

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
Design and Optimization of Single-Node HPL-AI Benchmark for a Heterogeneous Platform Composed of Kunpeng and Ascend
Received date: 2023-02-27
Online published: 2023-06-20
Supported by
the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2021A1515011798);the Open Foundation of Henan Key Laboratory of Cyberspace Situation Awareness(HNTS2022017)
Given the faster speed of low-precision floating point operations, more and more high-performance applications are using hybrid precision solutions to accelerate.The large AI (artificial intelligence) models that use this scheme to accelerate has also received wide attention. Recently, the HPL-AI (High Performance LINPACK for Accelerator Introspection) benchmark has been proposed to evaluate the mixed-precision computing performance of high-performance systems. For this benchmark test, this study designed and optimized the implementation of single-node HPL-AI benchmark test on Kunpeng and Ascend heterogeneous platforms. In order to balance the load of the AI processor, the tasks were evenly distributed to the AI processors through the cyclic task allocation strategy. The task allocation strategy with interval value was used to improve the continuity of data transmission to reduce the data transmission time between CPU and AI processor. Without affecting the calculation accuracy, the computation on the CPU side was reduced by the strategy of canceling the data scaling. The final experimental results show that the HPL-AI benchmark has the fastest mixed-precision floating-point arithmetic speed when the interval value is 8; at the same time, unscaling the data does not affect the accuracy of the HPL-AI benchmark results. Compared with the non-optimized HPL-AI benchmark implementation on the heterogeneous platform of Kunpeng and Ascend, the optimization strategy proposed in this paper improves the mixed-precision floating-point arithmetic speed by about 29%, which lays a solid foundation for the further optimization of single-node HPL-AI benchmark and the deployment of multi-node HPL-AI benchmark.
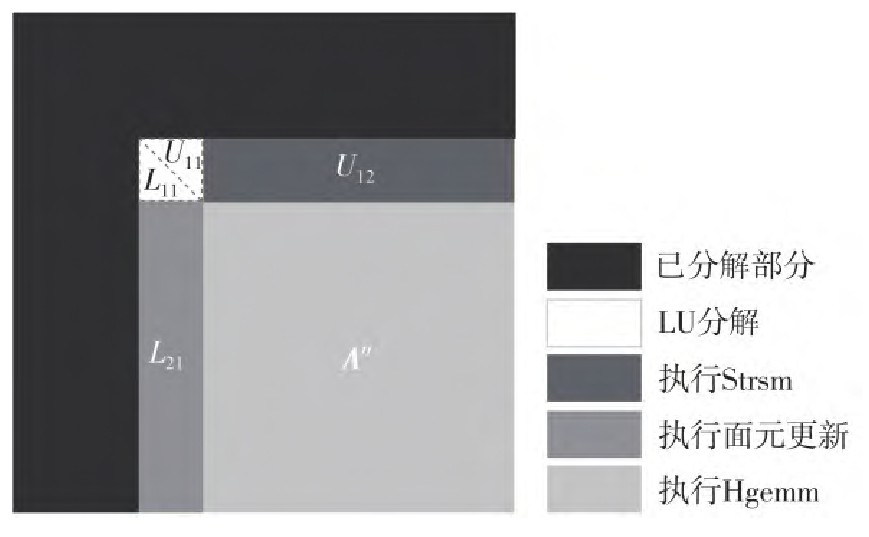
WU Haotian, REN Changqing, LU Lu, et al . Design and Optimization of Single-Node HPL-AI Benchmark for a Heterogeneous Platform Composed of Kunpeng and Ascend[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2024 , 52(2) : 13 -22 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230066
| 1 | DAVICES T, KARLSSON C, LIU H,et al .High performance LINPACK benchmark:a fault tolerant implementation without checkpointing[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Supercomputing.Tucson:ACM,2011:162-171. |
| 2 | STROHMAIER E, DONGARRA J, SIMON H,et al .TOP500 list[EB/OL].(2022-11-14) [2023-03-05].. |
| 3 | HU Y, LU L .Design of a simulation model for high performance LINPACK in hybrid CPU-GPU systems[J].The Journal of Supercomputing,2021,77(12):13739-13756. |
| 4 | OpenAI. GPT-4 technical report[EB/OL].(2023-03-27)[2023-05-14].. |
| 5 | DONGARRA J, LUSZCZEK P, TSAI Y M .HPL-AI mixed-precision benchmark[EB/OL].(2022-10-31)[2023-03-05].. |
| 6 | ABDELFATTAH A, ANZT H, BOMAN E G,et al .A survey of numerical linear algebra methods utilizing mixed-precision arithmetic[J].The International Journal of High Performance Computing Applications,2021,35(4):344-369. |
| 7 | MOLER, CLEVE B .Iterative refinement in floating point[J].Journal of the ACM,1967,14(2):316-321. |
| 8 | KURZAK J, DONGARRA J .Implementation of mixed precision in solving systems of linear equations on the CELL processor[J].Concurrency and Computation:Practice and Experience,2007,19(10):1371-1385. |
| 9 | LEI W, YUNQUAN Z, XIANYI Z,et al .Accelerating LINPACK performance with mixed precision algorithm on CPU+GPGPU heterogeneous cluster[C]∥Proceedings of the 2010 10th IEEE International Conference on Computer and Information Technology.Bradford:IEEE,2010:1169-1174. |
| 10 | BABOULIN M, BUTTARI A, DONGARRA J,et al .Accelerating scientific computations with mixed precision algorithms[J].Computer Physics Communications,2009,180(12):2526-2533. |
| 11 | HAIDAR A, TOMOV S, DONGARRA J,et al .Harnessing GPU tensor cores for fast FP16 arithmetic to speed up mixed-precision iterative refinement solvers[C]∥Proceedings of the SC18:International Conference for High Performance Computing,Networking,Storage and Analysis. Dallas:IEEE,2018:603-613. |
| 12 | HAIDAR A, WU P, TOMOV S,et al .Investigating half precision arithmetic to accelerate dense linear system solvers[C]∥Proceedings of the 8th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems. Denver:ACM,2017:1-8. |
| 13 | DEMMEL J, HIDA Y, KAHAN W,et al .Error bounds from extra-precise iterative refinement[J].ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software,2006,32(2):325-351. |
| 14 | OKTAY E, CARSON E .Multistage mixed precision iterative refinement[J].Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications,2022,29(4):e2434/1-24. |
| 15 | AMESTOY P, BUTTARI A, HIGHAM N J,et al .Combining sparse approximate factorizations with mixed-precision iterative refinement[J].ACM Transactions on Mathematical Software,2023,49(1):1-29. |
| 16 | RAKKA M, FOUDA M E, KHARGONEKAR P,et al .Mixed-precision neural networks:a survey[EB/OL].(2022-08-11)[2023-03-05].. |
| 17 | MICIKEVICIUS P, NARANG S, ALBEN J,et al .Mixed precision training[EB/OL].(2018-02-15)[2023-03-05].. |
| 18 | LATOTZKE C, CIESIELSKI T, GEMMEKE T .Design of high-throughput mixed-precision CNN accelerators on FPGA[C]∥Proceedings of the 2022 32nd International Conference on Field-Programmable Logic and Applications (FPL).Belfast:IEEE,2022:358-365. |
| 19 | DAS D, MELLEMPUDI N, MUDIGERE D,et al .Mixed precision training of convolutional neural networks using integer operations FPGA[EB/OL].(2018-02-23)[2023-03-05].. |
| 20 | LUSZCZEK P, TSAI Y M .Reference implementationof the HPL-AI benchmark[CP/OL].(2019-12-20) [2023-03-05].. |
| 21 | KUDO S, NITADORI K, INA T,et al .Implementation and numerical techniques for one EFlop/s HPL-AI benchmark on Fugaku[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE/ACM 11th Workshop on Latest Advances in Scalable Algorithms for Large-Scale Systems (ScalA).GA:IEEE,2020:69-76. |
| 22 | KUDO S, NITADORI K, INA T,et al .Prompt report on exa-scale HPL-AI benchmark[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE International Conference on Cluster Computing(CLUSTER).Kobe:IEEE,2020:418-419. |
| 23 | SATO M, KODAMA Y, TSUJI M,et al .Co-design and system for the supercomputer “Fugaku”[J].IEEE Micro,2021,42(2):26-34. |
| 24 | MATSUOKA S .Fugaku and A64FX:the first exascale supercomputer and its innovative arm CPU[C]∥Proceedings of the 2021 Symposium on VLSI Circuits.Kyoto:IEEE,2021:1-3. |
| 25 | DEMMEL J W, HIGHAM N J, SCHREIBER R S .Stability of block LU factorization[J].Numerical Linear Algebra with Applications,1995,2(2):173-190. |
| 26 | WILKINSON J H .Error analysis of direct methods of matrix inversion[J].Journal of the ACM,1961,8(3):281-330. |
| 27 | FASI M, HIGHAM N J .Matrices with tunable infinity-norm condition number and no need for pivoting in LU factorization[J].SIAM Journal on Matrix Analysis and Applications,2021,42(1):417-435. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |