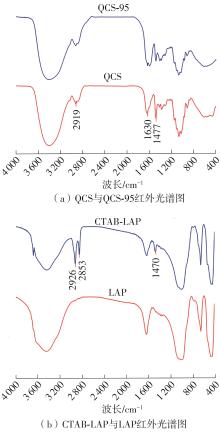
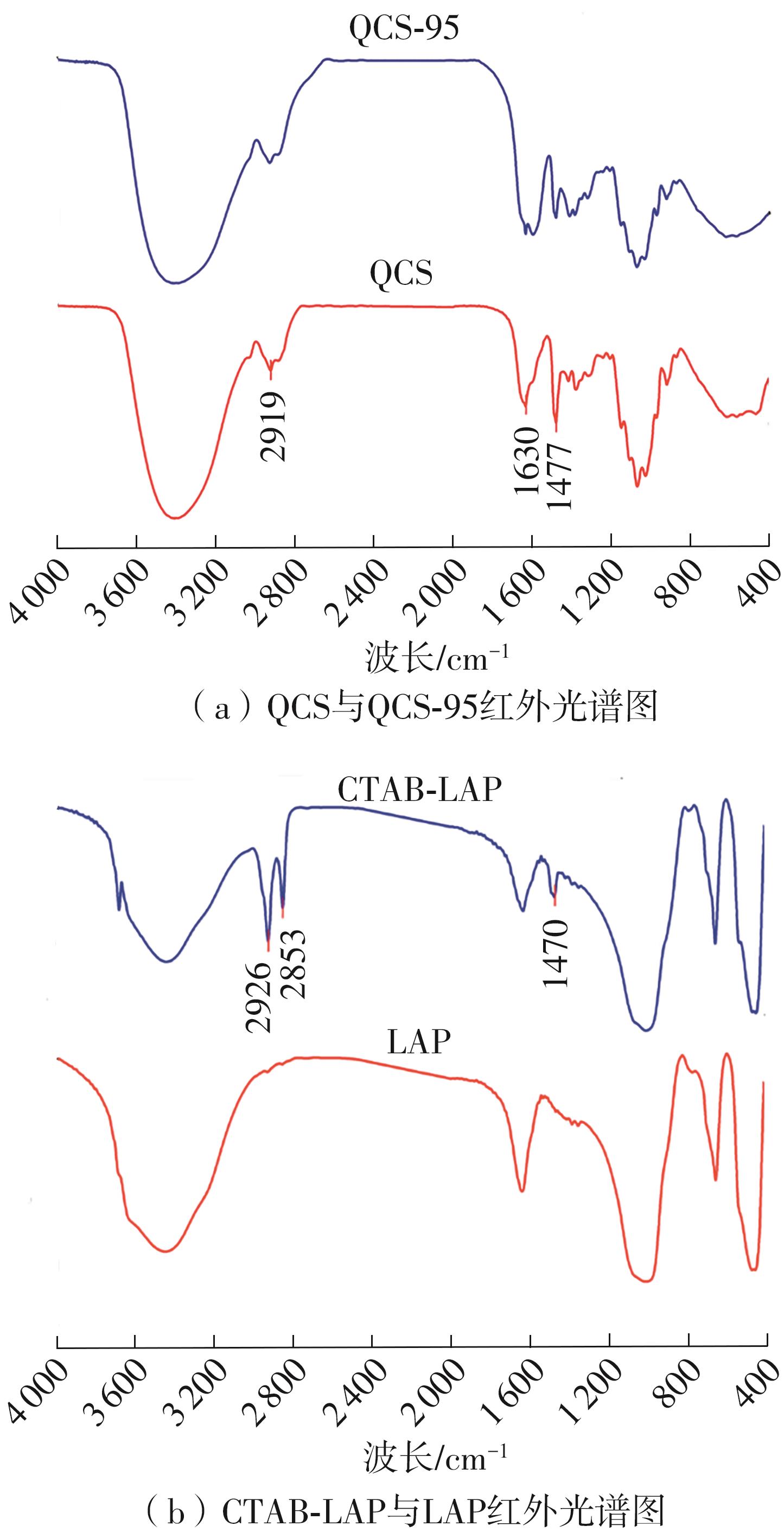
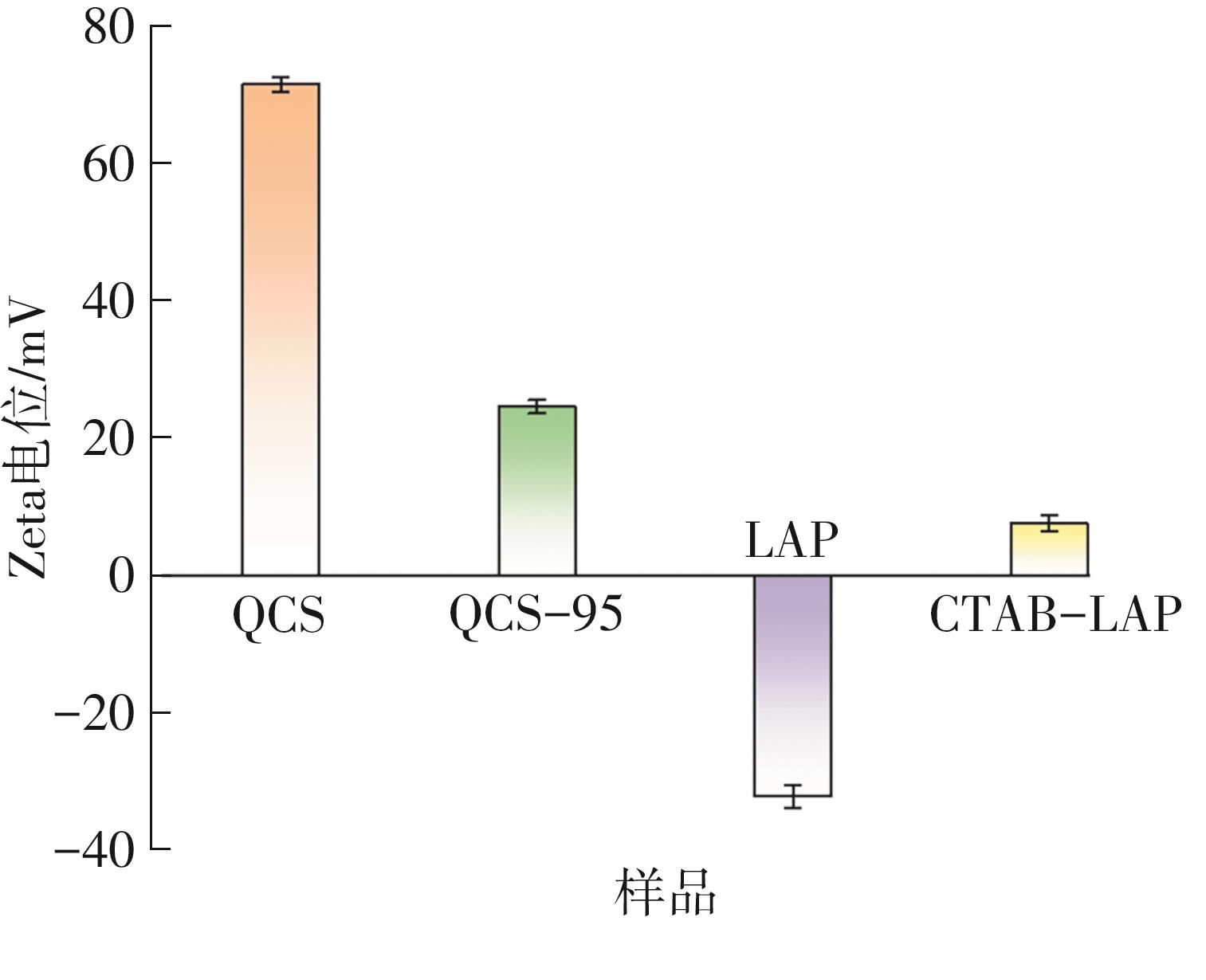
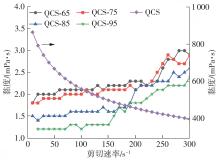
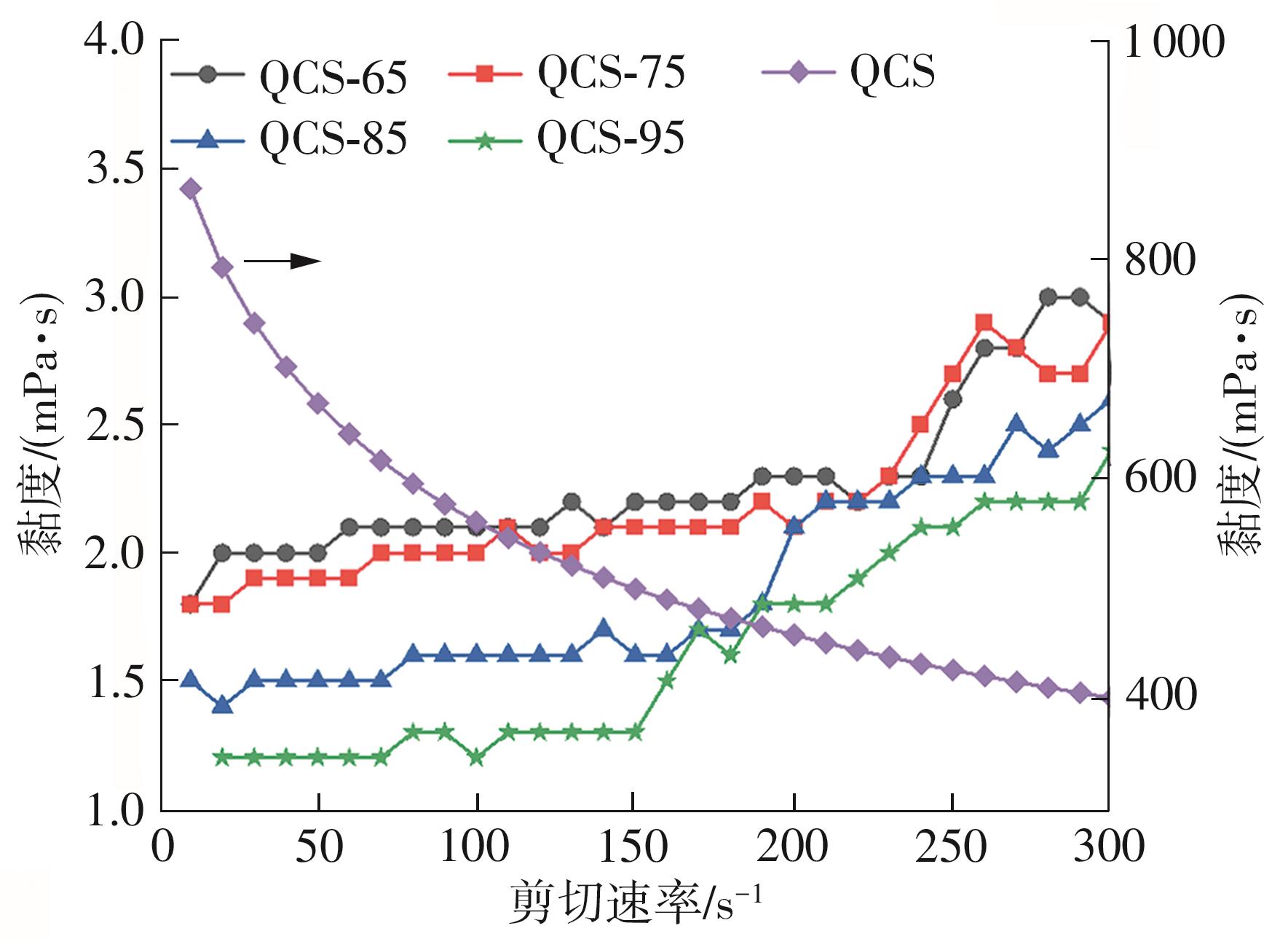
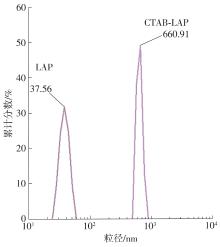
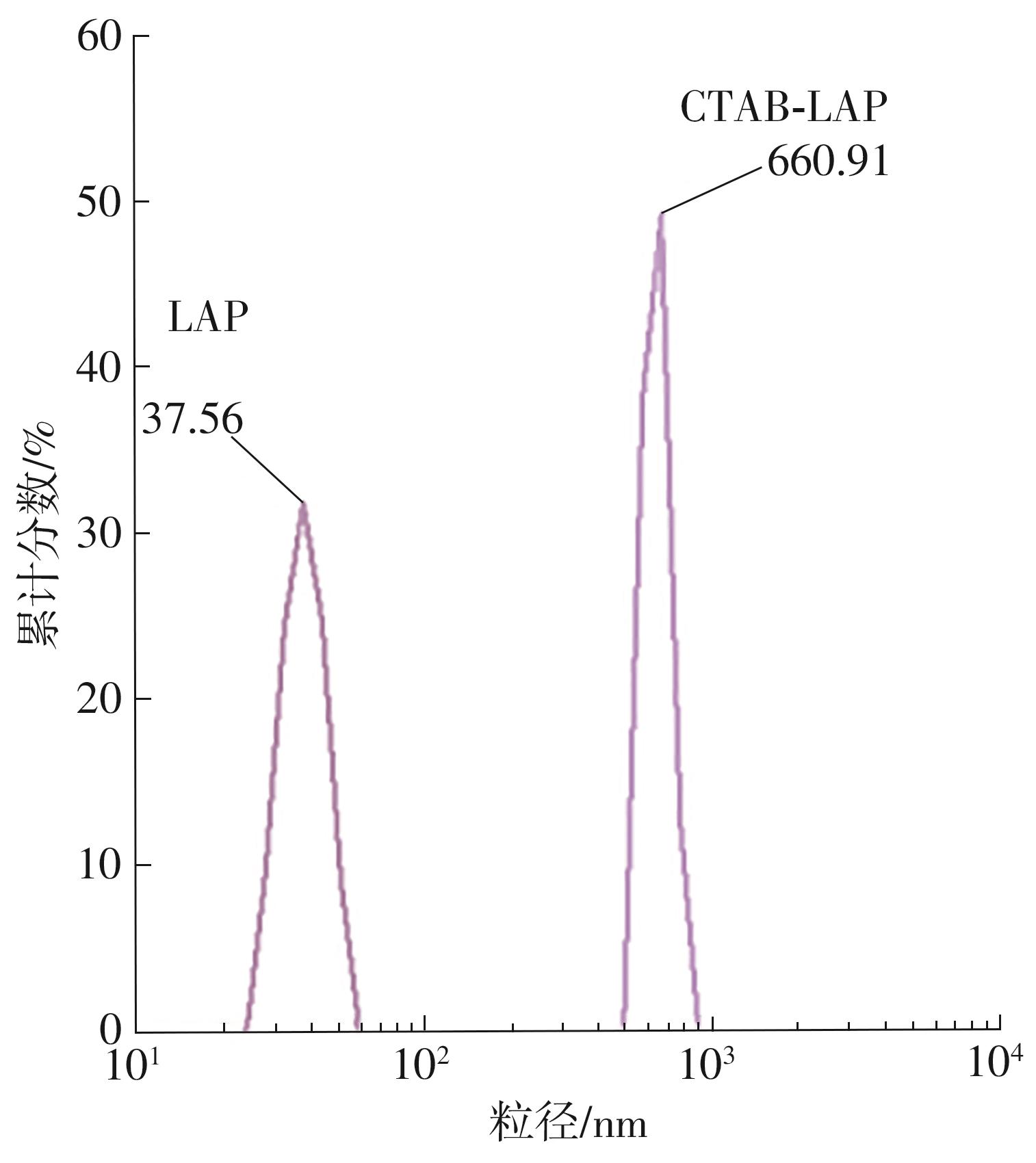
