

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
Deep Learning-Based Prediction of Contact Force in the Process of Shoveling Up Glass Subtrate
Received date: 2021-11-04
Online published: 2022-03-15
Supported by
the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51975587)
In view of the problem of insufficient characterization ability and poor versatility of action force modeling methods in existing robot contact operation tasks, this paper studied on the modeling methods of complex contact dynamics by taking the actual production process of glass substrate shoveling as an example. Considering the fact that the forces during the glass substrate shoveling are affected by the contact dynamics of multiple interfaces, exhibiting the multimodal, nonlinear, and non-stationarity properties, this paper proposed a method for the prediction of the contact force by integrating physical prior knowledge in different forms in the design and training process of deep learning models. According to the stress characteristics of the glass substrate’s shoveling up process, a deep learning model structure combining multi-scale convolutional kernel, attention mechanism and long and short-term memory network was proposed; the kinetic parameter randomization method and the contact force compensation measures based on material mechanics and fracture mechanics were proposed to make the simulation training data more robust to reflect the real contact situation; based on the mean square error loss function, the additional loss function was introduced for network training for the unreasonable physical “penetration” behavior. The experimental results show that the proposed model can accurately predict the horizontal and vertical forces with the root mean square error of 0.286 in the single-step prediction, and the multi-step prediction results are also good enough to meet the application requirements. The prediction performance of the model is superior to the existing mainstream models. The ablation experiment shows that the excellent prediction performance of the model proposed is the result of the joint contribution of the local feature extraction module, the attention mechanism module and the temporal feature extraction module. At the same time, the improved loss function improves the stability of the model training. Our method can be used in similar applications for the prediction of robotic contact force with the environment.
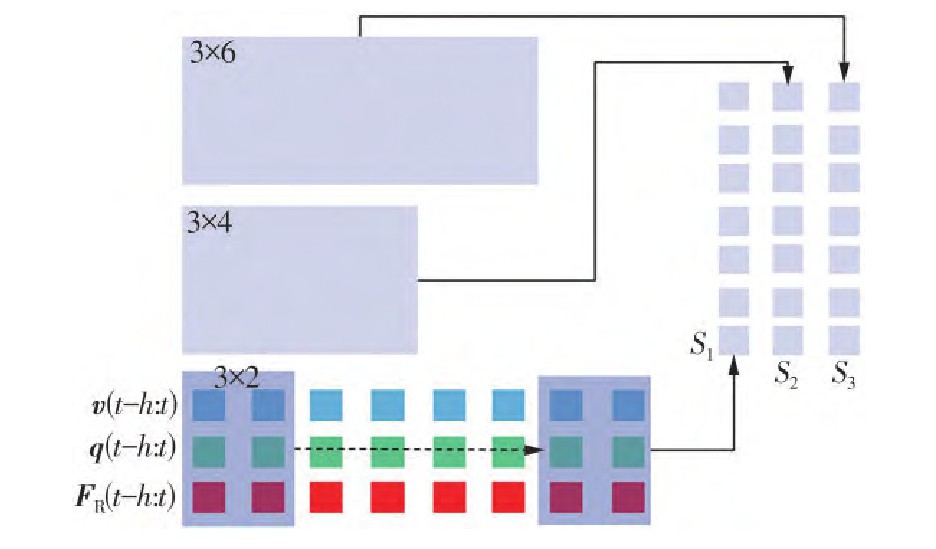
Key words: glass substrate; contact dynamics; force prediction; deep learning; physical priors
HOU Liwei, WANG Hengsheng, ZOU Haoran . Deep Learning-Based Prediction of Contact Force in the Process of Shoveling Up Glass Subtrate[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2022 , 50(8) : 71 -81 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210698
| 1 | 李继军,聂晓梦,李根生,等 .平板显示技术比较及研究进展[J].中国光学,2018,11(5):695-710. |
| 1 | LI Ji-jun, NIE Xiao-meng, LI Gen-sheng,et al .Comparison and research progress of flat panel display technology[J].Chinese Optics,2018,11(5):695-710. |
| 2 | WANG L, ZHANG K, SONG Z,et al .Ceria concentration effect on chemical mechanical polishing of optical glass[J].Applied Surface Science,2007,253(11):4951-4954. |
| 3 | 王恒升,章壮,杨会义,等 .一种平板显示玻璃起爪装置、起爪机械臂、自动上下料装置及起爪装置的使用方法:CN108726174A[P].2018-11-02. |
| 4 | AYDINOGLU A, PRECIADO V M, POSA M .Contact-aware controller design for complementarity systems[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Paris:IEEE,2020:1525-1531. |
| 5 | POSA M, CANTU C, TEDRAKE R .A direct method for trajectory optimization of rigid bodies through contact[J].The International Journal of Robotics Research,2014,33(1):69-81. |
| 6 | MU X, WU Q .On impact dynamics and contact events for biped robots via impact effects[J].IEEE Transactions on Systems,Man,and Cybernetics,Part B (Cyberne-tics),2006,36(6):1364-1372. |
| 7 | KOLBERT R, CHAVAN-DAFLE N, RODRIGUEZ A .Experimental validation of contact dynamics for in-hand manipulation[C]∥Proceedings of the International Symposium on Experimental Robotics.Tokyo:IEEE,2016:633-645. |
| 8 | EREZ T, TASSA Y, TODOROV E .Simulation tools for model-based robotics:comparison of Bullet,Havok,MuJoCo,ODE and PhysX[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Washington DC:IEEE,2015:4397-4404. |
| 9 | 郭胤,王家序,李峰,等 .弹性体摩擦的黏滞疲劳理论及实验研究[J].摩擦学学报,2013,33(5):443-448. |
| 9 | GUO Yin, WANG Jia-xu, LI Feng,et al .Theory of adhesion hysteresis-fatigue of elastomeric tribology and experimental demonstration[J].Tribology,2013,33(5):443-448. |
| 10 | FULLER D D .Theory and practice of lubrication for engineers[M].New York:Wiley,1984. |
| 11 | KOSHY C S, FLORES P, LANKARANI H M .Study of the effect of contact force model on the dynamic response of mechanical systems with dry clearance joints:computational and experimental approaches[J].Nonlinear Dynamics,2013,73(1):325-338. |
| 12 | FICUCIELLO F, MIGLIOZZI A, COEVOET E,et al .FEM-based deformation control for dexterous manipulation of 3D soft objects[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.Madrid:IEEE,2018:4007-4013. |
| 13 | NAGABANDI A, KONOLIGE K, LEVINE S,et al .Deep dynamics models for learning dexterous manipulation[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference on Robot Learning.Cambridge:[s. n.],2020:1101-1112. |
| 14 | BAUZA M, RODRIGUEZ A .A probabilistic data-driven model for planar pushing[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Singapore:IEEE,2017:3008-3015. |
| 15 | LI Y, WU J, TEDRAKE R,et al .Learning particle dynamics for manipulating rigid bodies,deformable objects,and fluids[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Learning Representations.New Orleans:[s. n.],2019. |
| 16 | FAZILI N, KOLBERT R, TEDRAKE R,et al .Para-meter and contact force estimation of planar rigid-bodies undergoing frictional contact[J].International Journal of Robotics Research,2017,36(13):1437-1454. |
| 17 | AJAY A, WU J, FAZELI N,et al .Augmenting physical simulators with stochastic neural networks:case study of planar pushing and bouncing[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.Madrid:IEEE,2018:3066-3073. |
| 18 | GOLTS A, FREEDMAN D, ELAD M .Unsupervised single image dehazing using dark channel prior loss[J].IEEE Transactions on Image Processing,2019,29:2692-2701. |
| 19 | CRANMER M, GREYDANUS S, HOYER S,et al .Lagrangian neural networks[EB/OL].(2020-07-30)[2021-10-12].. |
| 20 | UTGOFF, PAUL E .Machine learning of inductive bias[M].Boston:Springer Science & Business Media,2012. |
| 21 | 何彦,凌俊杰,王禹林,等 .基于长短时记忆卷积神经网络的刀具磨损在线监测模型[J].中国机械工程,2020,31(16):1959-1967. |
| 21 | HE Yan, LING Junjie, WANG Yulin,et al .In-process tool wear monitoring model based on LSTM-CNN[J].China Mechanical Engineering,2020,31(16):1959-1967. |
| 22 | PENG X B, ANDRYCHOWICZ M, ZAREMBA W,et al .Sim-to-real transfer of robotic control with dyna-mics randomization[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation.Brisbane:IEEE,2018:3803-3810. |
| 23 | JOZEFOWICZ R, WOJCIECH Z, ILYA S .An empirical exploration of recurrent network architectures[C]∥Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning.Lile:[s. n.],2015:2342-2350. |
| 24 | COUMANS E .Bullet physics simulation[C]∥Proceedings of the ACM SIGGRAPH 2015 Courses.Los Angeles:[s. n.],2015. |
| 25 | HOU L W, WANG H S, LIU R H .Research on mo-deling and experiment of glass substrate peeling based on adhesion theory[J].Tehni?ki Vjesnik,2019,26(6):1827-1832. |
| 26 | 刘润华,王恒升,侯力玮 .玻璃基板无损剥离的建模与分析[J].制造业自动化,2020,42(2):36-41. |
| 26 | LIU Run-hua, WANG Heng-sheng, HOU Li-wei .Mo-deling and analysis of nondestructive peeling of glass substrate[J].Manufacturing Automation,2020,42(2):36-41. |
| 27 | JANNER M, FU J, ZHANG M,et al .When to trust your model:model-based policy optimization[C]∥Proceedings of the Conference in Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.Vancouver:[s.n.],2019:12519-12530. |
| 28 | FUNABASHI S, OGASA S, ISOBE T,et al .Variable in-hand manipulations for tactile-driven robot hand via CNN-LSTM[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.Las Vegas:IEEE,2020:9472-9479. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |