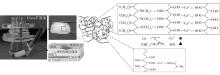
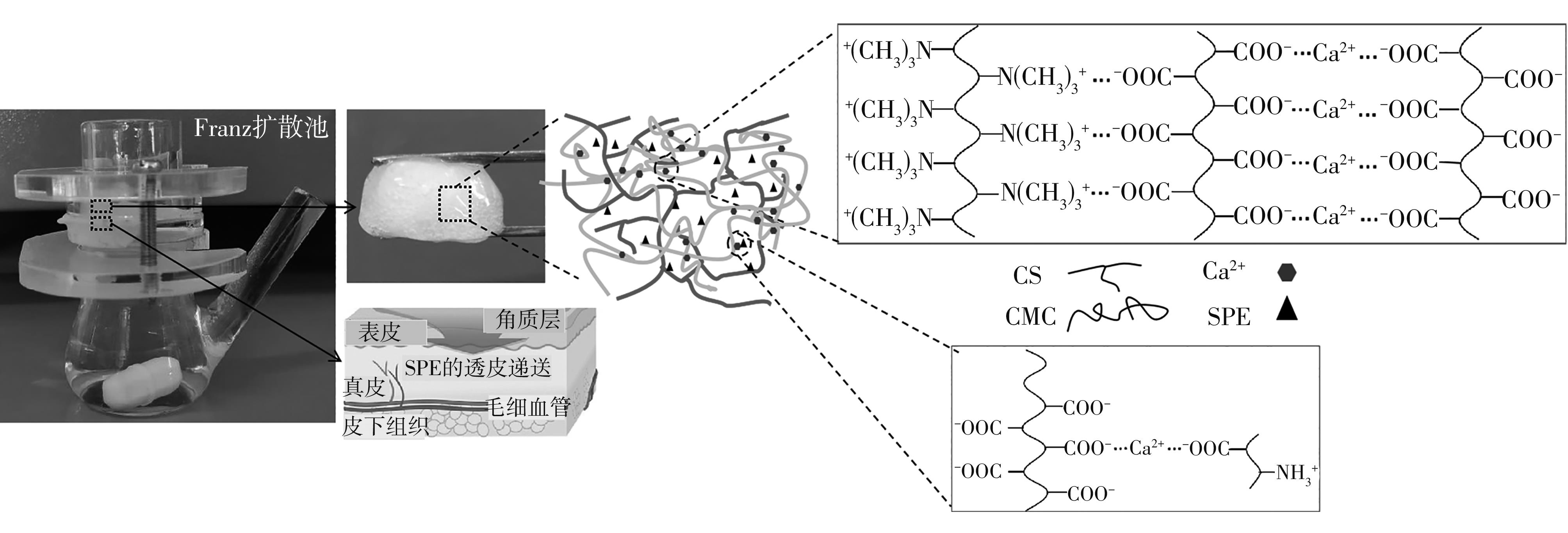
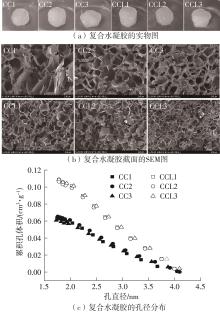
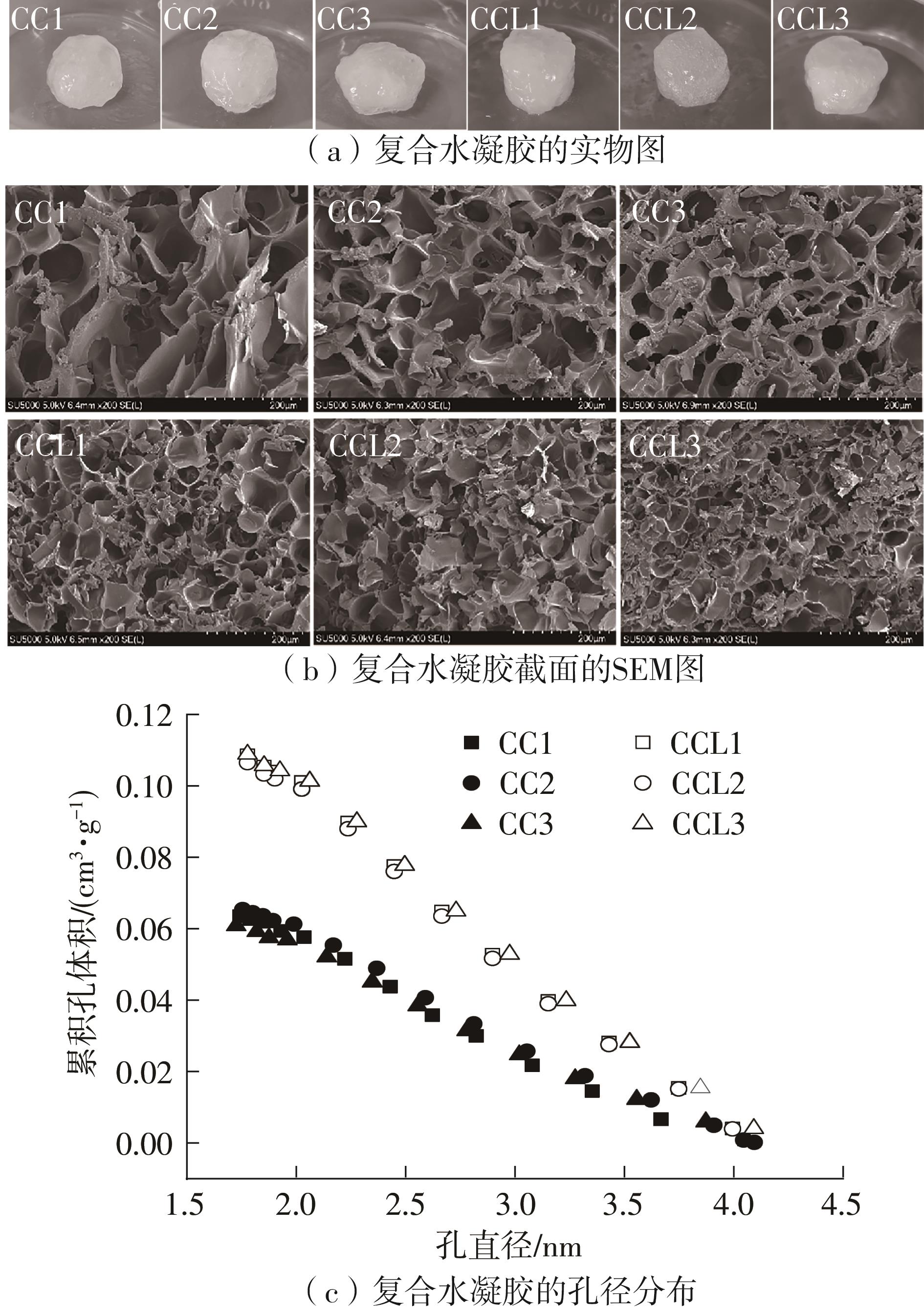
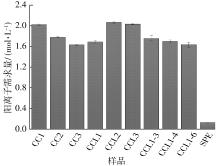
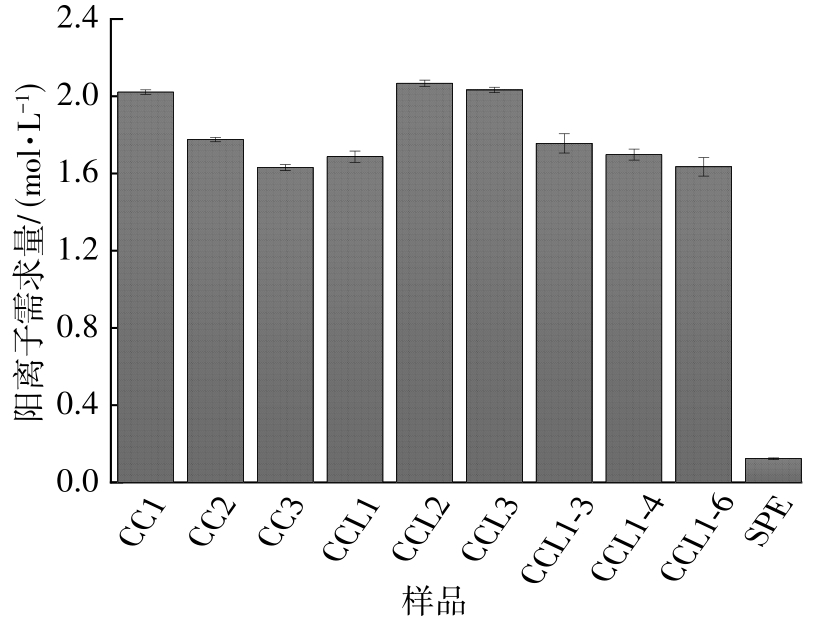
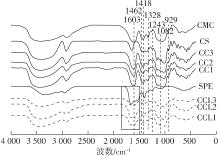
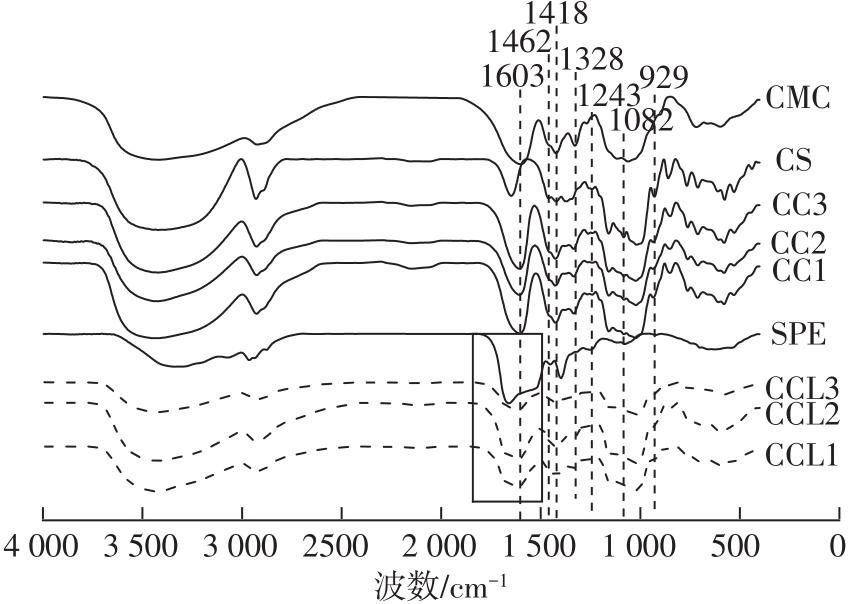
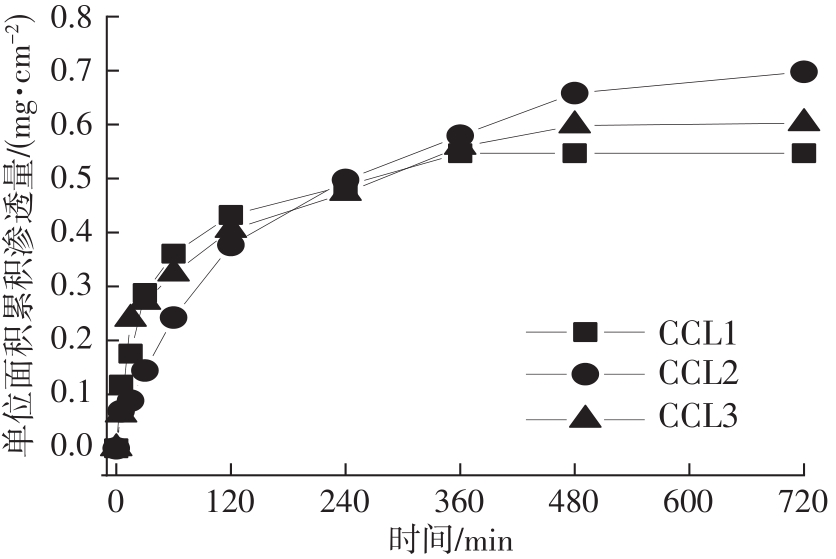
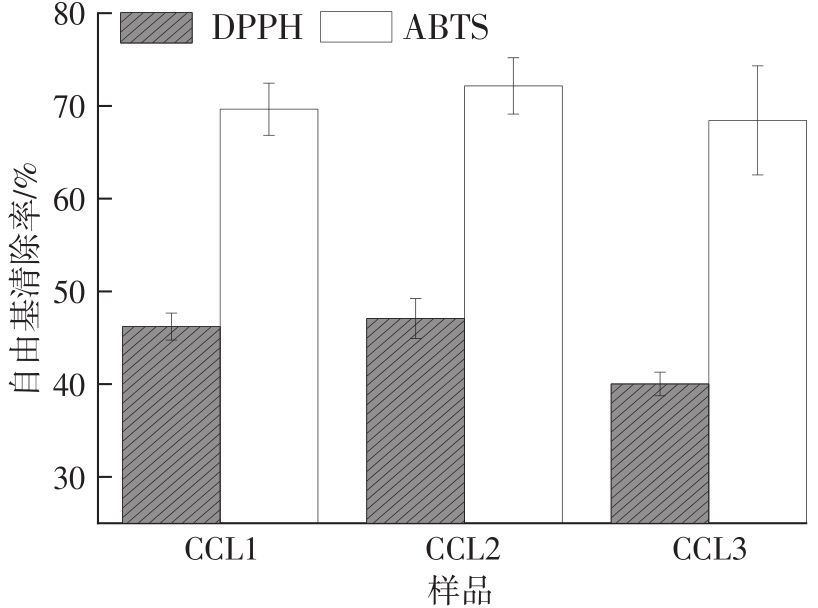
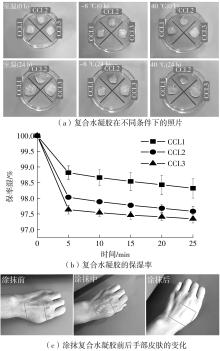
| 1 |
LIN Y, JIANG M, CHEN W,et al .Cancer and ER stress:mutual crosstalk between autophagy,oxidative stress and inflammatory response[J].Biomed Pharmacother,2019,118:109249/1-10.
|
| 2 |
ZHENG Y-Z, DENG G, ZHANG Y-C .Multiple free radical scavenging reactions of flavonoids[J].Dyes and Pigments,2022,198:109877/1-8.
|
| 3 |
NDREPEPA G .Myeloperoxidase - a bridge linking inflammation and oxidative stress with cardiovascular disease[J].Clin Chim Acta,2019,493:36-51.
|
| 4 |
HEMMATI-DINARVAND M, SAEDI S, VALILO M,et al .Oxidative stress and Parkinson’s disease: conflict of oxidant-antioxidant systems[J].Neurosci Lett,2019,709:134296.
|
| 5 |
KHAMBU B, YAN S, HUDA N,et al .Autophagy in non-alcoholic fatty liver disease and alcoholic liver disease[J].Liver Res,2018,2(3):112-119.
|
| 6 |
WANG X Q, WANG W, PENG M,et al .Free radicals for cancer theranostics[J].Biomaterials,2021,266:120474.
|
| 7 |
LIM H W, KOHLI I, RUVOLO E,et al .Impact of visible light on skin health: the role of antioxidants and free radical quenchers in skin protection[J].J Am Acad Dermatol,2022,86(3S):S27-S37.
|
| 8 |
ZHANG Q, TONG X, SUI X,et al .Antioxidant activity and protective effects of alcalase-hydrolyzed soybean hydrolysate in human intestinal epithelial Caco-2 cells[J].Food Res Int,2018,111:256-264.
|
| 9 |
DHARADHAR S, MAJUMDAR A, DHOBLE S,et al .Microneedles for transdermal drug delivery:a systematic review[J].Drug Dev Ind Pharm,2019,45(2):188-201.
|
| 10 |
LIU T, CHEN M, FU J,et al .Recent advances in microneedles-mediated transdermal delivery of protein and peptide drugs[J].Acta Pharm Sin B,2021,11(8):2326-2343.
|
| 11 |
GHOSH B, BHATTACHARYA D, KOTAL A,et al .Cytocompatible,thermostable hydrogel with utility to release drug over skin[J].Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology,2019,94(3):616-627.
|
| 12 |
STASAID M, BOUTEMAK K, IBTISSEM L,et al .Synthesis of carboxymethyl xanthan/double-walled carbon nanotube hybrid hydrogel nanocomposite for transdermal release of drug[J].Soft Materials,2021,20(2):168-182.
|
| 13 |
LADENHEIM D, MARTIN G P, MARRIOTT C,et al .An in-vitro study of the effect of hydrocolloid patch occlusion on the penetration of triamcinolone acetonide through skin in man[J].J Pharm Pharmacol,1996,48(8):806-811.
|
| 14 |
PARK S H, SHIN H S, PARK S N .A novel pH-responsive hydrogel based on carboxymethyl cellulose/2-hydroxyethyl acrylate for transdermal delivery of naringenin[J].Carbohyd Polym,2018,200:341-352.
|
| 15 |
CARVALHO S M, MANSUR A A P, CAPANEMA N S V,et al .Synthesis and in vitro assessment of anticancer hydrogels composed by carboxymethylcellulose-doxorubicin as potential transdermal delivery systems for treatment of skin cancer[J].Journal of Molecular Liquids,2018,266:425-440.
|
| 16 |
XU S, CAO L, WU R,et al .Salt and pH responsive property of a starch-based amphoteric superabsorbent hydrogel with quaternary ammonium and carboxyl groups (Ⅱ)[J].Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2006,101(3):1995-1999.
|
| 17 |
BERCEA M, BILIUTA G, AVADANEI M,et al .Self-healing hydrogels of oxidized pullulan and poly(vinyl alcohol)[J].Carbohyd Polym,2019,206:210-219.
|
| 18 |
SHU G, SHI X, CHEN L,et al .Antioxidant peptides from goat milk fermented by Lactobacillus casei L61:preparation,optimization,and stability evaluation in simulated gastrointestinal fluid[J].Nutrients,2018,10(6):797/1-13.
|
| 19 |
XU C, GUAN S, XU J,et al .Preparation,characterization and antioxidant activity of protocatechuic acid grafted carboxymethyl chitosan and its hydrogel[J].Carbohydr Polym,2021,252:117210.
|
| 20 |
PICHAYAKORN W, SUKSAEREE J, TAWEEPREDA W,et al .Polymer blended deproteinized natural rubber reservoirs for nicotine transdermal patches:in vitro drug release, permeation study,and stability test[J].Journal of Polymers and the Environment,2022,30(3):988-1000.
|
| 21 |
面膜: [S].
|
| 22 |
PENG Y, YAN B, LI Y,et al .Antifreeze and moisturizing high conductivity PEDOT/PVA hydrogels for wearable motion sensor[J].Journal of Materials Science,2020,55(3):1280-1291.
|
| 23 |
ELKENAWY N M, KARAM H M, ABOUL-MAGD D S .Development of gamma irradiated SSD-embedded hydrogel dyed with prodigiosin as a smart wound dressing:evaluation in a MDR infected burn rat model[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,211:170-182.
|
| 24 |
SALLAM M A, BOSCA M T M .Mechanistic analysis of human skin distribution and follicular targeting of adapalene-loaded biodegradable nanospheres with an insight into hydrogel matrix influence, in vitro skin irritation, and in vivo tolerability[J].Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences,2017,106(10):3140-3149.
|
| 25 |
叶君,叶芳,熊犍 .含Eu3+的PVA/CMC荧光水凝胶的结构与性能[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(9):37-45.
|
|
YE Jun, YE Fang, XIONG Jian .Structure and properties of Eu3+-containing PVA/CMC fluorescent hydrogels[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(9):37-45.
|
| 26 |
EABORN C .Compendium of chemical terminology:IUPAC recommendations[J].Journal of Organometallic Chemistry,1988,356(2):C76-C77.
|
| 27 |
SAPPIDI P, NATARAJAN U .Effect of salt valency and concentration on structure and thermodynamic behavior of anionic polyelectrolyte Na(+)-polyethacrylate aqueous solution[J].J Mol Model,2016,22(11):274.
|
| 28 |
BAO X L, LV Y, YANG B C,et al .A study of the soluble complexes formed during calcium binding by soybean protein hydrolysates[J].J Food Sci,2008,73(3):C117-C121.
|
| 29 |
SIMANAVICIUTE D, KLIMAVICIUTE R, RUTKAITE R .Equilibrium adsorption of caffeic,chlorogenic and rosmarinic acids on cationic cross-linked starch with quaternary ammonium groups[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,95:788-795.
|
| 30 |
POUR Z S, MAKVANDI P, GHAEMY M .Performance properties and antibacterial activity of crosslinked films of quaternary ammonium modified starch and poly(vinyl alcohol)[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2015,80:596-604.
|
| 31 |
XIONG J, LI Q Y, SHI Z X,et al .Interactions between wheat starch and cellulose derivatives in short-term retrogradation:rheology and FTIR study[J].Food Research International,2017,100:858-863.
|
| 32 |
JHA P, DHARMALINGAM K, NISHIZU T,et al .Effect of amylose-amylopectin ratios on physical,mechanical,and thermal properties of starch-based bionanocomposite films incorporated with CMC and nanoclay[J].Starch - Stärke,2020,72(1/2):1900121.
|
| 33 |
SHARRATT W N, LOPEZ C G, SARKIS M,et al .Ionotropic gelation fronts in sodium carboxymethyl cellulose for hydrogel particle formation[J].Gels,2021,7(2):44.
|
| 34 |
KIM A R, LEE S L, PARK S N .Properties and in vitro drug release of pH- and temperature-sensitive double cross-linked interpenetrating polymer network hydrogels based on hyaluronic acid/poly (N-isopropylacrylamide) for transdermal delivery of luteolin[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,118(Pt A):731-740.
|
| 35 |
WANG W, CHEN W, YANG H,et al .Textural and rheological properties of potato starch as affected by amino acids[J].International Journal of Food Properties,2017,20(Sup3):S3123-S3134.
|
| 36 |
KOUR P, AFZAL S, GANI A,et al .Effect of nanoemulsion-loaded hybrid biopolymeric hydrogel beads on the release kinetics,antioxidant potential and antibacterial activity of encapsulated curcumin[J].Food Chemistry,2022,376:131925.
|
| 37 |
ZHANG S, HOU J, YUAN Q,et al .Arginine derivatives assist dopamine-hyaluronic acid hybrid hydrogels to have enhanced antioxidant activity for wound healing[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2020, 392: 123775/1-10.
|
| 38 |
KIM B, KANG B, VALES T P,et al .Polyphenol-functionalized hydrogels using an interpenetrating chitosan network and investigation of their antioxidant activity[J].Macromolecular Research,2018,26(1):35-39.
|
| 39 |
ADEPU S, KHANDELWAL M .Ex-situ modification of bacterial cellulose for immediate and sustained drug release with insights into release mechanism[J].Carbohyd Polym,2020,249:116816/1-11.
|
| 40 |
GANJI F, VASHEGHANI-FARAHANI S, VASHEGHANI- FARAHANI E .Theoretical description of hydrogel swelling:a review[J].Iranian Polymer Journal,2010,19(5):375-398.
|
| 41 |
BRAZEL C S, PEPPAS N A .Dimensionless analysis of swelling of hydrophilic glassy polymers with subsequent drug release from relaxing structures[J].Biomaterials,1999,20(8):721-732.
|
| 42 |
RAMADON D, MCCRUDDEN M T C, COURTENAY A J,et al .Enhancement strategies for transdermal drug delivery systems:current trends and applications[J].Drug Deliv Transl Res,2022,12(4):758-791.
|