

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
Acoustic Scene Classification Method Based on Reducing High-Frequency Reverberation and RF-DRSN-EMA
Received date: 2024-10-14
Online published: 2025-01-13
Supported by
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52175234);the Programme of Introducing Talents of Discipline to Universities(B18027)
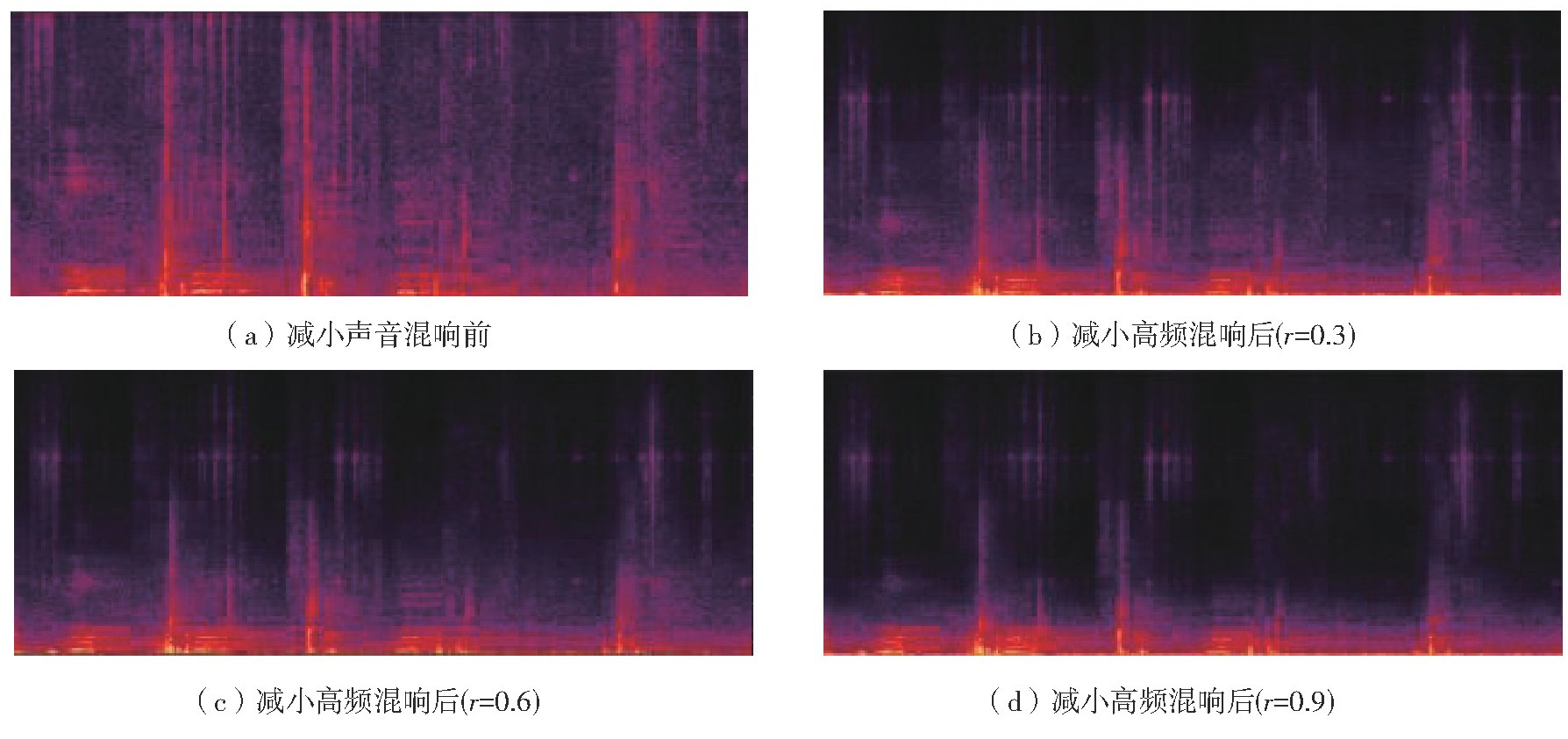
To address the issues of low classification accuracy and poor generalization in existing acoustic scene classification methods, this paper proposed a novel acoustic scene classification method based on reducing high-frequency reverberation and a frequency-domain residual shrinkage network with multi-scale attention, named RF-DRSN-EMA. Firstly, according to the principle of reducing sound reverberation, this paper introduced a redu-cing high-frequency reverberation method. This method attenuated only the high-frequency reverberation while preserving essential frequency information in other bands. As a result, speech intelligibility was enhanced, and the impact of speech distortion was minimized. Secondly, based on the deep residual shrinkage network, the proposed RF-DRSN-EMA integrates an improved frequency-domain self-calibration mechanism and a multi-scale attention module. The network used RF self-calibration module with a long-short residual structure to mitigate feature collapse, enabling efficient extraction of frequency-domain information. A multi-scale attention module was then applied at the output of each unit to highlight relevant information, further enhancing the model’s representation capacity. Finally, the proposed method is evaluated on three benchmark datasets: ESC-10, UrbanSound8K, and DCASE2020 Task 1A. The results show that the proposed high-frequency reverberation reduction method effectively suppresses high-frequency reverberation and background noise while eliminating redundant features, resulting in minimal speech quality degradation. The RF-DRSN-EMA network achieves efficient frequency-domain denoising and feature extraction, reaching classification accuracies of 98.00%, 93.42%, and 72.80% on the three datasets, respectively. These results confirm the effectiveness and generalizability of the proposed method.
CAO Yi , WANG Yanwen , LI Jie , ZHENG Zhi , SUN Hao . Acoustic Scene Classification Method Based on Reducing High-Frequency Reverberation and RF-DRSN-EMA[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2025 , 53(7) : 70 -79 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240508
| [1] | 董绍江,夏蒸富,方能炜,等 .基于颜色通道特征融合的环境声音分类方法[J].应用科学学报,2023,41(4):669-681. |
| DONG Shaojiang, XIA Zhengfu, FANG Nengwei,et al .Environmental sound classification method based on color channel feature fusion[J].Journal of Applied Sciences,2023,41(4):669-681. | |
| [2] | MAHYUB M, SOUZA L S, BATALO B,et al .Signal latent subspace:a new representation for environmental sound classification[J].Applied Acoustics,2024,225:110181/1-13. |
| [3] | ZHANG H Y, WU M L, CAI X C,et al .An event-scene cooperative analysis network with dual-stream attention convolution module and soft parameter-sharing[J].Applied Acoustics,2024,222:110066/1-9. |
| [4] | JESUDHAS P P, RANJAN P V .A novel approach to build a low complexity smart sound recognition system for domestic environment[J].Applied Acoustics,2024,221:110028/1-14. |
| [5] | HOU Y, KANG B, MITCHELL A,et al .Cooperative scene-event modelling for acoustic scene classification [J].IEEE/ACM Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2023,32:68-82. |
| [6] | MILLING M, LIU S, TRIANTAFYLLOPOULOS A,et al .Audio enhancement for computer audition:an iterative training paradigm using sample importance[J].Journal of Computer Science and Technology,2024,39(4):895-911. |
| [7] | SONG S Y, SONG Y J, MADHU N .Robust detection of background acoustic scene in the presence of foreground speech[J].Applied Sciences,2024,14(2):609/1-13. |
| [8] | YANG L P, TAO L J, CHEN X X,et al .Multi-scale semantic feature fusion and data augmentation for acou-stic scene classification[J].Applied Acoustics,2020,163:107238/1-10. |
| [9] | JIANG G, MA Z C, MAO Q,et al .Multi-level distance embedding learning for robust acoustic scene classification with unseen devices[J].Pattern Analysis and Applications,2023,26(3):1089-1099. |
| [10] | 曹毅,费鸿博,李平,等 .基于多流卷积和数据增强的声场景分类方法[J].华中科技大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(4):40-46. |
| CAO Yi, FEI Hongbo, LI Ping,et al .Acoustic scene classification method based on multi-stream convolution and data augmentation[J].Journal of Huazhong University of Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(4):40-46. | |
| [11] | GUZHOV A, RAUE F, HEES J,et al .ESResNet:environmental sound classification based on visual domain models[C]∥ Proceedings of the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition.Milan:IEEE,2021:4933-4940. |
| [12] | KARAM S, RUAN S J, HAP Q M,et al .Episodic memory based continual learning without catastrophic forgetting for environmental sound classification[J].Journal of Ambient Intelligence and Humanized Compu-ting,2023,14(4):4439-4449. |
| [13] | QU Y, LI X, QIN Z,et al .Acoustic scene classification based on three-dimensional multi-channel feature-correlated deep learning networks[J].Scientific Reports,2022,12:13730/1-11. |
| [14] | 曹毅,黄子龙,张威,等 . N-DenseNet的城市声音事件分类模型[J].西安电子科技大学学报,2019,46(6):9-16,94. |
| CAO Yi, HUANG Zilong, ZHANG Wei,et al .Urban sound event classification with the N-order dense convolutional network[J].Journal of Xidian University,2019,46(6):9-16,94. | |
| [15] | HUANG Z L, LIU C, FEI H B,et al .Urban sound classification based on 2-order dense convolutional net-work using dual features[J].Applied Acoustics,2020,164(2):107243/1-9. |
| [16] | 曹毅,黄子龙,盛永健,等 .D-2-DenseNet噪音鲁棒的城市音频分类模型[J].北京邮电大学学报,2021,44(1):86-91. |
| CAO Yi, HUANG Zi-long, SHENG Yong-jian,et al .Noise robust urban audio classification based on 2-order dense convolutional network using dual features[J].Journal of Beijing University of Posts and Telecommunications,2021,44(1):86-91. | |
| [17] | 高长丰,程高峰,张鹏远 .面向鲁棒自动语音识别的一致性自监督学习方法[J].声学学报,2023,48(3):578-587. |
| GAO Changfeng, CHENG Gaofeng, ZHANG Pengyuan. Consistency self-supervised learning method for robust automatic speech recognition[J].Acta Acustica, 2023,48(3):578-587. | |
| [18] | 费鸿博,吴伟官,李平,等 .基于梅尔频谱分离和LSCNet的声学场景分类方法[J].哈尔滨工业大学学报,2022,54(5):124-130. |
| FEI Hongbo, WU Weiguan, LI Ping,et al .Acoustic scene classification method based on Mel-spectrogram separation and LSCNet[J].Journal of Harbin Institute of Technology,2022,54(5):124-130. | |
| [19] | YOSHIOKA T, NAKATANI T .Generalization of multi-channel linear prediction methods for blind MI-MO impulse response shortening[J].IEEE Transactions on Audio,Speech,and Language Processing,2012,20(10):2707-2720. |
| [20] | YANG Z, ZHANG M, CHEN J .Distributed speech dereverberation using weighted prediction error[J].Signal Processing,2024,225:109577/1-5. |
| [21] | ADELMAN N W, JEONG C .Investigation on accep-table reverberation time at various frequency bands in halls that present amplified music[J].Applied Acou-stics,2018,129:104-107. |
| [22] | ZHANG X, JIANG S .Application of Fourier transform and butterworth filter in signal denoising[C]∥ Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Intelligent Computing and Signal Processing.Xian:IEEE,2021:1277-1281. |
| [23] | ZHAO M, ZHONG S, FU X,et al .Deep residual shrinkage networks for fault diagnosis[J].IEEE Tran-sactions on Industrial Informatics,2020,16(7):4681-4690. |
| [24] | FENG Q, HAN L, ZHAO B,et al .Microseismic events recognition via joint deep clustering with residual shrinkage dense network[J].IEEE Transactions on Geoscience and Remote Sensing,2023,61:1-11. |
| [25] | WANG L, ZOU T, CAI K,et al .Rolling bearing fault diagnosis method based on improved residual shrinkage network[J].Journal of the Brazilian Society of Mechanical Sciences and Engineering,2024,46(3):172/1-12. |
| [26] | OUYANG D, HE S, ZHANG G Z,et al .Efficient multi-scale attention module with cross-spatial learning [C]∥ Proceedings of 2023 IEEE International Confe-rence on Acoustics,Speech and Signal Processing.Rhodes Island:IEEE,2023:1-5. |
| [27] | PICZAKI K J .ESC:dataset for environmental sound classification[C]∥ Proceeding of the 23rd ACM International Conference on Multimedia.New York:ACM,2015:1015-1018. |
| [28] | SALAMON J, JACOBY C, BELLO J P .A dataset and taxonomy for urban sound research[C]∥ Procee-ding of the 22nd ACM International Conference on Multimedia.New York:ACM,2014:1041-1044. |
| [29] | HEITTOLA T, MESAROS A, VIRTANEN T .TAU urban acoustic scenes 2020 mobile, development dataset [DB/OL]. (2020-06-01)[2024-10-14].. |
| [30] | 王玥,钱志鸿,王雪,等 .基于伽马通滤波器组的听觉特征提取算法研究[J].电子学报,2010,38(3):525-528. |
| WANG Yue, QIAN Zhi-hong, WANG Xue,et al .An auditory feature extraction algorithm based on γ-tone filter-banks[J].Acta Electronica Sinica,2010,38(3):525-528. | |
| [31] | SALAMON J, BELLO J P .Deep convolutional neural networks and data augmentation for environmental sound classification[J].IEEE Signal Processing Le-tters,2017,24(3):279-283. |
| [32] | GUPTA S S, HOSSAIN S, KIM K D .Recognize the surrounding:development and evaluation of convolutional deep networks using gammatone spectrograms and raw audio signals[J].Expert Systems with Applications,2022,200:116998/1-15. |
| [33] | HEITTOLA T, MESAROS A, VIRTANEN T .Acou-stic scene classification in DCASE 2020 challenge:generalization across devices and low complexity solutions [EB/OL].(2020-01-02)[2024-10-14].. |
| [34] | SHAO Y F, MA X X, MA Y,et al .Deep semantic learning for acoustic scene classification[J].EURASIP Journal on Audio, Speech and Music Processing,2024,2024:1/1-15. |
| [35] | GAO W, McDONNELL M D .Acoustic scene classification using deep residual networks with focal loss and mild domain adaptation[R].Adelaide:University of South Australia,2020:1-2. |
| [36] | ABDOLI S, CARDINAL P, KOERICH A L .End-to-end environmental sound classification using a 1D convolutional neural network[J].Expert Systems with Applications,2019,136:252-263. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |