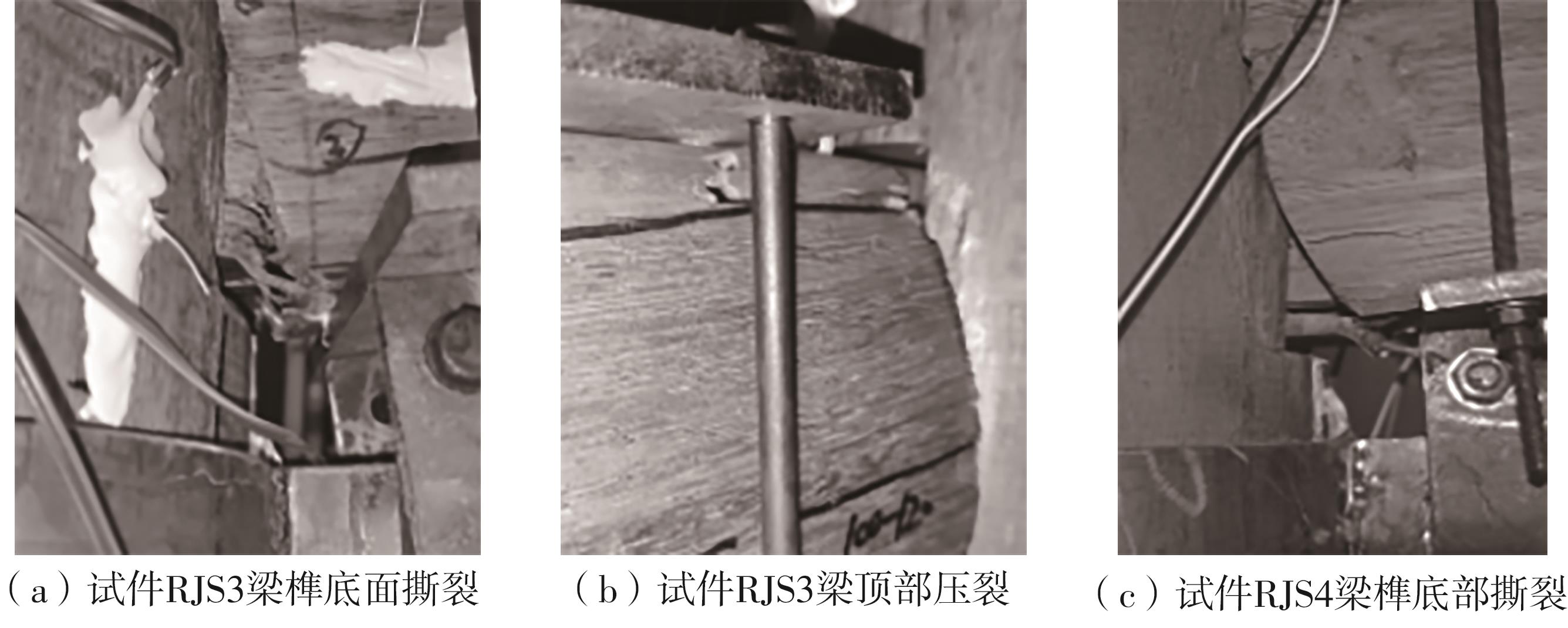
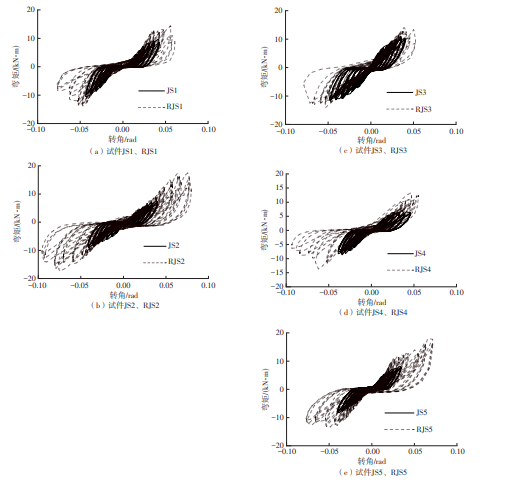
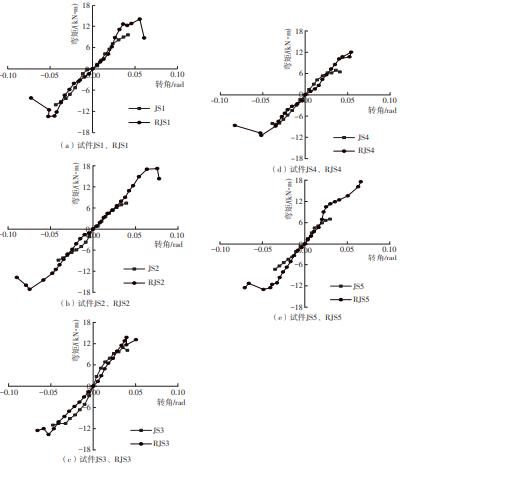
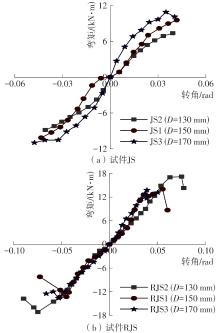
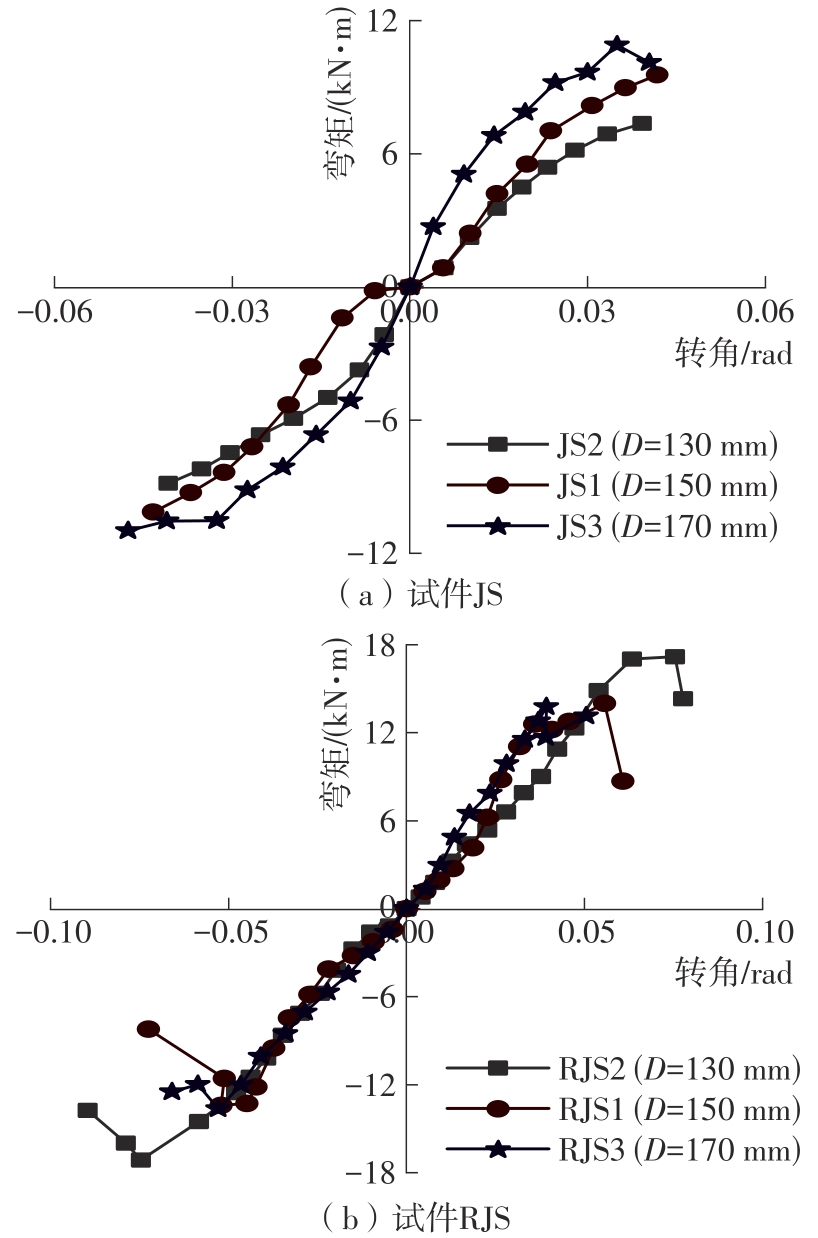
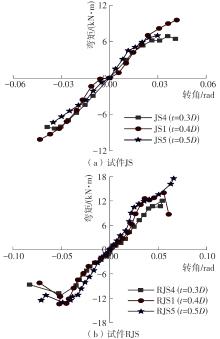
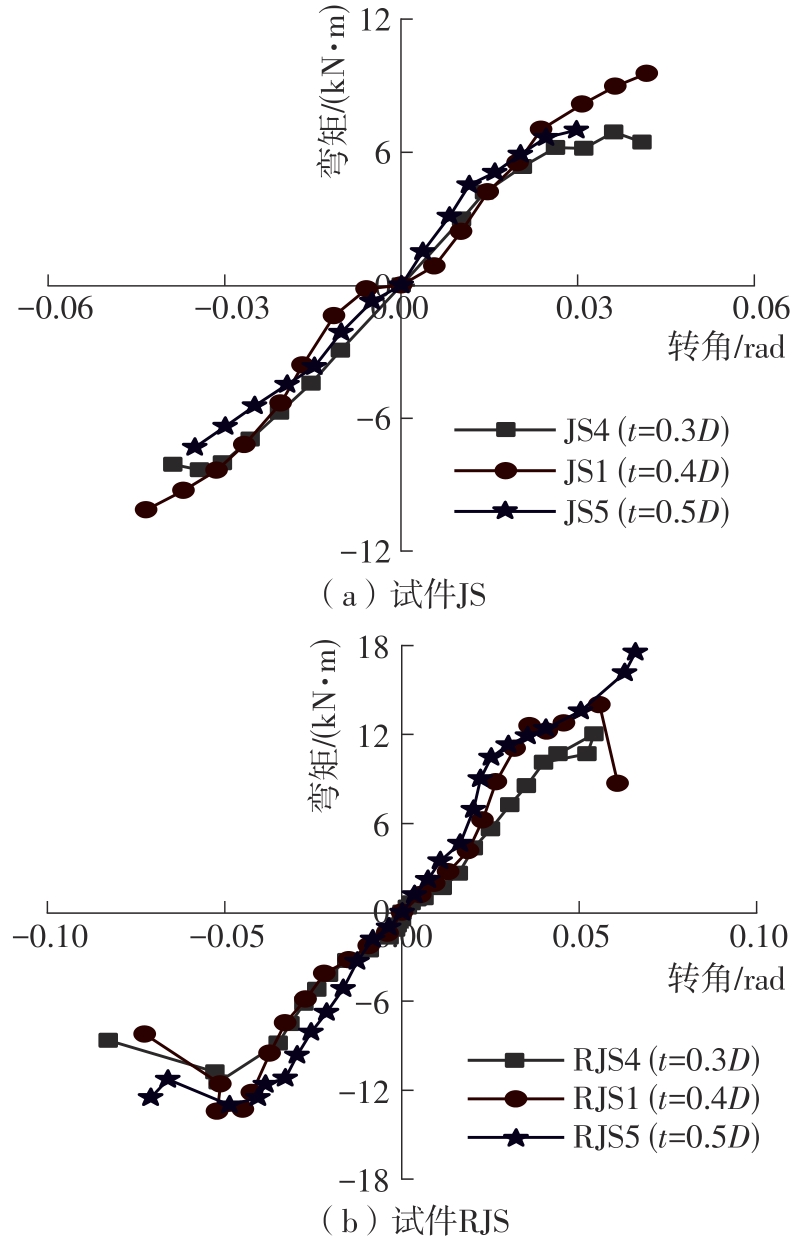
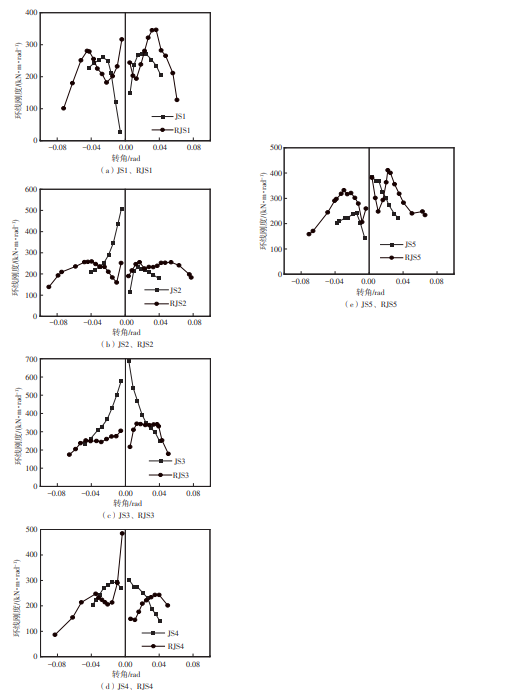
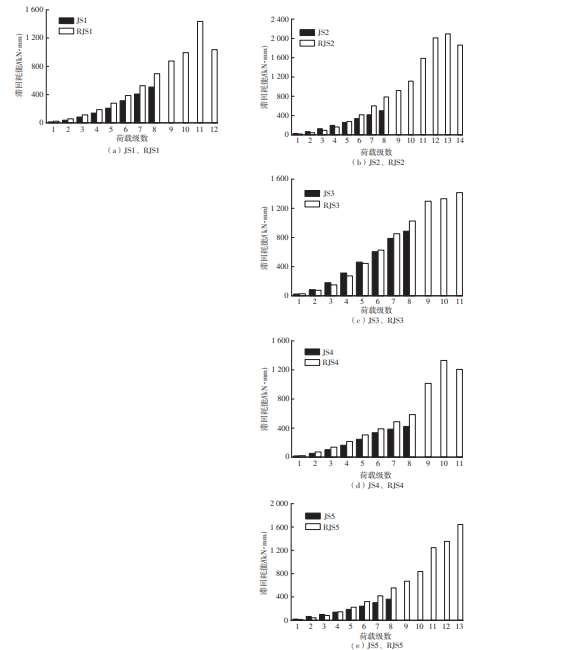
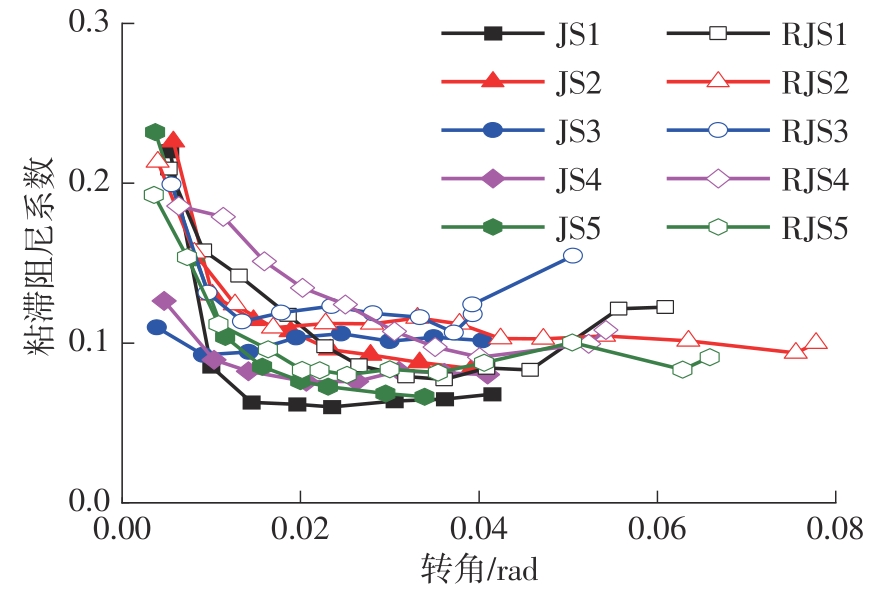
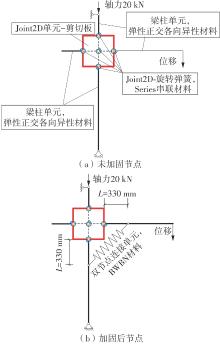
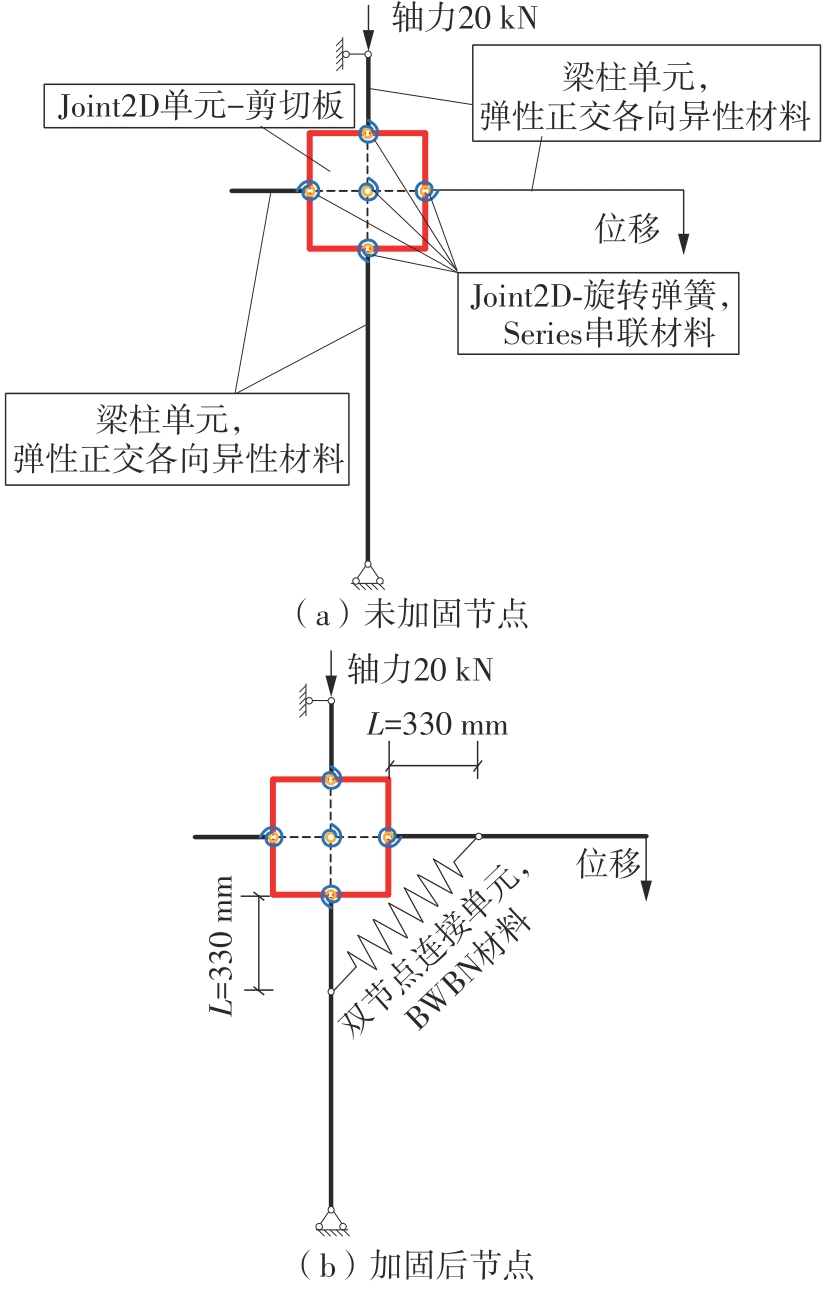
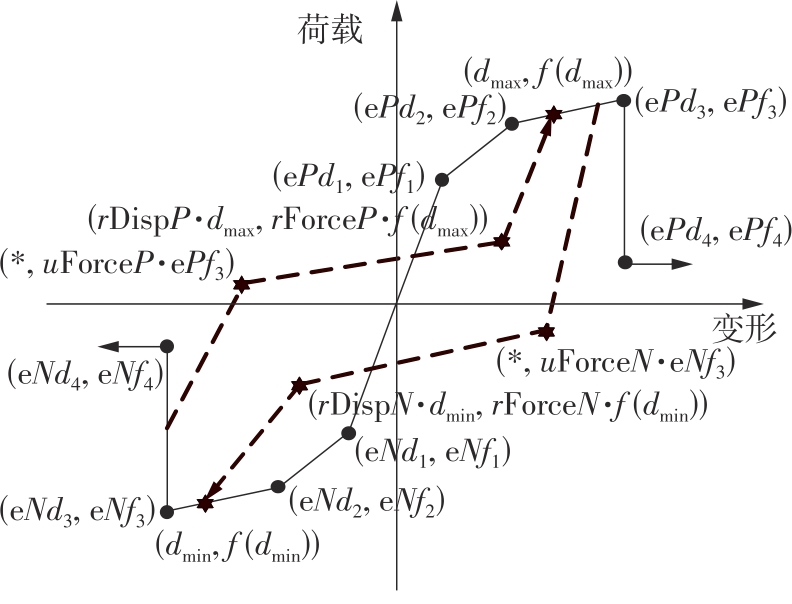
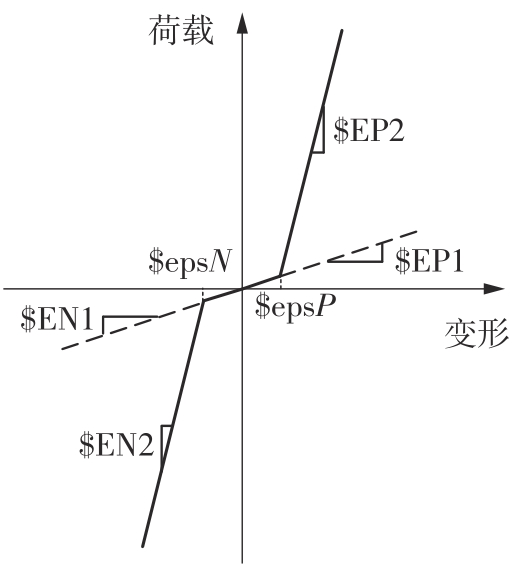
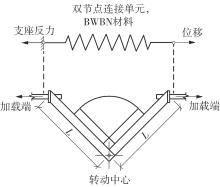
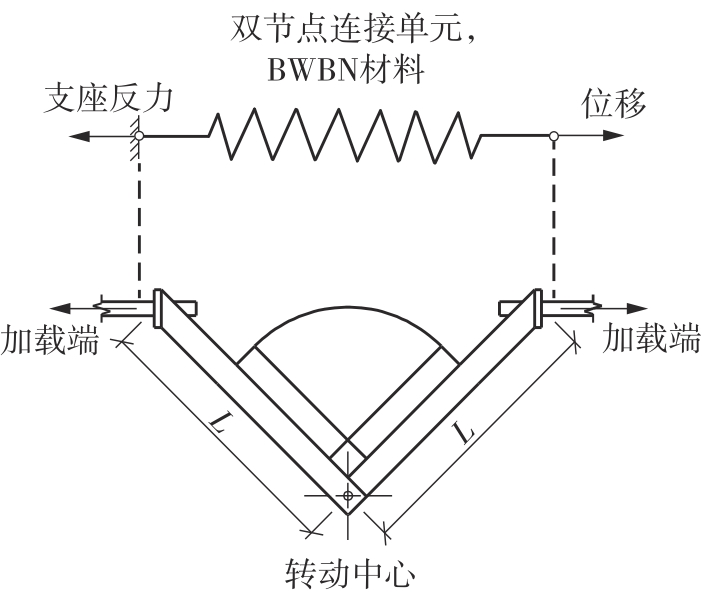
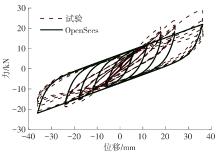
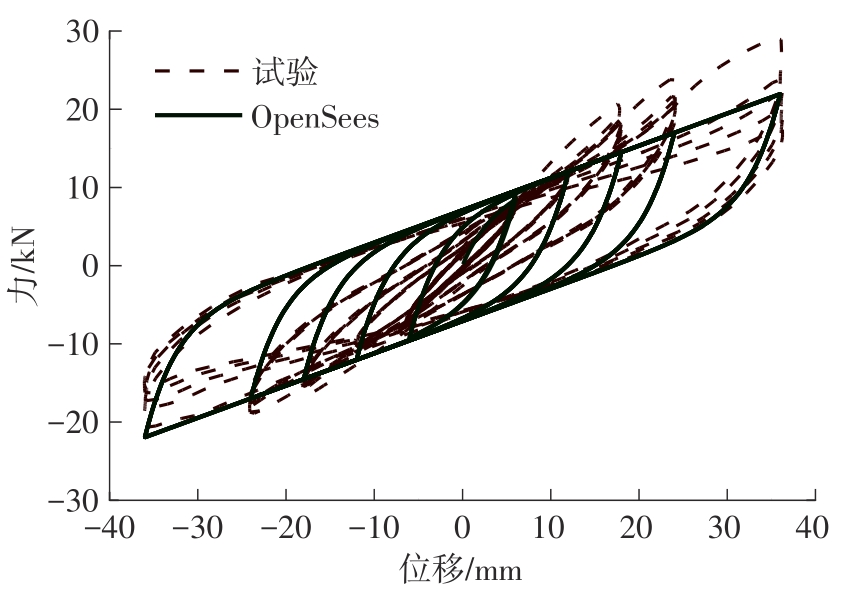
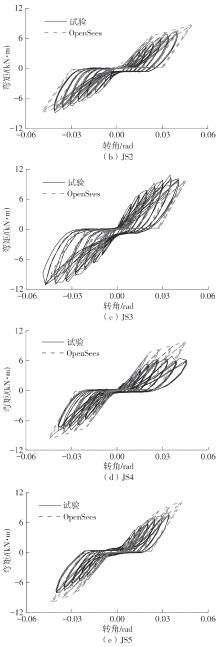
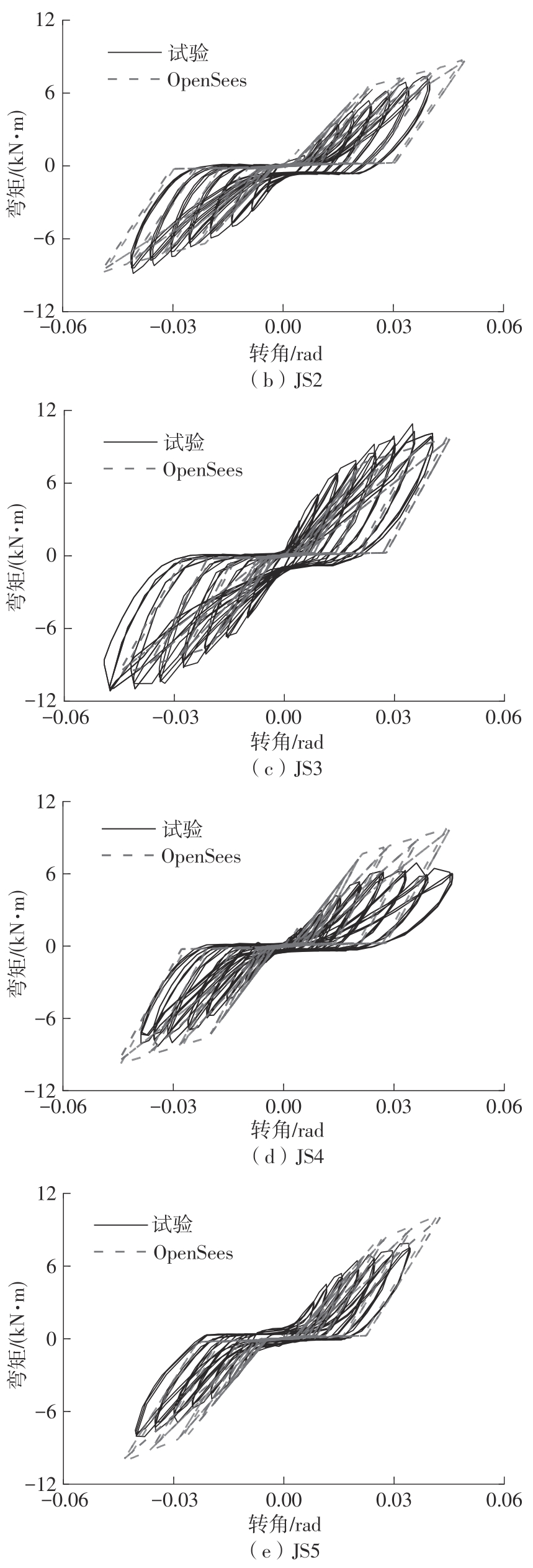
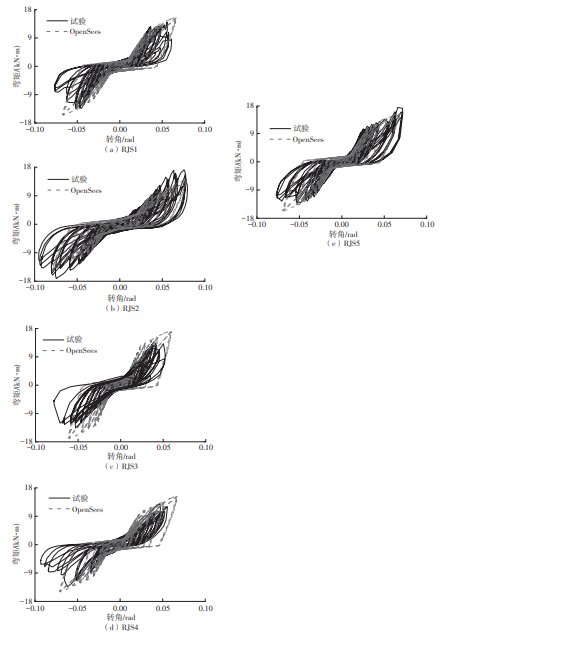
为了给广府木结构的修复提供理论依据,采用菠萝格木材设计制作了5个箍头榫节点试件。考虑到榫卯构造尺寸的影响,首先进行了未加固无损节点的拟静力试验。然后,采用对原有外观影响较小的雀替型阻尼器对上述节点损坏试件进行加固,以尽可能保留建筑的原始风貌。最后,对加固节点进行拟静力试验,以研究节点的抗震性能变化以及阻尼器的加固效果。结果表明:采用阻尼器加固后的节点试件在加载至破坏时,榫卯处压痕明显,梁外榫外侧劈裂、脱榫现象明显,阻尼器脚部的橡胶与钢板有一定的脱离现象;对节点增设阻尼器能够弥补节点初期损伤导致的受力性能下降,为残损榫卯节点提供较好的后期刚度,提高节点的承载能力和耗能能力;与未加固试件相比,增设阻尼器后,试件的后期刚度、极限承载力、总滞回耗能均有所增加,分别提高18%、19%、20%以上。文中还在已有简化力学模型的基础上,结合OpenSees,提出了一种应用于箍头榫木结构的宏观模型建模方法。采用该方法得到的节点滞回曲线与试验结果吻合良好,可以有效模拟阻尼器加固的箍头榫木节点的滞回耗能特性。
中图分类号:
引用本文
陈庆军, 雷浚, 李冰州, 等. 增设角部阻尼器箍头榫木节点的抗震性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(7): 119-134.
CHEN Qingjun, LEI Jun, LI Bingzhou, et al. Seismic Performance of Hoop Head Tenon Timber Joint with Added Corner Dampers[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(7): 119-134.
| 1 | 潘毅,陈建,安仁兵,等 .山地古建筑木结构抗震性能研究评述[J].土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2022,44(2):10-21. |
| PANG Yi, CHEN Jian, AN Renbing,et al .A review seismic performance of ancient timber structures on sloped lands[J].Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2022,44(2):10-21. | |
| 2 | 谢启芳,赵鸿铁,薛建阳,等 .中国古建筑木结构榫卯节点加固的试验研究[J].土木工程学报,2008,41(1):28-34. |
| XIE Qifang, ZHAO Hongtie, XUE Jianyang,et al .An experimental study on the strengthening of mortise-tenon joints in ancient Chinese wooden buildings[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2008,41(1):28-34. | |
| 3 | 周乾,闫维明,李振宝,等 .古建筑榫卯节点加固方法振动台试验研究[J].四川大学学报(工程科学版),2011,43(6):70-78. |
| ZHOU Qian, YAN Wei-ming, LI Zhen-bao,et al .Aseismic strengthening methods on Chinese ancient tenon-mortise joint by shaking table tests[J].Journal of Sichuan University (Engineering Science Edition),2011,43(6):70-78. | |
| 4 | 郇君虹,马东辉,郭小东,等 .扁钢加固半榫、透榫及燕尾榫抗震性能试验研究[J].北京工业大学学报,2019,45(8):763-771. |
| HUAN Junhong, MA Donghui, GUO Xiaodong,et al .Experimental study of aseismic behaviors of flexural tenon joint,through tenon joint and dovetail joint strengthened with flat steel devices[J].Journal of Beijing University of Technology,2019,45(8):763-771. | |
| 5 | 薛建阳,任国旗,张家珩,等 .角钢加固传统民居十字形半榫节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2021,42(1):103-112. |
| XUE Jianyang, REN Guoqi, ZHANG Jiaheng,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of cross-shaped half-tenon joint reinforced by angle in traditional dwellings[J].Journal of Building Structures,2021,42(1):103-112. | |
| 6 | 金昱成,苏何先,潘文,等 .木结构榫卯节点抗震性能及加固对比试验研究[J].土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2022,44(2):138-147. |
| JIN Yucheng, SU Hexian, PAN Wen,et al .Experimental research on seismic performance and reinforcement comparison of mortise-tenon joints in timber structures[J].Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2022,44(2):138-147. | |
| 7 | 潘毅,王超,唐丽娜,等 .古建筑直榫节点扁钢与阻尼器加固比较研究[J].西南交通大学学报,2014.49(6):981-986,1031. |
| PAN Yi, WANG Chao, TANG Lina,et al .Comparative research on flat steel and damper strengthening of straight type of tenon-mortise joints[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2014,49(6):981-986,1031. | |
| 8 | 高永林,陶忠,叶燎原,等 .传统穿斗木结构榫卯节点附加黏弹性阻尼器振动台试验[J].土木工程学报,2016,49(2):59-68. |
| GAO Yonglin, TAO Zhong, YE Liaoyuan,et al .Shaking table tests of mortise-tenon joints of a traditional Chuan-Dou wood structure attached with viscoelastic dampers[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2016,49(2):59-68. | |
| 9 | 高永林,陶忠,叶燎原,等 .带有黏弹性阻尼器穿斗木结构振动台试验研究[J].振动与冲击,2017,36(1):240-247. |
| GAO Yonglin, TAO Zhong, YE Liaoyuan,et al .Shaking table tests for a Chuan-dou timber building with viscoelastic dampers[J].Journal of Vibration and Shock,2017,36(1):240-247. | |
| 10 | XUE J, WU C, ZHANG X,et al .Effect of pre-tension in superelastic shape memory alloy on cyclic behavior of strengthened mortise-tenon joints[J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,241:118-136. |
| 11 | XUE J, WU C, ZHANG X,et al .Experimental study on seismic behavior of mortise-tenon joints strengthened with shape memory alloy[J].Engineering Structures,2020,218:110-839. |
| 12 | 聂雅雯,陶忠,高永林 .黏弹性阻尼器增强传统木结构燕尾榫节点试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2021,42(1):125-133. |
| NIE Yawen, TAO Zhong, GAO Yonglin .Experimental study on dovetail mortise-tenon joints with viscoelastic dampers in traditional timber structures[J].Journal of Building Structures,2021,42(1):125-133. | |
| 13 | 陆伟东,吴伟强,施程凯,等 .含内嵌卯口耗能器的榫卯节点抗震性能试验研究[J].土木与环境工程学报(中英文),2022,44(2):30-37. |
| LU Weidong, WU Weiqiang, SHI Chengkai,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of mortise-tenon joint with embedded dampers[J].Journal of Civil and Environmental Engineering,2022,44(2):30-37. | |
| 14 | 陆伟东,姜伟波,张坤,等 .含耗能雀替的榫卯节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2021,42(11):213-221. |
| LU Weidong, JIANG Weibo, ZHANG Kun,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of mortise-tenon joints with Queti damper[J].Journal of Building Structures,2021,42(11):213-221. | |
| 15 | DAI B, GAO Y, TAO Z,et al .Fan shaped shear dampers strengthen mortise tenon joints in Chinese traditional timber structures[J].International Journal of Architectural Heritage,2022,17(7):1079-1092. |
| 16 | 肖旻,杨扬 .广府祠堂建筑尺度模型研究[J].华中建筑,2012,30(6):147-151. |
| XIAO Min, YANG Yang .Study on the scale mode of ancestral halls incanton[J].Huazhong Architecture,2012,30(6):147-151. | |
| 17 | 陈庆军,彭章锋,蔡健,等 .广府古建筑木结构箍头榫节点抗震性能研究[J].建筑结构学报,2019,40(10):168-179. |
| CHEN Qingjun, PENG Zhangfeng, CAI Jian,et al .Seismic behavior of hoop head tenon-mortise joint in ancient wood structures in Guangfu[J].Journal of Building Structures,2019,40(10):168-179. | |
| 18 | 常鹏,冯秋歌,韩乐,等 .松动残损下箍头榫节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2023,44(10):86-96. |
| CHANG Peng, FENG Qiuge, HAN Le,et al .Experimental study on seismic behavior of Gutou mortise-tenon joint with loose damage[J].Journal of Building Structures,2023,44(10):86-96. | |
| 19 | 陈庆军,李冰州,陈奕年,等 .雀替型阻尼器加固箍头榫木框架结构的抗震性能[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(4):9-20. |
| CHEN Qingjun, LI Bingzhou, CHEN Yinian,et al .Seismic performance of hoop head tenon frame structure reinforced by sparrow brace type damper[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,51(4):9-20. | |
| 20 | 梁松,程从密,王绍怀,等 .土木工程材料(上册)[M].广州:华南理工大学出版社,2007. |
| 21 | 《木结构设计手册》编辑委员会 .木结构设计手册[M].北京:中国建筑工业出版社,2021. |
| 22 | Forest Products Laboratory .Wood handbook—Wood as an engineering material,General Technical Report FPL-GTR-190[R].Madison:USA Department of Agriculture,Forest Service,Forest Products Laboratory,2010. |
| 23 | CHUN Q, YUE Z, PAN J .Experimental study on seismic characteristics of typical mortise-tenon joints of Chinese southern traditional timber frame buildings[J].Science China Technological Sciences,2011,54(9):2404-2411. |
| 24 | 薛建阳,任国旗,许丹,等 .传统民居穿斗式木结构栓榫节点抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2019,40(10):158-167. |
| XUE Jianyang, REN Guoqi, XU Dan,et al .Experimental study on seismic performance of dowel joints in traditional Chuan-Dou style timber structures[J].Journal of Building Structures,2019,40(10):158-167. | |
| 25 | The University of California .OpenSees User Documentation[EB/OL].[2023-09-24].. |
| 26 | 陈庆军,何永鹏,邱凯祥,等 .广府古建筑木结构箍头榫节点弯矩-转角关系理论分析[J].湖南大学学报报(自然科学版),2019,46(1):65-75. |
| CHEN Qingjun, HE Yongpeng, QIU Kaixiang,et al .Theoretical analysis on moment-rotation relationship of hoop head tenon-mortise joint for ancient timber structure in Guangfu[J].Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences),2019,46(1):65-75. |
| [1] | 丁发兴, 蔡勇强, 王莉萍, 等. 焊接多腔双钢板-混凝土组合剪力墙抗震性能分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024, 52(1): 15-25. |
| [2] | 甄晓霞, 刘桂源, 董春光, 等. 索网-阻尼器系统自振特性研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(7): 61-71. |
| [3] | 陈庆军, 李冰州, 陈奕年, 等. 雀替型阻尼器加固箍头榫木框架结构的抗震性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 51(4): 9-20. |
| [4] | 郑一峰 钱盛域. 黏滞阻尼器与钢阻尼器在桥梁横向震动控制中的应用研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 49(12): 89-100. |
| [5] | 黄海斌, 王彦超, 刘亚洲, 等. 分离式竖向加劲板钢管混凝土柱 - 梁节点的抗震性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2020, 48(3): 55-66. |
| [6] | 戴岩 聂少锋 周天华. 环梁式圆钢管约束H型钢混凝土柱-钢梁节点的抗震性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(5): 110-122. |
| [7] | 徐艳 童川 李建中. 设置纵桥向粘滞阻尼器的斜拉桥的简化动力模型[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(4): 90-98. |
| [8] | 马宏伟 陈丰收. 基于粗粒度并行遗传算法的阻尼器优化布置[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(11): 104-112. |
| [9] | 曾繁良 黄炎生 周靖. 结构抗震承载力利用系数的可靠度校核 [J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 47(1): 56-63. |
| [10] | 李培振 舒欣 杨金平. 黏弹性阻尼器减震结构考虑SSI的参数分析[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2018, 46(4): 121-128,136. |
| [11] | 马宏伟 林朗 刘和星. 蜂窝组合梁-复合螺旋箍混凝土柱节点试验[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(12): 120-127. |
| [12] | 陈庆军 邱凯祥 汤序霖 袁国财 肖旻 杨春. 广府木祠堂箍头榫节点力学性能试验研究[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(10): 96-103. |
| [13] | 郭猛 刘志元 黄炜 王双娇 袁泉. 加气混凝土砌块组合墙加固震损框架抗震性能试验[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2016, 44(10): 117-124. |
| [14] | 陈庆军 薛华 汤序霖 左志亮 陈映瑞. 梁贯通式圆钢管混凝土柱-混凝土梁边节点抗震性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(7): 33-41. |
| [15] | 雷真 屈俊童 王勇. 纤维加固震损钢筋混凝土- 砖组合开洞墙体的抗震性能[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2015, 43(7): 84-91. |
| 阅读次数 | ||||||
|
全文 |
|
|||||
|
摘要 |
|
|||||