华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (8): 89-97.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220177
所属专题: 2023年电子、通信与自动控制
应用于高精度定位定向的可重构GNSS射频接收机
李斌1 王日炎1,2 陈志坚1 钟世广2 彭恒2 张芳芳2 贺黉胤2 杨昆明2
- 1.华南理工大学 微电子学院,广东 广州 510640
2.广州润芯信息技术有限公司,广东 广州 510663
Reconfigurable GNSS RF Receiver for High-Precision Positioning and Orientation
LI Bin1 WANG Riyan1,2 CHEN Zhijian1 ZHONG Shiguang2 PENG Heng2 ZHANG Fangfang2 HE Hongyin2 YANG Kunming2
- 1.School of Microelectronics,South China University of China,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangzhou Runxin Information Technology Co. ,Ltd. ,Guangzhou 510663,Guangdong,China
摘要:
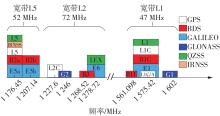
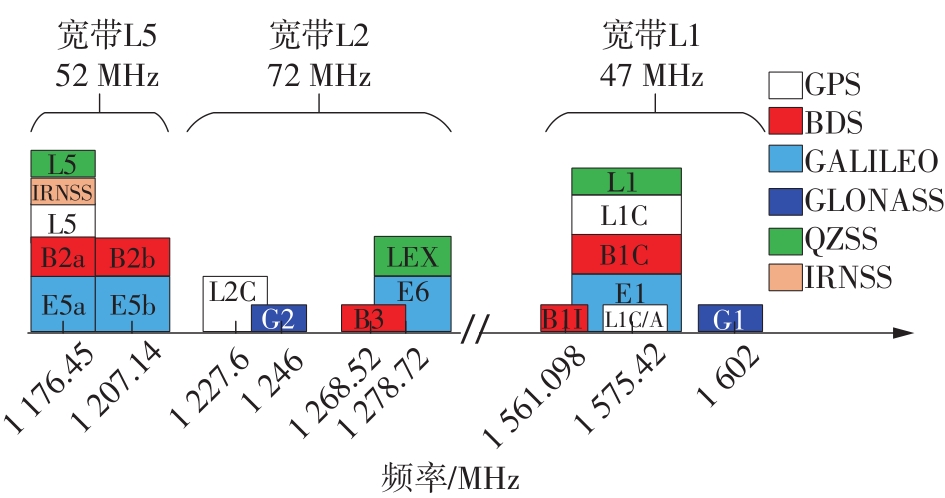
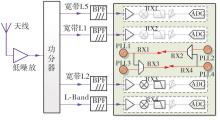
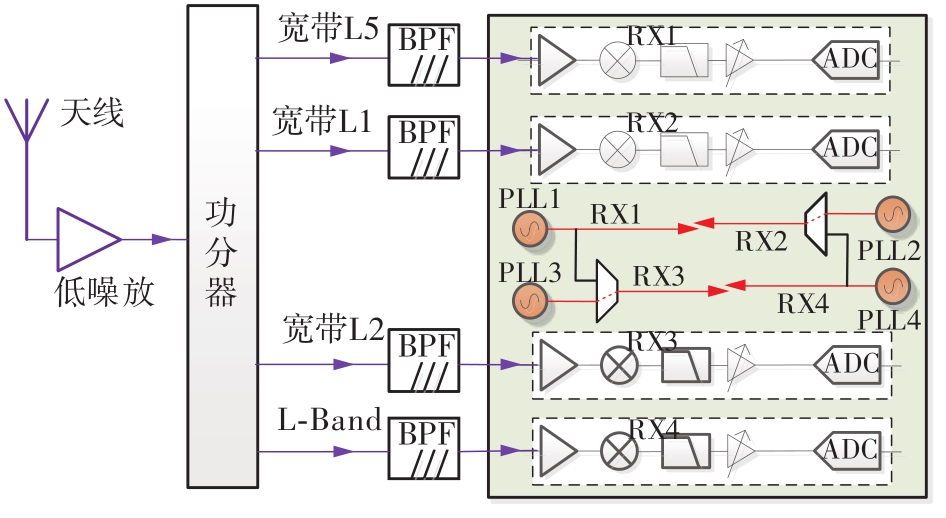
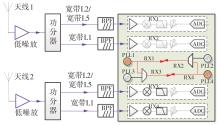
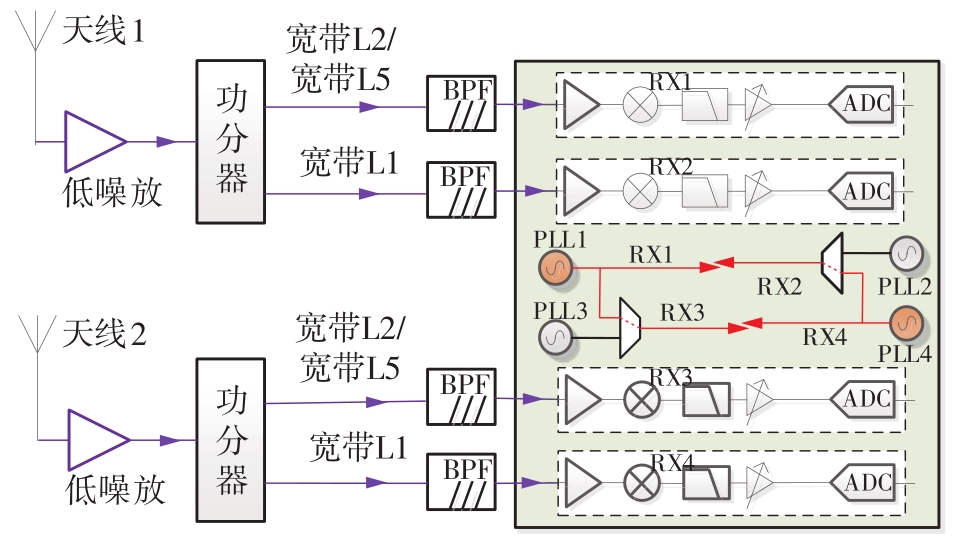
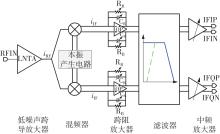
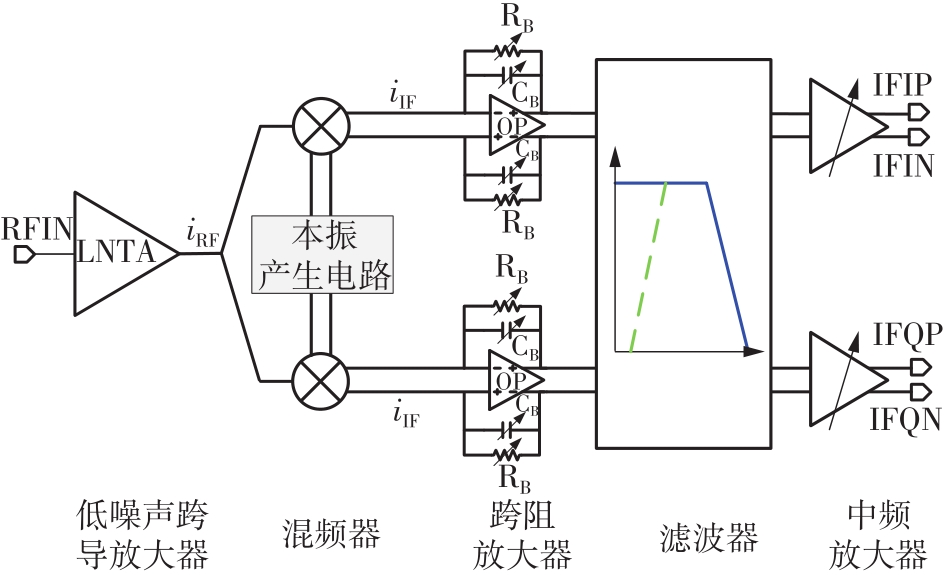
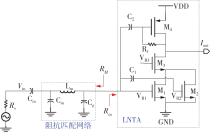
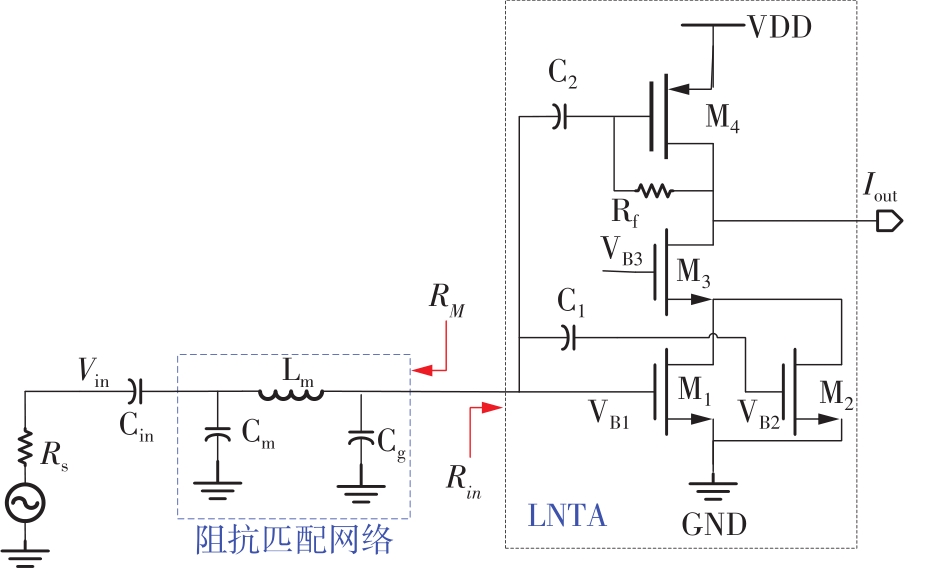
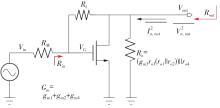
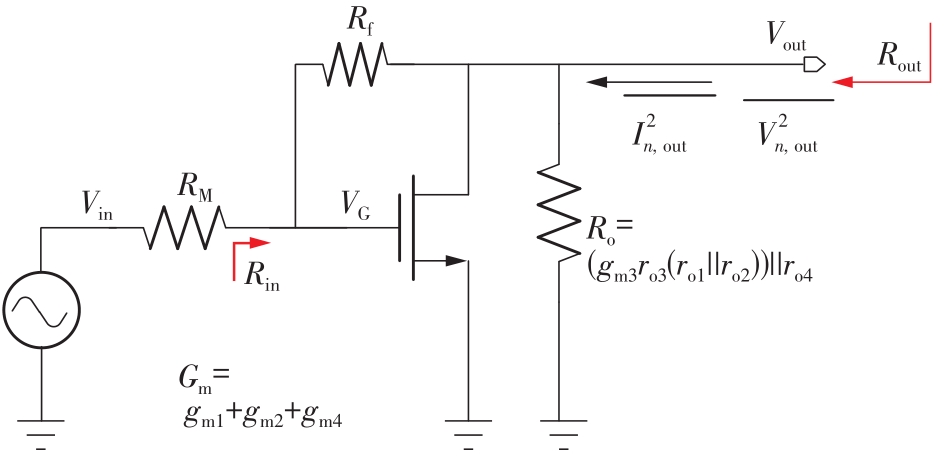
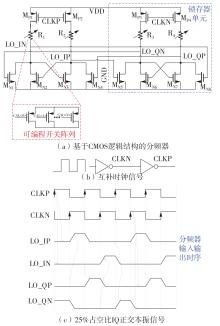
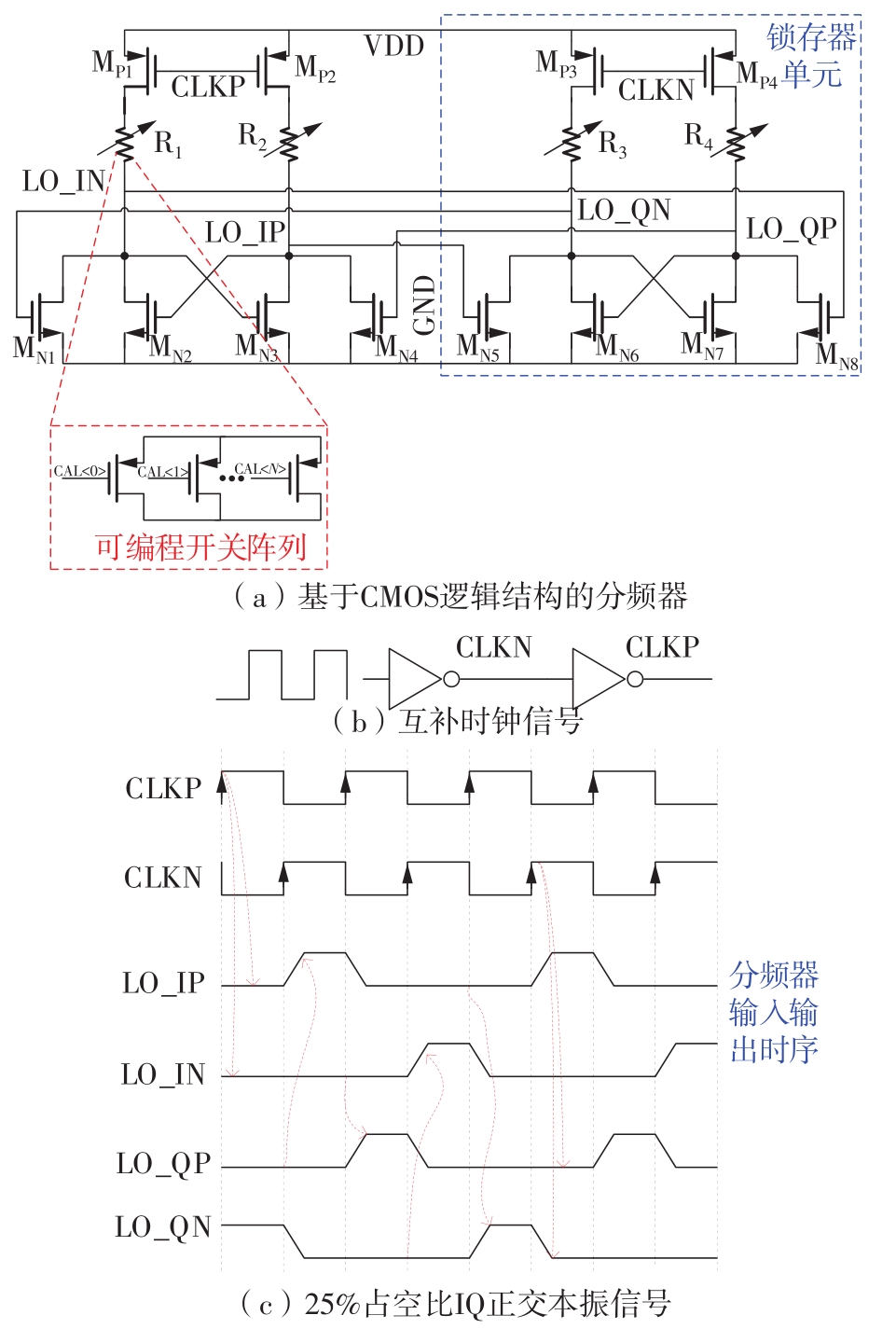
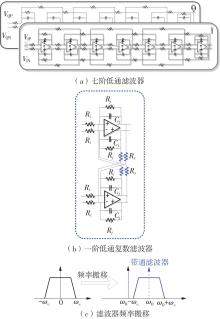
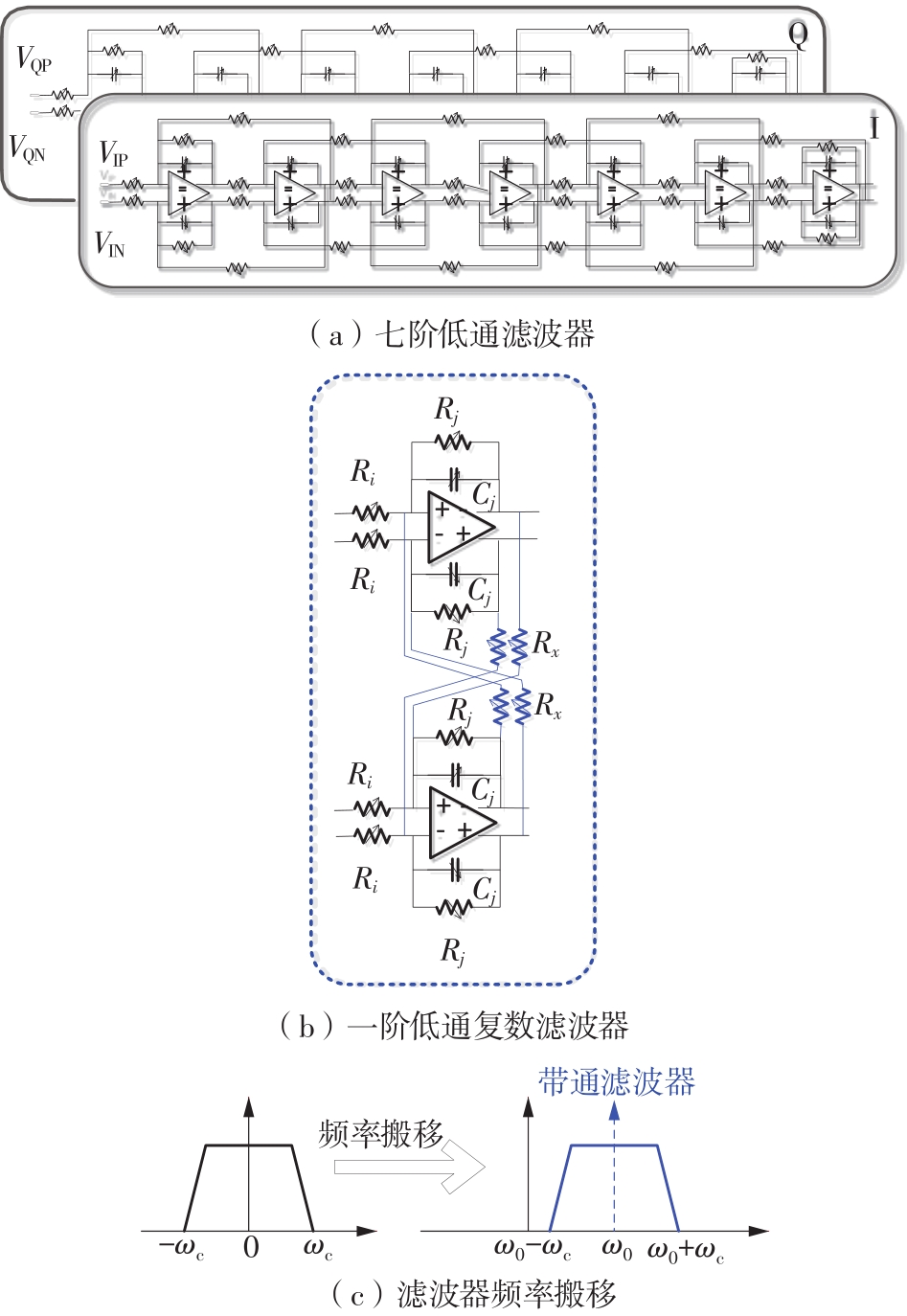
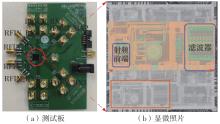
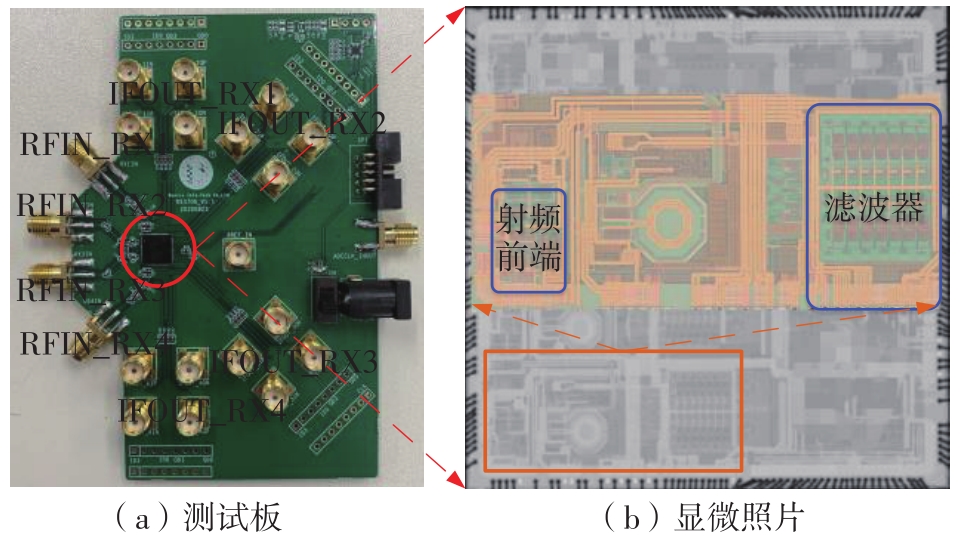
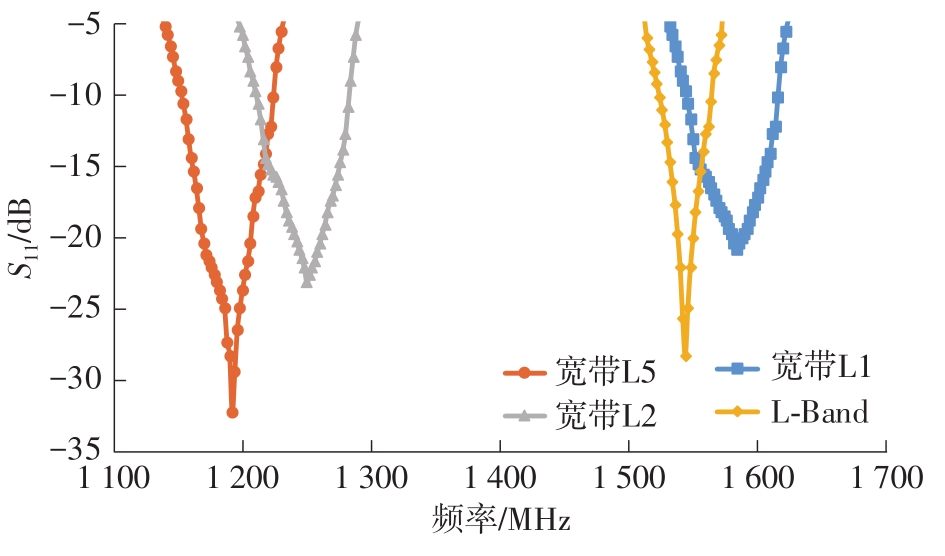
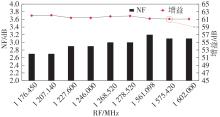
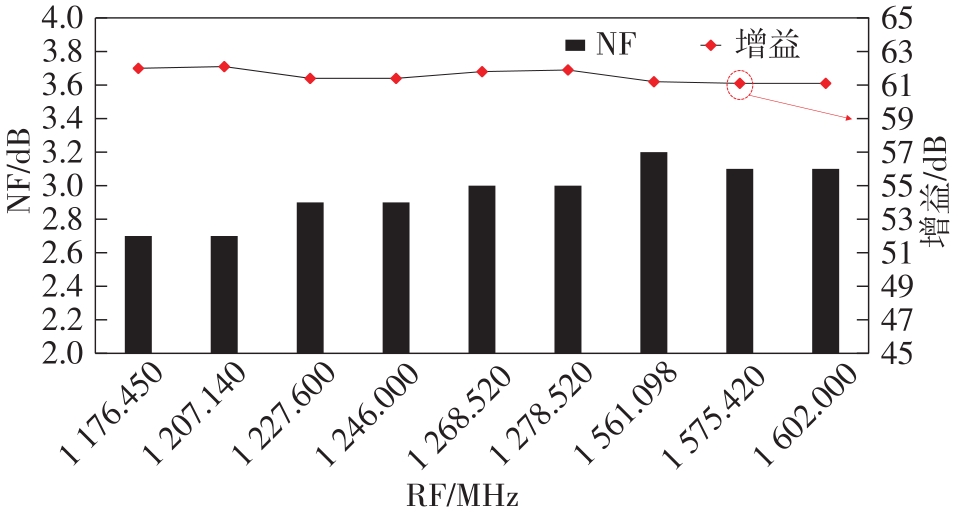
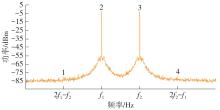
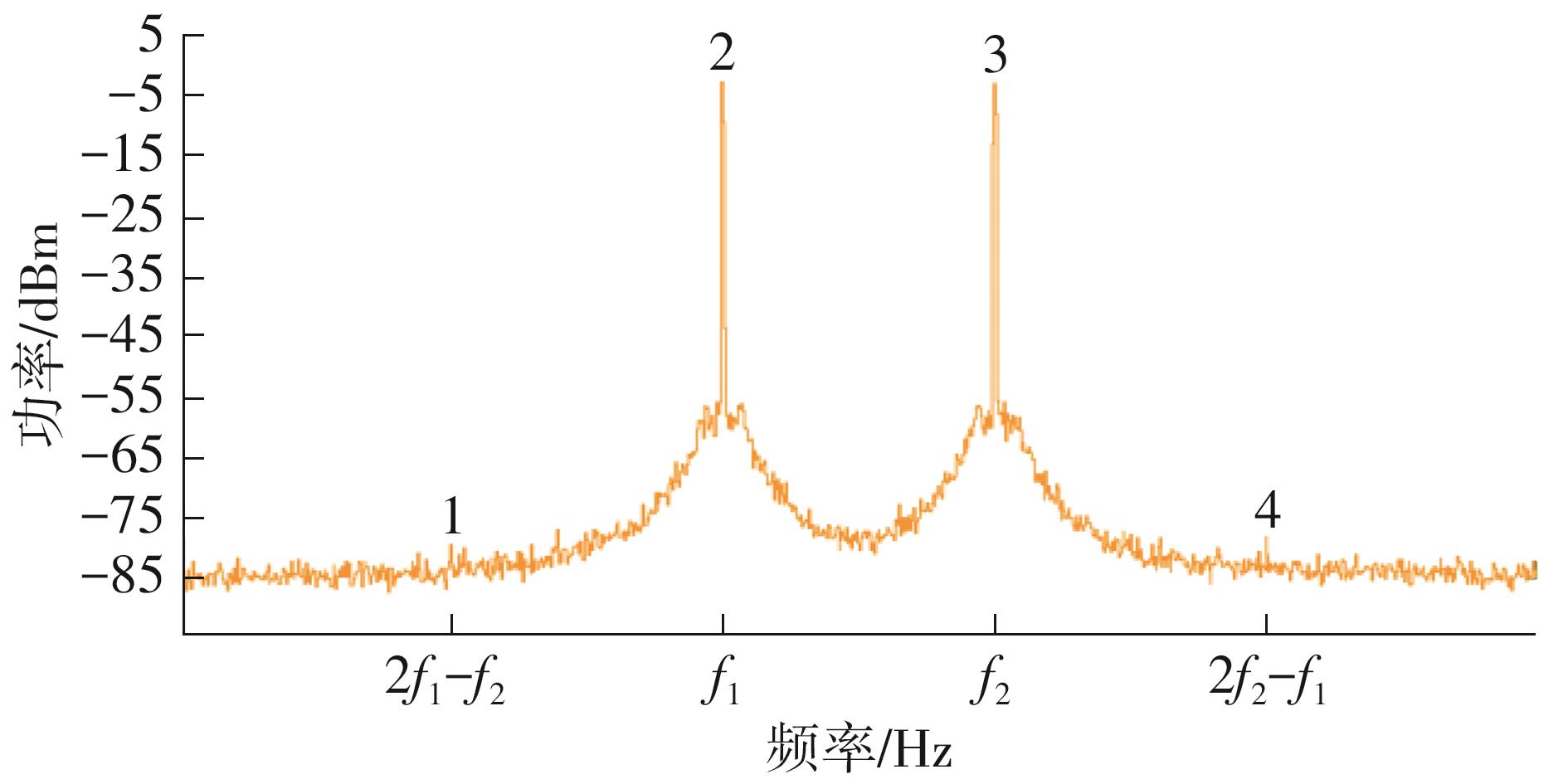
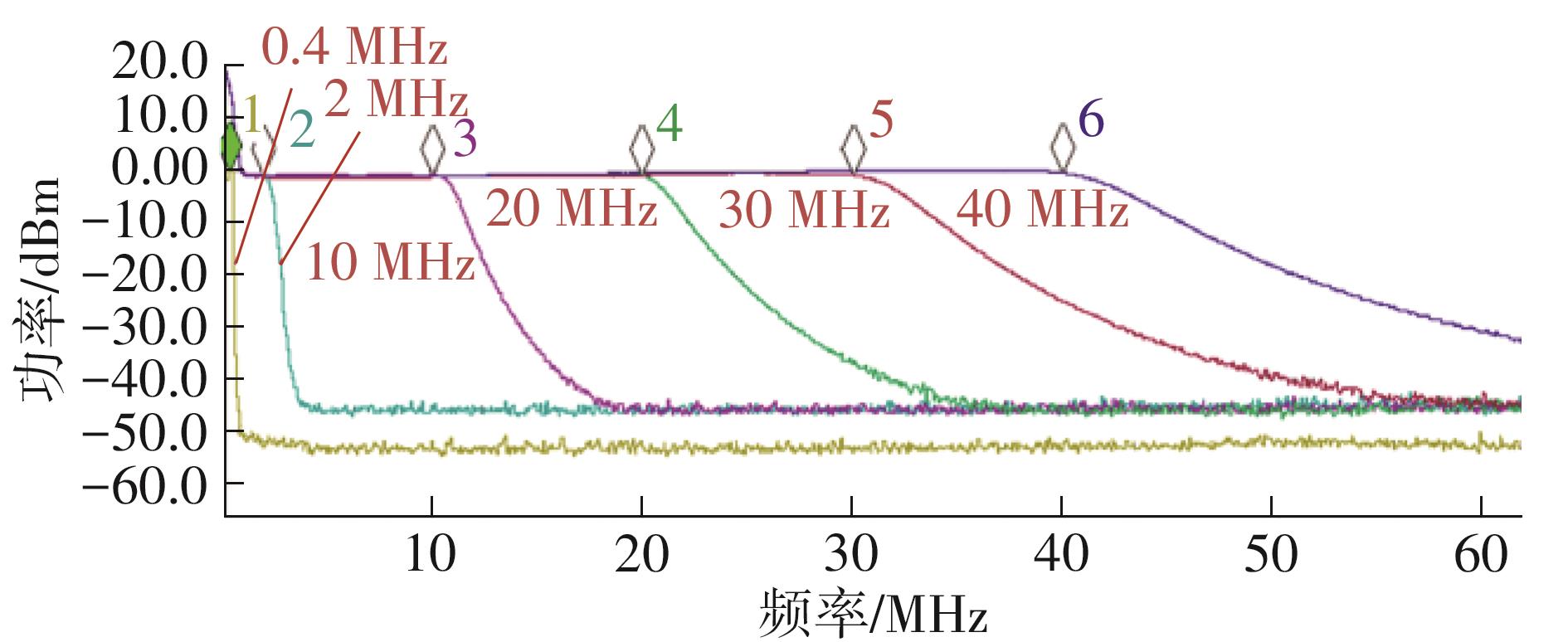
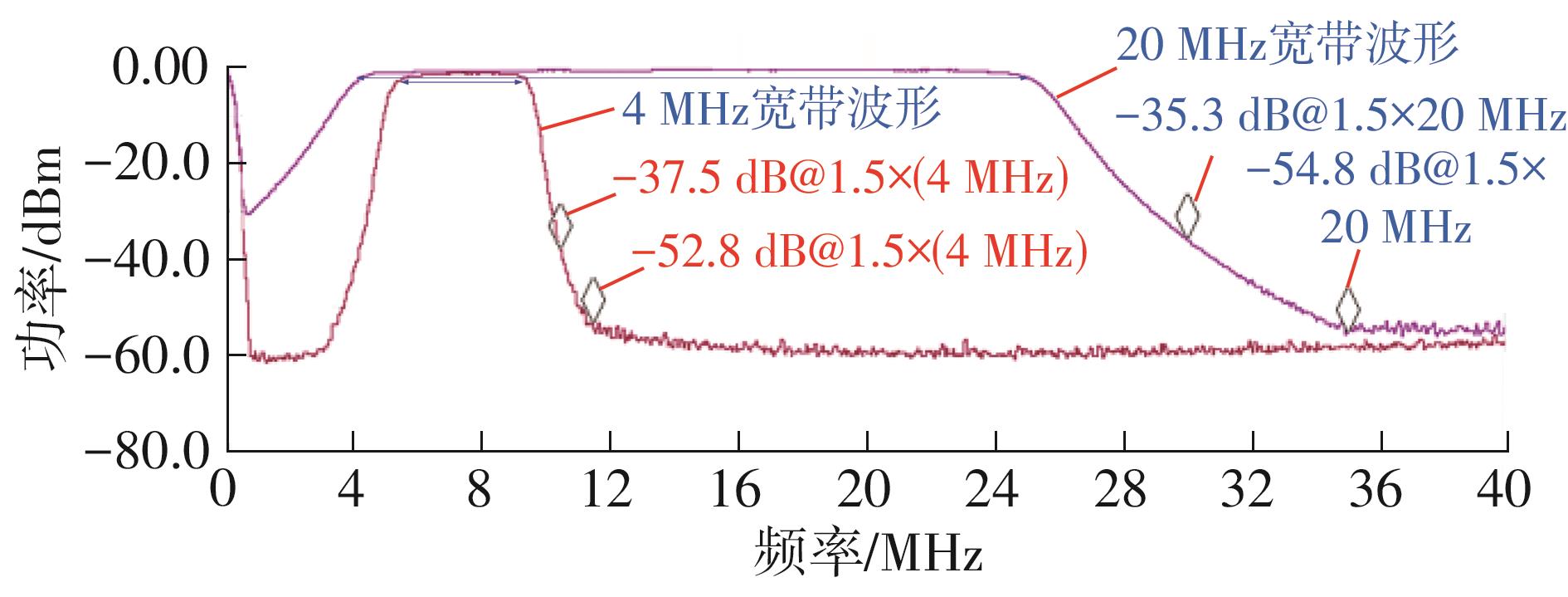
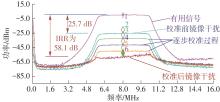
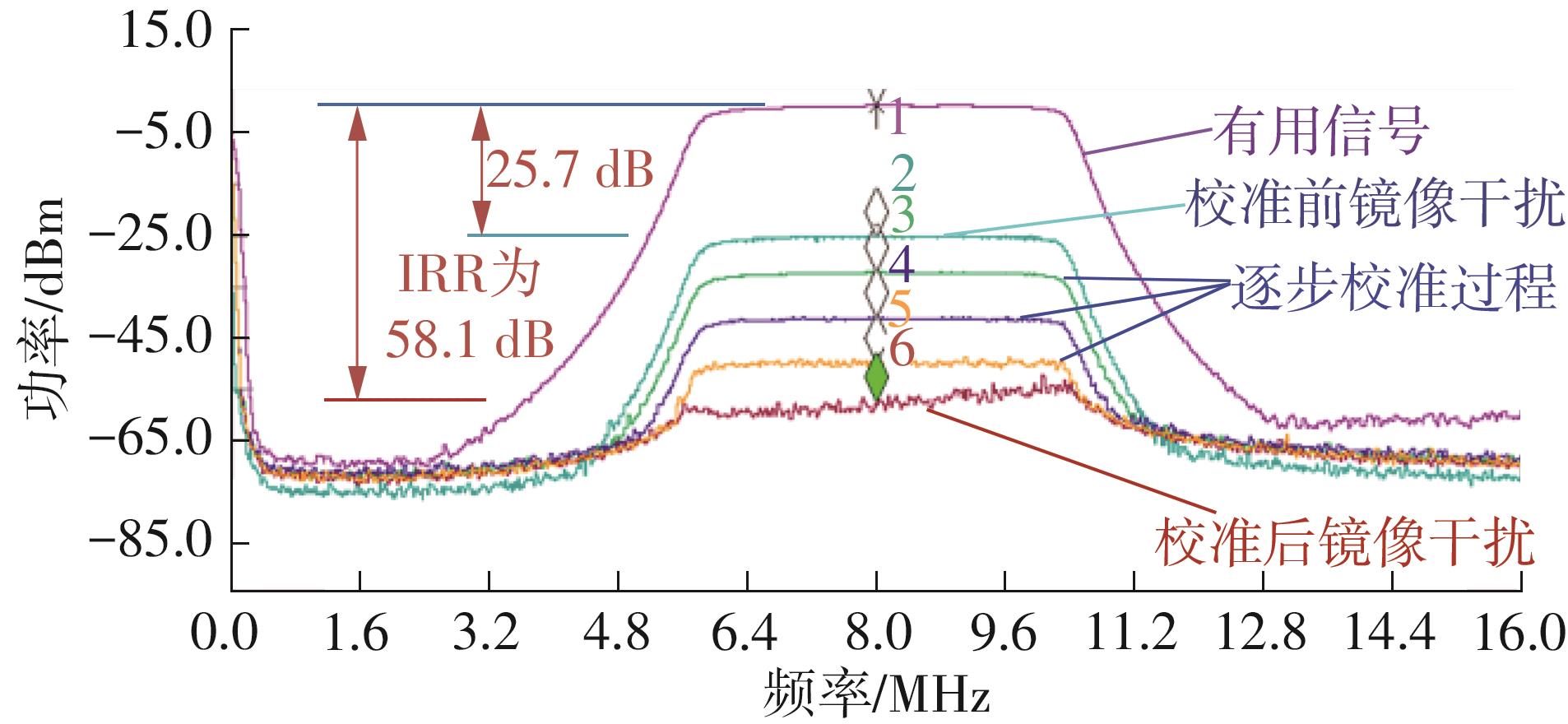
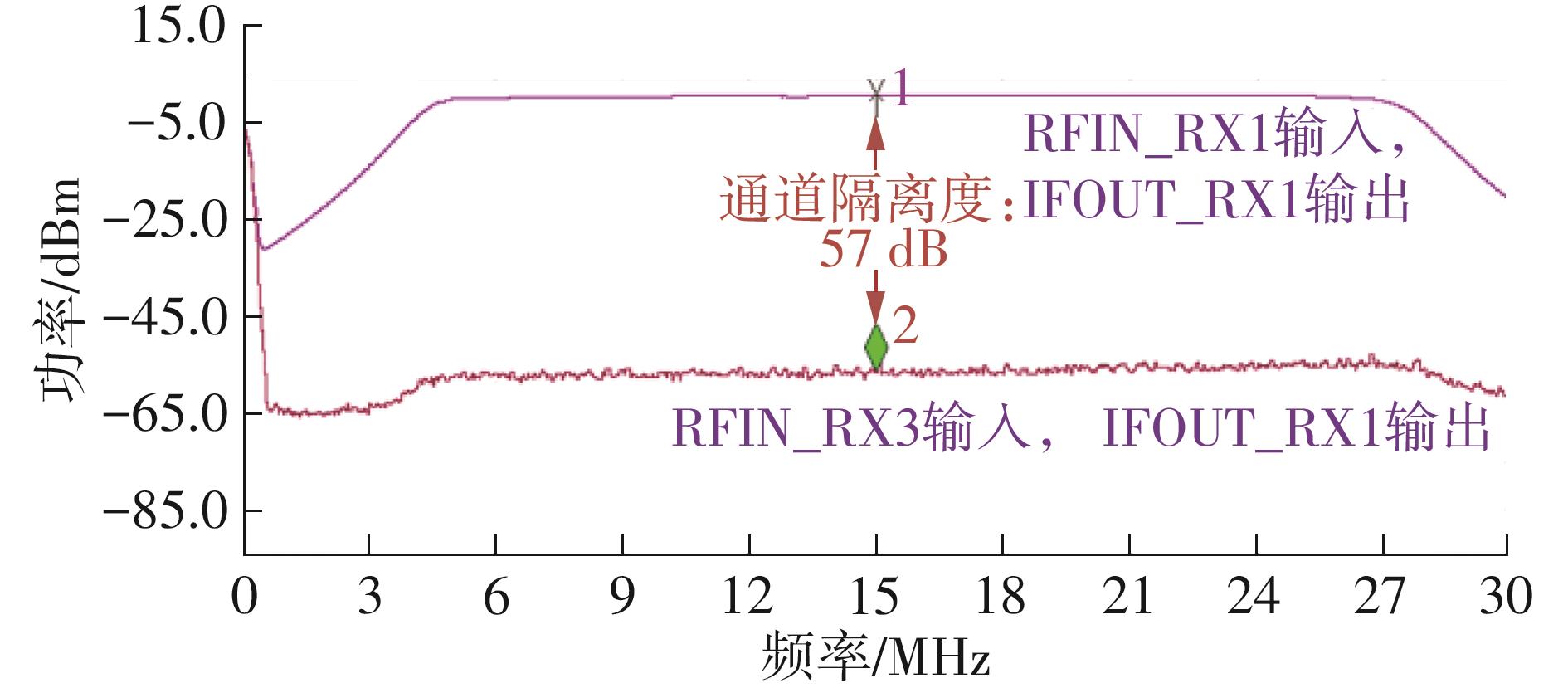
针对卫星导航高精度定位定向射频(RF)接收机面临的需求种类多、体积大的问题,介绍一种应用于高精度定位定向的高集成可重构全球导航卫星系统(GNSS)射频接收机。通过采用集成四个可重构接收通道的架构,并行接收全频段GNSS信号的方法,实现了单芯片支持高精度定位或定向应用,显著降低了导航终端的体积和成本。为改善宽带信号接收,提出了一种新型无电感的高线性低噪声跨导放大器(LNTA),消除了源极电感和负载电感的使用,减少工作在不同频点导航信号时的增益和噪声波动,有利于多模多频接收的重构和降低LNTA的功耗;针对IQ相位不平衡问题,提出了一种新型的补偿方法,直接在二分频电路的钟控锁存器通路上设计阻抗可变的可编程开关阵列,通过改变25%占空比正交本振的延迟时间实现相应支路输出本振相位调整,实现了IQ不平衡的校准,提升了射频接收机的镜像抑制和处理镜像干扰的能力。测试数据表明,射频接收机实现了1.15~1.65 GHz的GNSS全频段信号覆盖,2.7 dB的最小噪声系数(NF),34.7 dBm的输出三阶交调截点功率。采用低中频、零中频可重构的架构,可灵活接收0.8~80 MHz带宽的多模GNSS信号。通过IQ不平衡补偿和通道版图布局改进,实现了58.1 dB的镜像抑制(IRR)和57 dB的通道隔离度,可有效降低镜像干扰和通道间干扰的影响。在1.2 V供电下接收通道功耗仅24.7 mW,可满足高精度定位定向GNSS射频接收机的高集成和多样化应用需求。
中图分类号: