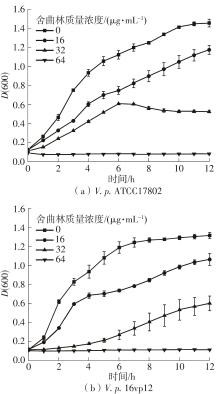
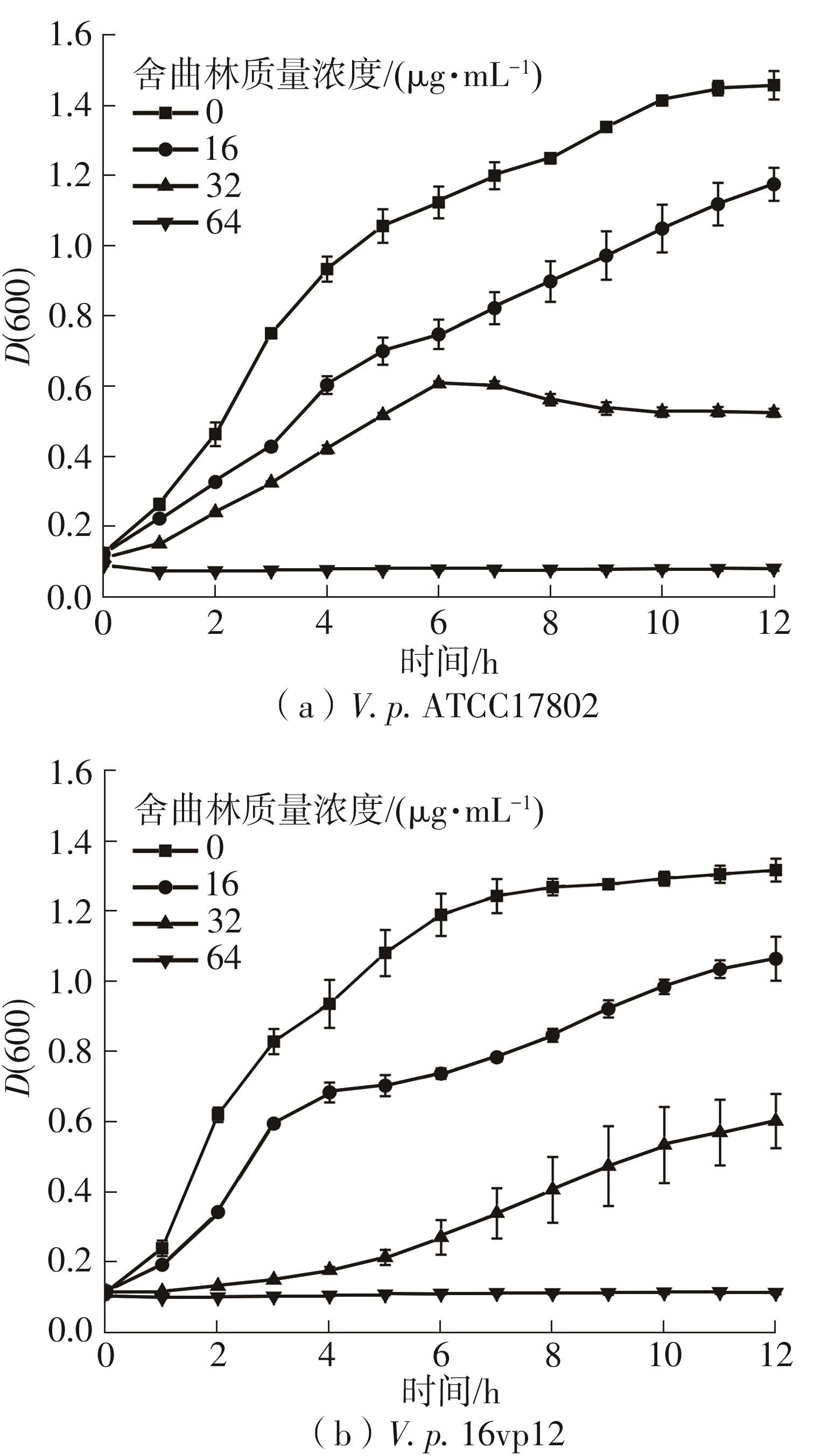
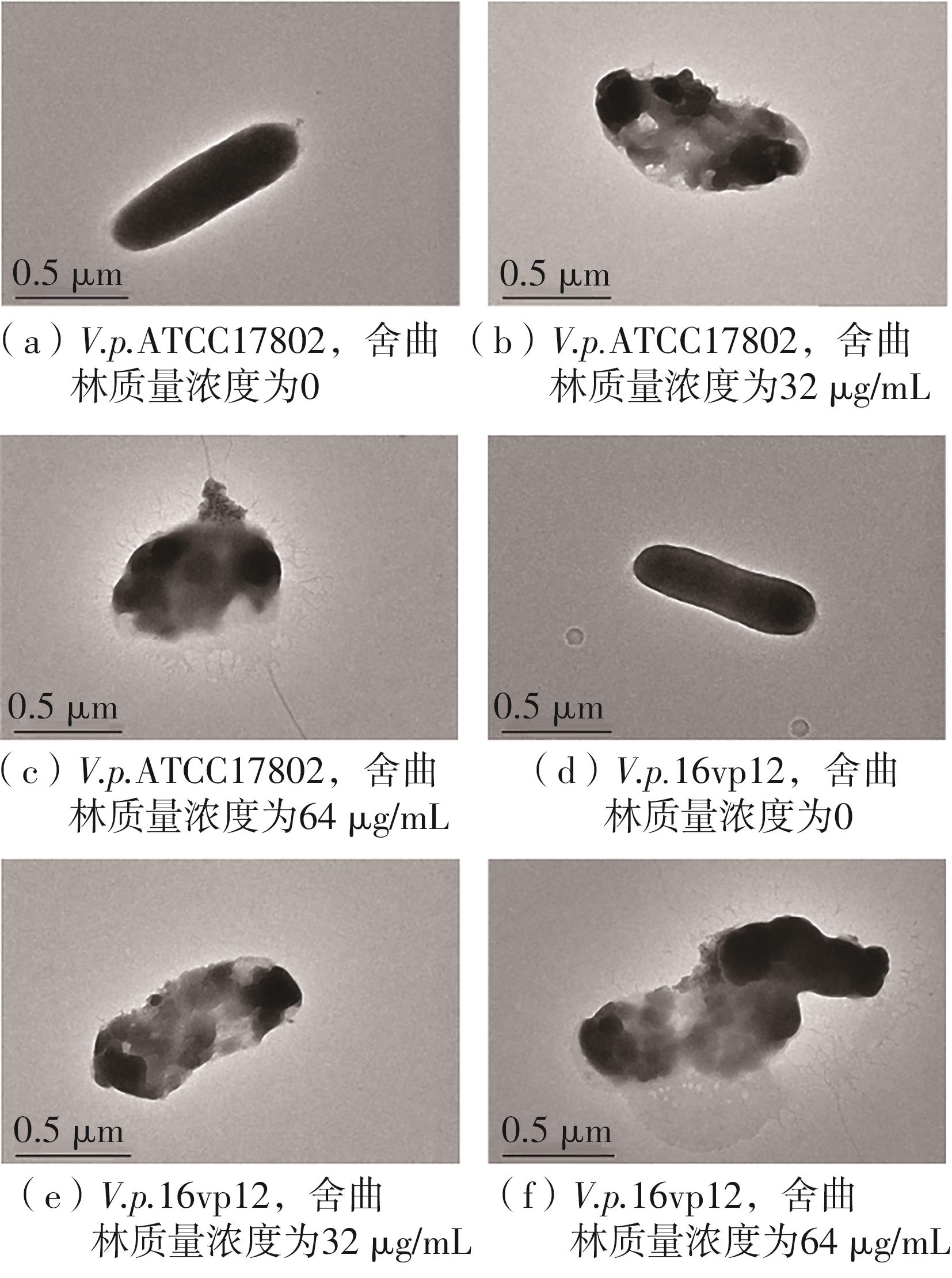
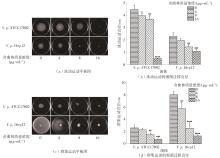
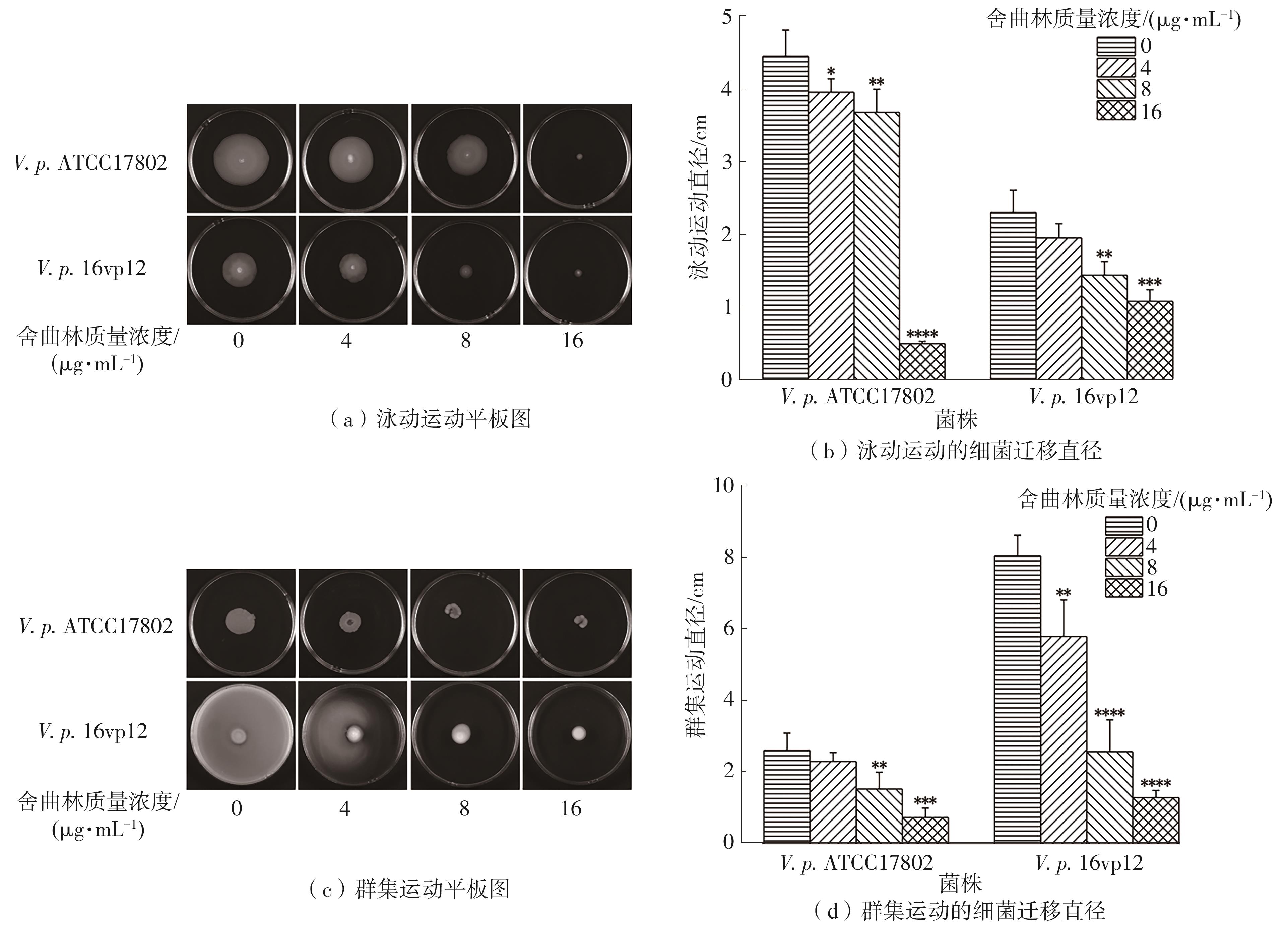
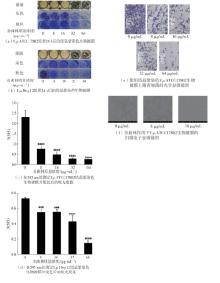
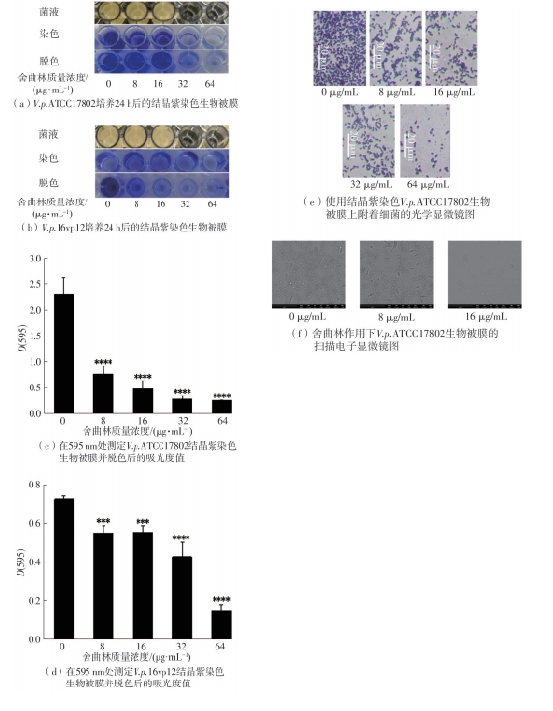
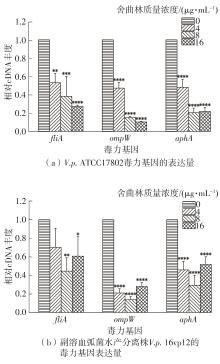
| 1 |
BAKER-AUSTIN C, OLIVER J D, ALAM M,et al . Vibrio spp. infections[J].Nature Reviews Disease Primers,2018,4(1):1-19.
|
| 2 |
LIU H L, ZHU W X, CAO Y,et al .Punicalagin inhibits biofilm formation and virulence gene expression of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].Food Control,2022,139:109045.
|
| 3 |
PARK K S,ONO T, ROKUDA M,et al .Functional characterization of two type III secretion systems of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].Infection and Immunity,2004,72(11):6659-6665.
|
| 4 |
ROY P K, SONG M G, JEON E B,et al .Antibiofilm efficacy of quercetin against Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilm on food-contact surfaces in the food industry[J].Microorganisms,2022,10(10):1902.
|
| 5 |
MIZAN M, JAHID I K, KIM M,et al .Variability in biofilm formation correlates with hydrophobicity and quorum sensing among Vibrio parahaemolyticus isolates from food contact surfaces and the distribution of the genes involved in biofilm formation[J].Biofouling,2016,32(4):497-509.
|
| 6 |
MALCOLM T, CHANG W S, LOO Y Y,et al .Simulation of improper food hygiene practices:a quantitative assessment of Vibrio parahaemolyticus distribution[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2018,284:112-119.
|
| 7 |
LIU J, BAI L, LI W,et al .Trends of foodborne diseases in China:lessons from laboratory-based surveillance since 2011[J].Frontiers of Medicine,2018,12(1):48-57.
|
| 8 |
PACKIAVATHY I A, SASIKUMAR P, PANDIAN S K,et al .Prevention of quorum-sensing-mediated biofilm development and virulence factors production in Vibrio spp. by curcumin [J].Applied Microbiology and Biotechnology,2013,97(23):10177-10187.
|
| 9 |
ZHU S, KOJIMA S, HOMMA M .Structure,gene regulation and environmental response of flagella in Vibrio [J].Frontiers in Microbiology,2013,4:410.
|
| 10 |
LASARRE B, FEDERLE M J. Exploiting quorum sensing to confuse bacterial pathogens[J].Microbiology and Molecular Biology Reviews,2013,77(1):73-111.
|
| 11 |
HENKE J M, BASSLER B L .Quorum sensing regulates type Ⅲ secretion in Vibrio harveyi and Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].Journal of Bacteriology,2004,186(12):3794-3805.
|
| 12 |
ZHU J, MILLER M B, VANCE R E,et al .Quorum-sensing regulators control virulence gene expression in Vibrio cholerae [J].Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences,2002,99(5):3129-3134.
|
| 13 |
AHMED H A, EL B R, HUSSEIN M A,et al .Molecular characterization,antibiotic resistance pattern and biofilm formation of Vibrio parahaemolyticus and V.cholerae isolated from crustaceans and humans[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2018,274:31-37.
|
| 14 |
BRANNON J R, HADJIFRANGISKOU M .The arsenal of pathogens and antivirulence therapeutic strategies for disarming them[J].Drug Design Development and Therapy,2016,10:1795-1806.
|
| 15 |
PISOSCHI A M,POP A, GEORGESCU C,et al .An overview of natural antimicrobials role in food[J].European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry,2018,143:922-935.
|
| 16 |
ASHBURN T T, THOr K B .Drug repositioning:identifying and developing new uses for existing drugs[J].Nature Reviews Drug Discovery,2004,3(8):673-683.
|
| 17 |
FARHA M A, BROWN E D .Drug repurposing for antimicrobial discovery[J].Nature Microbiology,2019,4(4):565-577.
|
| 18 |
JOURDAN J P, BUREAU R, ROCHAIS C,et al .Drug repositioning:a brief overview[J].Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology,2020,72(9):1145-1151.
|
| 19 |
AYAZ M, SUBHAN F, AHMED J,et al .Sertraline enhances the activity of antimicrobial agents against pathogens of clinical relevance [J].Journal of Biological Research-Thessaloniki,2015,22:1-8.
|
| 20 |
BOTTEGA A, SERAFIN M B, ROSA T F DA,et al .Antimicrobial and antineoplastic properties of sertraline[J].American Journal of Therapeutics,2020,27(6):e632-e635.
|
| 21 |
GOWRI M, JAYASHREE B, JEYAKANTHAN J,et al .Sertraline as a promising antifungal agent:inhibition of growth and biofilm of Candida auris with special focus on the mechanism of action in vitro[J].Journal of Applied Microbiology,2020,128(2):426-437.
|
| 22 |
MUTHU D, GOWRI M, SURESH KUMAR G,et al .Repurposing of antidepression drug sertraline for antimicrobial activity against Staphylococcus aureus:a potential approach for the treatment of osteomyelitis [J].New Journal of Chemistry,2019,43(14):5315-5324.
|
| 23 |
ROSATO A, ALTINI E, SBLANO S,et al .Synergistic activity of new diclofenac and essential oils combinations against different Candida spp.[J].Antibiotics,2021,10(6):688/1-10.
|
| 24 |
CLSI .Performance standards for antimicrobial susceptibility testing(M100-Ed33)[M].M100-Ed33 ed.Wayne:Clinical and Laboratory Standards Institute,2023.
|
| 25 |
ROY P K, SONG M G, PARK S Y .Impact of quercetin against Salmonella typhimurium biofilm formation on food-contact surfaces and molecular mechanism pattern [J].Foods,2022,11(7):977/1-14.
|
| 26 |
ROY P K, QAMAR A Y, FANG X,et al .Chitosan nanoparticles enhance developmental competence of in vitro-matured porcine oocytes[J].Reproduction in Domestic Animals,2021,56(2):342-350.
|
| 27 |
FALEYE O S, SATHIYAMOORTHI E, LEE J,et al .Inhibitory effects of cinnamaldehyde derivatives on biofilm formation and virulence factors in Vibrio species[J].Pharmaceutics,2021,13(12):2176/1-20.
|
| 28 |
GUO D, YANG Z, ZHENG X,et al .Thymoquinone inhibits biofilm formation and attachment-invasion in host cells of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].Foodborne Pathogens and Disease,2019,16(10):671-678.
|
| 29 |
MA Y, SUN X, XU X,et al .Investigation of reference genes in Vibrio parahaemolyticus for gene expression analysis using quantitative RT-PCR[J].PLoS One,2015,10(12):e144362.
|
| 30 |
ZAYED M A, HAWASH M F, FAHMEY M A,et al .Structure investigation of sertraline drug and its iodine product using mass spectrometry,thermal analyses and MO-calculations[J].Spectrochimica Acta Part A:Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy,2007,68(3):970-978.
|
| 31 |
KRZYZEK P, FRANICZEK R, KRZYZANOWSKA B,et al .In vitro activity of sertraline,an antidepressant,against antibiotic-susceptible and antibiotic-resistant Helicobacter pylori strains[J].Pathogens,2019,8(4):228/1-21.
|
| 32 |
WANG Y, LI L, CAI P,et al .Antimicrobial activity of sertraline on Listeria monocytogenes [J].International Journal of Molecular Sciences,2023,24(5):4678/1-12.
|
| 33 |
PARANJPYE R N, JOHNSON A B, BAXTER A E,et al .Role of type IV pilins in persistence of Vibrio vulnificus in Crassostrea virginica oyster[J].Applied Environmental Microbiology,2007,73(15):5041-5044.
|
| 34 |
ROY P K, PARK S H, SONG M G,et al .Antimicrobial efficacy of quercetin against Vibrio parahaemolyticus biofilm on food surfaces and downregulation of virulence genes[J].Polymers,2022,14(18):3847/1-15.
|
| 35 |
OLIVEIRA A S, MARTINEZ-DE-OLIVEIRA J, DONDERS G,et al .Anti-Candida activity of antidepressants sertraline and fluoxetine:effect upon pre-formed biofilms [J].Medical Microbiology and Immunology,2018,207:195-200.
|
| 36 |
WANG J, ZHAN Y, SUN H,et al .Regulation of virulence factors expression during the intestinal colonization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].Foodborne Pathogens and Disease,2022,19(3):169-178.
|
| 37 |
GU D, MENG H, LI Y,et al .A GntR family transcription factor (VPA1701) for swarming motility and colonization of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].Pathogens,2019,8(4):235/1-13.
|
| 38 |
RITTER A,COM E, BAZIRE A,et al .Proteomic studies highlight outer-membrane proteins related to biofilm development in the marine bacterium Pseudoalteromonas sp. D41[J].Proteomics,2012,12(21):3180-3192.
|
| 39 |
CHENG W, JUANG F M, CHEN J C .The immune response of Taiwan abalone Haliotis diversicolor supertexta and its susceptibility to Vibrio parahaemolyticus at different salinity levels[J].Fish & Shellfish Immunology,2004,16(3):295-306.
|
| 40 |
XU C, REN H, WANG S,et al .Proteomic analysis of salt-sensitive outer membrane proteins of Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].Research in Microbiology,2004,155(10):835-842.
|
| 41 |
WANG L, LING Y, JIANG H,et al .AphA is required for biofilm formation,motility,and virulence in pandemic Vibrio parahaemolyticus [J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2013,160(3):245-251.
|