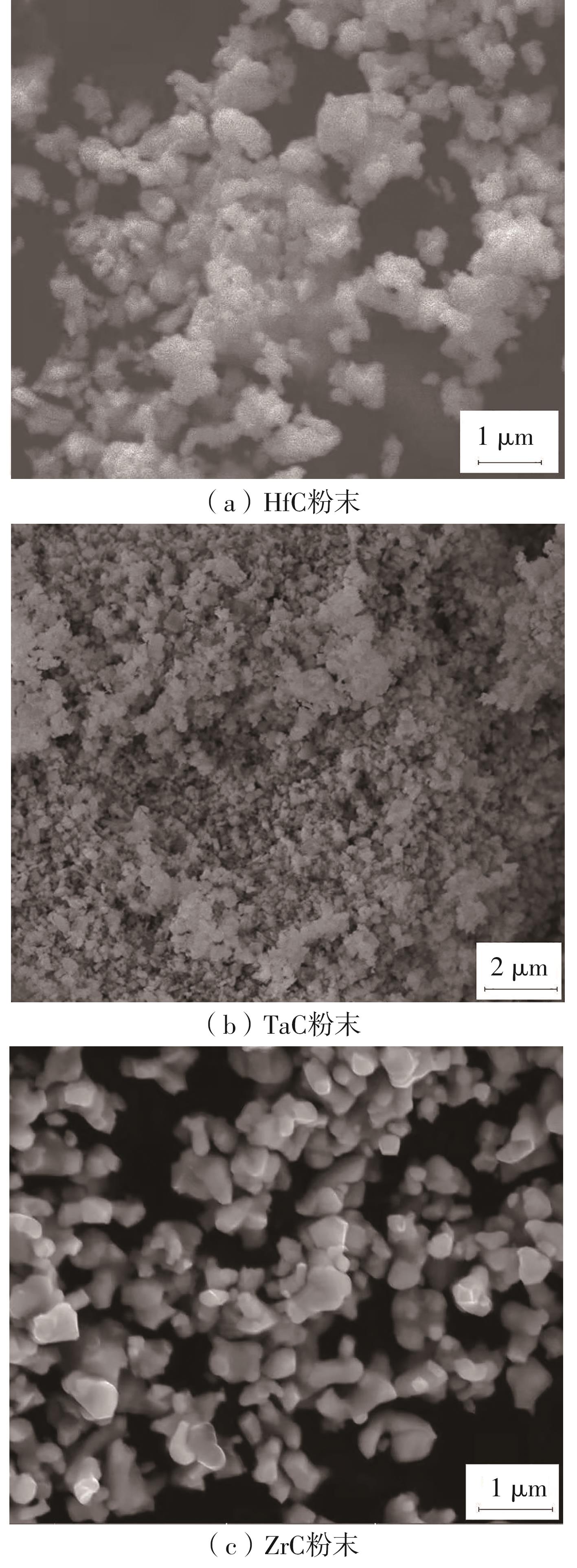
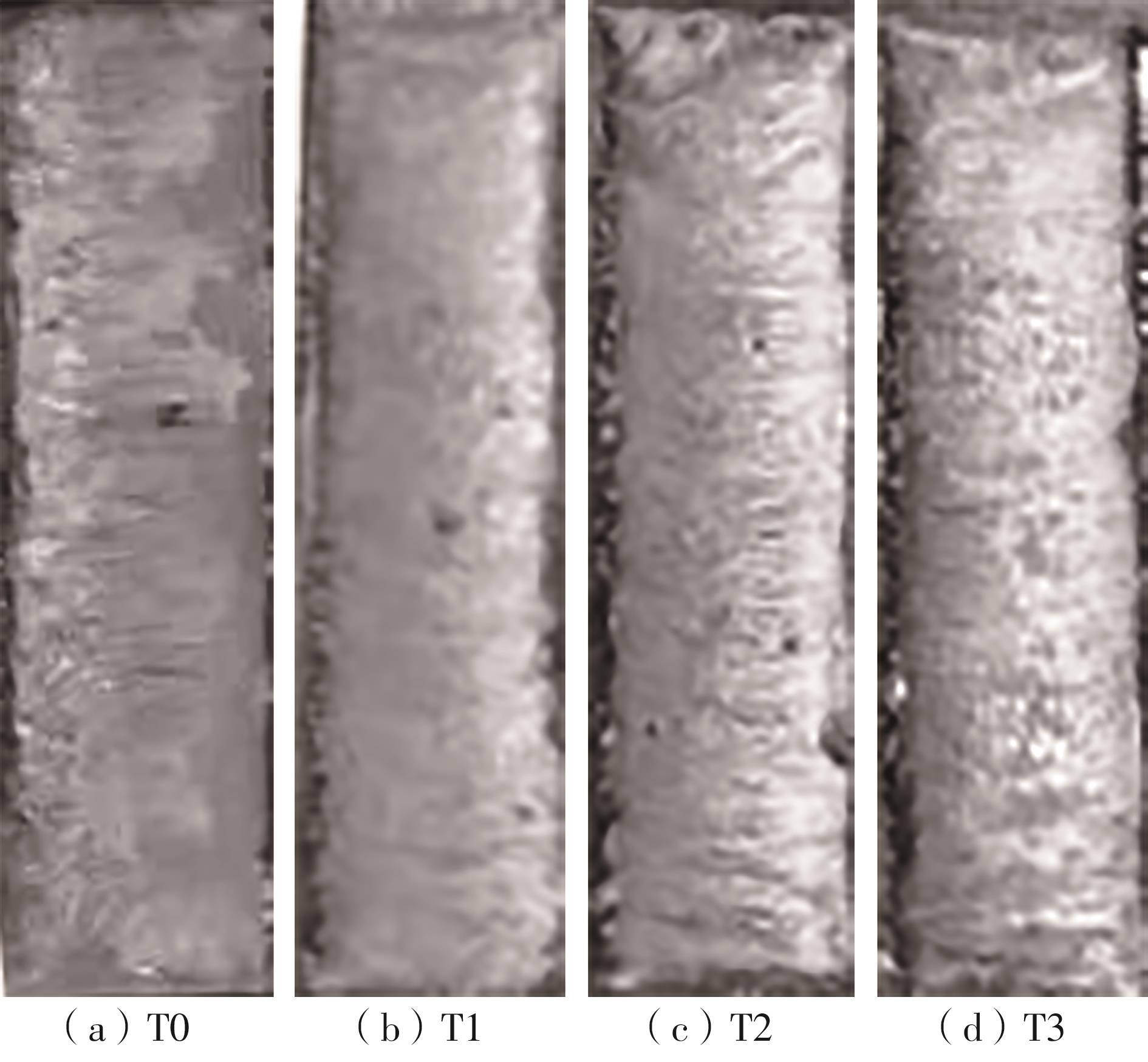
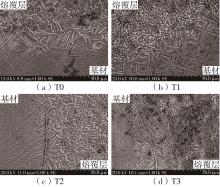
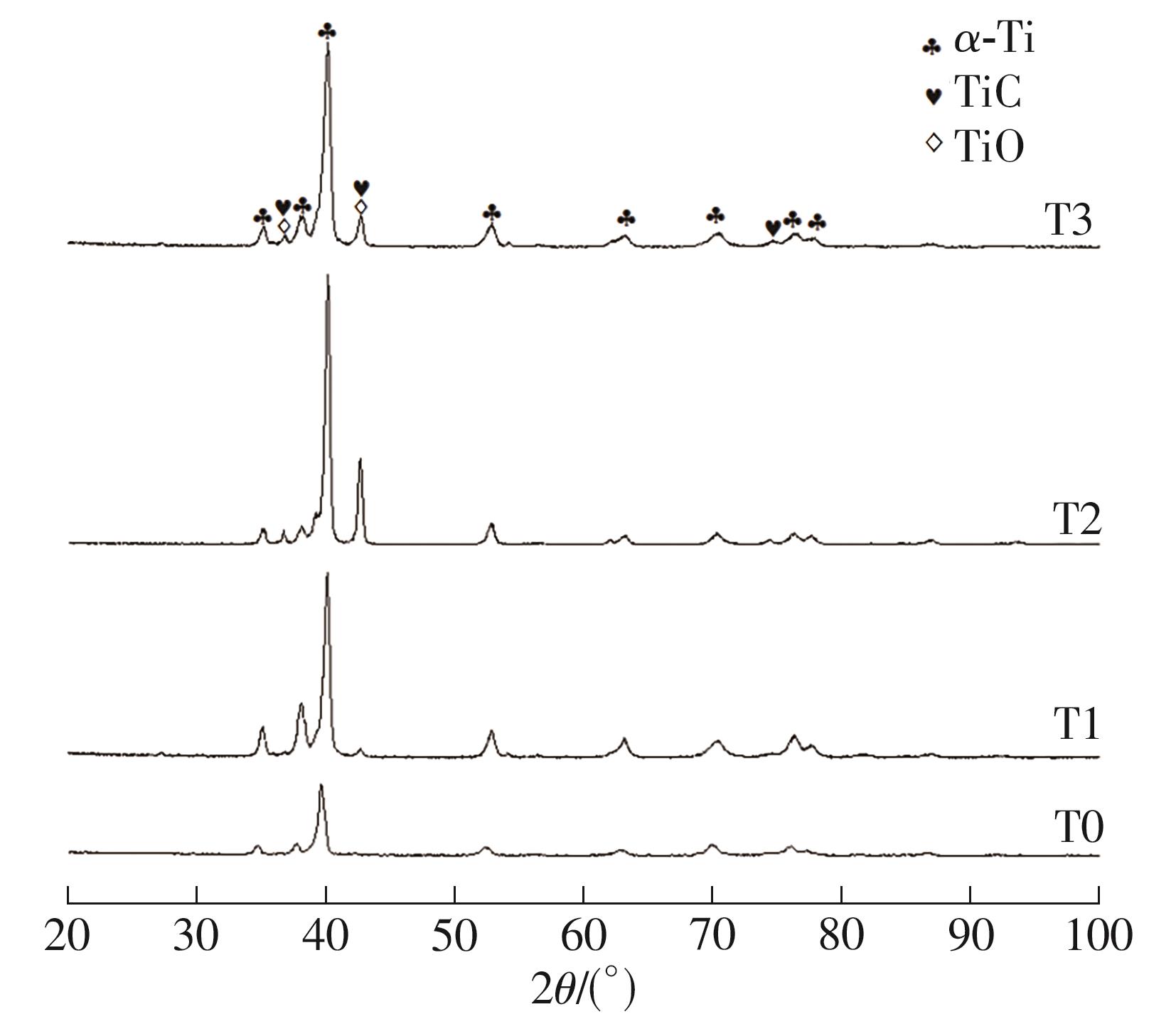
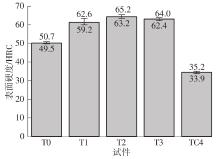
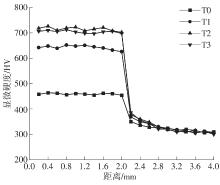
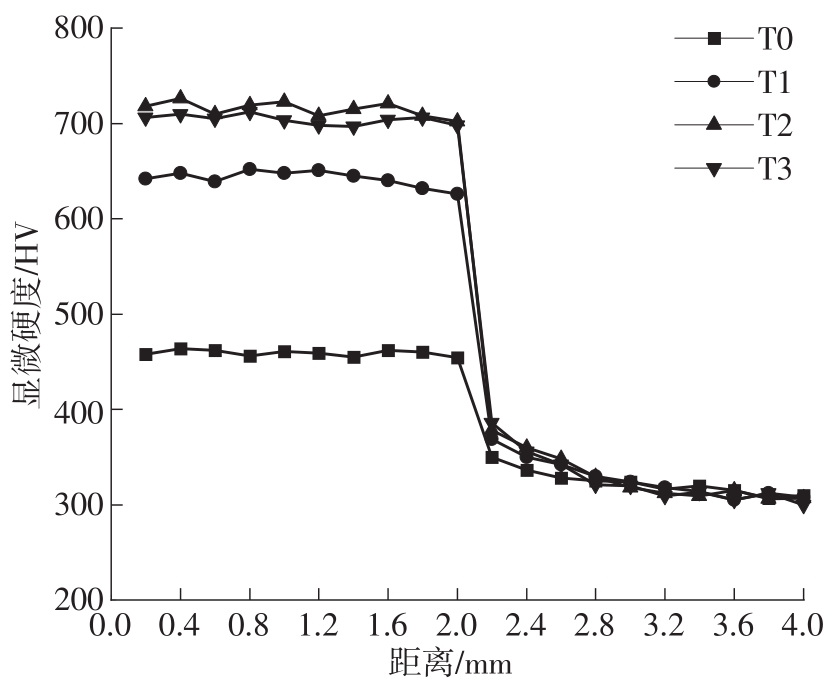
| 1 |
赵永庆,葛鹏,辛社伟 .近五年钛合金材料研发进展[J].中国材料进展,2020,39(Z1):527-534,557-558.
|
|
ZHAO Yongqing, GE Peng, XIN Shewei .Progresses of R&D on Ti-alloy materials in recent 5 years [J].Materials China,2020,39(Z1):527-534,557-558.
|
| 2 |
覃鑫,祁文军,左小刚 .TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆 NiCrCoAlY-Cr3C2复合涂层的摩擦和高温抗氧化性能[J].材料工程,2021,49(12):107-114.
|
|
QIN Xin, QI Wenjun, ZUO Xiaogang .Friction and high temperature oxidation resistance of laser cladding NiCrCoAlY-Cr3C2 composite coating on TC4 titanium alloy [J].Journal of Materials Engineering,2021,49(12):107-114.
|
| 3 |
LIU Y, LIANG C P, LIU W S .Dilution of Al and V through laser powder deposition enables a continuously compositionally Ti/Ti6Al4V graded structure [J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2018,763:376-383.
|
| 4 |
孟祥军,沈颖,张少瑜,等 .Ti6Al4V合金激光熔覆Co-Ti3SiC2复合涂层的组织和摩擦学性能[J].金属热处理,2021,46(12):199-203.
|
|
MENG Xangjun, SHEN Ying, ZHANG Shaoyu,et al .Microstructure and tribological properties of laser clad Co-Ti3SiC2 composite coating on Ti6Al4V alloy [J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2021,46(12):199- 203.
|
| 5 |
柯金,刘秀波,庄宿国,等 .Ti6Al4V合金激光熔覆NiMoSi复合涂层的高温抗氧化性能[J].中国表面工程,2018,31(6):109-117.
|
|
KE Jin, LIU Xiubo, ZHUANG Suguo,et al .High temperature oxidation resistance of NiMoSi composite coatings on Ti6AI4V alloy by laser cladding [J].China Surface Engineering,2018,31(6):109-117.
|
| 6 |
王涛,刘佳奇,秦令超 .激光功率对CoNiCrAlY熔 覆涂层显微组织及硬度的影响[J].热加工工艺,2018,47(24):142-145,151.
|
|
WANG Tao,LIU Jiaqi,QIN Lingchao,Effects of laser power on microstructure and hardness of CoNiCrAlY cladding coatings [J].Hot Working Technology,2018,47(24):142-145,151.
|
| 7 |
林英华,雷永平,符寒光,等 .激光原位制备硼化钛与镍钛合金增强钛基复合涂层[J].金属学报,2014,50(12):1513-1519.
|
|
LIN Yinghua, LEI Yongping, FU Hanguang,et al .Laser in-situ synthessized titanium diboride and nitinol reinforce titanium matrix composite coatings [J].Acta Metallurgica Sinica,2014,50(12):1513-1519.
|
| 8 |
ZHANG Q, ZHANG P L, LI M H,et al .Microstructure wear resistanceand oxidation behavior of Ni-Ti-Si coatings fabricated on Ti6Al4V by laser cladding [J].Materials,2017,10(11):1248-1250.
|
| 9 |
FENG Y Q, FENG K, TAO C W,et al .Microstructure and properties of in-situ synthesized (Ti3Al+TiB)/Ti composites by laser cladding [J].Materials & Design,2018,157:258-272.
|
| 10 |
林基辉,温亚辉,范文博,等 .钛合金表面激光改性技术研究进展[J].金属热处理,2022,47(3):215-221.
|
|
LIN Jihui, WEN Yahui, FAN Wenbo,et al .Research progress of laser modification technology for titanium alloy surface [J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2022,47(3):215-221.
|
| 11 |
LI J N, CHEN C Z, ZONG L .Microstructure characteristics of Ti3Al/TiC ceramic layer deposited by laser cladding[J].International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2011,29(1):49-53.
|
| 12 |
LI J, CHEN C, SQUARTINI T,et al .A study on wear resistance and microcrack of the Ti3Al/TiAl+TiC ceramic layer deposited by laser cladding on Ti-6Al-4V Alloy [J].Applied Surface Science,2010,257(5):1550-1555.
|
| 13 |
GAO Q S, YAN H, QIN Y, al et,Laser cladding Ti-Ni/TiN/TiW+TiS/WS self-lubricating wear resistant composite coating on Ti-6Al-4V alloy [J].Optics & Laser Technology,2019,113:182-191.
|
| 14 |
SONG R, LI J, SHAO J Z,et al .Microstructural evolution and wear behaviors of laser cladding Ti2Ni/α(Ti) dual-phase coating reinforced by TiB and TiC [J].Applied Surface Science,2015,355:298-309.
|
| 15 |
孙帅,李崇桂,李帅,等 .WC含量对激光熔覆Al2O3/TiO2涂层组织与性能的影响[J].金属热处理,2018,43(12):78-82.
|
|
SUN Shuai, LI Chonggui, LI Shuai,et al .Effect of WC content on microstructure and properties of laser cladding Al2O3/TiO2 coating [J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2018,43(12):78-82.
|
| 16 |
唐友亮,蔡维平,张锦 .激光熔覆TiC-WC增强NiCrMn合金涂层组织与性能[J].热加工工艺,2017,46(16):152-157.
|
|
TANG Youling, CAI Weiping, ZHANG Jin .Microstructure and property of laser cladding NiCrMn alloy coating reinforced by TiC-WC [J].Hot Working Technology.2017,46(16):152-157.
|
| 17 |
ZHOU S, LEI J, DAI X,et al .A comparative study of the tructure and wear resistance of NiCrBSi/50 wt% WC composite coatings by laser cladding and laser induction hybrid cladding [J].International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2016,60:17-27.
|
| 18 |
LUO X, LI J, LI G J .Effect of NiCrBSi content on microstructural evolution,cracking susceptibility and wear behaviors of laser cladding WC/Ni-NiCrBSi composite coatings [J].Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2015,626:102-111.
|
| 19 |
张海云,张金,朱磊,等 .WC含量对激光熔覆TC4涂层组织及性能的影响[J].热加工工艺,2022,51(8):83-87,93.
|
|
ZHANG Haiyun, ZHANG Jin, ZHU Lei,et al .Effects of WC content on microstructure and properties of TC4 composite prepared by laser cladding [J].Hot Working Technology,2022,51(8):83-87,93.
|
| 20 |
李蕊,王浩 .Ti811和TC4钛合金基材属性对激光熔 覆自润滑耐磨复合涂层组织与性能的影响[J].复合材料学报,2022,39(12):5984-5995.
|
|
LI Rui, WANG Hao. Effect of Ti811 and TC4 Titanium alloy substrate on microstructures and properties of laser cladding self-lubricating composite coatings [J].Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(12):5984-5995.
|
| 21 |
刘丹,陈志勇,陈科培,等 .TC4钛合金表面激光熔覆复合涂层的组织和耐磨性[J].金属热处理,2015,40(3):58-62.
|
|
LIU Dan, CHEN Zhiyong, CHEN Kepei,et al .Microstructure and wear resistance of laser clad composite coating on TC4 titanium alloy surface [J].Heat Treatment of Metals,2015,40(3):58-62.
|
| 22 |
孙荣禄,杨贤金 .激光熔覆TiC陶瓷涂层的组织和摩擦磨损性能研究[J].光学技术,2006,32(2):287-289.
|
|
SUN Ronglu, YANG Xianjin .Microstructure and friction wear properties of TiC laser clad layer [J].Optical Technique,2006,32(2):287-289.
|