

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
Contrastive Knowledge Distillation Method Based on Feature Space Embedding
Received date: 2022-10-24
Online published: 2023-01-16
Supported by
the Key-Area R&D Program of Guangdong Province(2021B0101420003)
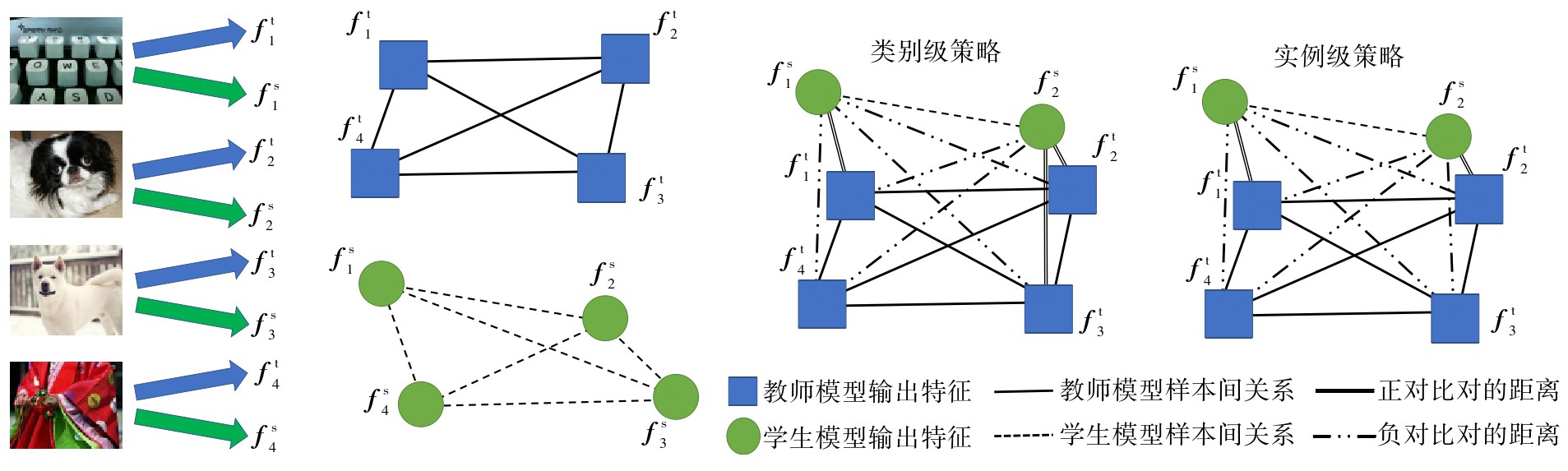
Because of its important role in model compression, knowledge distillation has attracted much attention in the field of deep learning. However, the classical knowledge distillation algorithm only uses the information of a single sample, and neglects the importance of the relationship between samples, leading to its poor performance. To improve the efficiency and performance of knowledge transfer in knowledge distillation algorithm, this paper proposed a feature-space-embedding based contrastive knowledge distillation (FSECD) algorithm. The algorithm adopts efficient batch construction strategy, which embeds the student feature into the teacher feature space so that each student feature builds N contrastive pairs with N teacher features. In each pair, the teacher feature is optimized and fixed, while student feature is to be optimized and tunable. In the training process, the distance for positive pairs is narrowed and the distance for negative pairs is expanded, so that student model can perceive and learn the inter-sample relations of teacher model and realize the transfer of knowledge from teacher model to student model. Extensive experiments with different teacher/student architecture settings on CIFAR-100 and ImageNet datasets show that, FSECD algorithm achieves significant performance improvement without additional network structures and data when compared with other cutting-edge distillation methods, which further proves the importance of the inter-sample relations in knowledge distillation.
YE Feng, CHEN Biao, LAI Yizong . Contrastive Knowledge Distillation Method Based on Feature Space Embedding[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2023 , 51(5) : 13 -23 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220684
| 1 | SIMONYAN K, ZISSERMAN A .Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition [EB/OL].(2015-04-10)[2022-10-20].. |
| 2 | HE K, ZHANG X, REN S,et al .Deep residual learning for image recognition[C]∥ Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas:IEEE,2016:770-778. |
| 3 | ZHANG X, ZHOU X, LIN M,et al .ShuffleNet:an extremely efficient convolutional neural network for mobile devices[C]∥ Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:6848-6856. |
| 4 | MA N, ZHANG X, ZHENG H-T,et al .ShuffleNet V2:practical guidelines for efficient CNN architecture design[C]∥ Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich:Springer,2018:122-138. |
| 5 | SANDLER M, HOWARD A, ZHU M,et al .MobileNetV2:inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks [C]∥ Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:4510-4520. |
| 6 | ZAGORUYKO S, KOMODAKIS N .Wide residual networks[EB/OL].(2017-06-14)[2022-10-20].. |
| 7 | REDMON J, DIVVALA S, GIRSHICK R,et al .You only look once:unified,real-time object detection[C]∥ Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Las Vegas:IEEE,2016:779-788. |
| 8 | LIU W, ANGUELOV D, ERHAN D,et al .SSD:single shot multibox detector[C]∥ Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam:Springer,2016:21-37. |
| 9 | HE K, GKIOXARI G, DOLLáR P,et al .Mask R-CNN[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:2961-2969. |
| 10 | ZHAO H, SHI J, QI X,et al .Pyramid scene parsing network[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:2881-2890. |
| 11 | LUO J-H, WU J, LIN W .ThiNet:a filter level pruning method for deep neural network compression[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:5058-5066. |
| 12 | JACOB B, KLIGYS S, CHEN B,et al .Quantization and training of neural networks for efficient integer-arithmetic-only inference[C]∥ Proceedings of 2018 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:2704-2713. |
| 13 | YU X, LIU T, WANG X,et al .On compressing deep models by low rank and sparse decomposition[C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Honolulu:IEEE,2017:7370-7379. |
| 14 | HINTON G, VINYALS O, DEAN J .Distilling the knowledge in a neural network[EB/OL].(2015-05-09)[2022-10-20].. |
| 15 | PARK W, KIM D, LU Y,et al .Relational knowledge distillation[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:3967-3976. |
| 16 | TIAN Y, KRISHNAN D, ISOLA P .Contrastive representation distillation[C]∥ Proceedings of the 8th International Conference on Learning Representations.Addis Ababa:OpenReview.net,2020:1-19. |
| 17 | ROMERO A, BALLAS N, KAHOU S E,et al .FitNets:hints for thin deep nets[C]∥ Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Learning Representations.San Diego:OpenReview.net,2015:1-13. |
| 18 | ZAGORUYKO S, KOMODAKIS N .Paying more attention to attention:improving the performance of convolutional neural networks via attention transfer[C]∥ Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Learning Representations.Toulon:OpenReview.net,2017:1-13. |
| 19 | HEO B, KIM J, YUN S,et al .A comprehensive overhaul of feature distillation[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:1921-1930. |
| 20 | GOU J, YU B, MAYBANK S J,et al .Knowledge distillation:a survey[J].International Journal of Computer Vision,2021,129(6):1789-1819. |
| 21 | ZHAO B, CUI Q, SONG R,et al .Decoupled knowledge distillation[C]∥ Proceedings of 2022 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:11953-11962. |
| 22 | GOU J, SUN L, YU B,et al .Multi-level attention-based sample correlations for knowledge distillation[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics,2022,DOI:10.1109/TII.2022.3209672 . |
| 23 | CHEN T, KORNBLITH S, NOROUZI M,et al .A simple framework for contrastive learning of visual representations[C]∥ Proceedings of the Thirty-seventh International Conference on Machine Learning.Vienna:IMLS,2020:1597-1607. |
| 24 | RADFORD A, KIM J W, HALLACY C,et al .Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision[C]∥ Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning.Vienna:IMLS,2021:8748-8763. |
| 25 | XU G, LIU Z, LI X,et al .Knowledge distillation meets self-supervision[C]∥ Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:588-604. |
| 26 | KRIZHEVSKY A .Learning multiple layers of features from tiny images[D].Toronto:University of Toronto,2009. |
| 27 | DENG J, DONG W, SOCHER R,et al .ImageNet:a large-scale hierarchical image database[C]∥ Proceedings of 2009 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Miami:IEEE,2009:248-255. |
| 28 | HOWARD A G, ZHU M, CHEN B,et al .MobileNets:efficient convolutional neural networks for mobile vision applications[EB/OL].(2017-04-17)[2022-10-20].. |
| 29 | Van der MAATEN L, HINTON G .Visualizing data using t-SNE[J].Journal of Machine Learning Research,2008,9(11):2579-2605. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |