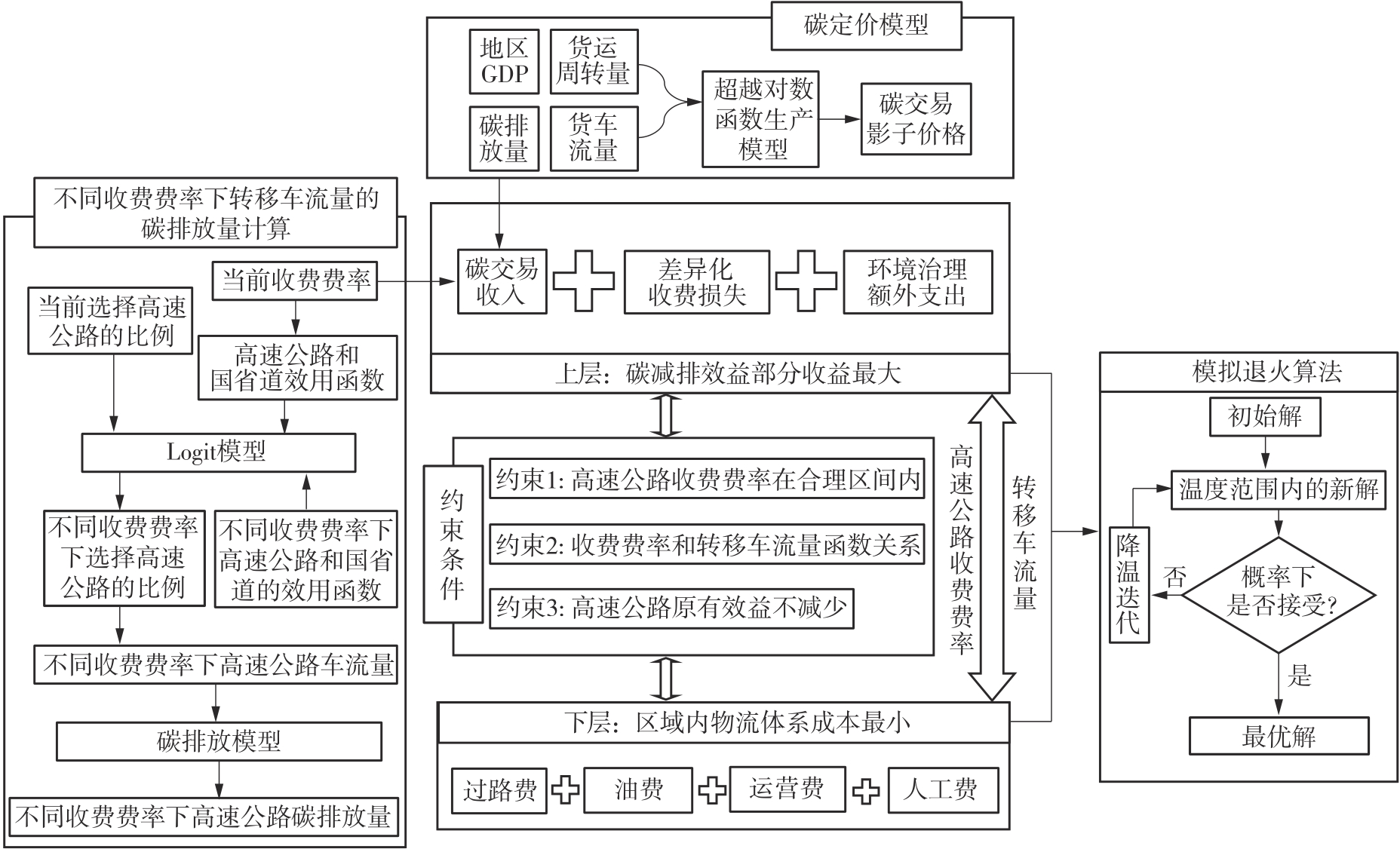
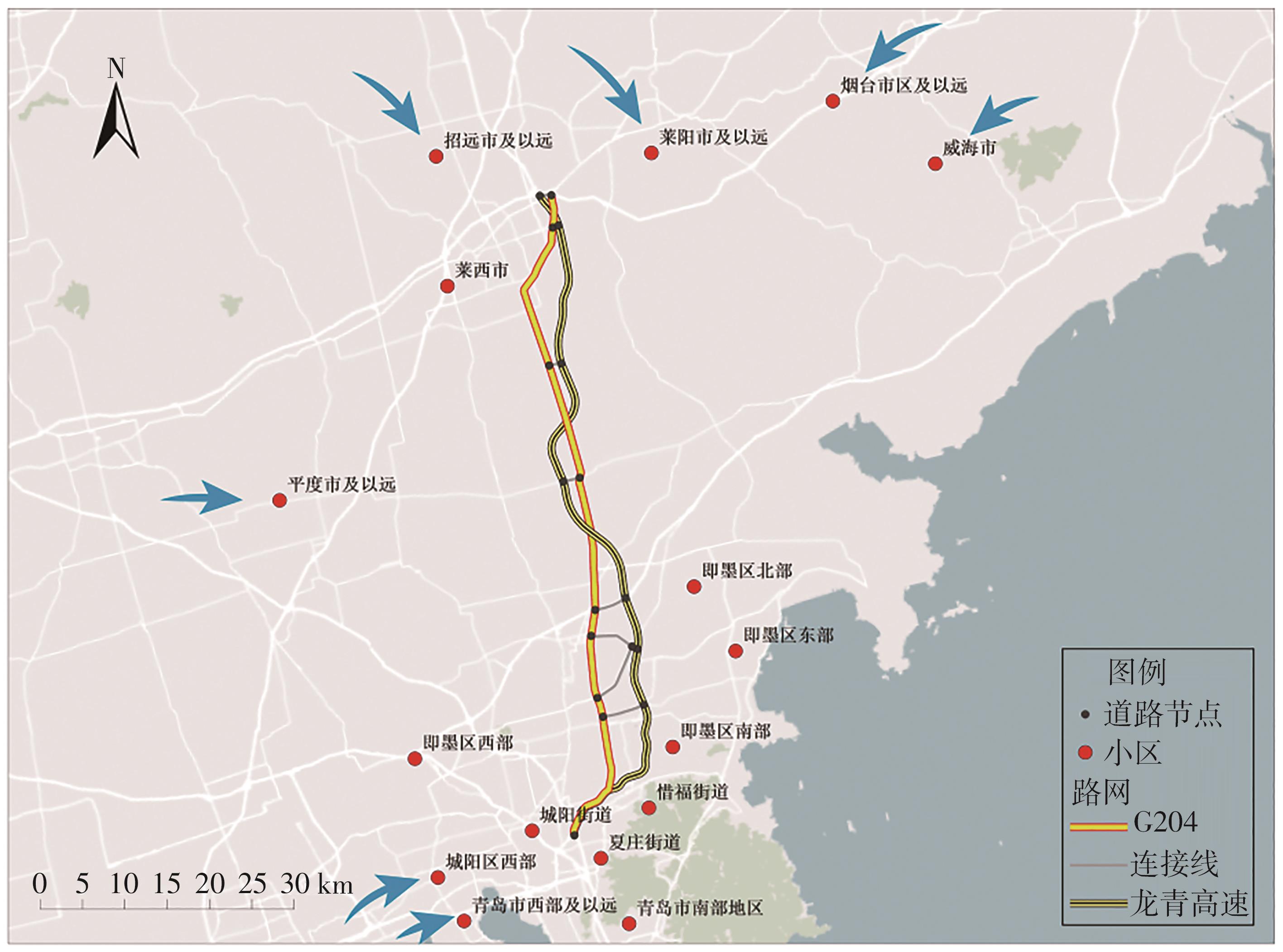
| 1 |
马明娟,李强,殷文琦,等 .碳中和目标下基于GA-BP神经网络的碳交易定价模型及其模拟研究[J].生态经济,2022,38(3):40-46.
|
|
MA Mingjuan, LI Qiang, YIN Wenqi,et al .The study of carbon trading pricing model based on GA-BP neural network and its simulation under the goal of carbon neutrality[J].Ecological Economy,2022,38(3):40-46.
|
| 2 |
ZOU J, CHEN P, FU X,et al .Does carbon trading affect the bond spread of high-carbon enterprises?:evidence from China[J].Journal of Cleaner Production,2023,417:137882/1-11.
|
| 3 |
梁喜,阮实惠 .基于影子价格下的城市交通运输系统碳交易货币化方法研究[J].公路,2016,61(3):115-120.
|
|
LIANG Xi, RUAN Shi-hui .Research on method of carbon trading currency in city transport system based on shadow price[J].Highway,2016,61(3):115-120.
|
| 4 |
关晓轲 .基于灰色理论的碳市场交易价格预测研究[D].成都:西南交通大学,2016.
|
| 5 |
周正骏 .国内外碳排放权交易价格影响因素比较研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学,2016.
|
| 6 |
PIGOU A C .The economics of welfare[M].London:Macmillan,1920.
|
| 7 |
HENDERSON J V .Road congestion:a reconsideration of pricing theory[J].Journal of Urban Economics,1974,1(3):346-365.
|
| 8 |
肖清榆,袁振洲,吴玥琳,等 .差异化收费条件下的货车出行行为研究[J].交通信息与安全,2019,37(5):133-140.
|
|
XIAO Qingyu, YUAN Zhenzhou, WU Yuelin,et al .A study on travel behaviors of trucks under differentiated charge[J].Journal of Traffic Information and Safety,2019,37(5):133-140.
|
| 9 |
曹一铄 .高速公路货车差异化收费定价策略研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学,2022.
|
| 10 |
李凯新 .基于碳减排收益的高速公路差异化收费定价研究[D].北京:北京交通大学,2023.
|
| 11 |
温惠英,靳文舟,桂寿平 .货物运输与物流[J].华南理工大学学报(社会科学版),2001,3(3):19-22.
|
|
WEN Huiying, JIN Wenzhou, GUI Shouping .Freight transportation and logistics[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Social Science Edition),2001,3(3):19-22.
|
| 12 |
CHANG T H, TSENG J S, HSIEH T H,et al .Green transportation implementation through distance-based road pricing[J].Transportation Research Part A:Policy and Practice,2018,111:53-64.
|
| 13 |
PERERA L, THOMPSON R G, WU W .A multi-class toll-based approach to reduce total emissions on roads for sustainable urban transportation[J].Sustai-nable Cities and Society,2020,63:102435/1-16.
|
| 14 |
交通运输部 .2020年交通运输行业发展统计公报[J].交通财会,2021(6):92-97.
|
|
Department Transportation .Statistical bulletin of transportation industry development in 2020[J].Finance & Accounting for Communications,2021(6):92-97.
|
| 15 |
蒋斌 .JXD物流公司运输成本控制研究[D].咸阳:西北农林科技大学,2020.
|
| 16 |
王爽,赵鹏 .基于Logit模型的客运专线旅客选择行为分析[J].铁道学报,2009,31(3):6-10.
|
|
WANG Shuang, ZHAO Peng .Analysis of passengers’choice behavior for dedicated passenger railway lines based on Logit model[J].Journal of the China Railway Society,2009,31(3):6-10.
|
| 17 |
林旭坤,张扬,罗芷晴,等 .高速公路网车辆碳排放测算方法研究[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(9):22-28.
|
|
LIN Xukun, ZHANG Yang, LUO Zhiqing,et al .Study on measuring method of vehicle carbon emission in expressway network[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(9):22-28.
|
| 18 |
阮实惠 .城市交通运输系统的碳排放交易货币化模型研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学,2017.
|
| 19 |
徐建闽,首艳芳,卢凯 .基于双层规划模型的交通信号区域协调控制[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2011,39(3):95-100,106.
|
|
XU Jian-min, SHOU Yan-fang, LU Kai .Area coordinated control of traffic signals based on bi-level programming model[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2011,39(3):95-100,106.
|
| 20 |
闫丹丹 .基于两部制的高速公路收费定价研究[D].昆明:昆明理工大学,2021.
|
| 21 |
张杰 .基于预售时段的高速铁路旅客票价差异化研究[D].兰州:兰州交通大学,2020.
|
| 22 |
刘明磊,朱磊,范英 .我国省级碳排放绩效评价及边际减排成本估计:基于非参数距离函数方法[J].中国软科学,2011(3):106-114.
|
|
LIU Ming-lei, ZHU Lei, FAN Ying .Evaluation of carbon emission performance and estimation of marginal CO2 abatement costs for provinces of China:a non-parametric distance function approach[J].China Soft Science,2011(3):106-114.
|
 ), LI Xiudong, SONG Zhifan, GUO Enyi
), LI Xiudong, SONG Zhifan, GUO Enyi