

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
Electrochemical Performance of Rb-Doped Na1.25V3O8 Nanorods as Cathode for Zinc-Ion Batteries
Received date: 2022-05-31
Online published: 2022-08-26
Supported by
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51672086);the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2017B030308005)
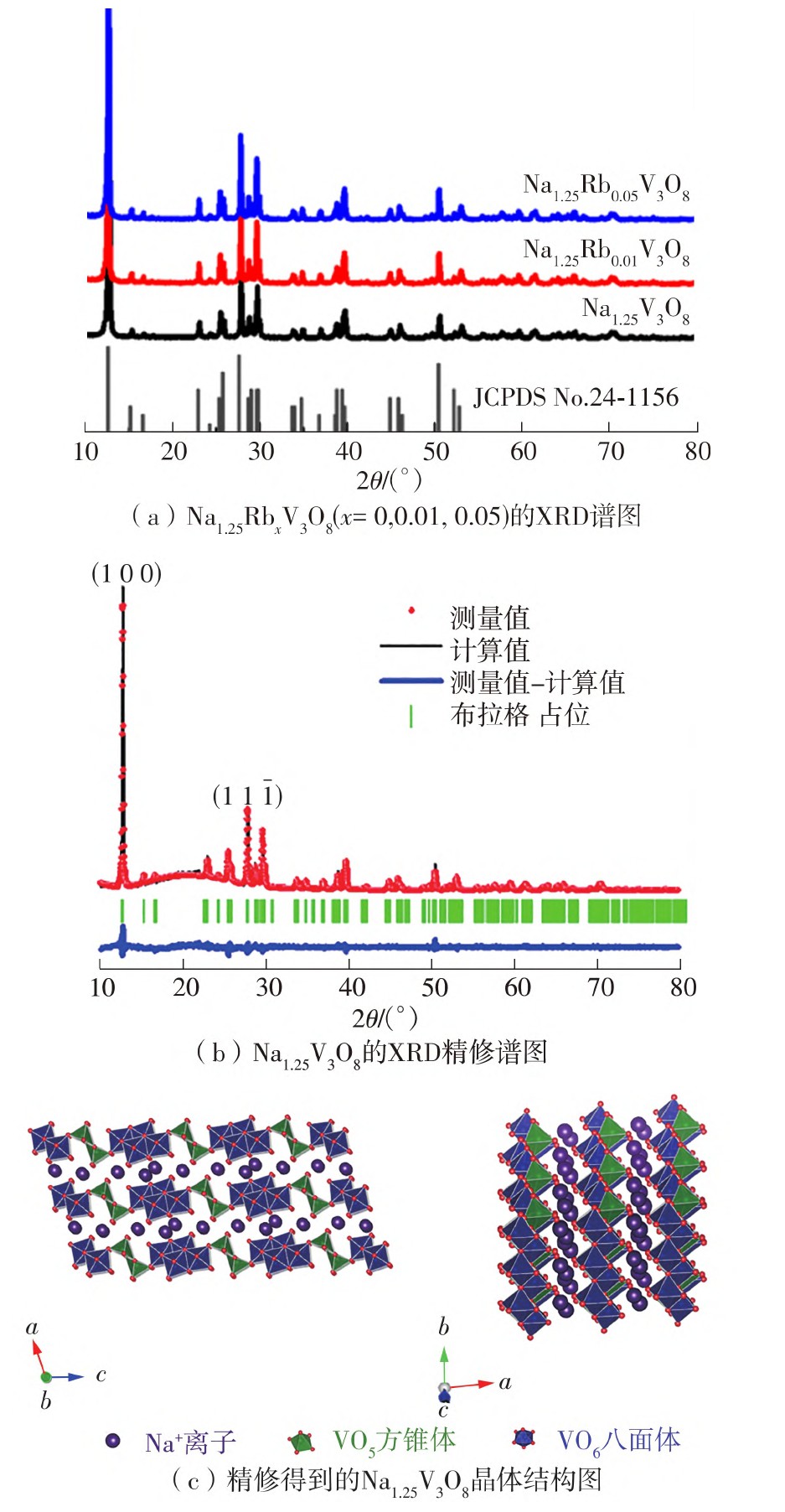
In order to know whether there is space for the improvement of the electrochemical performance of Na1.25V3O8 as cathode for zinc-ion batteries, this study successfully synthesized pure Na1.25V3O8 and Rb+ ion doped Na1.25V3O8 nanorods through hydrothermal method and solid phase method. With the help of XRD patterns, the diffraction peak shifts to a low angle and no new diffraction peak is generated with the increase of rubidium content, indicating that the Na1.25Rb x V3O8 sample is pure phase and maintain the structural symmetry of P21/m space group. This result indicate that rubidium ions have successfully entered the interlayer of Na1.25Rb x V3O8 layered compound. The results of SEM images and TEM images analysis show that, with the insertion of Rb+, scale of Na1.25V3O8 nanorods become thicker and larger, which would reduce the specific surface and lead to the increase of impedance and reducing the ion diffusion coefficients, resulting in poor electrochemical performance. EIS and GITT results further confirm that the insertion of Rb+ will lead to the decrease in capacity. Electrochemical testing results show that bare Na1.25V3O8 nanorods exhibit about 370 mA·h/g initial capacity, but it decreases fast with the increasing times of charge and discharge circle. After 100 cycles of discharge and charge processes at current density of 100 mA/g, discharge capacity decays about 50% compared to initial capacity. Although the specific capacity of Rb+-doped nanorods is reduced, their cycle stability and rate performance are significantly improved. When the amount of doped Rb is 1%, the initial capacity is 336 mA·h/g, but after 100 cycles of discharge and charge processes under the same conditions, the discharge capacity only decays about 6% compared to initial discharge capacity. When the amount of Rb increases to 5%, the initial capacity is merely 217 mA·h/g, but no capacity lost compared to initial capacity. The mechanism of zinc ion storage was analyzed through in-situ XRD and ex-situ XPS. The redox reaction mechanism of Na1.25Rb x V3O8 cathode material in the ZIBs is mainly based on chemical conversion reaction, in which only the charging reaction process is reversible.
Key words: zinc-ion batteries; cathode material; Na1.25V3O8; Rb-doped; nanorods
ZHAO Yanming, LIAO Jinhui . Electrochemical Performance of Rb-Doped Na1.25V3O8 Nanorods as Cathode for Zinc-Ion Batteries[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2023 , 51(3) : 63 -73 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220326
| 1 | WHITTINGHAM M S .Introduction:batteries[J]?.Chemical Reviews,2014,114(23):11413. |
| 2 | YAN M Y, HE P, CHEN Y,et al .Water-lubricated intercalation in V2O5·nH2O for high-capacity and high-rate aqueous rechargeable zinc batteries[J].Advanced Materials,2018,30(1):1703725-1-6. |
| 3 | ZHU K Y, WU T, HUANG K V .NaCa0.6V6O16·3H2O as an ultra-stable cathode for Zn-ion batteries:The roles of pre-inserted dual-cations and structural water in V3O8 layer[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2019,9(38):190 1968-1-12. |
| 4 | MUENCH S, WILD A, FRIEBE C,et al .Polymer-based organic batteries[J].Chemical Reviews,2016,116(16):9438-9484. |
| 5 | AKINYELE D O, RAYUDU R K .Review of energy storage technologies for sustainable power networks[J].Sustainable Energy Technologies and Assessments,2014,8:74-91. |
| 6 | HAMEER S, VAN NIEKERK J L .A review of large-scale electrical energy storage[J].International Journal of Energy Research,2015,39(9):1179-1195. |
| 7 | GOODENOUGH J B, KIM Y .Challenges for rechargeable Li batteries[J].Chemistry of Materials,2010,22(3):587-603. |
| 8 | HU P, ZHU T, WANG X P,et al .Highly durable Na2V6O16·1.63H2O nanowire cathode for aqueous zinc-ion battery[J].Nano Letters,2018,18(3):1758-1763. |
| 9 | PAN H L, SHAO Y Y, YAN P F,et al .Reversible aqueous zinc/manganese oxide energy storage from conversion reactions[J].Nature Energy,2016,1(5):1-17. |
| 10 | XU C J, LI B H, DU H D,et al .Energetic zinc ion chemistry:The rechargeable zinc ion battery[J].Angewandte Chemie,2012,124(4):957-959. |
| 11 | ALFARUQI M H, MATHEW V,GIM J,et al .Electrochemically induced structural transformation in a γ- MnO2 cathode of a high capacity zinc-ion battery system[J].Chemistry of Materials,2015,27(10):3609-3620. |
| 12 | ZHANG N, CHENG F Y, LIU Y C,et al .Cation-deficient spinel ZnMn2O4 cathode in Zn(CF3SO3)2 electrolyte for rechargeable aqueous Zn-ion battery[J].Journal of the American Chemical Society,2016,138(39):12894-12901. |
| 13 | ZHANG B H, LIU Y, WU X W,et al .An aqueous rechargeable battery based on zinc anode and Na0.95MnO2 [J].Chemical Communications,2014,50(10):1209-1211. |
| 14 | LIU Z, PULLETIKURTHI G, ENDRES F .A Prussian blue/zinc secondary battery with a bio-ionic liquid-water mixture as electrolyte[J].ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(19):12158-12164. |
| 15 | ZHANG L Y, CHEN L, ZHOU X F,et al .Morphology-dependent electrochemical performance of zinc hexacyanoferrate cathode for zinc-ion battery[J].Scientific Reports,2015,5(1):18263. |
| 16 | HOU Z G, ZHANG X Q, LI X N,et al .Surfactant widens the electrochemical window of an aqueous electrolyte for better rechargeable aqueous sodium/zinc battery[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(2):730-738. |
| 17 | ZHANG L Y, CHEN L, ZHOU X F,et al .Towards high-voltage aqueous metal-ion batteries beyond 1.5 V:The zinc/zinc hexacyanoferrate system[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2015,5(2):1400930-1-5. |
| 18 | MING J, GUO J, XIA C,et al .Zinc-ion batteries:Materials,mechanisms,and applications[J].Materials Science & Engineering,2019,135:58-84. |
| 19 | 衡永丽,谷振一,郭晋芝,等 .水系锌离子电池用钒基正极材料的研究进展[J].物理化学学报,2021,37(3):2005013-1-16. |
| HENG Yong-li, GU Zhen-yi, GUO Jin-zhi,et al .Research progresses on vanadium-based cathode materials for aqueous zinc-ion batteries[J].Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2021,37(3):2005013-1-16. | |
| 20 | HE H N, JIN G H, WANG H Y,et al .Annealed NaV3O8 nanowires with good cycling stability as a novel cathode for Na-ion batteries[J].Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2014,2(10):3563-3570. |
| 21 | CAO Y H, FANG D, WANG C,et al .Novel aligned sodium vanadate nanowire arrays for high-performance lithium-ion battery electrodes[J].RSC Advances,2015,5(53):42955-42960. |
| 22 | CAO Y H, WANG J Y, CHEN X T,et al .Nanostructured sodium vanadate arrays as an advanced cathode material in high-performance sodium-ion batteries[J].Materials Letters,2019,237:122-125. |
| 23 | KIM S J, TANG C R, SINGH G,et al .New insights into the reaction mechanism of sodium vanadate for an aqueous Zn ion battery[J].Chemistry of Materials,2020,32(5):2053-2060. |
| 24 | HE P, ZHANG G B, LIAO X B,et al .Sodium ion stabilized vanadium oxide nanowire cathode for high-performance zinc-ion batteries[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2018,8(10):1702463-1-6. |
| 25 | DONG Y F, LI S, ZHAO K N,et al .Hierarchical zigzag Na1.25V3O8 nanowires with topotactically encoded superior performance for sodium-ion battery cathodes[J].Energy & Environmental Science,2015,8(6):1267-1275. |
| 26 | WANG J, POLLEUX J,LIM J,et al .Pseudocapacitive contributions to electrochemical energy storage in TiO2 (anatase) nanoparticles[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2007,111(140):14925-14931. |
| 27 | SIMON P, GOGOTSI Y, DUNN B .Where do batteries end and supercapacitors begin[J].Science,2014,343(6176):1210-1211. |
| 28 | CONWAY B E, BIRSS V, WOJTOWICZ J .The role and utilization of pseudocapacitance for energy storage by supercapacitors[J].Journal of Power Sources,1997,66(1/2):1-14. |
| 29 | LINDATROM H, SODERGREN S, SOLBRAND A,et al .Li+ ion insertion in TiO2 (anatase).2.Voltammetry on nanoporous films[J].Journal of Physical Chemistry B,1997,101(39):7717-7722. |
| 30 | SOUNDHARRAJAN V, SAMBANDAM B, KIM S,et al .Na2V6O16·3H2O barnesite nanorod:An open door to display a stable and high energy for aqueous rechargeable Zn-ion batteries as cathodes[J].Nano Letters,2018,18(4):2402-2410. |
| 31 | GUO X, FANG G Z, ZHANG W Y,et al .Mechanistic insights of Zn2+ storage in sodium vanadates[J].Advanced Energy Materials,2018,8(27):1801819-1-7. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |