华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (12): 107-117.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220555
所属专题: 2023年能源、动力与电气工程
紫丁香基木质素二聚体模化物热解的动力学机理
楼波 李森浩 卢菘 周达恒
- 华南理工大学 电力学院/广东省能源高效清洁利用重点实验室,广东 广州 510640
Kinetic Mechanism of Pyrolysis of Lilac Lignin Dimer Memes
LOU Bo LI Senhao LU Song ZHOU Daheng
- School of Electric Power Engineering/Guangdong Province Key Laboratory of Energy Efficient and Clean Utilization,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
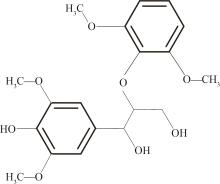
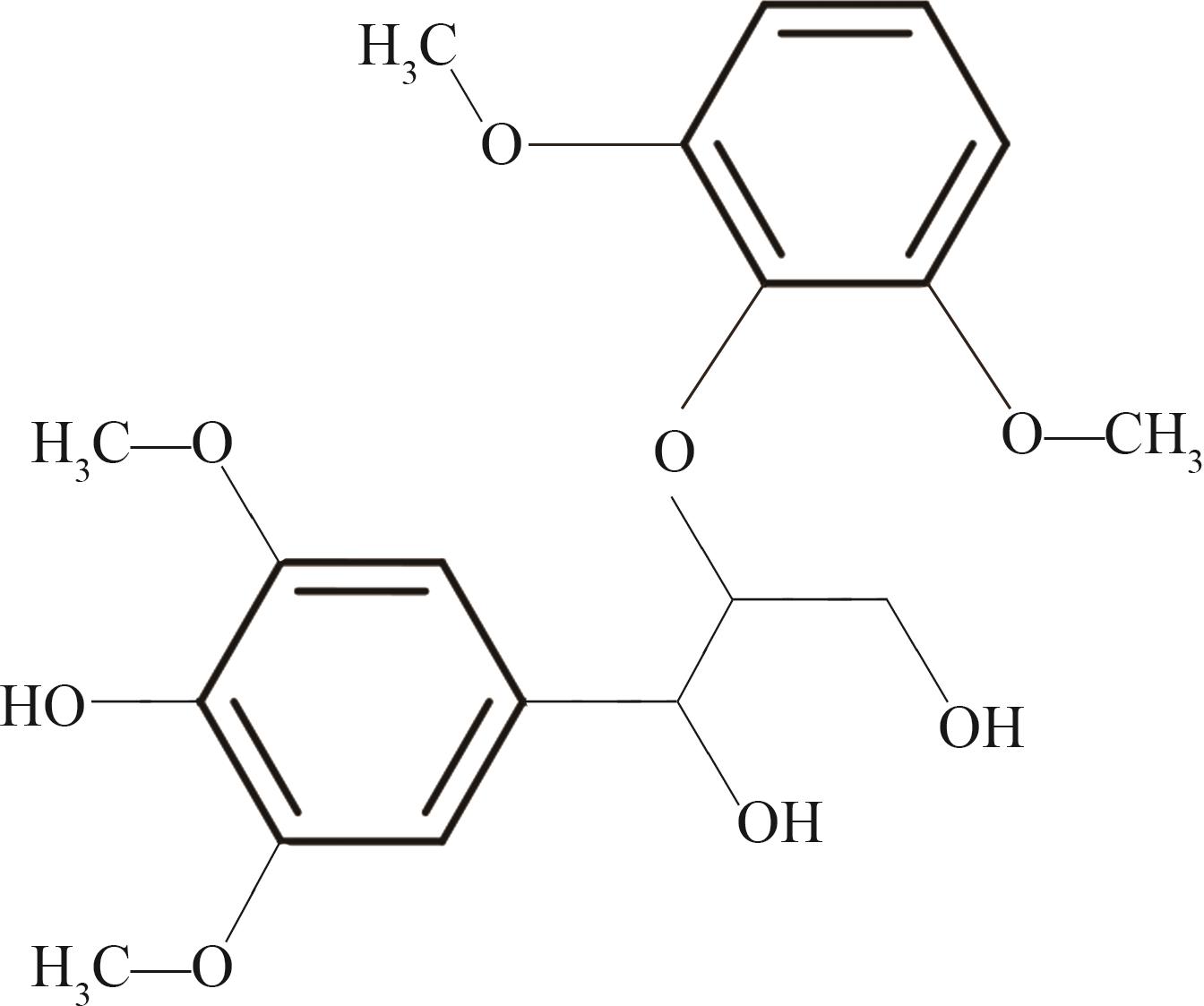
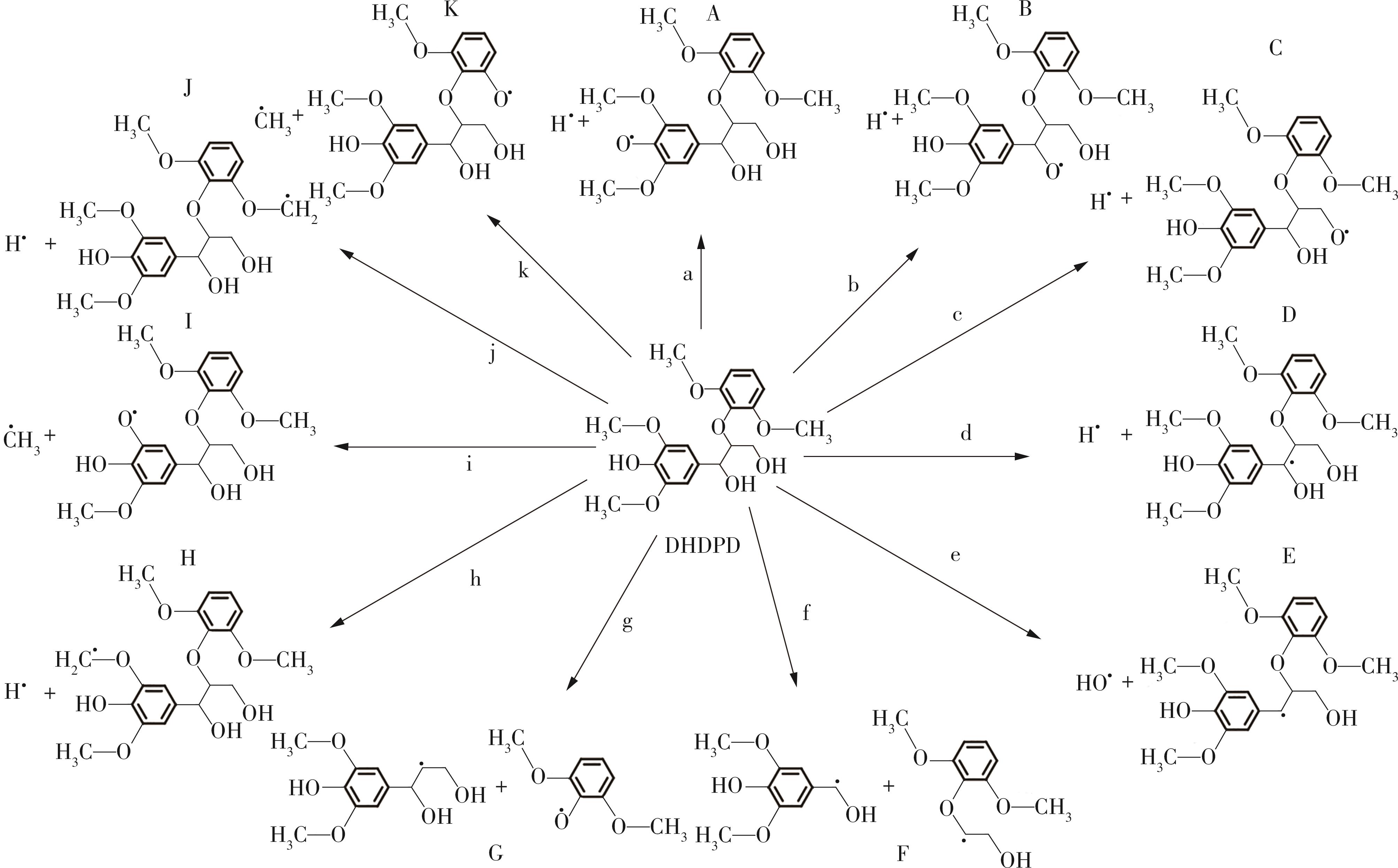
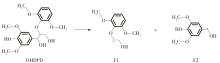
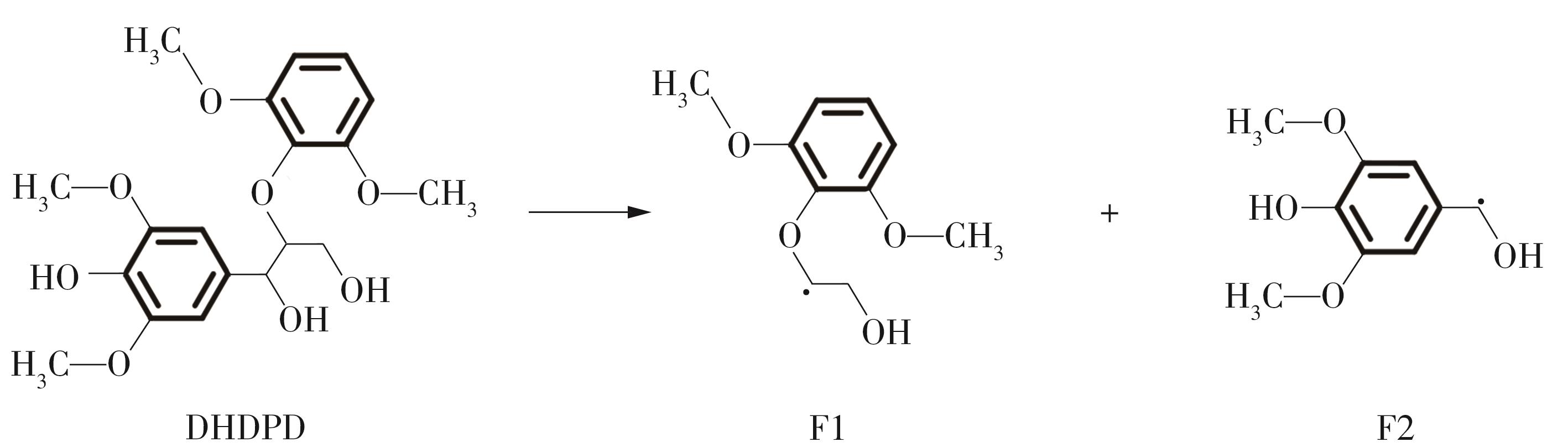
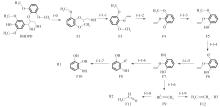
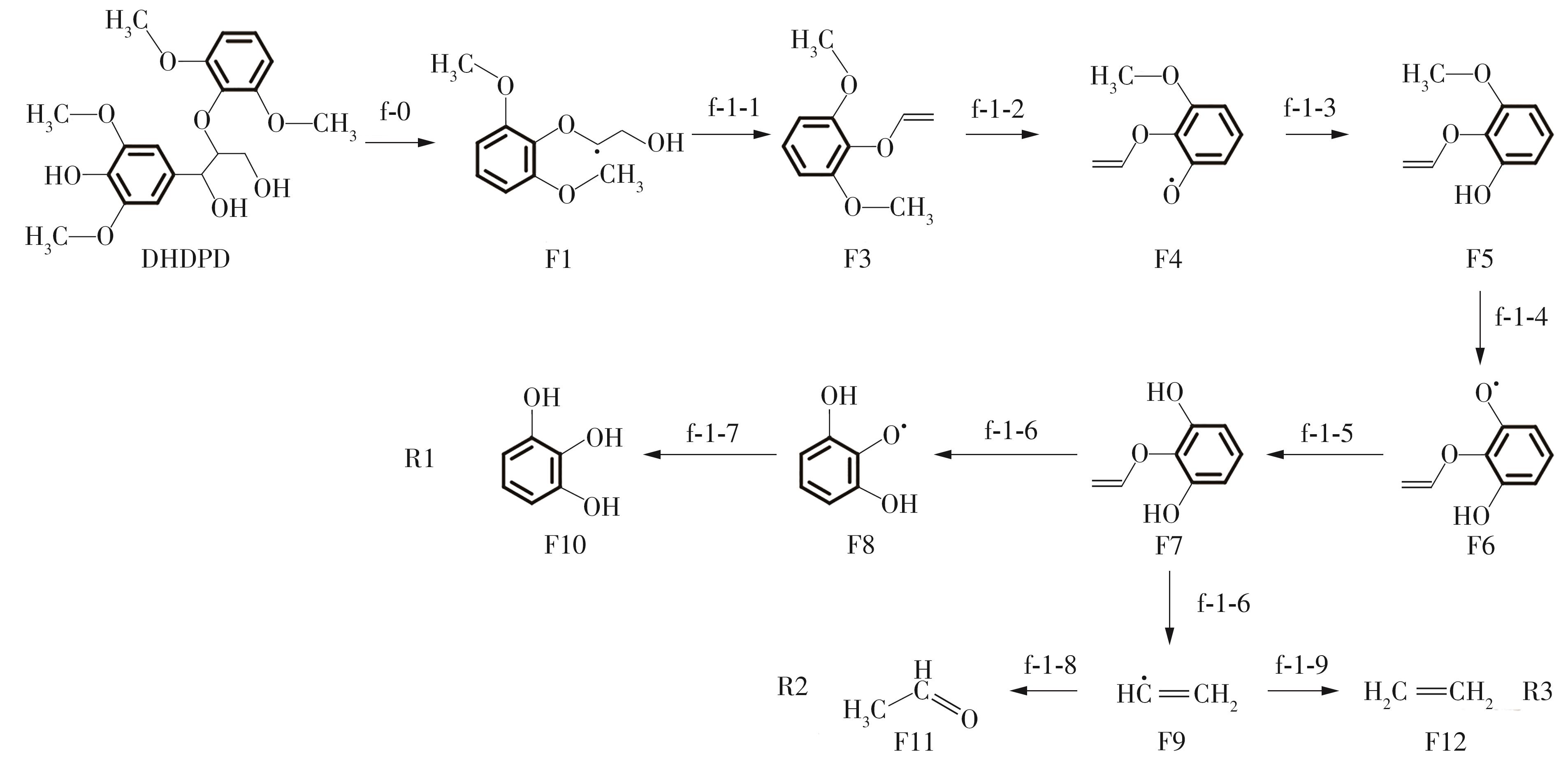
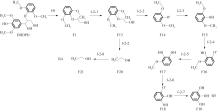
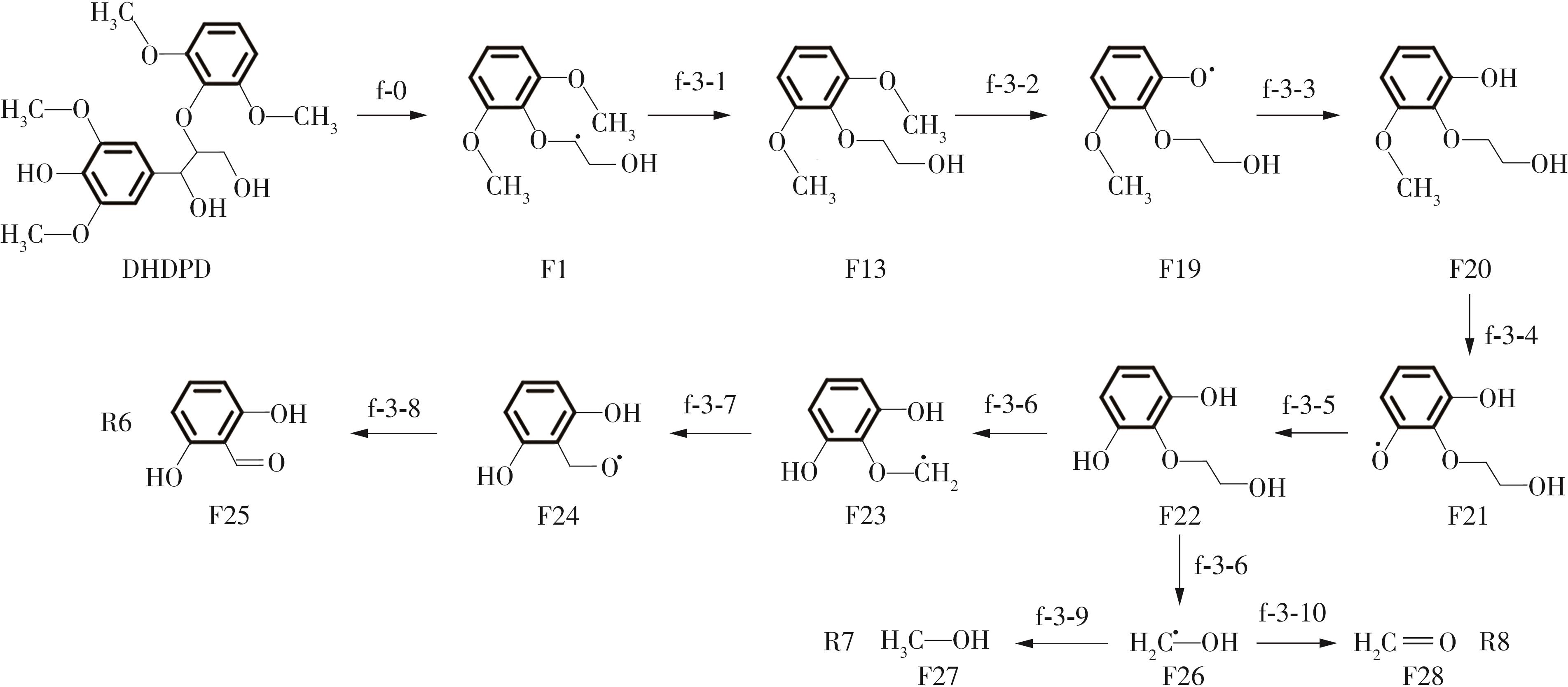
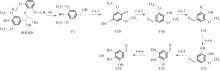
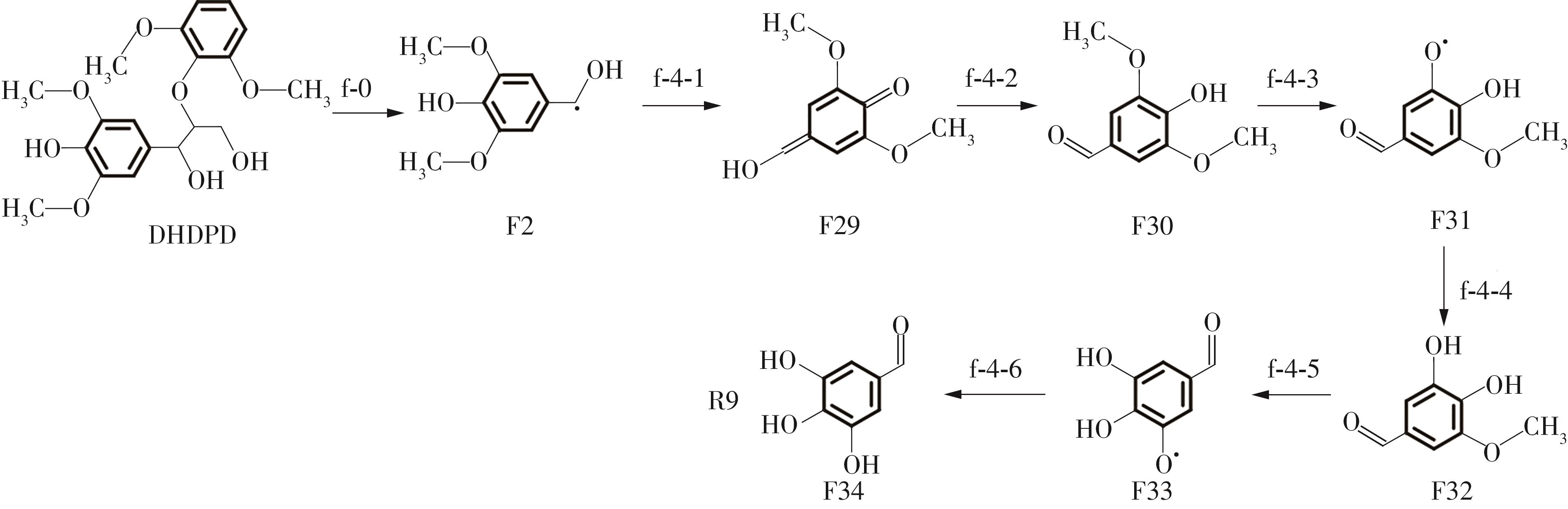
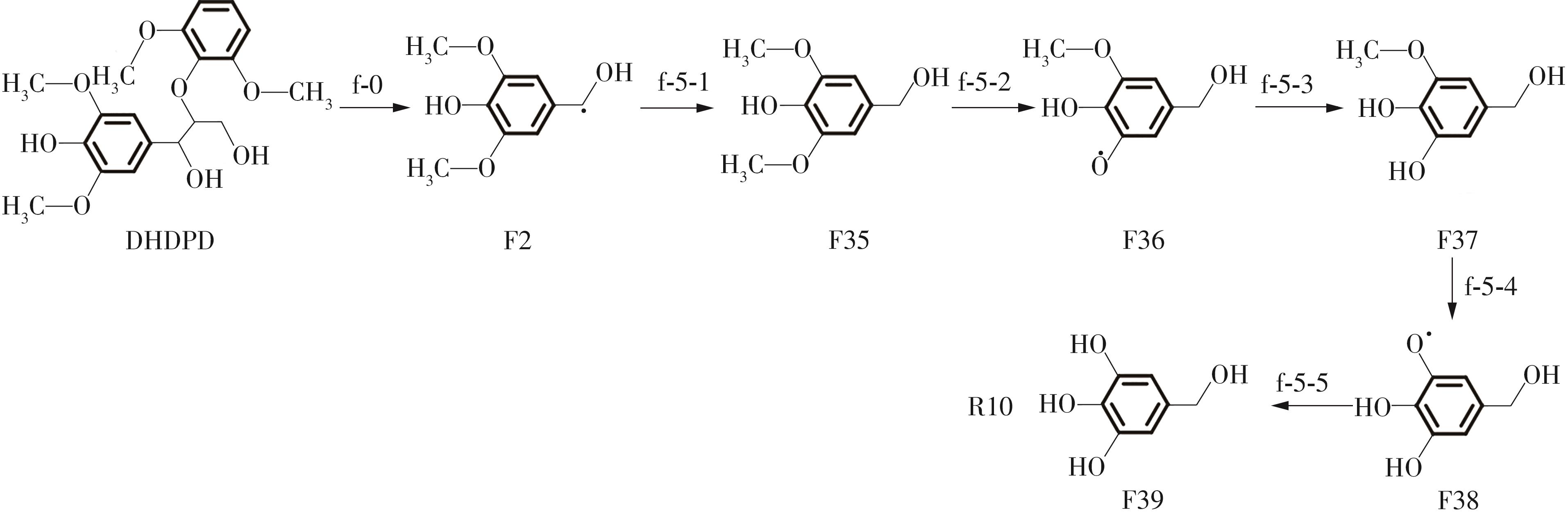
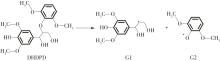
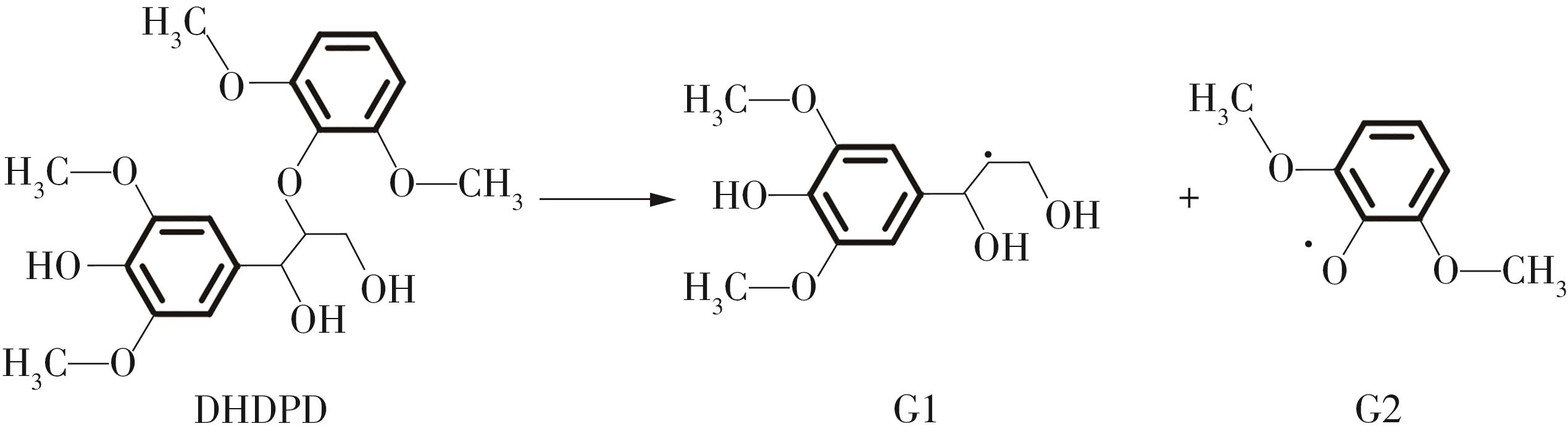
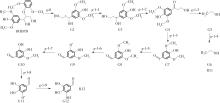
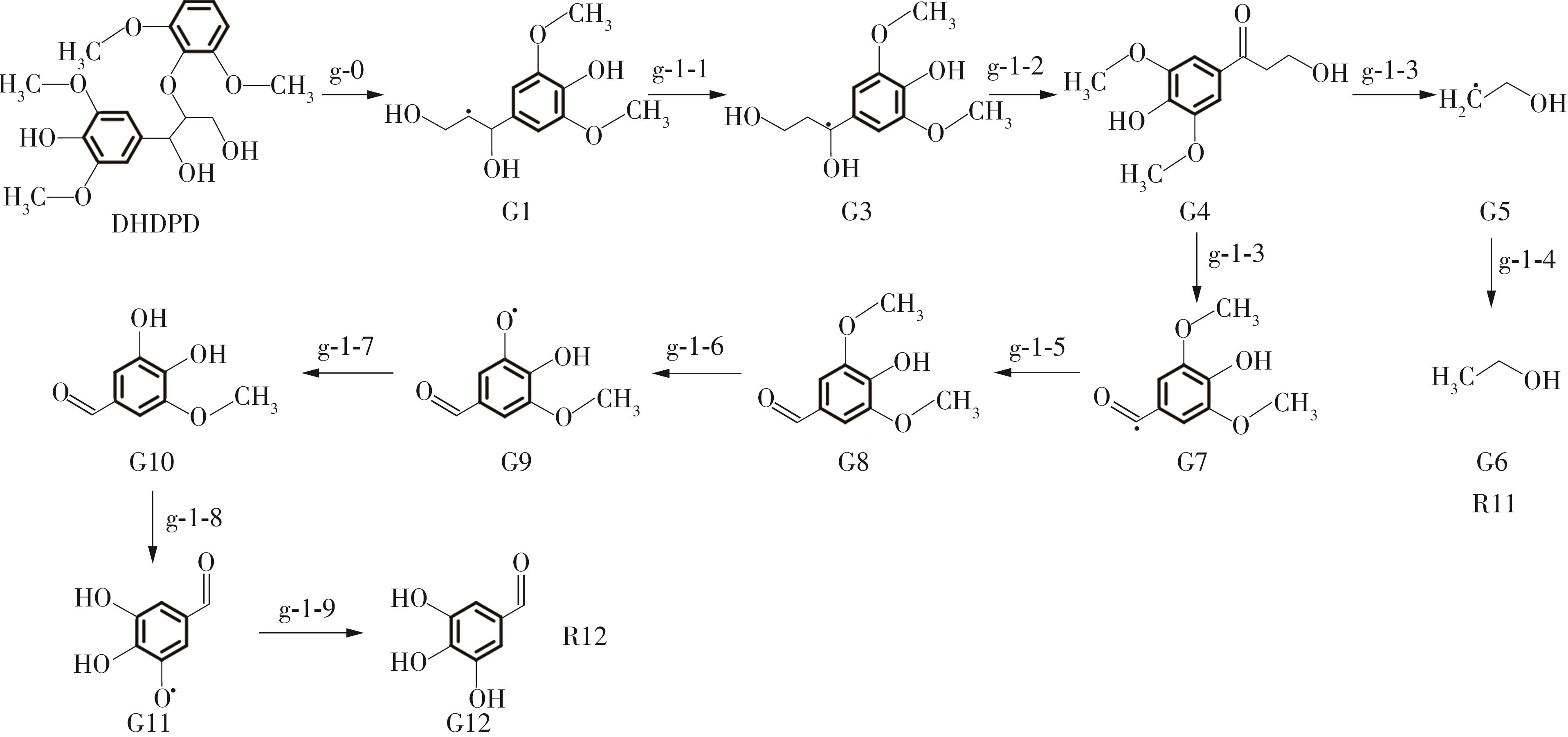
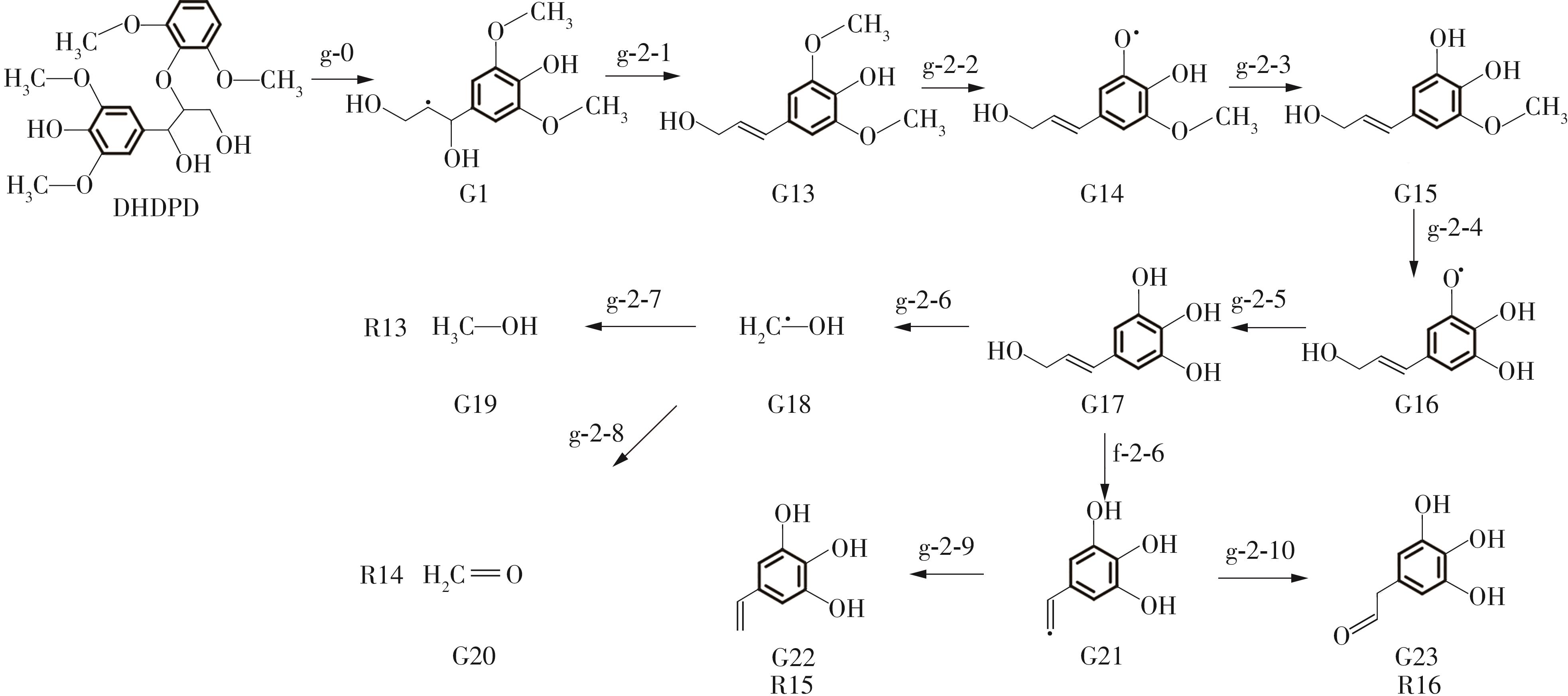
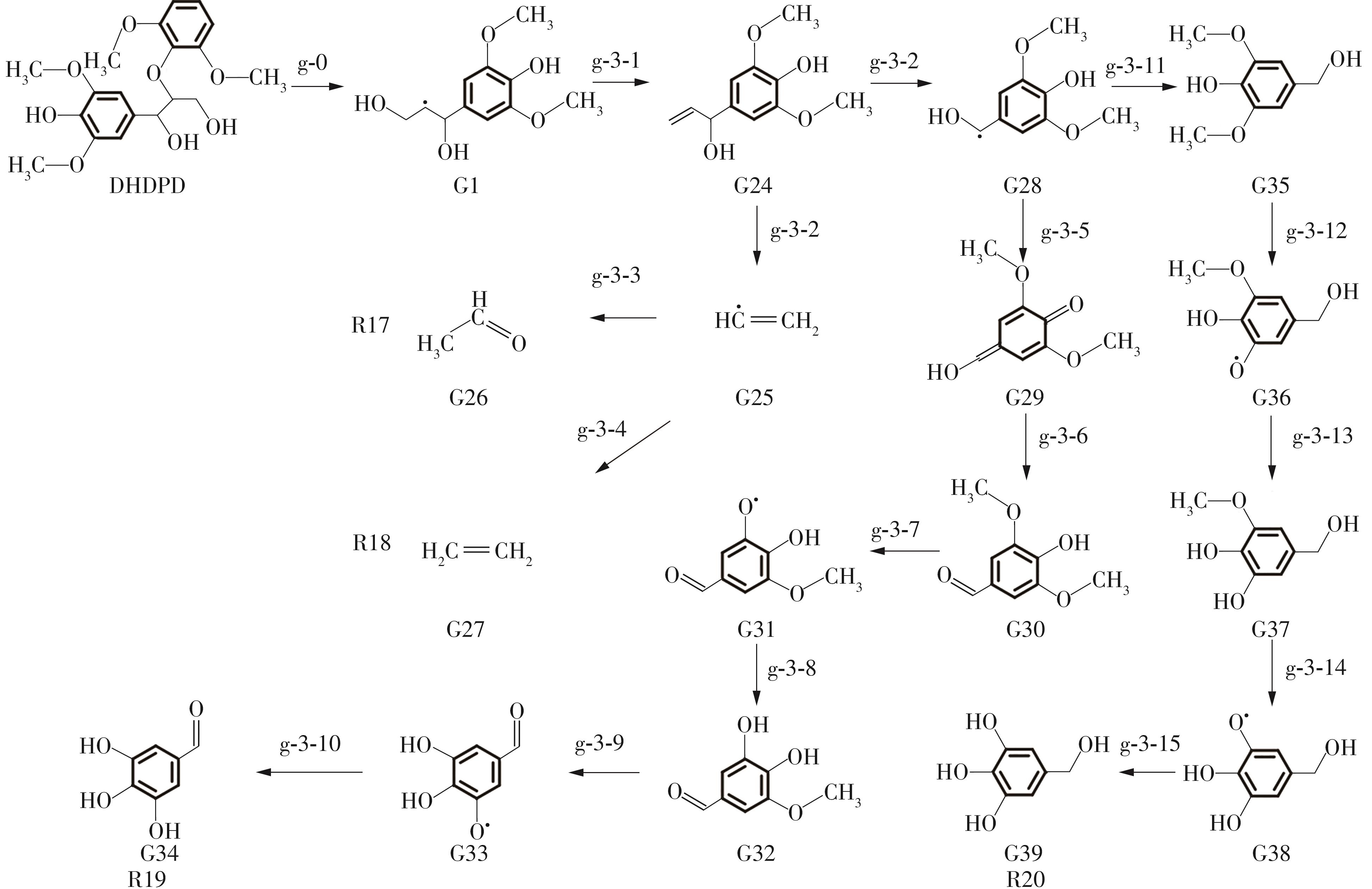
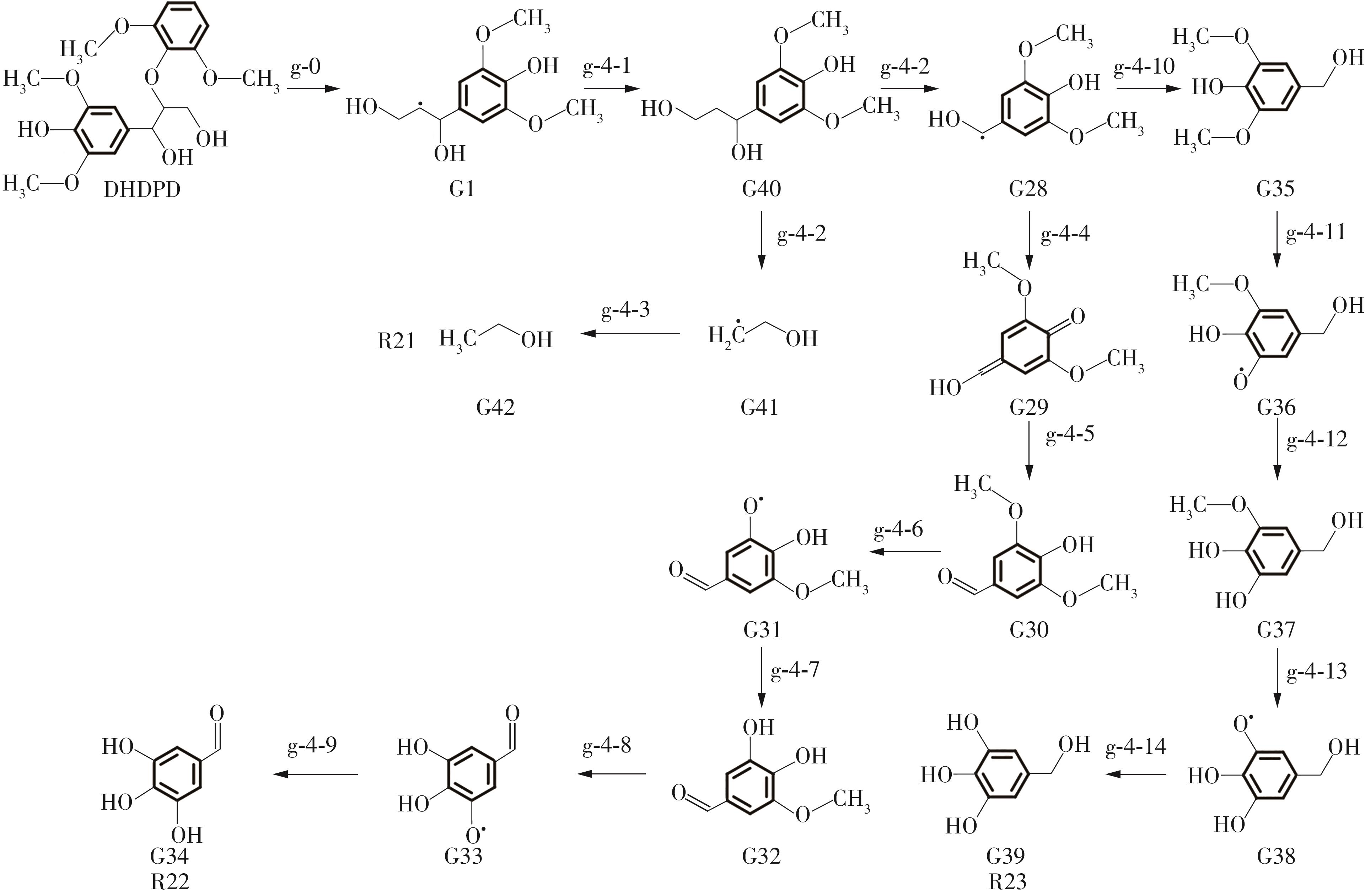
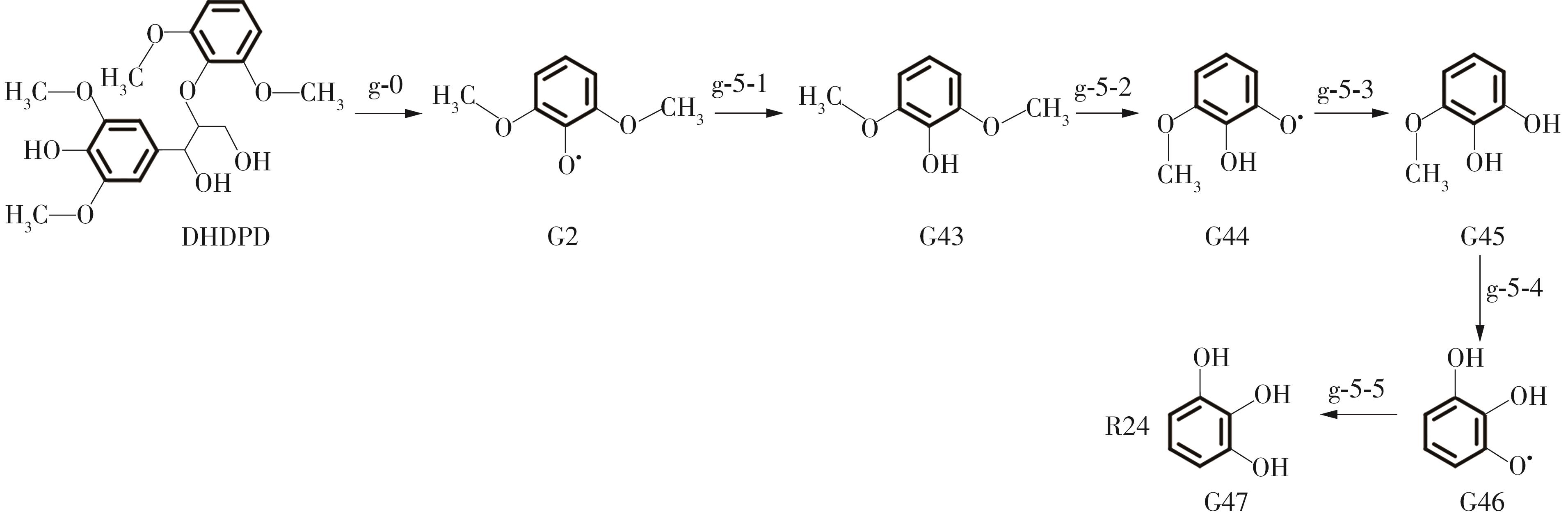
紫丁香基木质素是一种重要的木质素,天然木质素也大多通过β-O-4键连接成网状结构,β-O-4型紫丁香基木质素二聚体模化物在前人研究的模化物基础上增加了多个甲氧基基团,更接近实际的紫丁香基木质素结构。在软件Materials Studio 2019的Dmol3模块中,基于密度泛函理论利用B3LYP杂化泛函,对β-O-4型紫丁香基木质素二聚体模化物在875 K、101 kPa条件下的热解反应路径进行模拟,计算每步反应的反应物与生成物的焓值,并通过Vibration Analysis模块进行频率分析确认只有实频,没有虚频;计算每步反应的焓变并对反应路径总焓变进行比较,总焓变越小表明该路径在热力学上越容易发生,进而得到其较具优势的反应路径,最终得到对应路径的热解产物。结果表明,β-O-4型紫丁香基木质素二聚体模化物在875 K、101 kPa下的初步热解较有可能发生C α —C β 键的断裂与β-O-4键的断裂,其中最可能发生β-O-4键的断裂;较具优势的反应路径包括总焓变为-59.65 kJ/mol的R4、总焓变为-219.44 kJ/mol的R10、总焓变为-14.93 kJ/mol的R12、总焓变为-389.29 kJ/mol的R21、总焓变为-466.24 kJ/mol的R23与总焓变为-276.72 kJ/mol的R24,其中最具优势的路径为R21、R23与R24;热解的主要产物是邻苯三酚、3,4,5-三羟基苯甲醇、3,4,5-三羟基苯甲醛及乙醇,其中邻苯三酚、3,4,5-三羟基苯甲醇与乙醇为R21、R23与R24的热解产物。本研究得到的模拟结果可以为生成生物质焦的进一步模拟计算奠定基础。
中图分类号: