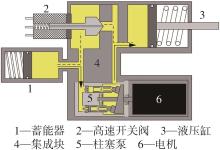
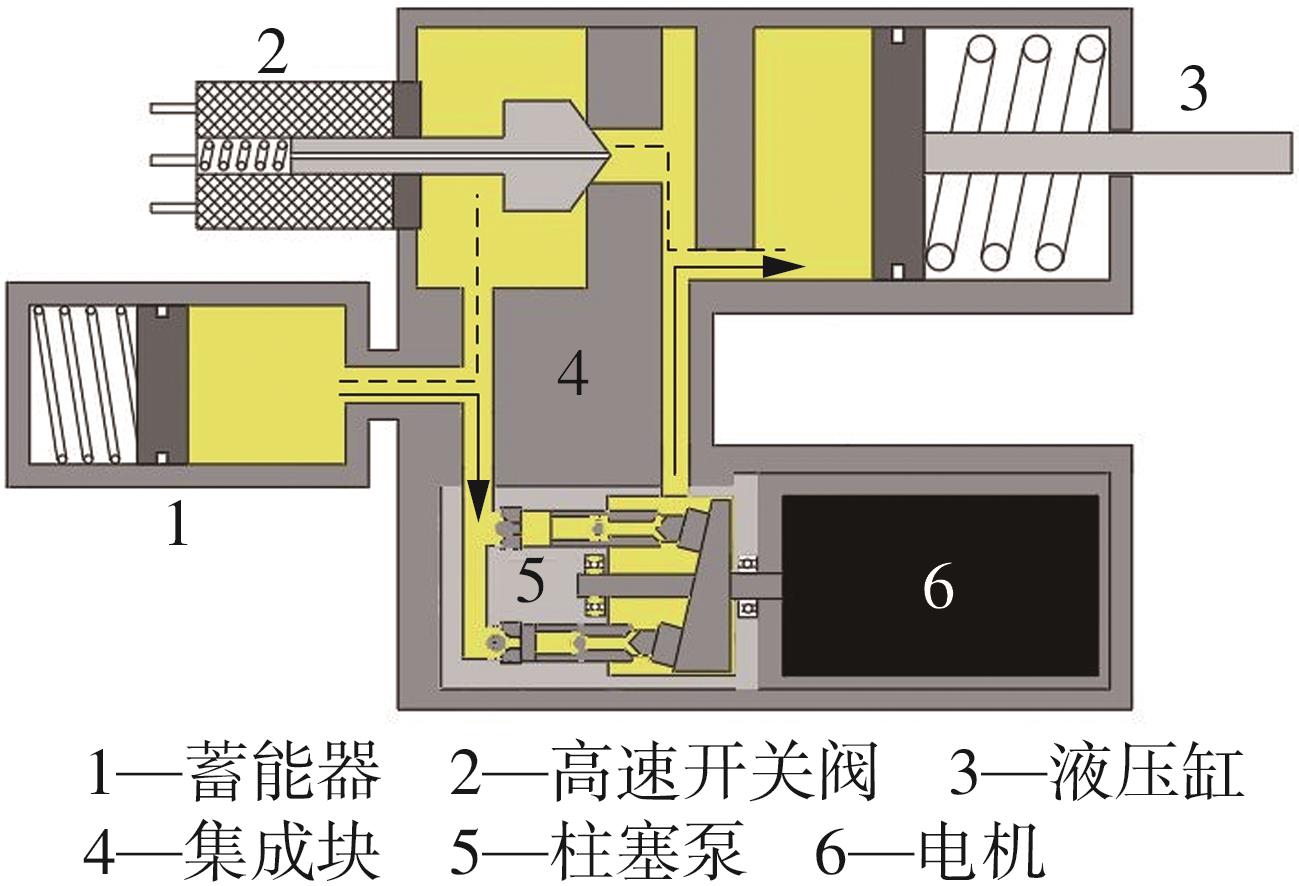
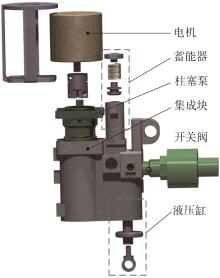
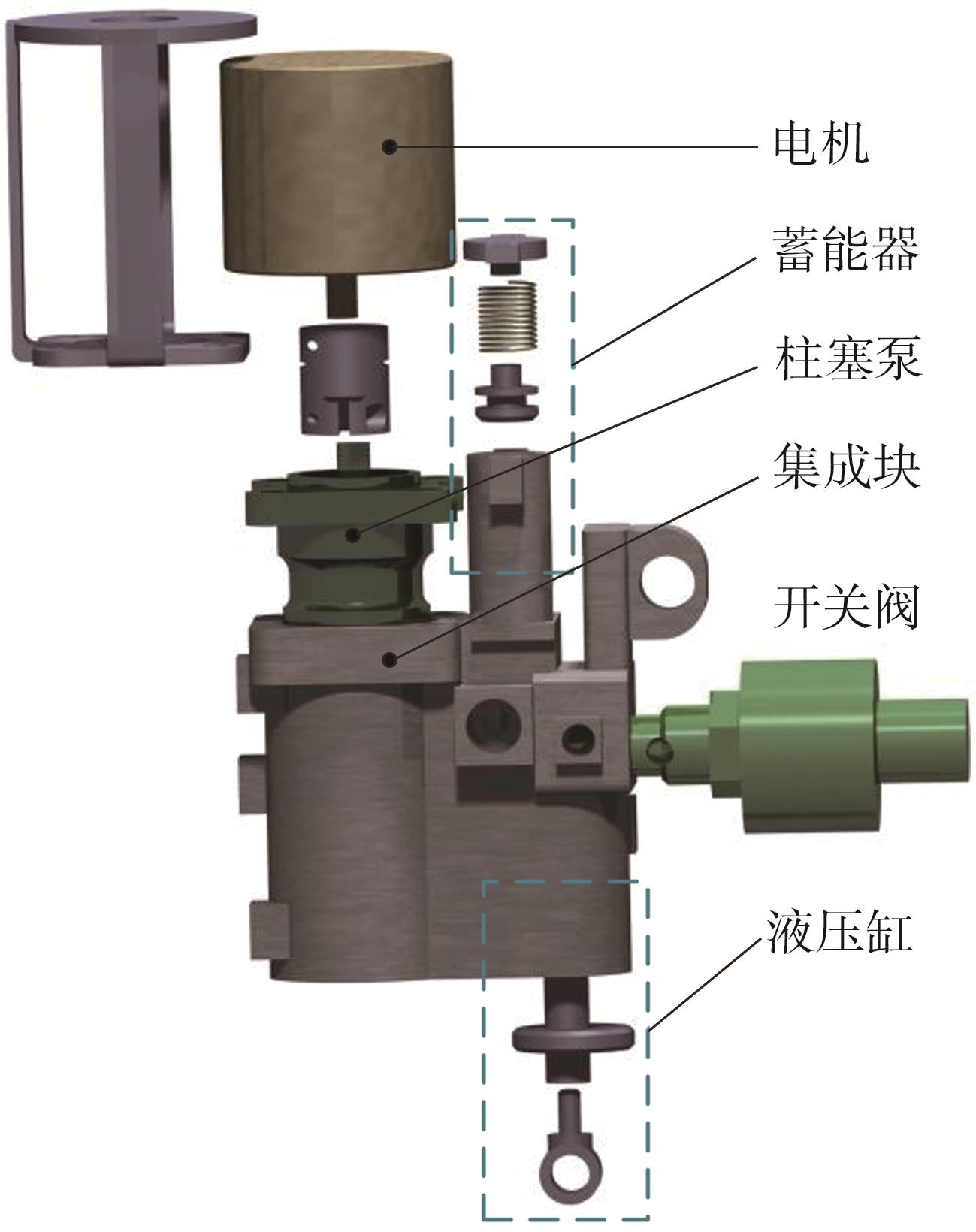
华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (9): 72-80.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230567
所属专题: 2024年机械工程
电液直驱主被动混合踝关节假肢设计与分析
庞浩1( ), 单绍鹏1, 韩阳2, 李振男1, 张森1, 刘春宝1,3(
), 单绍鹏1, 韩阳2, 李振男1, 张森1, 刘春宝1,3( )
)
- 1.吉林大学 机械与航空航天工程学院,吉林 长春 130022
2.中国科学院长春光学精密机械与物理研究所,吉林 长春 130022
3.吉林大学工程仿生教育部重点实验室,吉林 长春 130022
Design and Analysis of the Active-Passive Hybrid Ankle Prosthesis Based on Electro-Hydraulic Actuation
PANG Hao1( ), SHAN Shaopeng1, HAN Yang2, LI Zhennan1, ZHANG Sen1, LIU Chunbao1,3(
), SHAN Shaopeng1, HAN Yang2, LI Zhennan1, ZHANG Sen1, LIU Chunbao1,3( )
)
- 1.School of Mechanical and Aerospace Engineering,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,Jilin,China
2.Changchun Institute of Optics,Fine Mechanics and Physics,Chinese Academy of Sciences,Changchun 130022,Jilin,China
3.Key Laboratory of Bionic Engineering,Ministry of Education,Jilin University,Changchun 130022,Jilin,China
摘要:
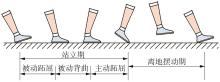
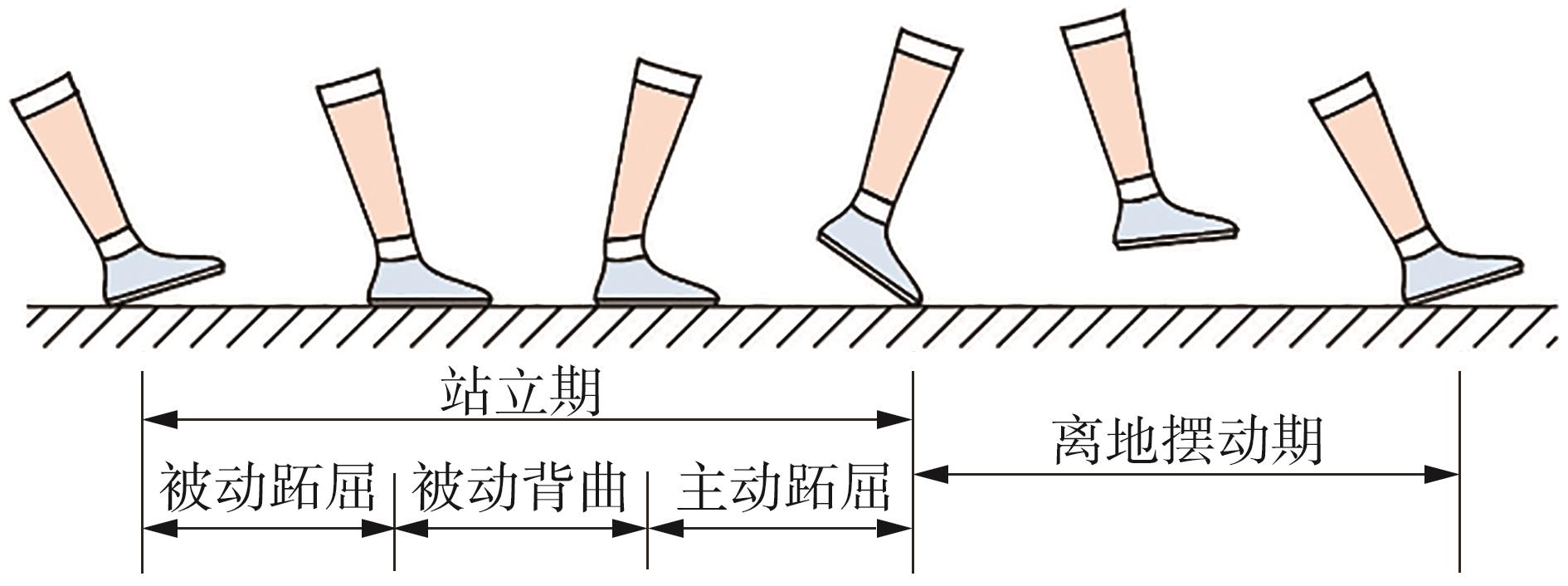
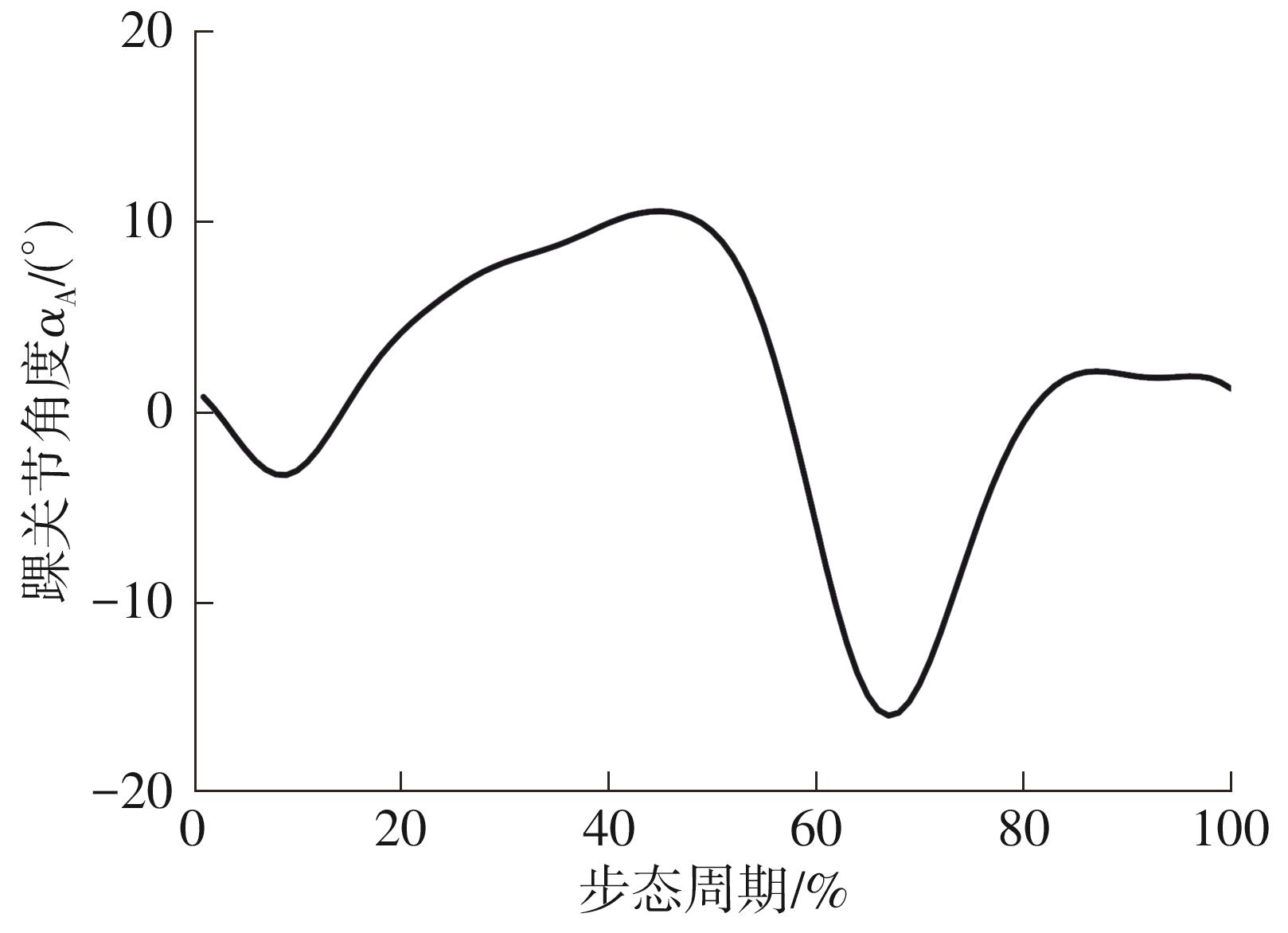
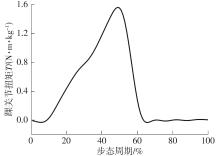
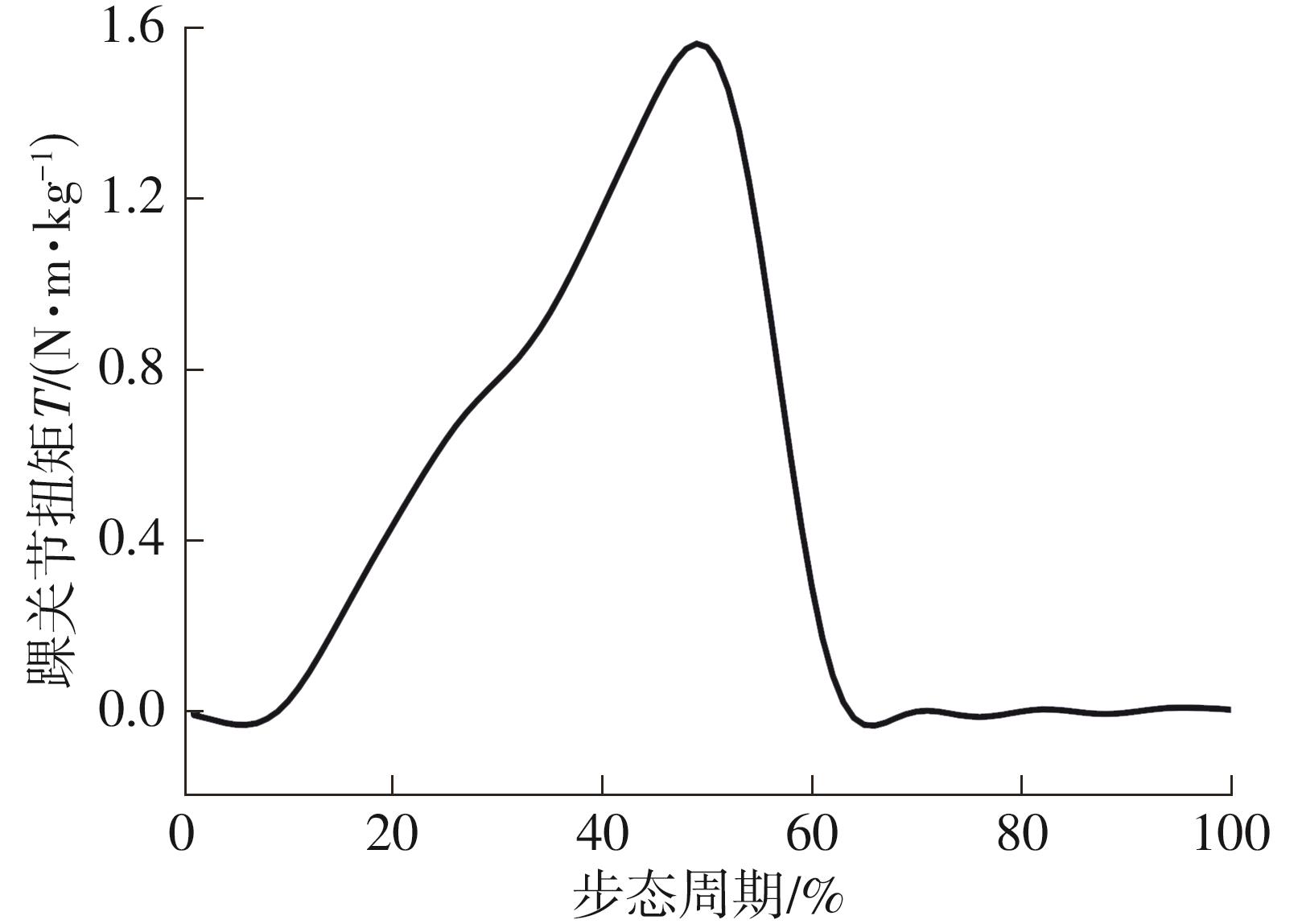
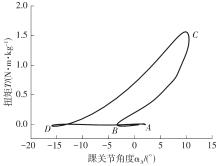
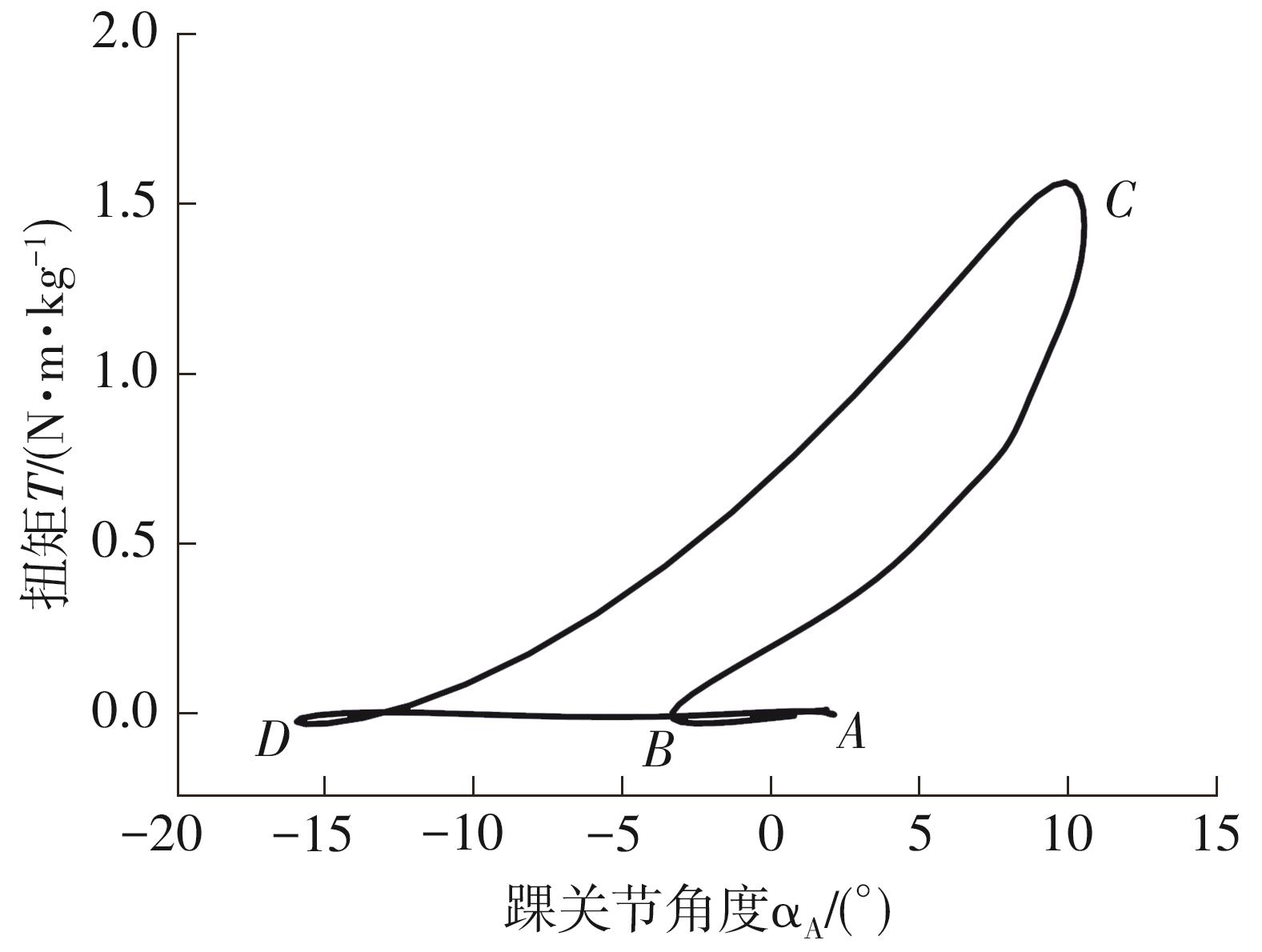
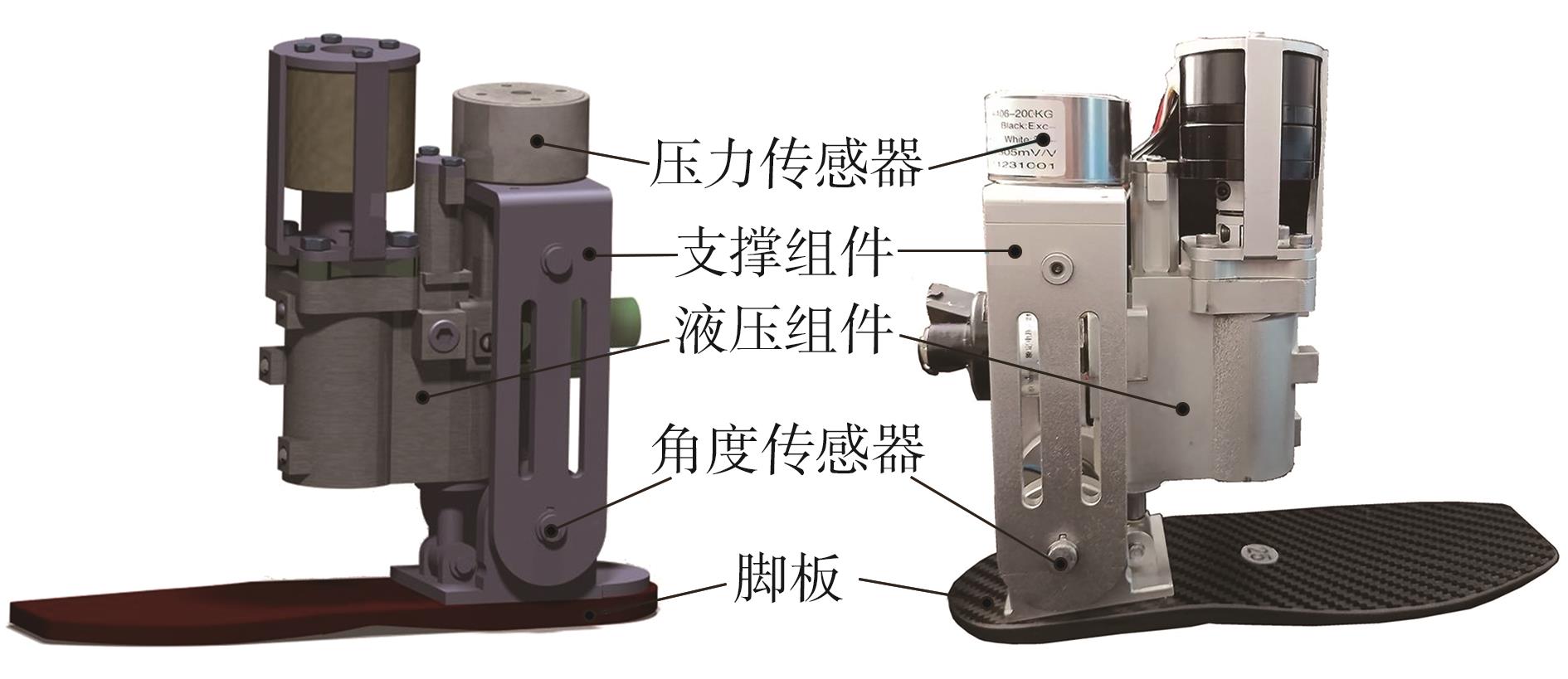
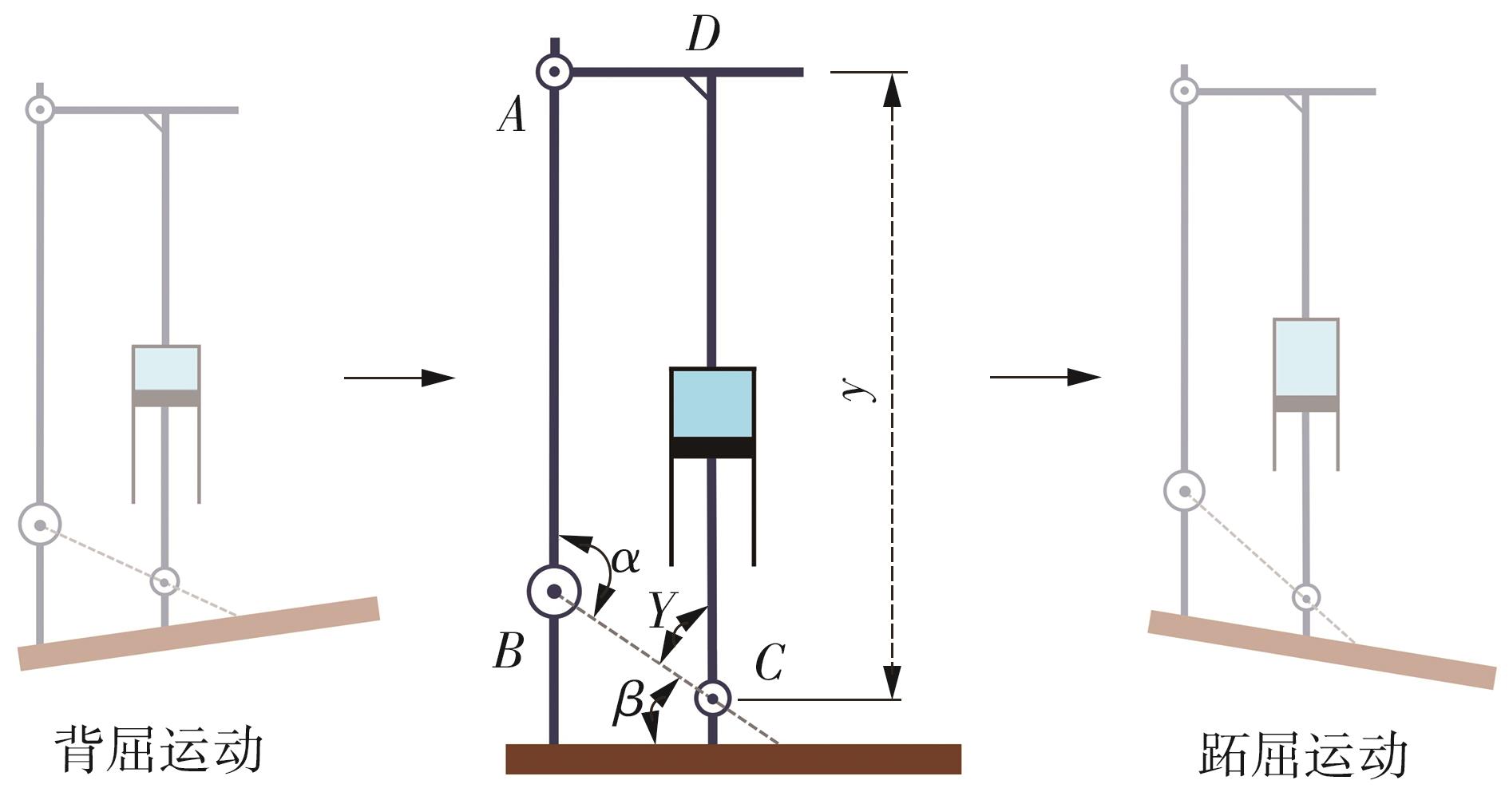
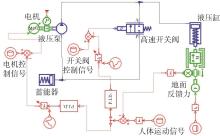
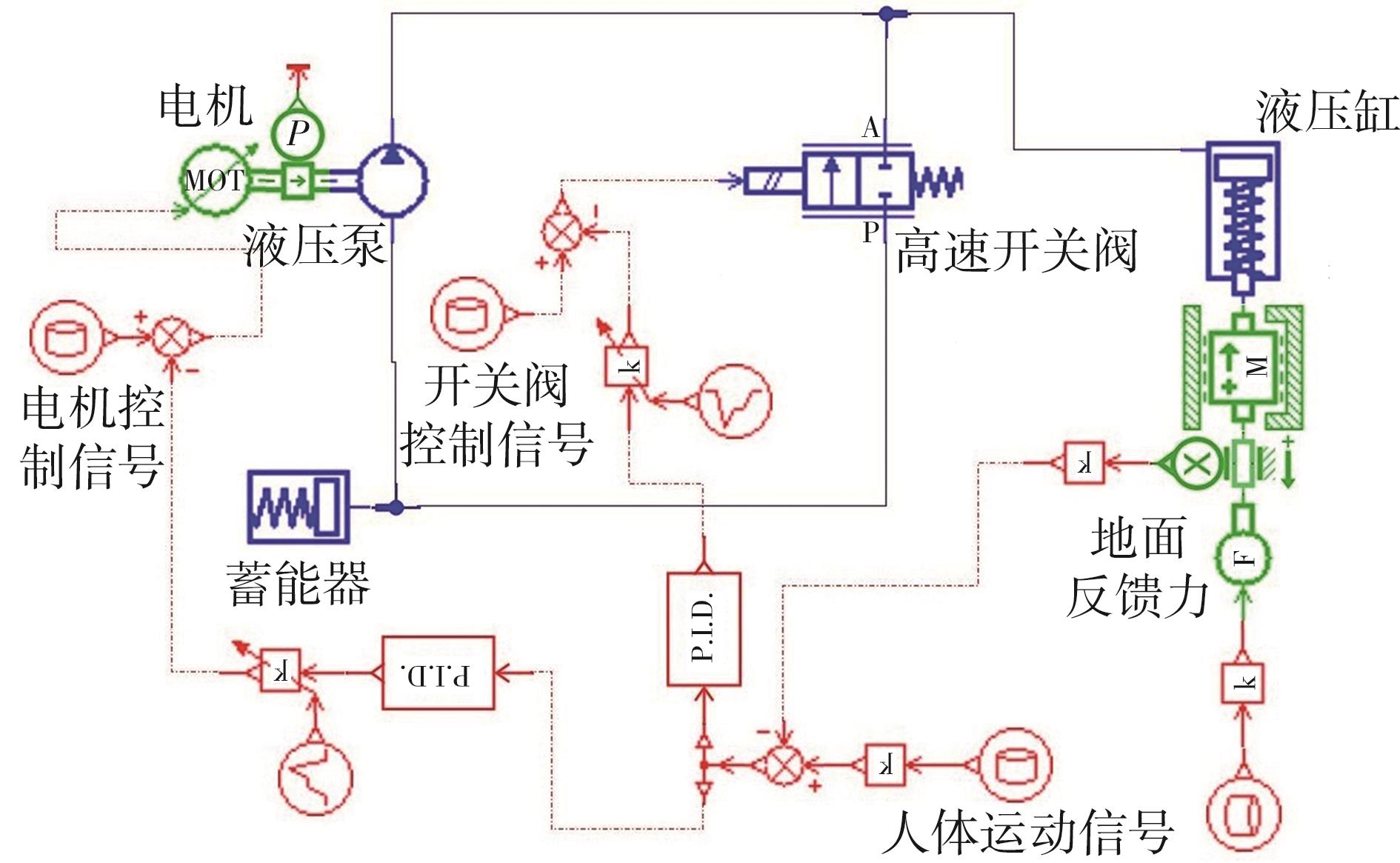
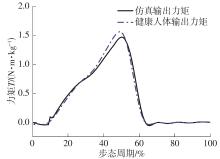
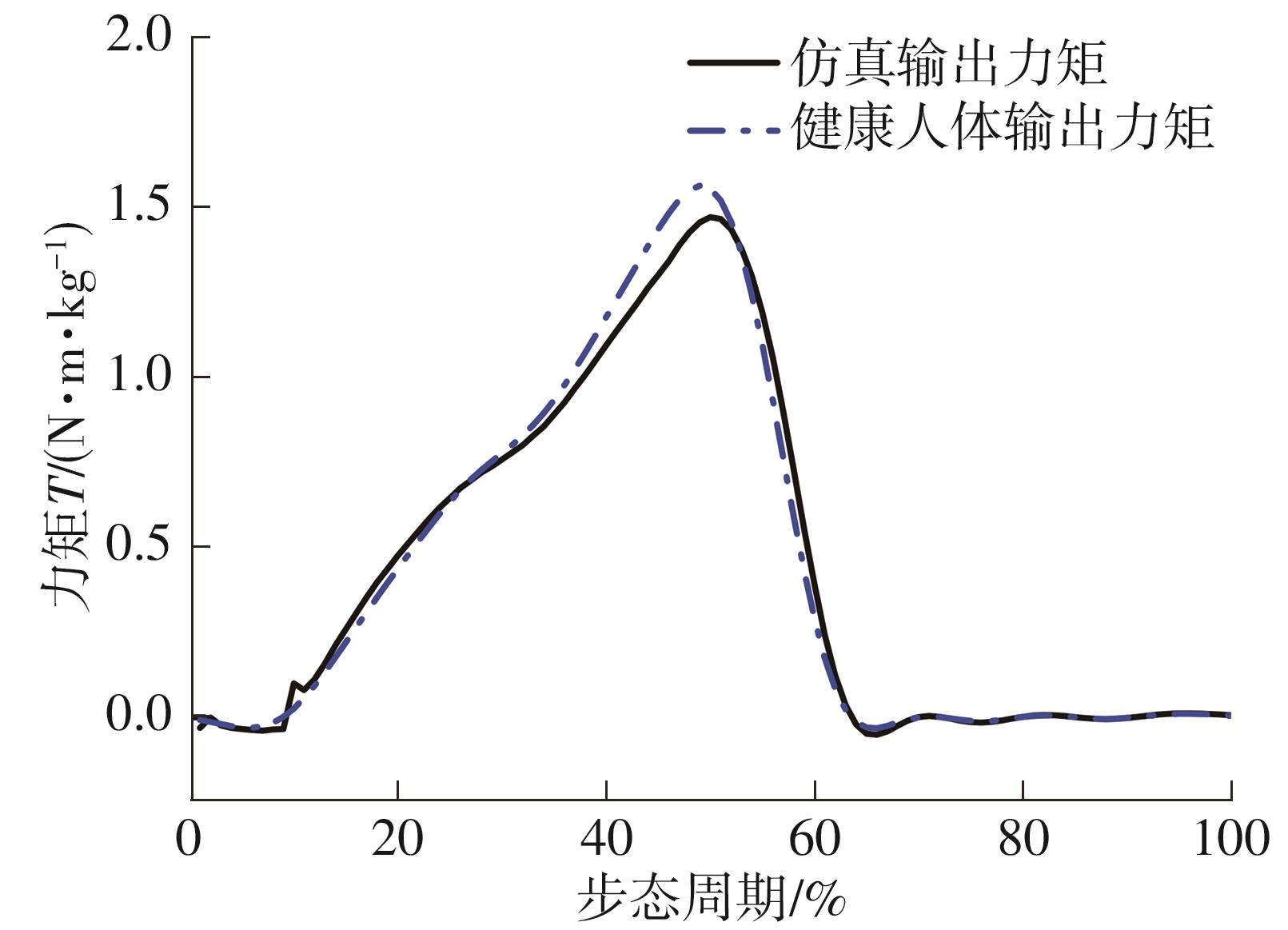
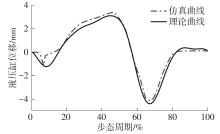
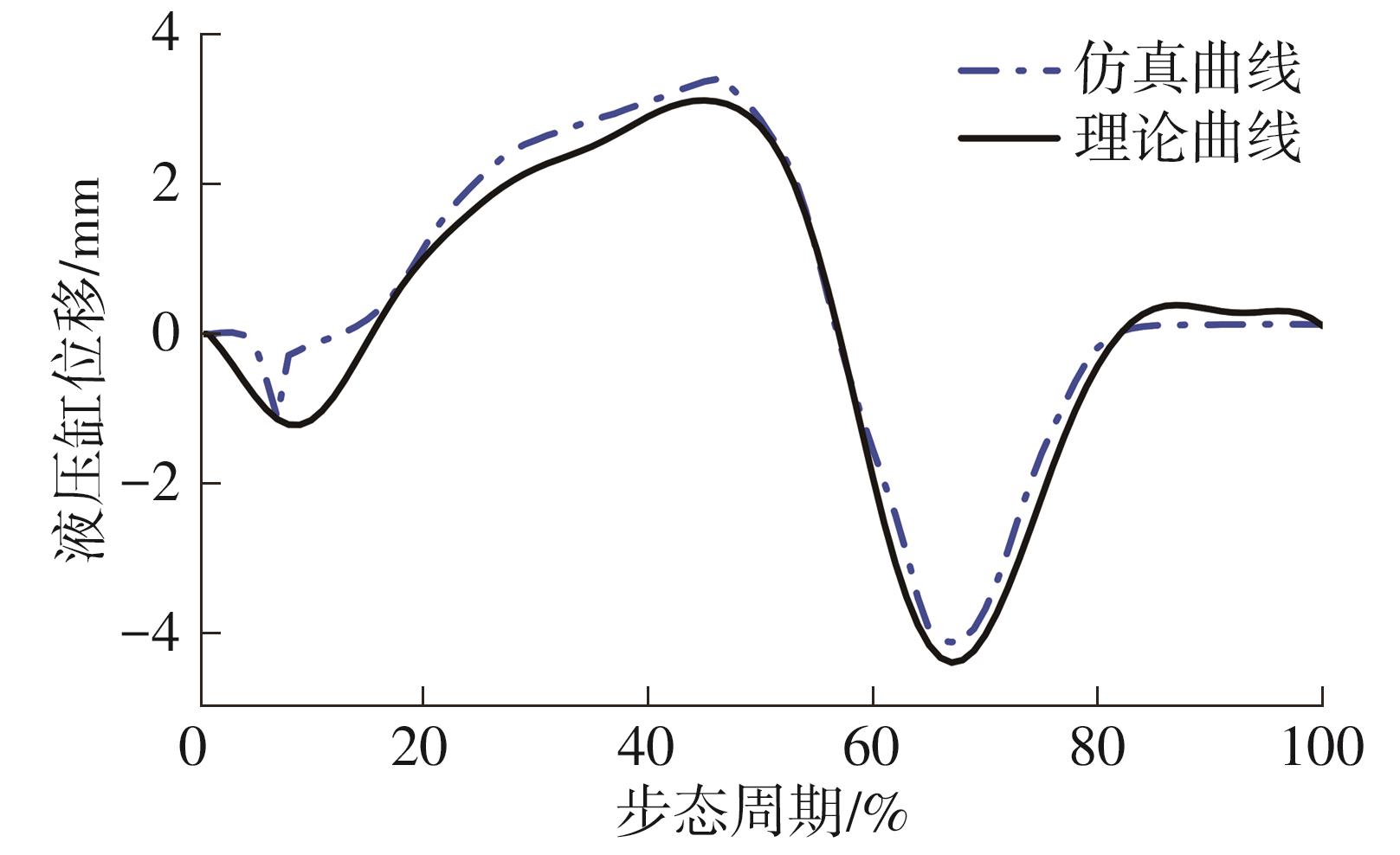
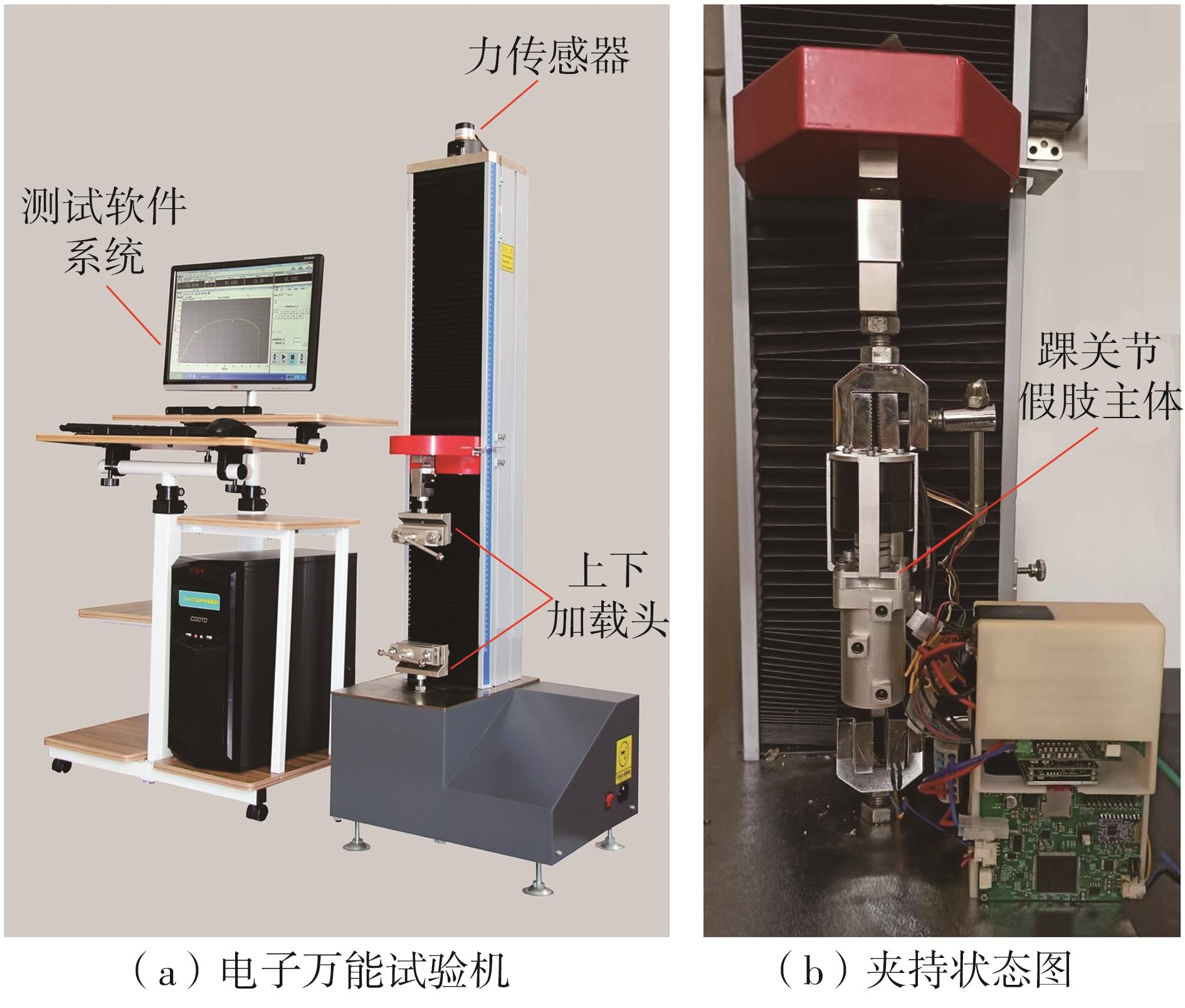
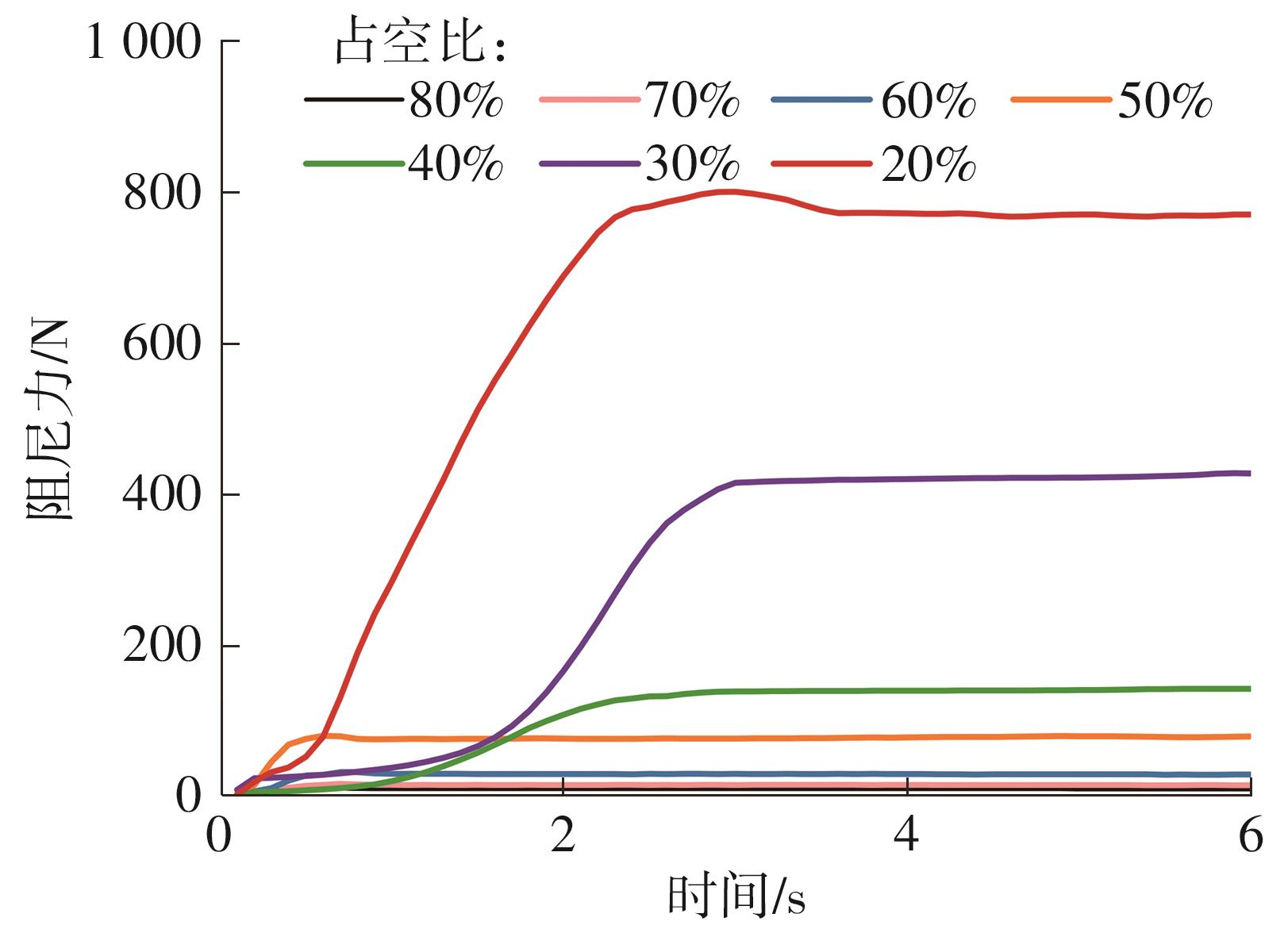
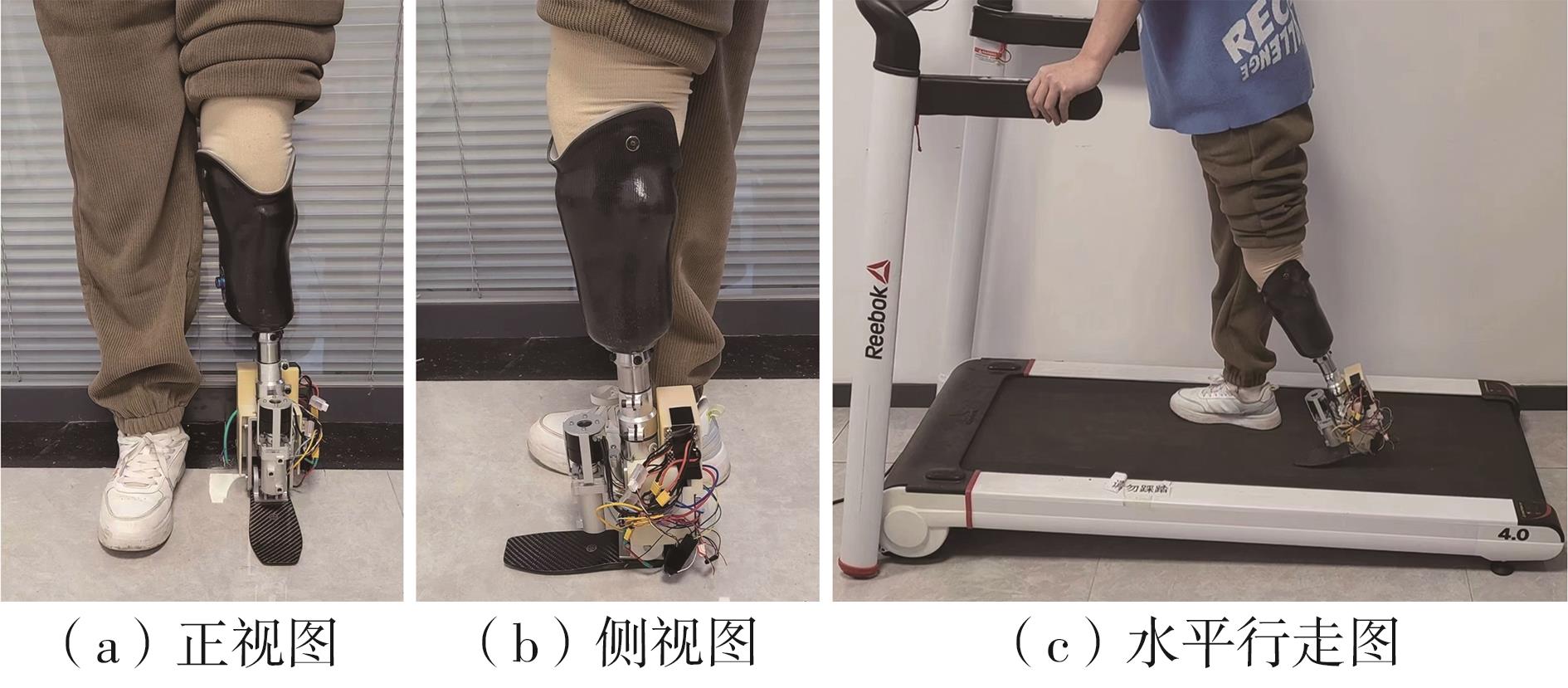
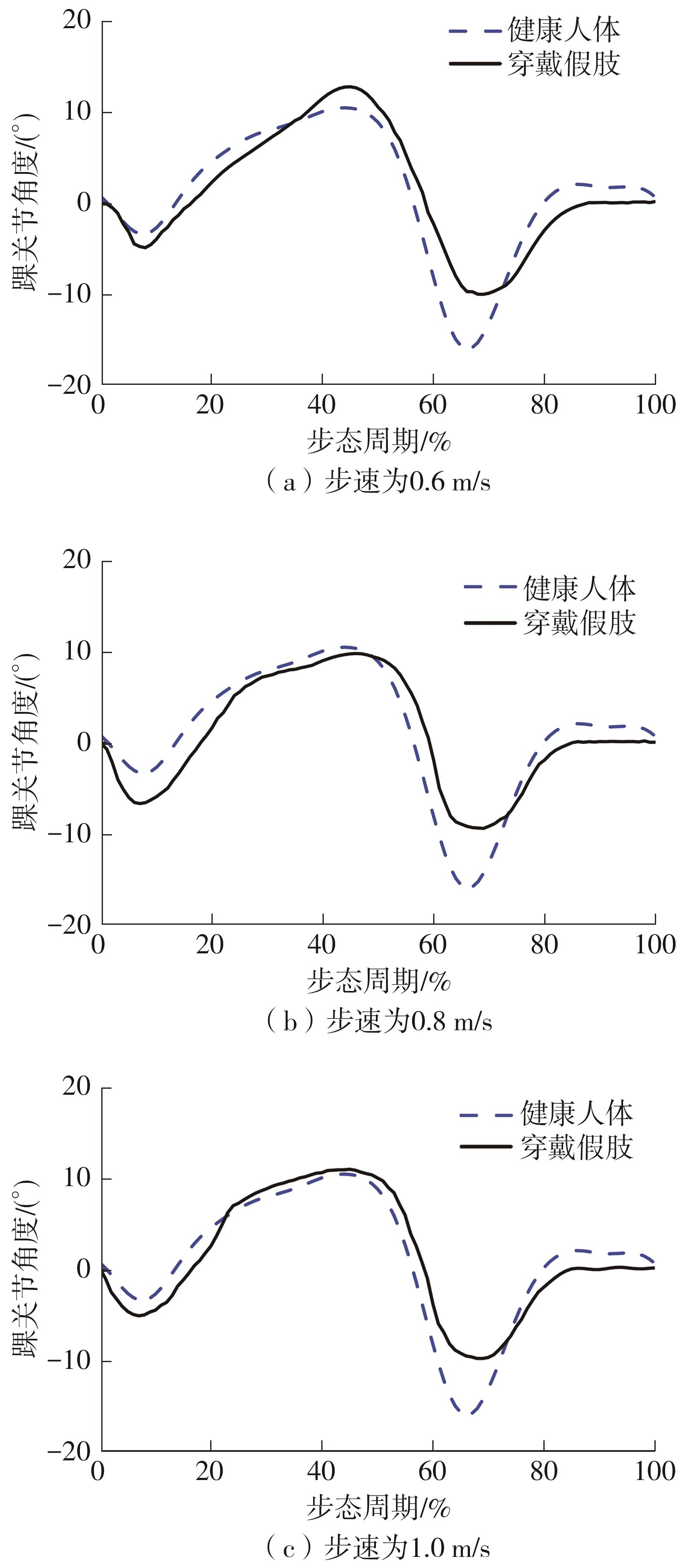
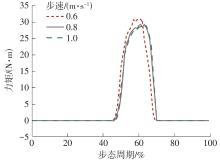
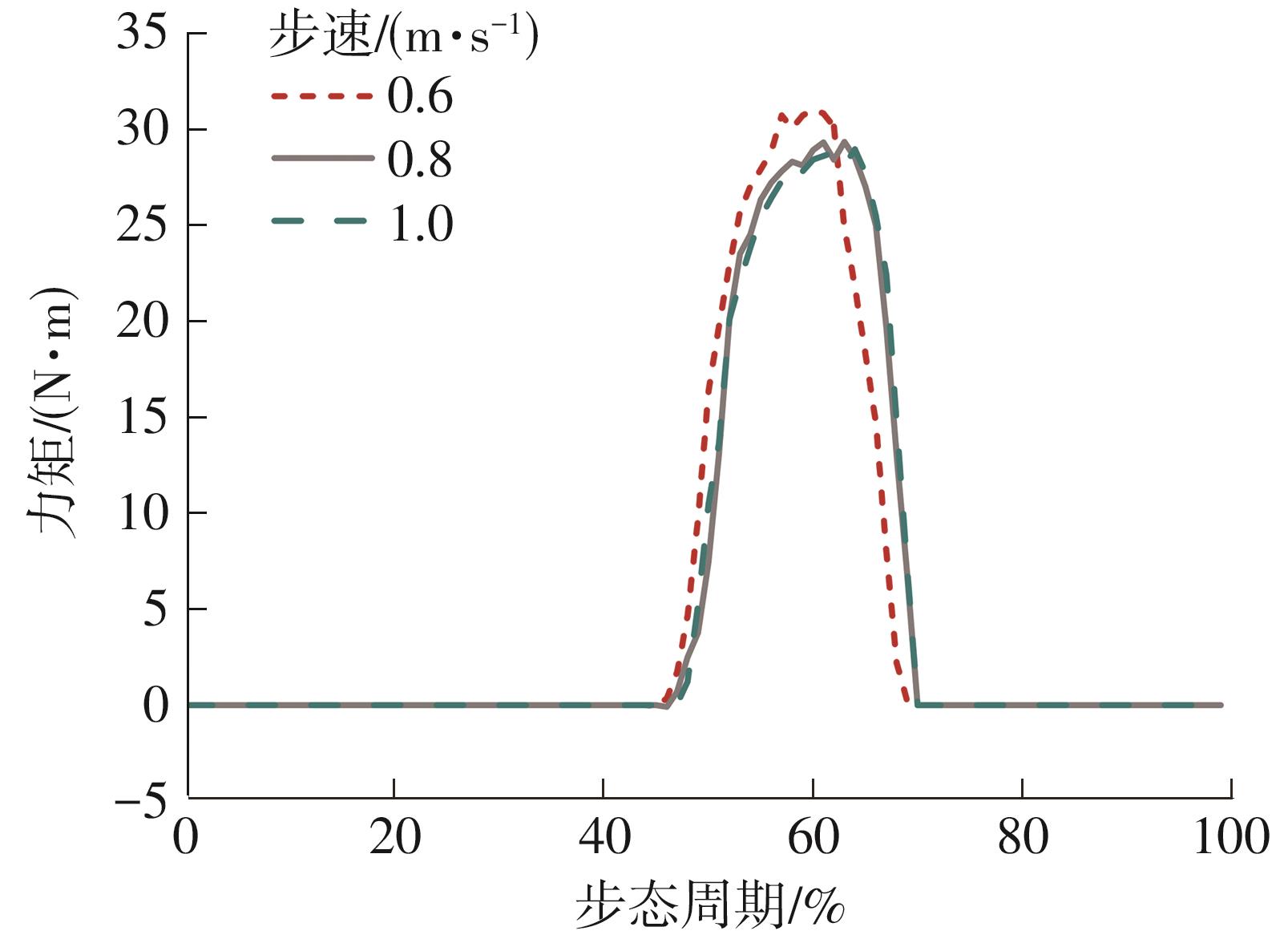
穿戴踝关节假肢是膝下截肢患者恢复行走能力的重要手段。下肢假肢按照能否主动输出转矩分为被动假肢和动力假肢,其中动力假肢分为主动假肢和主被动混合假肢。被动踝关节假肢不能提供主动扭矩,应用场景有限;动力踝关节假肢能够输出主动扭矩,但存在低被动摩擦与高主动传动比不兼容问题。为了提高踝关节假肢的性能和适应性,从实际应用角度出发,基于电液直驱原理,提出了一种主被动混合踝关节假肢的新构型。首先,基于对人体踝关节角度及扭矩的分析,设计了踝关节假肢驱动系统,并提出了主被动混合踝关节假肢的总体设计方案;然后,建立了假肢系统的数学模型,通过对假肢液压系统的仿真分析验证了的假肢系统的合理性,并研制了假肢原理样机;最后,通过台架测试和人体穿戴假肢行走实验对假肢的性能进行了验证。实验结果显示:适配者行走步速为1.0 m/s(接近成年人的平均行走速度)时,假肢踝关节主动输出最大扭矩为28 N·m。研究结果表明:提出的主被动混合踝关节假肢可以实现人体行走过程中的主动助力功能,并能较好拟合人体踝关节运动姿态,增强了穿戴适应性,同时使假肢的体积和质量得到了进步的减小,为动力型下肢假肢的研究提供了设计思路和参考依据。
中图分类号: