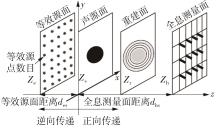
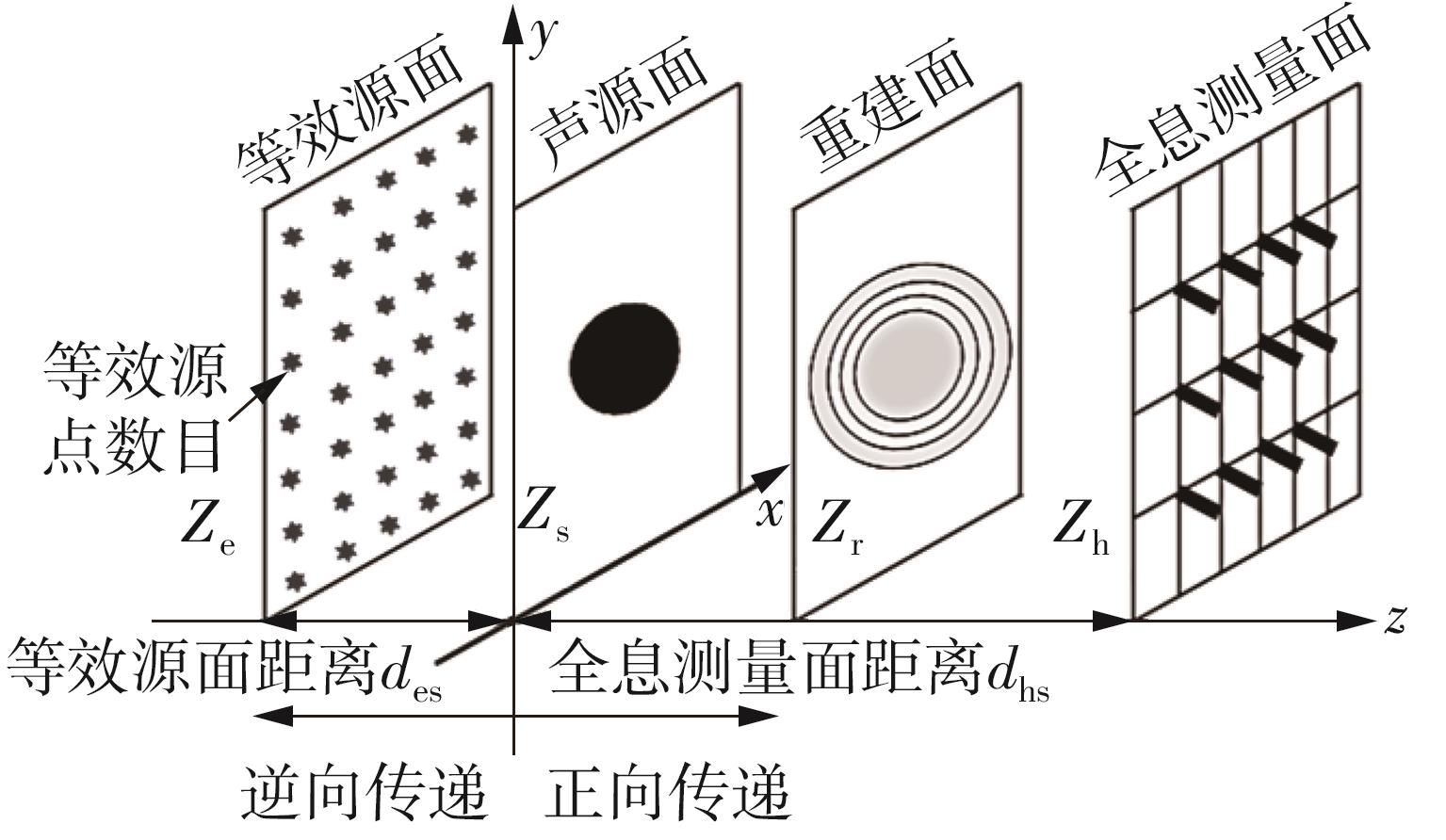
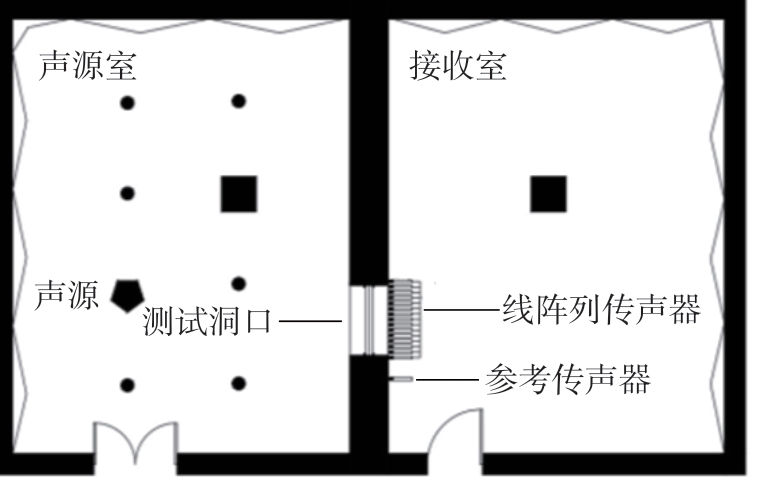
| 1 |
KYLLIÄINEN M, TALUS L, LIETZÉN J,et al .Assessment of the low frequency procedure in the field measurements of impact sound insulation between dwellings [J].Applied Acoustics,2022,185:1083992/1-7.
|
| 2 |
周广林,陈剑,毕传兴,等 .双传声器声强测量系统误差分析与不确定度评定[J].农业机械学报,2003,34(5):126-129,122.
|
|
ZHOU Guanglin, CHEN Jian, BI Chuanxing,et al .Error analysis and evaluation of uncertainty of a two-microphone sound intensity measurement system[J].Transactions of the Chinese Society for Agricultural Machinery,2003,34(5):126-129,122.
|
| 3 |
SHI T Y, BOLTON J S, THOR W .Acoustic far-field prediction based on near-field measurements by using several different holography algorithms[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,2022,151(3):2171-2180.
|
| 4 |
CHARDON G, DAUDET L, PEILLOT A,et al .Near-field acoustic holography using sparse regularization and compressive sampling principles[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,2012,132(3):1521-1534.
|
| 5 |
侯俊剑,张玉琦,房占鹏 .利用3维声场空间特征诊断轴承故障[J].振动、测试与诊断,2021,41(5):933-938,1034.
|
|
HOU Junjian, ZHANG Yuqi, FANG Zhanpeng .Diagnosing bearing faults using spatial features of three-dimensional sound field[J].Journal of Vibration,Measurement & Diagnosis,2021,41(5):933-938,1034.
|
| 6 |
LEETE K M, GEE K L, LIU J H,et al .Near-field acoustical holography and acoustic power analysis of a simulated,highly heated supersonic jet[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,2022,151(3):1989-2001.
|
| 7 |
高塬,杨博全,郭强,等 .基于单元辐射叠加法的水下矩形板声场重建[J].哈尔滨工程大学学报,2024,45(5):922-929.
|
|
GAO Yuan, YANG Boquan, GUO Qiang,et al .Sound field reconstruction of an underwater rectangular plate based on element radiation superposition method[J].Journal of Harbin Engineering University,2024,45(5):922-929.
|
| 8 |
王红卫,熊威,王翘楚,等 .联合扩散场激励与近场声全息重建的建筑构件隔声测量方法[J].声学学报,2023,48(5):1021-1035.
|
|
WANG Hongwei, XIONG Wei, WANG Qiaochu,et al .Sound insulation measurement of building components combining diffuse acoustic field excitation and near-field acoustic holography reconstruction[J].Acta Acustica,2023,48(5):1021-1035.
|
| 9 |
CHAITANYA S K, SRIRAMAN S, SRINIVASAN S,et al .Machine learning aided near-field acoustic holography based on equivalent source method[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,2023,153(2):940-951.
|
| 10 |
JING W Q, LIU G S .Compressive equivalent source method based on particle velocity measurements for near-field acoustic holography[J].Measurement and Control,2023,56(7/8):1471-1482.
|
| 11 |
李冰茹,王宣银,葛辉良 .圆柱壳体近场辐射噪声预报与实验研究[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2010,44(3):563-568.
|
|
LI Bingru, WANG Xuanyin, GE Huiliang .Prediction and experiment for near field sound radiation of cylindrical shells[J].Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2010,44(3):563-568.
|
| 12 |
赵玉贵 .联合等效声源与近场声全息的声场重构插值方法研究[D].青岛:青岛理工大学,2019.
|
| 13 |
魏晟弘,伍松,郑贤 .压缩感知等效源法近场声全息关键参数选取[J].广西科技大学学报,2021,32(4):50-57.
|
|
WEI Shenghong, WU Song, ZHENG Xian .Research on key parameters selection of near field acoustic holography based on compressed sensing equivalent source method[J].Journal of Guangxi University of Science and Technology,2021,32(4):50-57.
|
| 14 |
魏富康 .基于等效源法的封闭空间近场声全息技术研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工程大学,2022.
|
| 15 |
胡博,杨德森,时胜国,等 .水中运动声源的声全息参数选取研究[J].机械工程学报,2011,47(18):15-22.
|
|
HU Bo, YANG Desen, SHI Shengguo,et al. Investigations on parameter selection of acoustic holography of underwater moving noise sources[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2011,47(18):15-22.
|
| 16 |
熊威,王红卫,张光耀 .建筑构件隔声现场测量的近场声全息方法及其应用研究[J].建筑科学,2023,39(6):32-39.
|
|
XIONG Wei, WANG Hongwei, ZHANG Guangyao .Study on near-field acoustic holography method and its application in field measurement of sound insulation of building components[J].Building Science,2023,39(6):32-39.
|
| 17 |
熊威,王红卫,张光耀,等 .近场声全息隔声测量技术重建参数的选取[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(5):109-117.
|
|
XIONG Wei, WANG Hongwei, ZHANG Guangyao,et al .Selection of reconstruction parameters for sound insulation measurement based on near-field acoustic holography[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(5):109-117.
|
| 18 |
声学 建筑和建筑构件隔声测量 第3部分:建筑构件空气声隔声的实验室测量: [S].
|
| 19 |
熊威 .基于近场声全息的建筑构件空气声隔声测量方法研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2022.
|
| 20 |
KOOPMANN G H, SONG L M, FAHNLINE J B .A method for computing acoustic fields based on the principle of wave superposition[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,1989,86(6):2433-2438.
|
| 21 |
张永斌 .基于等效源法和质点振速测量的近场声全息技术[D].合肥:合肥工业大学,2010.
|
| 22 |
UOSUKAINEN S .On the use of the waterhouse correction[J].Journal of Sound and Vibration,1995,186(2):223-230.
|
| 23 |
SONG L M, KOOPMANN G H, FAHNLINE J B .Numerical errors associated with the superposition method for computing acoustic fields[J].The Journal of the Acoustical Society of America,1991,89(6):2625-2633.
|
 ), 张光耀1, 沈涛3(
), 张光耀1, 沈涛3( ), 李淑洁1, 杨晨曦1, 张阳1
), 李淑洁1, 杨晨曦1, 张阳1
 ), ZHANG Guangyao1, SHEN Tao3(
), ZHANG Guangyao1, SHEN Tao3( ), LI Shujie1, YANG Chenxi1, ZHANG Yang1
), LI Shujie1, YANG Chenxi1, ZHANG Yang1