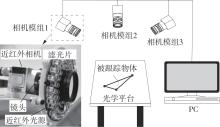
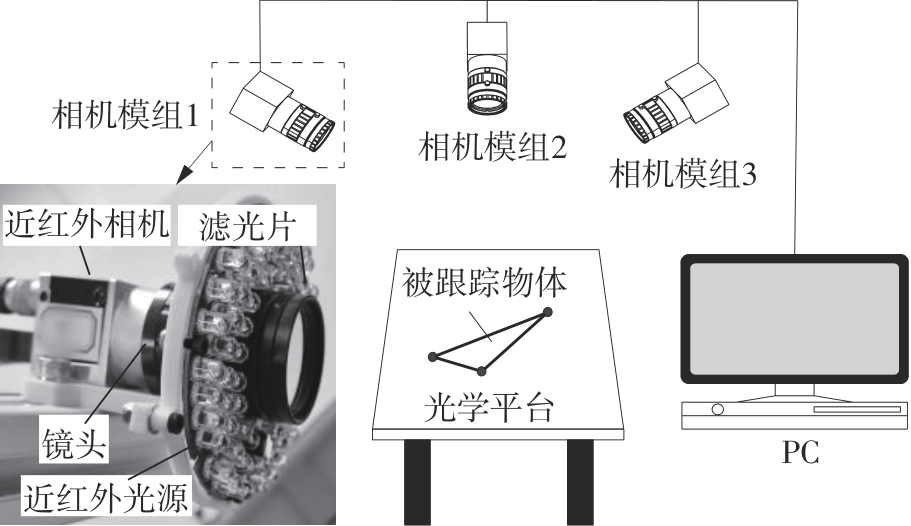
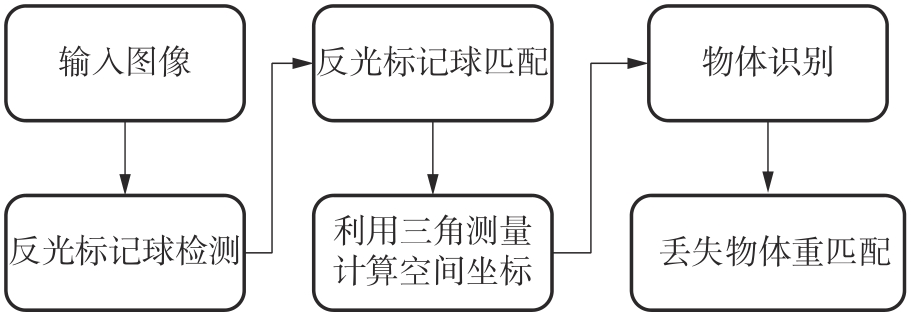
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (7): 31-38.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240427
• Mechanical Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
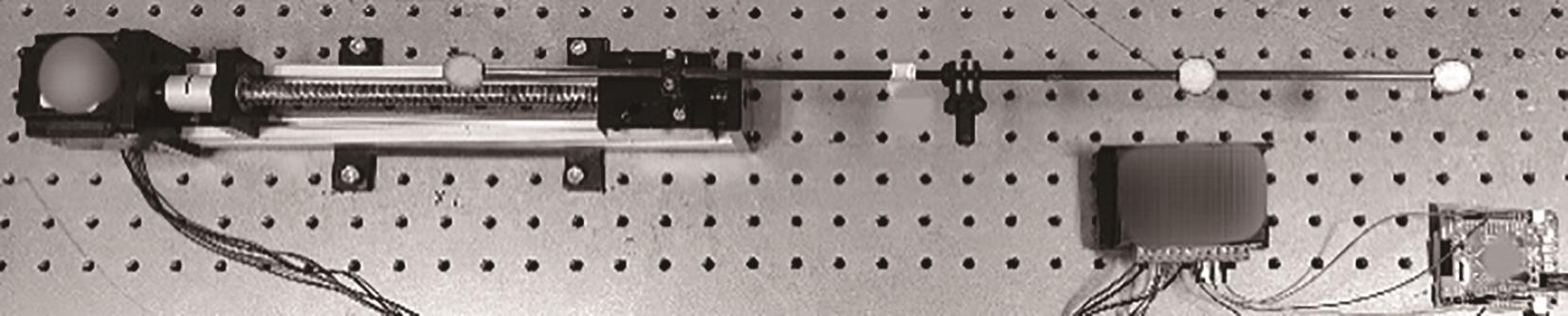
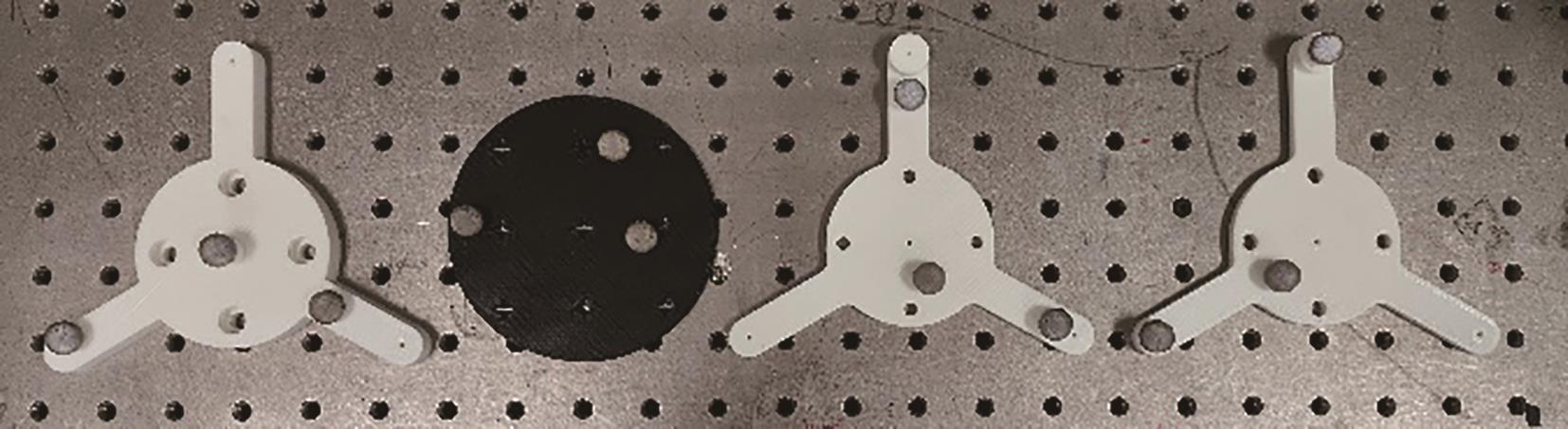
Multi-Object Real-Time Tracking Method Based on Multi-View Near-Infrared Vision
CHEN Zhong, WANG Aochen, GAO Xinyi, HE Lihui, ZHANG Xianmin
- School of Mechanical and Automotive Engineering,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China