

Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science) >
A Force-Sensorless Dragging Teaching Method Based on Disturbance Kalman Filter for Robot
Received date: 2021-12-10
Online published: 2022-02-10
Supported by
the Key Field Research and Development Project of Guangdong Province(2021B0101420003)
The dragging teaching method is easy to operate and has high teaching efficiency, which is more in line with modern flexible production. To realize the dragging teaching of industrial robots, it is necessary to accurately measure the external force and control the motion caused by the external force. In order to measure the external force exerted by the operator without torque sensor, an external force observer based on disturbance Kalman filter was designed. The observer takes the external joint torque as the disturbance term, and introduces generalized momentum to establish the state space equation of the robot system, and then uses the Kalman filter algorithm to obtain the optimal observed value of the external torque. Among them, in order to improve the estimation accuracy, the robot dynamic model was established by combining the rigid-body dynamic model and a deep neural network, which not only avoids modeling the complex friction torque but also compensates for the unmodeled factors through the deep neural network. Besides, in order to realize the leading control of the robot in the process of dragging teaching, the dynamic response relationship between the teaching motion and the external torque is equivalent to a mass damping system. An admittance control method with adaptive damping was proposed to convert the observed external torque into the desired joint angle of the teaching motion, and adaptively adjust the system damping parameters according to the change trend of the external torque to improve the teaching effect of the robot. The experiment results show that the proposed dynamic model has a lower mean square root error in the prediction torque, which can reduce the error by no less than 20%. The proposed control scheme can realize the dragging teaching without torque sensors on the six-degree-of-freedom industrial robot, and the adaptive damping method can reduce the torque required to rotate the joint by about 19%, which is more conducive to the start and stop of the teaching motion.
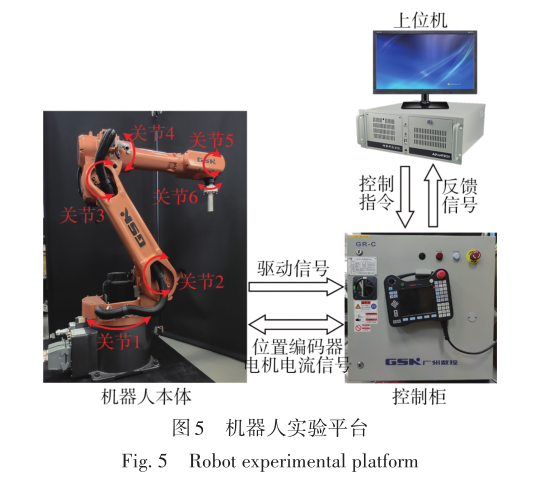
ZHANG Tie, XU Jinsheng, ZOU Yanbiao . A Force-Sensorless Dragging Teaching Method Based on Disturbance Kalman Filter for Robot[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science), 2022 , 50(9) : 116 -125 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210781
| 1 | ALBUSCHAFFER A, HADDADIN S,OTT C,et al .The DLR lightweight robot:design and control concepts for robots in human environments[J].Industrial Robot,2007,34(5):376-385. |
| 2 | ZHANG H, AHMAD S, LIU G .Torque estimation for robotic joint with harmonic drive transmission based on position measurements[J].IEEE Transactions on Robotics,2015,31(2):322-330. |
| 3 | ZHANG S, WANG S, JING F,et al .A sensorless hand huiding scheme based on model identification and control for industrial robot[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Informatics,2019,15(9):5204-5213. |
| 4 | RAGAGLIA M, ZANCHETTIN A M, BASCETTA L,et al .Accurate sensorless lead-through programming for lightweight robots in structured environments[J].Robotics and Computer Integrated Manufacturing,2016,39:9-21. |
| 5 | WAHRBURG A,BOS J, LISTMANN K D,et al .Motor- current-based estimation of cartesian contact forces and torques for robotic manipulators and its application to force control[J].IEEE Transactions on Automation Science and Engineering,2018,15(2):879-886. |
| 6 | HU J, XIONG R .Contact force estimation for robot manipulator using semi-parametric model and disturbance kalman filter[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2018,65(4):3365-3375. |
| 7 | WAHRBURG A, MORARA E, CESARI G,et al .Cartesian contact force estimation for robotic manipulators using kalman filters and the generalized momentum[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Automation Science and Engineering. Sweden:IEEE,2015:1230-1235. |
| 8 | 游有鹏,张宇,李成刚 .面向直接示教的机器人零力控制[J].机械工程学报,2014,50(3):10-17. |
| 8 | YOU Youpeng, ZHANG Yu, LI Chenggang .Force-free control for the direct teaching of robots[J].Journal of Mechanical Engineering,2014,50(3):10-17. |
| 9 | YUAN J J, WANG S, WAN W,et al .Direct teaching of industrial manipulators using current sensors[J].Assembly Automation,2018,38(2):216-225. |
| 10 | GOTO S, USUI T, KYURA N,et al .Forcefree control with independent compensation for industrial articulated robot arms[J].Control Engineering Practice,2007,15(6):627-638. |
| 11 | HOGAN N .Impedance control-an approach to manipulation.I - Theory.II - Implementation.III - Applications[J].Journal of Dynamic Systems Measurement and Control,1985,107:1-24. |
| 12 | CAPURSO M, ARDAKANI M, JOHANSSON R,et al .Sensorless kinesthetic teaching of robotic manipulators assisted by observer-based force control[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation. Singapore:IEEE,2017:945-950. |
| 13 | STOLT A, ROBERTSSON A, JOHANSSON R .Robotic force estimation using dithering to decrease the low velocity friction uncertainties[C]∥IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation,Seattle:IEEE,2015:3896-3902. |
| 14 | 耿令波 .工业机器人动力学参数辨识方法研究[D].南京:南京航空航天大学,2013. |
| 15 | MARQUES F, FLORES P, CLARO J,et al .A survey and comparison of several friction force models for dynamic analysis of multibody mechanical systems[J].Nonlinear Dynamics,2016,86(3):1407-1443. |
| 16 | CHEN W H, YANG J, GUO L,et al .Disturbance-observer-based control and related methods—an overview[J].IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2016,63(2):1083- 1095. |
| 17 | AXELSSON P, GUSTAFSSON F .Discrete-time solutions to the continuous-time differential lyapunov equation with applications to kalman filtering[J].Automatic Control IEEE Transactions on,2015,60(3):632-643. |
| 18 | SOUSA C D, CORTESAO R .Physical feasibility of robot base inertial parameter identification:A linear matrix inequality approach[J].International Journal of Robotics Research,2014,33(6):931-944. |
| 19 | SWEVERS J, VERDONCK W, SCHUTTER J D .Dynamic model identification for industrial robots[J].IEEE Control Systems,2007,27(5):58-71. |
| 20 | JIN J F, GANS N .Parameter identification for industrial robots with a fast and robust trajectory design approach[J].Robotics and Computer-Integrated Manufacturing,2015,31:21-29. |
| 21 | KINGMA D, BA J .Adam:a method for stochastic optimization[C]∥International Conference on Learning Representations. San Diego:OpenReview.net,2015:1-15. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |