

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
Image Sentiment Transformation Based on Adaptive Brightness Adjustment
Received date: 2022-03-29
Online published: 2022-07-01
Supported by
the Joint Fund of the National Natural Science Foundation of China and Guandong Province(U1801262)
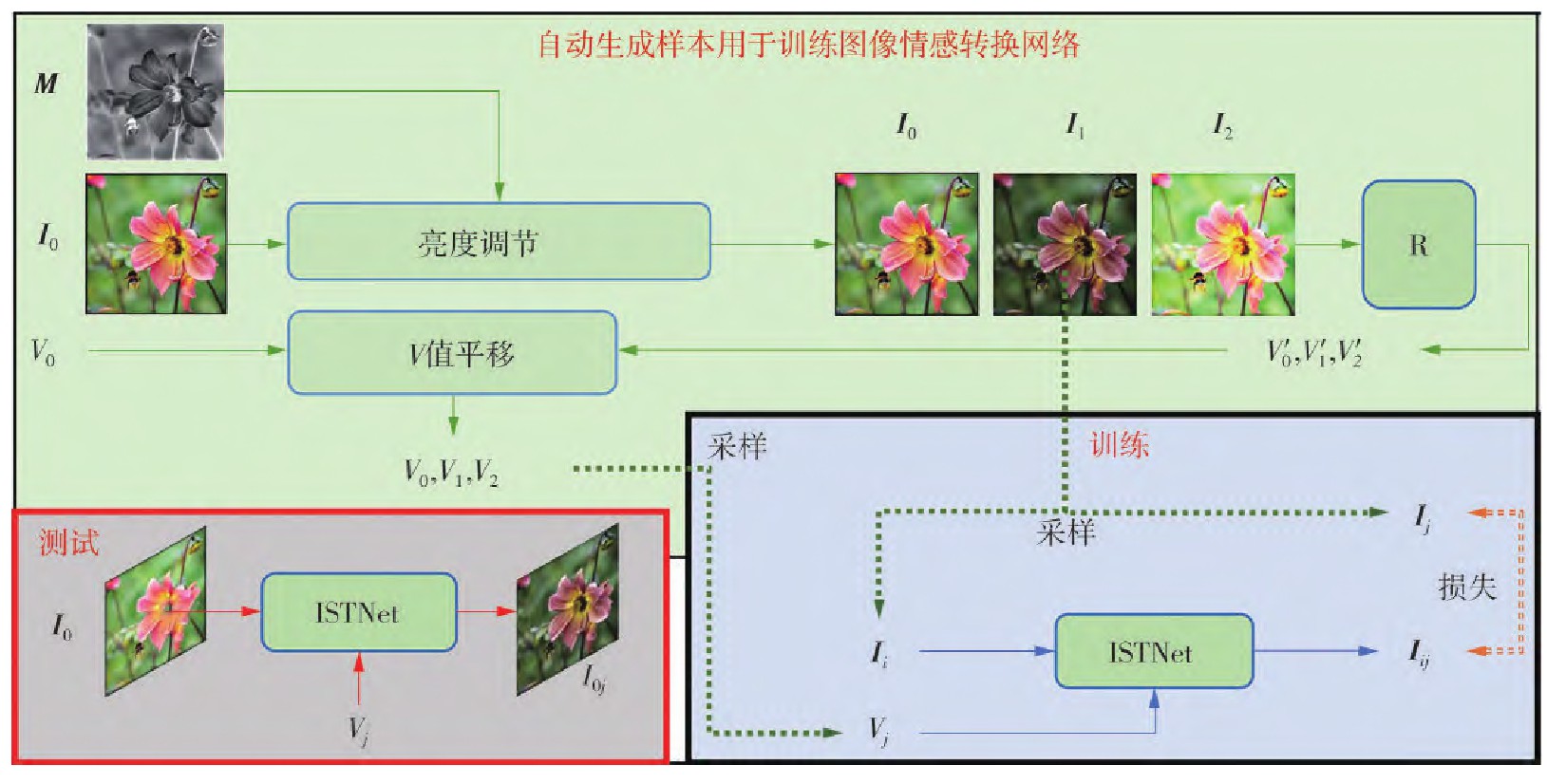
Common image sentiment transformation methods are based on the assumption that transferring image color can transfer image sentiment. However, due to the influence of image content, transferring image color cannot completely transfer image sentiment, and it is necessary to obtain a suitable reference image before transferring image color. However, in practical application, there will be difficulties in obtaining reference images that are similar to the target image in sentiments and similar to the source image in content, and the semantic consistency of local objects need to be considered when transferring image color. Therefore, this paper proposed an image sentiment transformation method based on adaptive brightness adjustment. According to the significant correlation between image brightness and image sentiment (also known as Valence value, abbreviated as V value) in psychology, the method adaptively adjusts brightness through deep neural network ISTNet to convert the image to target image sentiment. First, an image and its corresponding true V value were obtained from the existing image emotion dataset. By changing the image brightness, a series of images with different brightness can be obtained. Then, the pseudo V values corresponding to the images with the same content but different brightness were predicted by the pre-trained image V value regression. Finally, ISTNet was trained with these images and pseudo V values to learn the internal relationship between image brightness adjustment and sentimental change. In practical application, without any reference image, directly input the image and the target V value into the neural network ISTNet to obtain the output image of the corresponding sentimental tag. The experimental results show that the performance of this method is better than the existing color based image sentiment transformation methods.
XING Xiaofen, LI Minsheng, XU Xiangmin . Image Sentiment Transformation Based on Adaptive Brightness Adjustment[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2022 , 50(12) : 1 -12 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220165
| 1 | YANG C K, PENG L K .Automatic mood-transferring between color images [J].IEEE Computer Graphics and Applications,2008,28(2):52-61. |
| 2 | HE L, QI H, ZARETZKI R .Image color transfer to evoke different emotions based on color combinations [J].Signal,Image and Video Processing,2015,9(8):1965-1973. |
| 3 | WANG X, JIA J, CAI L .Affective image adjustment with a single word [J].Visual Computer,2013,29(11):1121-1133. |
| 4 | LIU S, PEI M .Texture-aware emotional color transfer between images [J].IEEE Access,2018,6:31375-31386. |
| 5 | SU Y Y, SUN H M .Emotion-based color transfer of images using adjustable color combinations [J].Soft Compu-ting,2019,23(3):1007-1020. |
| 6 | PENG K C, CHEN T, SADOVNIK A,et al .A mixed bag of emotions:model,predict,and transfer emotion distributions [C]∥ Proceedings of 2015 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Boston:IEEE,2015:860-868. |
| 7 | KIM H R, KANG H, LEE I K .Image recoloring with valence-arousal emotion model [J].Computer Graphics Forum,2016,35(7):209-216. |
| 8 | ALI A R,ALI M .Automatic image transformation for inducing affect[EB/OL].(2017-07-25)[2022-03-31]..53yu.com/abs/1707.08148. |
| 9 | LUO X, ZHANG J, WU G,et al .Arbitrary image emotionalizing with style transfer [C]∥ Proceedings of the 19th Pacific-Rim Conference on Multimedia.Hefei:Springer,Cham,2018:407-416. |
| 10 | CHEN T, XIONG W, ZHENG H,et al .Image sentiment transfer [C]∥ Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Multimedia.Seattle:ACM,2020:4407-4415. |
| 11 | AN J, CHEN T, ZHANG S,et al .Global image sentiment transfer [C]∥ Proceedings of 2020 the 25th International Conference on Pattern Recognition.Milan:IEEE,2021:6267-6274. |
| 12 | VALDEZ P, MEHRABIAN A .Effects of color on emotions [J].Journal of Experimental Psychology:General,1994,123(4):394-409. |
| 13 | WANG Z, BOVIK A C, SHEIKH H R,et al .Image quality assessment:from error measurement to structural similarity [J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2004,13(1):600-613. |
| 14 | LIU D, JIANG Y, PEI M,et al .Emotional image color transfer via deep learning [J].Pattern Recognition Letters,2018,110:16-22. |
| 15 | LIU S, WANG H, PEI M .Facial-expression-aware emotional color transfer based on convolutional neural network [J].ACM Transactions on Multimedia Computing,Communications,and Applications,2022,18(1):1-19. |
| 16 | EKMAN P, FRIESEN W V, ELLSWORTH P .What emotion categories or dimensions can observers judge from facial behavior? [M].Emotion in the human face.Fairview Park:Pergamon Press,1972:67-75. |
| 17 | RUSSELL J A .A circumplex model of affect [J].Journal of Personality and Social Psychology,1980,39(6):1161-1178. |
| 18 | LANG P J, BRADLEY M M, CUTHBERT B N .International affective picture system (IAPS):technical manual and affective ratings [Z].Gainesville:NIMH Center for the Study of Emotion and Attention,1997:39-58. |
| 19 | BAI L, MA H, HUANG Y X,et al .The development of native Chinese affective picture system:a pretest in 46 college students [J].Chinese Mental Health Journal,2005,19(11):719-722. |
| 20 | BRADLEY M M, LANG P J .Measuring emotion:the self-assessment manikin and the semantic differential [J].Journal of Behavior Therapy and Experimental Psychiatry,1994,25(1):49-59. |
| 21 | WANG S, DING R .A qualitative and quantitative study of color emotion using valence-arousal [J].Frontiers of Computer Science,2012,6(4):469-476. |
| 22 | 杨圣豪,吴玥悦,毛佳昕,等 .基于半监督学习的涉及未成年人案件文书识别方法 [J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(1):29-38,46. |
| 22 | YANG Shenghao, WU Yueyue, MAO Jiaxin,et al .Juvenile case documents recognition method based on semi-supervised learning [J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(1):29-38,46. |
| 23 | LEE D H .Pseudo-label:the simple and efficient semi-supervised learning method for deep neural networks [C]∥ Proceedings of ICML 2013:Challenges in Re-presentation Learning.Atlanta:JMLR,2013:896-901. |
| 24 | SOHN K, BERTHELOT D, CARLINI N,et al .FixMatch:simplifying semi-supervised learning with consistency and confidence [J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,2020,33:596-608. |
| 25 | MORAN S, MARZA P, McDONAGH S,et al .DeepLPF:deep local parametric filters for image enhancement [C]∥ Proceedings of 2020 IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Seattle:IEEE,2020:12826-12835. |
| 26 | ZENG H, CAI J, LI L,et al .Learning image-adaptive 3D lookup tables for high performance photo enhancement in real-time [J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2022,44(4):2058-2073. |
| 27 | JIANG Y, GONG X, LIU D,et al .EnlightenGAN:deep light enhancement without paired supervision [J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2021,30:2340-2349. |
| 28 | ZHAO S, ZHAO X, DING G,et al .EmotionGAN:unsupervised domain adaptation for learning discrete probability distributions of image emotions [C]∥ Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia.Seoul:ACM,2018:1319-1327. |
| 29 | ZHAO S, LIN C, XU P,et al .CycleEmotionGAN:emotional semantic consistency preserved cycleGAN for adapting image emotions [C]∥ Proceedings of the 33rd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Honolulu:AAAI,2019:2620-2627. |
| 30 | HE K, ZHANG X, REN S,et al .Deep residual lear-ning for image recognition [C]∥ Proceedings of 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vegas:IEEE,2016:770-778. |
| 31 | GLOROT X, BORDES A, BENGIO Y .Deep sparse rectifier neural networks [C]∥ Proceedings of the 14th International Conference on Artificial Intelligence and Statistics.Fort Lauderdale:JMLR,2011:315-323. |
| 32 | ZHU J Y, PARK T, ISOLA P,et al .Unpaired image-to-image translation using cycle-consistent adversarial networks [C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:2223-2232. |
| 33 | PEREZ E, STRUB F, de VRIES H,et al .FiLM:visual reasoning with a general conditioning layer [C]∥ Proceedings of the 32nd AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.New Orleans:AAAI,2018:2819-2826. |
| 34 | RONNEBERGER O, FISCHER P, BROX T .U-Net:convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation [C]∥ Proceedings of the 18th International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention.Munich:Springer,2015:234-241. |
| 35 | HUANG X, BELONGIE S .Arbitrary style transfer in real-time with adaptive instance normalization [C]∥ Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:1501-1510. |
| 36 | MAAS A L, HANNAN A Y, NG A Y .Rectifier nonlinearities improve neural network acoustic models[EB/OL].(2013-05-16) [2022-03-31].. |
| 37 | ULYANOV D, VEDALDI A, LEMPITSKY V .Instance normalization:the missing ingredient for fast stylization[EB/OL].(2017-11-06)[2022-03-31]..53yu.com/abs/1607.08022. |
| 38 | KINGMA D, BA J .Adam:a method for stochastic optimization [EB/OL].(2017-01-30)[2022-03-31].. |
| 39 | ZHU Siqi .Sentiment image generation:learning continuous emotional distribution with brightness [DB/OL].(2021-08-10)[2022-03-31].. |
| 40 | WARRINER A B, KUPERMAN V, BRYSBAERT M .Norms of valence,arousal,and dominance for 13915 English lemmas [J].Behavior Research Methods,2013,45(4):1191-1207. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |