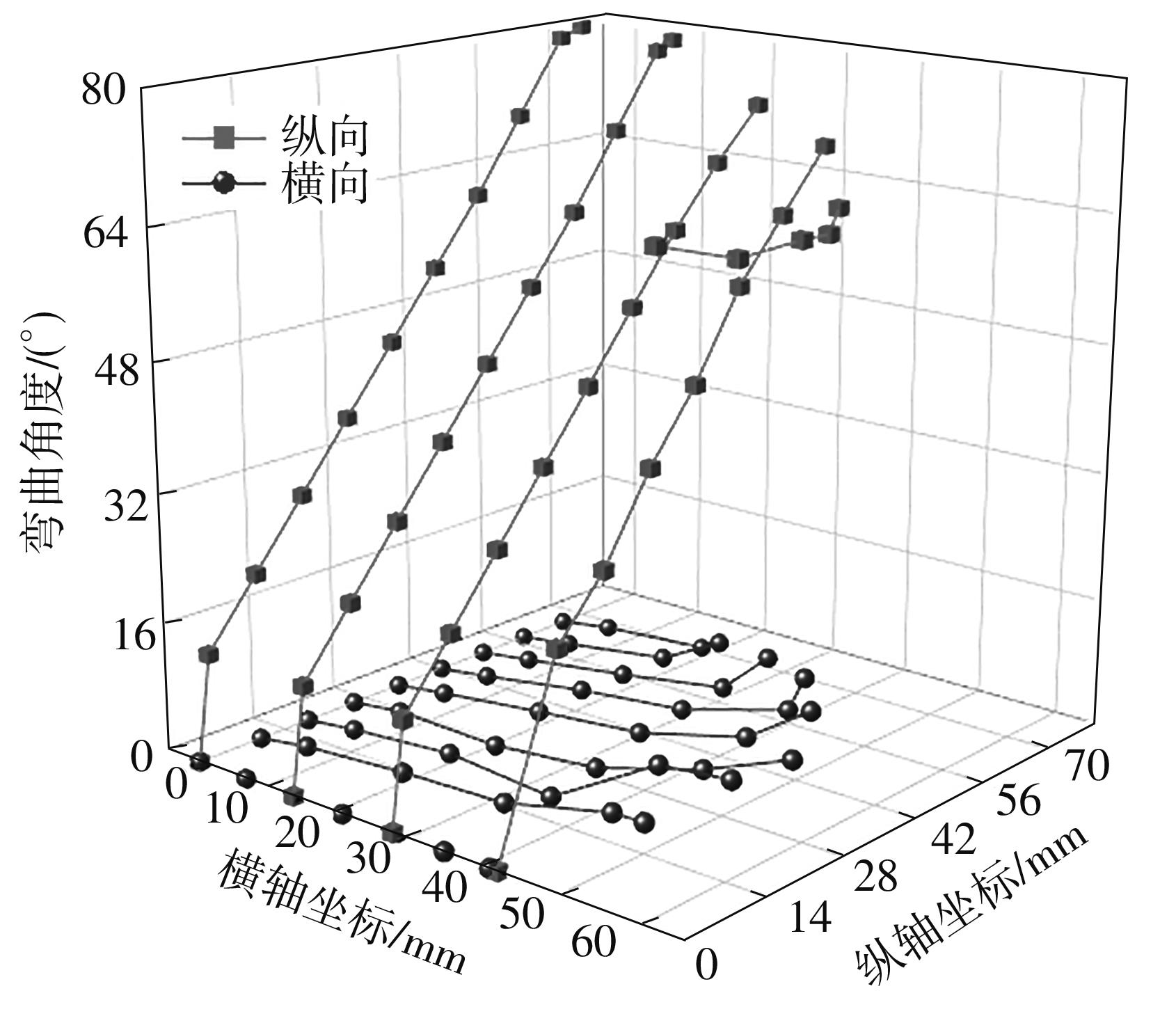
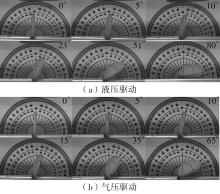
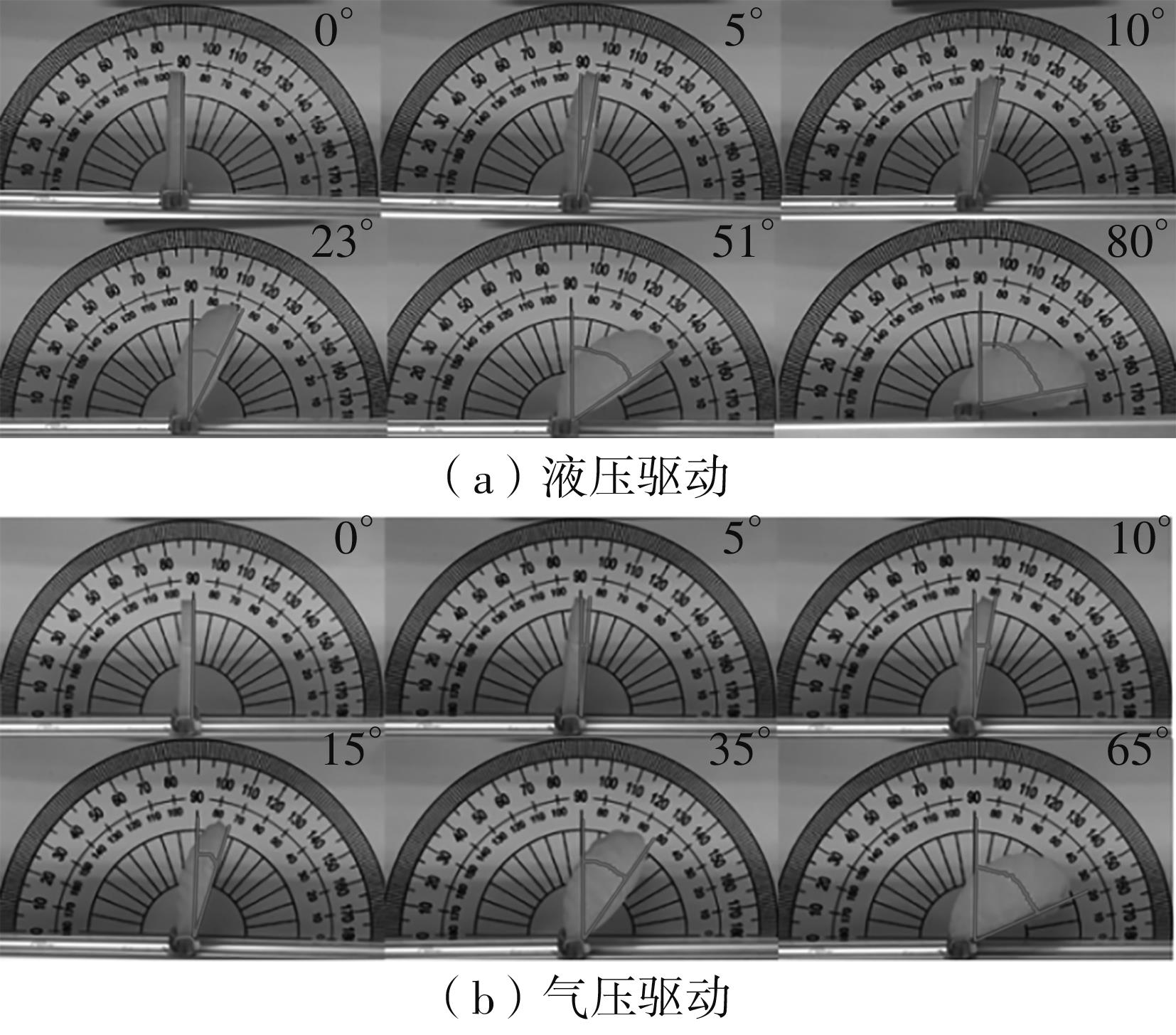
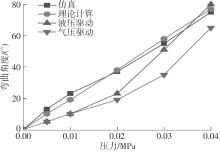
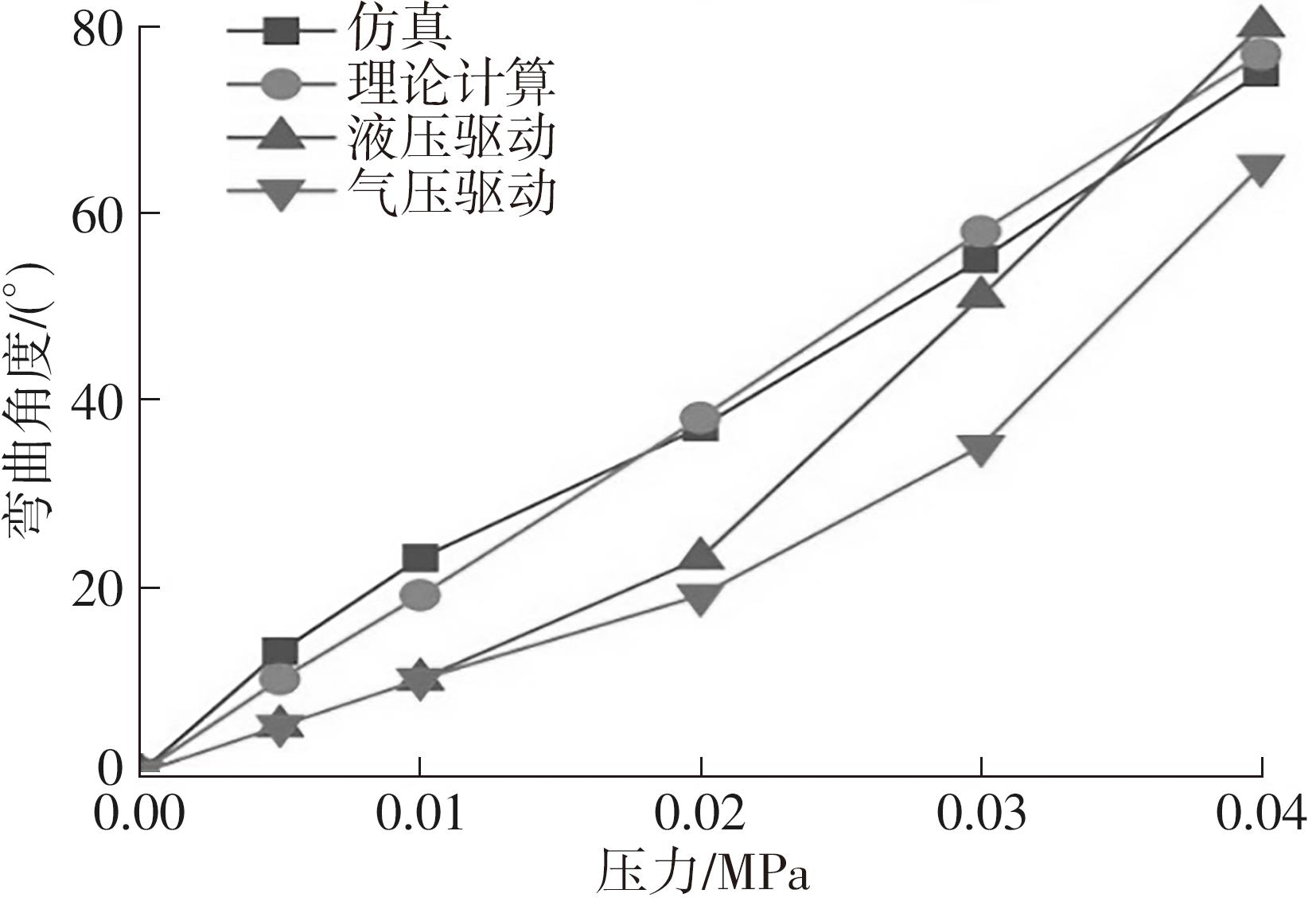
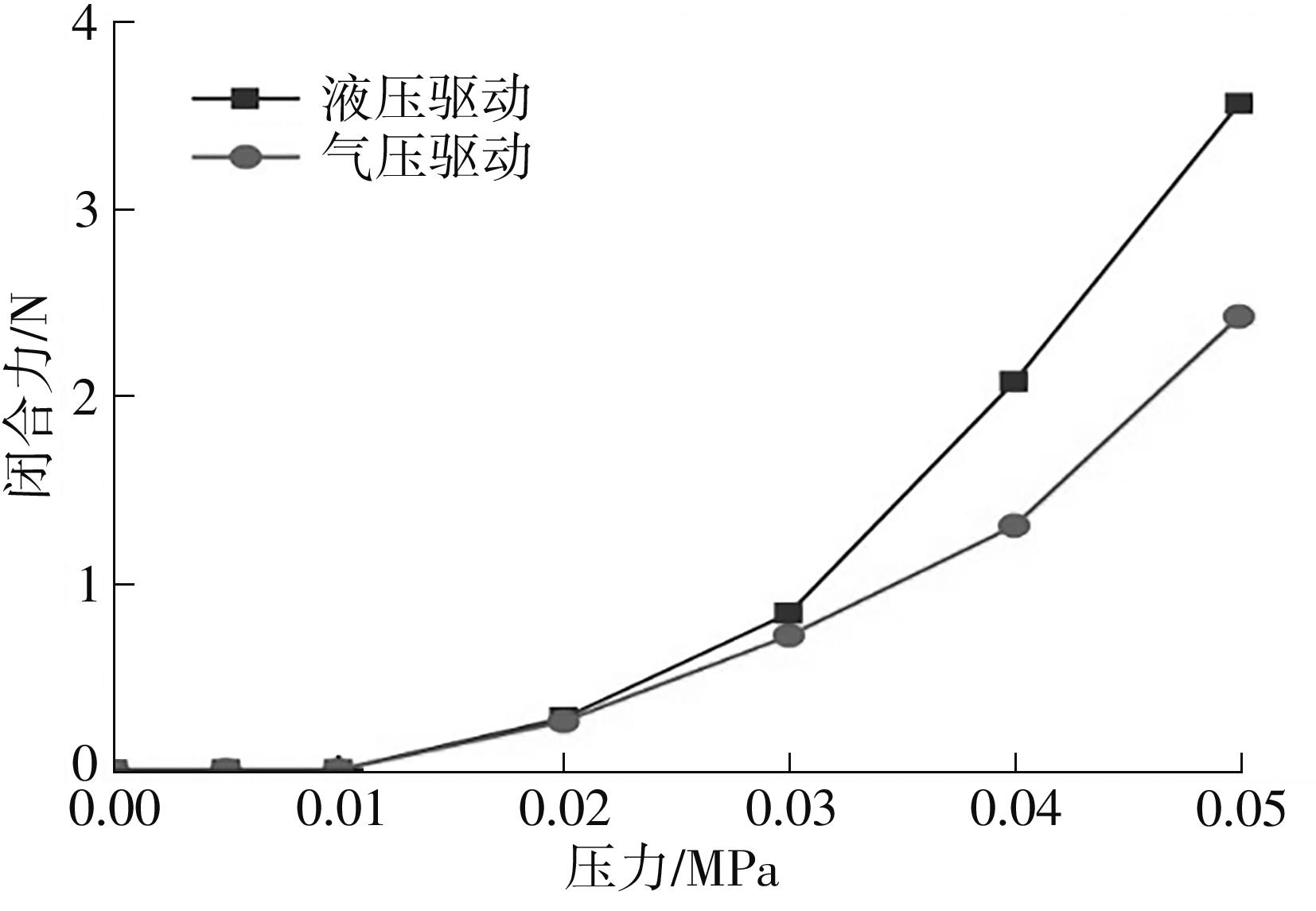
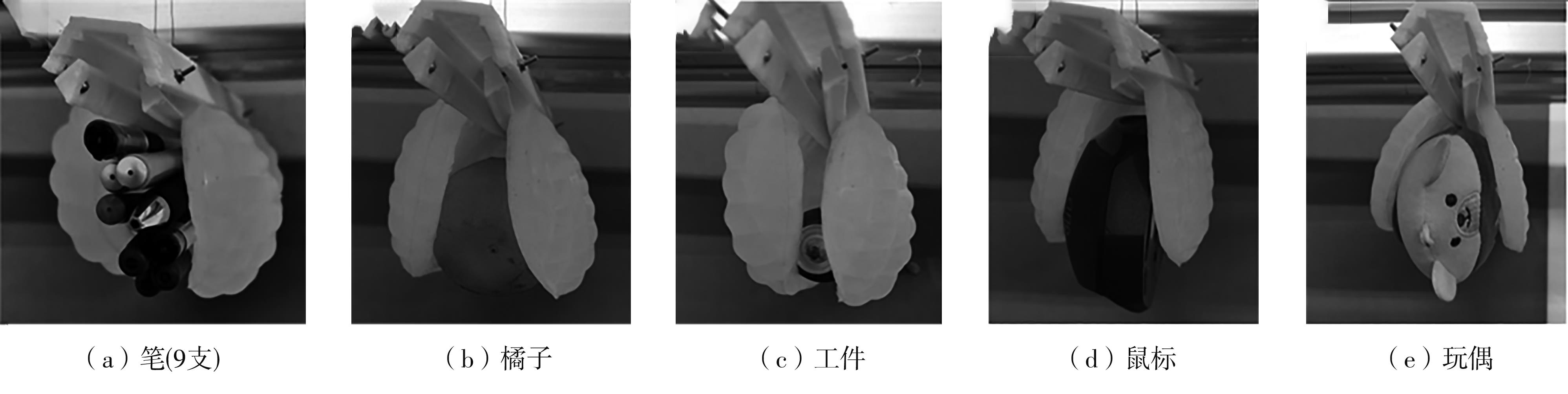
| 1 |
王海涛,彭熙凤,林本末 .软体机器人研究进展[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2020,48(2):94-106.
|
|
WANG Hai-tao, PENG Xi-feng, LIN Ben-mo .Research progress of soft robotics[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,48(2):94-106.
|
| 2 |
张进华,王韬,洪军,等 .软体机械手研究综述[J].机械工程学报,2017,53(13):19-28.
|
|
ZHANG Jin-hua, WANG Tao, HONG Jun,et al .A review of research on software manipulators[J].Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2017,53(13):19-28.
|
| 3 |
曹玉君,尚建忠,梁科山,等 .软体机器人研究现状综述[J].机械工程学报,2012,48(3):25-33.
|
|
CAO Yu-jun, SHANG Jian-zhong, LIANG Ke-shan,et al .A review of the research status of software robots[J].Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2012,48(3):25-33.
|
| 4 |
范需,戴宁,王宏涛,等 .气压驱动网格软体驱动器弯曲变形预测方法[J].中国机械工程,2020,31(9):1108-1114.
|
|
FAN Xu, DAI Ning, WANG Hong-tao,et al .Bending deformation prediction method of air pressure driven mesh software driver[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2020,31(9):1108-1114.
|
| 5 |
陈英龙,闫迪,张增猛,等 .基于水压直驱的软体单元的动静态特性[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2019,53(8):1602-1609,1617.
|
|
CHEN Ying-long, YAN Di, ZHANG Zeng-meng,et al .Dynamic and static characteristics of soft element based on hydraulic direct drive[J].Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Edition),2019,53(8):1602-1609,1617.
|
| 6 |
GALLOWAY K C, BECKER K P, PHILLIPS B,et al .Soft robotic grippers for biological sampling on deep reefs[J].Soft Robotics,2016,3(1):23-33.
|
| 7 |
POLYGERINOS P, WANG Z, GALLOWAY K C,et al .Soft robotic glove for combined assistance and at-home rehabilitation[J].Robotics and Autonomous Systems,2015,73:135-143.
|
| 8 |
刘会聪,杨梦柯,袁鑫,等 .液态金属柔性感知的人机交互软体机械手[J].中国机械工程,2021,32(12):1470-1478.
|
|
LIU Hui-cong, YANG Meng-ke, YUAN Xin,et al .Human-computer interaction software manipulator based on liquid metal flexible perception[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2021,32(12):1470-1478.
|
| 9 |
WANG H, XU H, ABU-DAKKA F,et al .A bidirectional soft biomimetic hand driven by water hydraulic for dexterous underwater grasping[J].IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters,2022,7(2):2186-2193.
|
| 10 |
张氢,覃昶,孙远韬 .气动人工肌肉驱动灵巧手的设计与研究[J].液压与气动,2018(5):93-97.
|
|
ZHANG Qing, QIN Chang, SUN Yuan-tao .Dexterous hand actuated by pneumatic artificial muscle[J].Chinese Hydraulics & Pneumatics,2018(5):93-97.
|
| 11 |
WANG H, XU H, YANG C,et al .Underwater soft robotic hand with multi-source coupling bio-inspired soft palm and six fingers driven by water hydraulic[J/OL].(2021-07-13)[2021-12-15]..
|
| 12 |
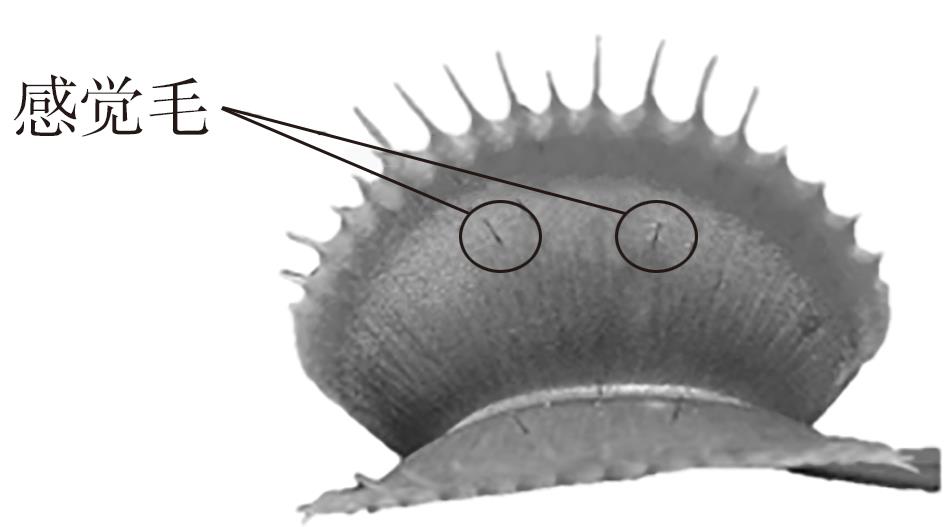
周奕轩,张晨夕,别之龙,等 .捕蝇草的捕虫机理及应用前景研究进展[J].植物生理学报,2020,56(10):2047-2060.
|
|
ZHOU Yi-xuan, ZHANG Chen-xi, BIE Zhi-long,et al .Research progress on insect trapping mechanism and application prospect of Venus flytrap[J].Chinese Journal of Plant Physiology,2020,56(10):2047-2060.
|
| 13 |
HEDRICH R, NEHER E .Venus flytrap:how an excitable,carnivorous plant works[J].Trends in Plant Science,2018,23(3):220-234.
|
| 14 |
MOSADEGH B, POLYGERINOS P, KEPLINGER C,et al .Pneumatic networks for soft robotics that actuate rapidly[J].Advanced Functional Materials,2014,24(15):2163-2170.
|
| 15 |
WAKIMOTO S, SUZUMORI K, OGURA K .Miniature pneumatic curling rubber actuator generating bidirectional motion with one air-supply tube[J].Advanced Robotics,2011,25(9/10):1311-1330.
|
| 16 |
ROBERT F S, ADAM A S, RUI M D N,et al .Soft machines that are resistant to puncture and that self seal[J].Advanced Materials,2013,25(46):6709-6713.
|
| 17 |
余家泉,陈雄,周长省,等 .EPDM薄膜橡胶包覆材料的粘-超弹本构模型研究[J].推进技术,2015,36(3):465-470.
|
|
YU Jia-quan, CHEN Xiong, ZHOU Chang-sheng,et al .Research on visco-hyperelastic constitutive model of EPDM film rubber coating material[J].Propulsion Technology,2015,36(3):465-470.
|
| 18 |
王国权,刘萌,姚艳春,等 .不同本构模型对橡胶制品有限元法适应性研究[J].力学与实践,2013,35(4):40-47.
|
|
WANG Guoquan, LIU Meng, YAO Yanchu,et al .Application of different constitutive models in the nonlinear finite element method for rubber parts[J].Mechanics in Engineering,2013,35(4):40-47.
|