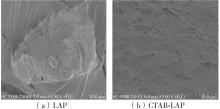
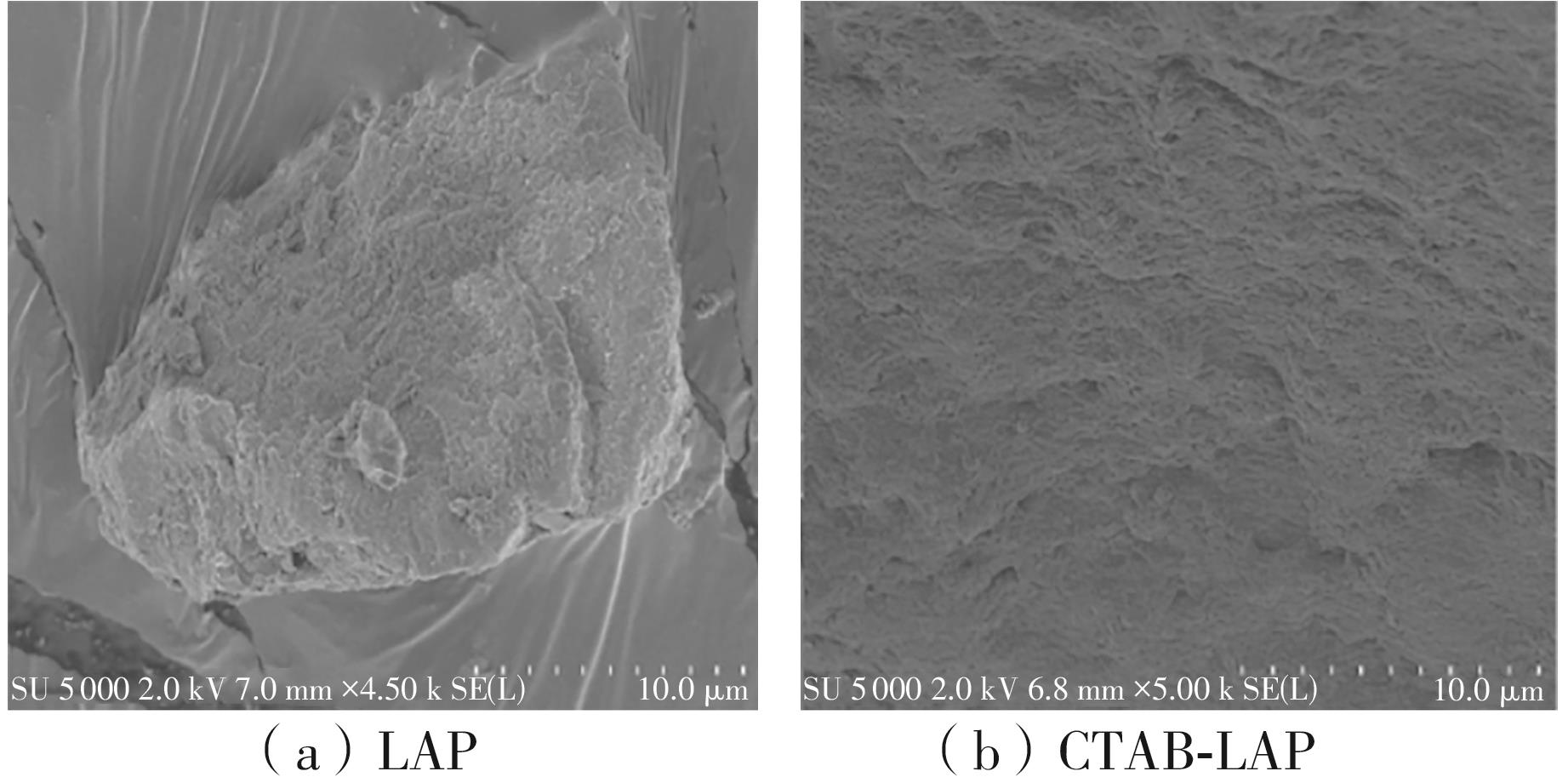
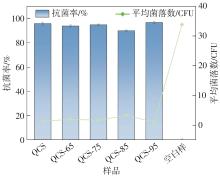
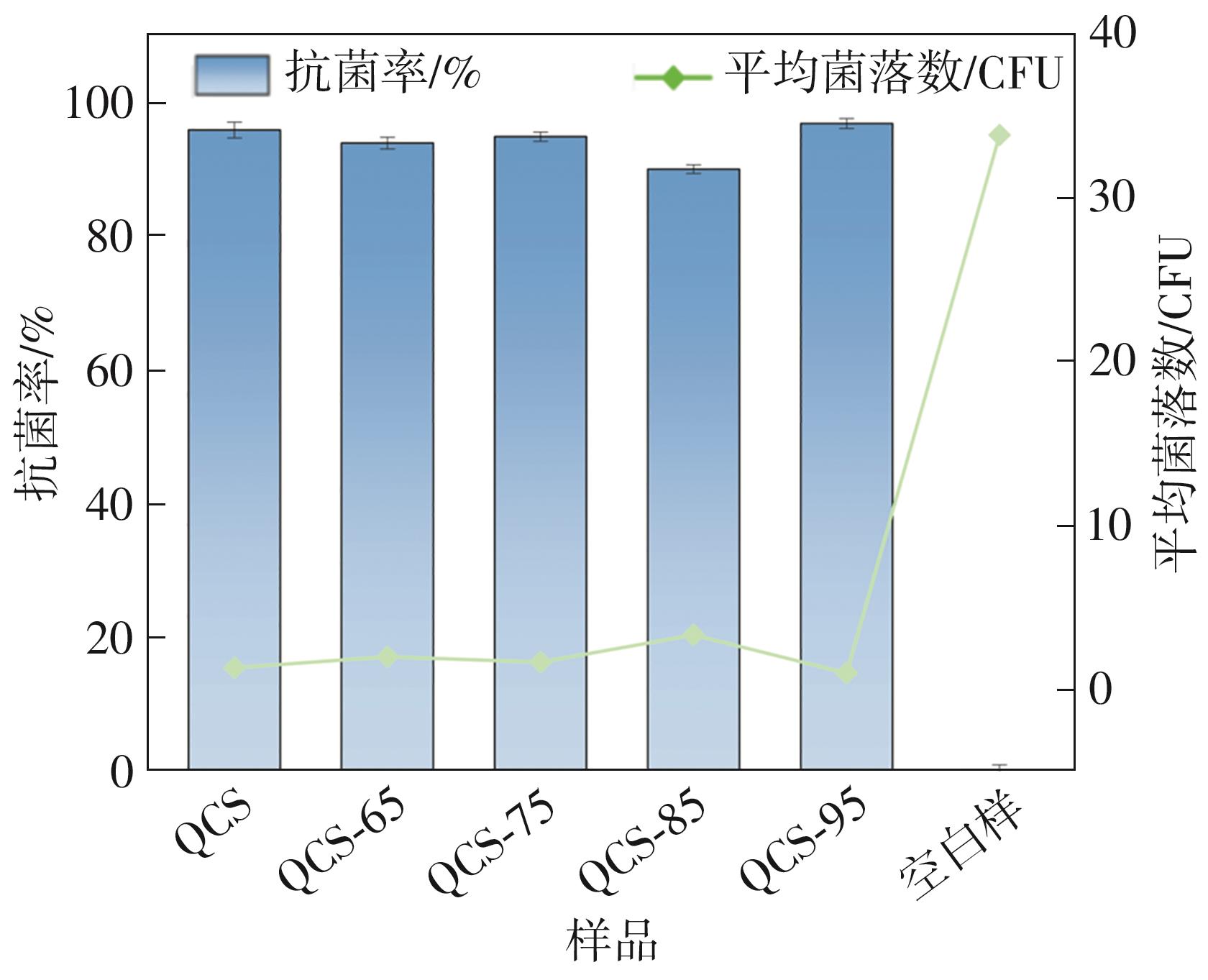
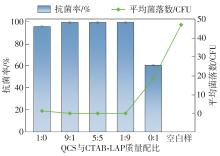
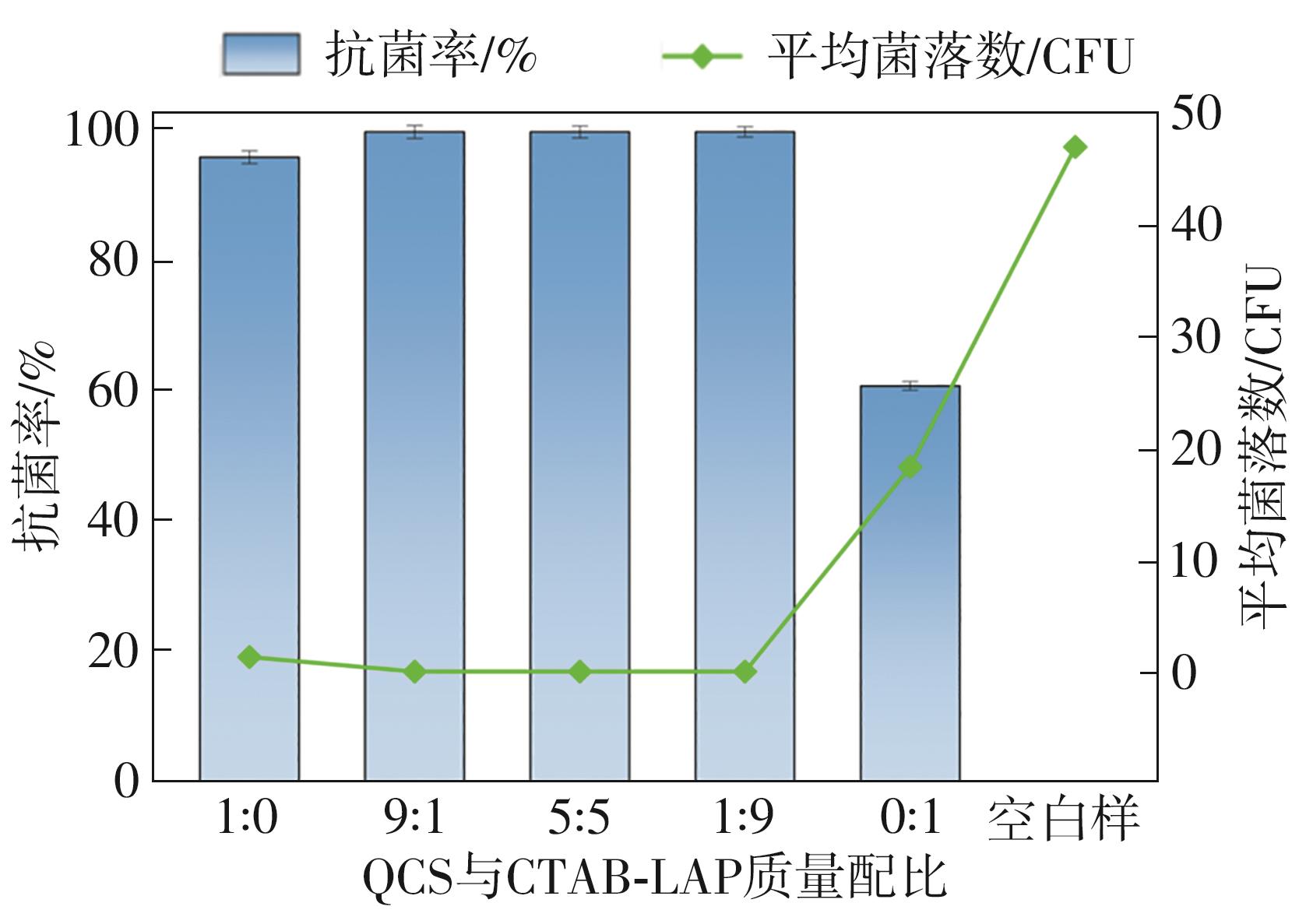
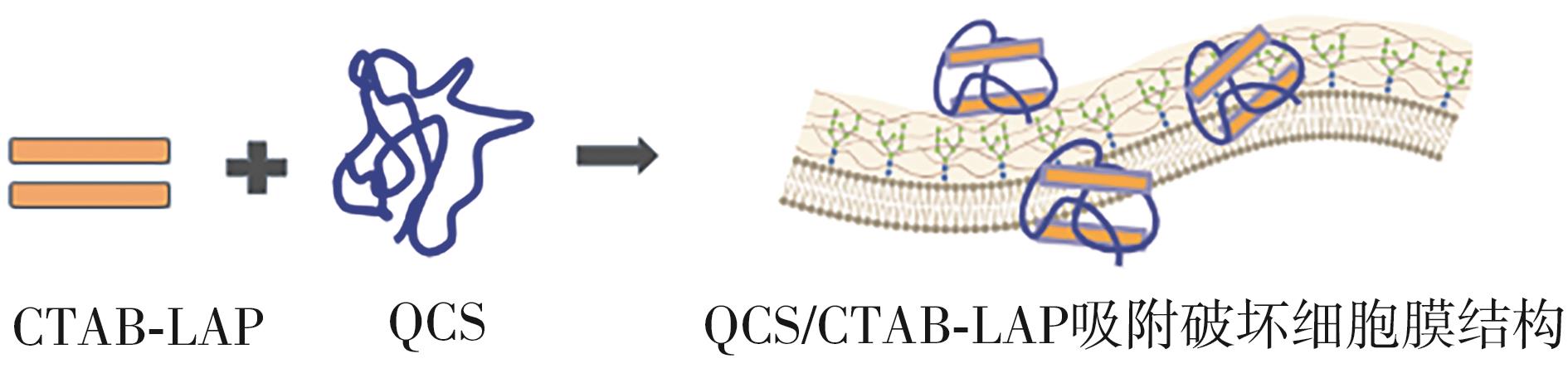
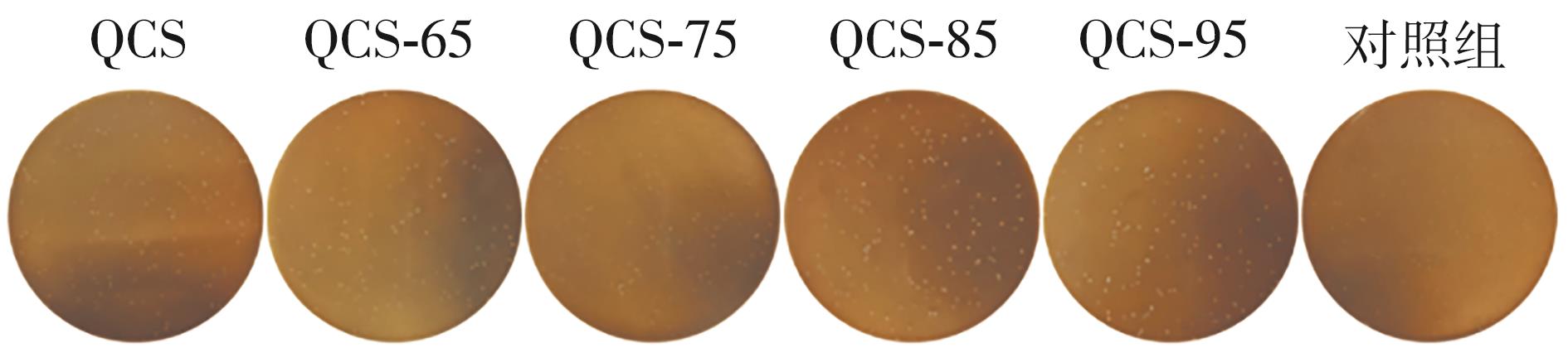
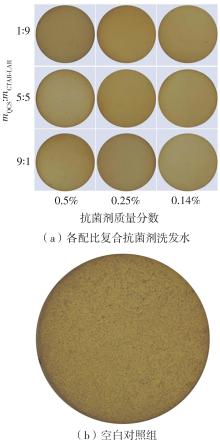
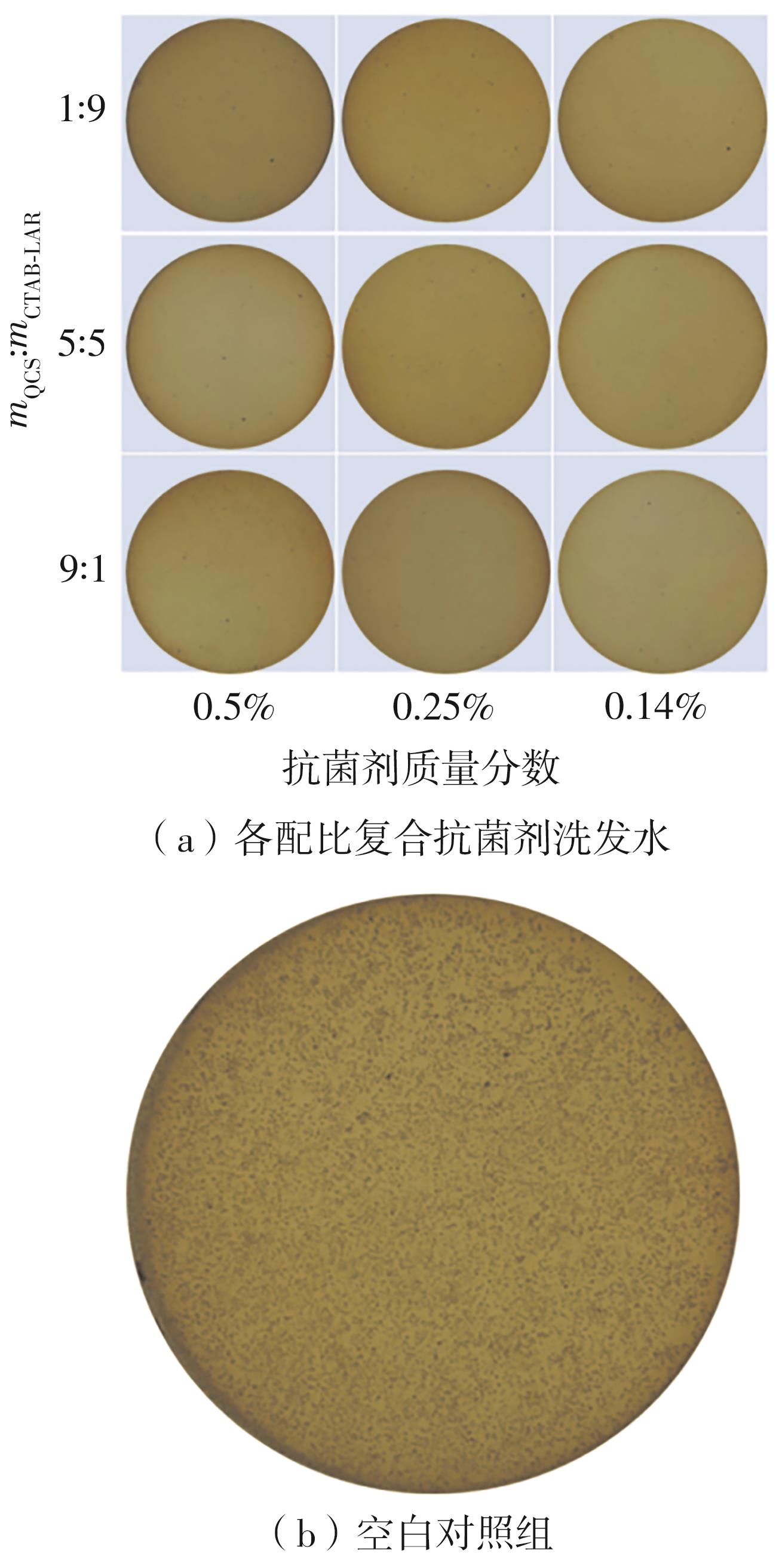
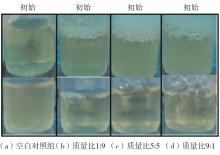
| [1] |
FAERGEMANN J .Malassezia yeasts and pityriasis versicolor[J].Current Opinion in Infectious Diseases,2009,22(2):128-133.
|
| [2] |
HAY R J, GRAHAM-BROWN R A .Dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis: causes and Management[J]. Clinical and Experimental Dermatology,1997,22(1):3-6.
|
| [3] |
RO B I, DAWSON T L .The role of sebaceous gland activity and scalp microfloral metabolism in the etiology of dandruff[J].Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings,2005,10(3):194-197.
|
| [4] |
TURNER G A, HOPTROFF M, HARDING C R .Stratum corneum dysfunction in dandruff[J].International Journal of Cosmetic Science,2012,34(4):298-306.
|
| [5] |
ZHANG Y, ZHANG X, LIU M .Malassezia species in seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff:a systematic review and meta-analysis[J].Mycoses,2013,56(3):267-275.
|
| [6] |
GRICE E A, SEGRE J A .The skin microbiome[J]. Nature Reviews Microbiology,2011,9(4):244-253.
|
| [7] |
DEANGELIS Y M, GEMMER C M, KACZVINSKY J R,et al .Three etiologic factors in dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis:malassezia fungi,sebaceous lipids,and individual sensitivity[J].Journal of Investigative Dermatology Symposium Proceedings,2005,10(3):295-297.
|
| [8] |
PONZIO R R, SURBER C .Safety and efficacy of pyrithione zinc in the treatment of dandruff[J].American Journal of Clinical Dermatology,2019,20(3): 351-358.
|
| [9] |
DRAELOS Z D .The effect of antidandruff shampoos on hair quality[J].International Journal of Cosmetic Science,2010,34(6):455-459.
|
| [10] |
MORAIS M G, FILHO P .The role of natural ingredients in treating dandruff[J].Journal of Cosmetic Dermatology,2005,14(2):151-157.
|
| [11] |
Commission European .Commission Regulation (EU) 2021/1902 of amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 as regards zinc pyrithione [Z].Luxembourg: Publications Office of the European Union,2021.
|
| [12] |
LIU W R, YANG Y Y, LIU Y S .Biocides in the river system of a highly urbanized region:a systematic investigation involving runoff input[J].Science of the Total Environment,2018,624(5):1023-1030.
|
| [13] |
MUXIKA A, ETXABIDE A, URANGA J,et al .Chitosan as a bioactive polymer:processing, properties and applications[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,105(Pt2):1358-1368.
|
| [14] |
MOUZAHIM M EL, EDDRARAI E M, ELADAOUI S,et al .Food packaging composite film based on chitosan,natural kaolinite clay,and Ficus carica leaves extract for fresh-cut apple slices preservation[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,233:123430/1-11.
|
| [15] |
TANPICHAI S, SRIMARUT Y, WORAPRAYOTE W,et al .Chitosan coating for the preparation of multilayer coated paper for food-contact packaging:wettability,mechanical properties,and overall migration[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2022,213(7):534-545.
|
| [16] |
AKBARI-ALAVIJEH S, SHADDEL R, JAFARI S M . Encapsulation of food bioactives and nutraceuticals by various chitosan-based nanocarriers[J].Food Hydrocolloids,2020,105:105774/1-11.
|
| [17] |
XING X, HAN Y, CHENG H .Biomedical applications of chitosan/silk fibroin composites:a review[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2023,240:124407/1-20.
|
| [18] |
AUGUSTINE R, REHMAN S R U, AHMED R,et al .Electrospun chitosan membranes containing bioactive and therapeutic agents for enhanced wound healing[J].International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,156(8):153-170.
|
| [19] |
FENG P, LUO Y, KE C,et al .Chitosan-based functional materials for skin wound repair: mechanisms and applications[J].Frontiers in Bioengineering and Biotechnology,2021,9:650598/1-15.
|
| [20] |
ZHAO R, MA T, ZHAO S,et al .Uniform and stable immobilization of metal-organic frameworks into chitosan matrix for enhanced tetracycline removal from water[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,382:122893/1-11.
|
| [21] |
QIU Y L, LI Y, ZHANG G L,et al .Quaternary-ammonium chitosan, a promising packaging material in the food industry[J].Carbohydrate Polymers,2024,323:121384/1-14.
|
| [22] |
KIAEE G, DIMITRAKAKIS N, SHARIFZADEH S,et al .Laponite-based nanomaterials for drug delivery[J].Advanced Healthcare Materials,2022,11(7):e2102054/1-39.
|
| [23] |
MI Y, TAN W, ZHANG J,et al .Modification of hydroxypropyltrimethyl ammonium chitosan with organic acid:synthesis, characterization,and antioxidant activity[J].Polymers,2020,12(11):2460/1-16.
|
| [24] |
MOHAMMED M, SYEDA J, WASAN K M,et al . An overview of chitosan nanoparticles and its application in non-parenteral drug delivery[J].Pharmaceutics,2017,9(4):53-60.
|
| [25] |
ISLAM M M, MONDAL M I H, AHMED F .Study on prawn shell waste into chitosan and its derivatives as value added products for cellulosic fibres[J].Research Journal of Textile and Apparel,2017,21(2):134-145.
|
| [26] |
MA B, TAN W, ZHANG J,et al .Preparation and characterization of chitosan derivatives bearing imidazole ring with antioxidant,antibacterial,and antifungal activities[J].Starch-Stärke,2023,75(3/4):2200204.
|
| [27] |
YAO Y, YE Z, ZHANG Y,et al .Quaternary ammonium compounds and their composites in antimicrobial applications[J].Advanced Materials Interfaces,2024,11:2300946/1-19.
|
| [28] |
FREITAS E D, MORAIS C F, JONAS K,et al .An overview of current knowledge on the properties,synthesis and applications of quaternary chitosan derivatives[J].Polymers,2020,12(12):2878-2890.
|
| [29] |
RABEA E I, BADAWY M E, STEVENS C V,et al . Chitosan as antimicrobial agent:applications and mode of action[J].Biomacromolecules,2003,4(6):1457-1465.
|
| [30] |
MCBAIN A J, LEDDER R G, SMITH T,et al .Effects of quaternary-ammonium-based formulations on bacterial community dynamics and antimicrobial susceptibility[J].Applied and Environmental Microbiology,2004,70(6):3449-3456.
|
| [31] |
TISCHER M, PRADEL G, OHLSEN K,et al .Quaternary ammonium salts and their antimicrobial potential:targets or nonspecific interactions[J]. ChemMedChem,2012,7(1):22-31.
|