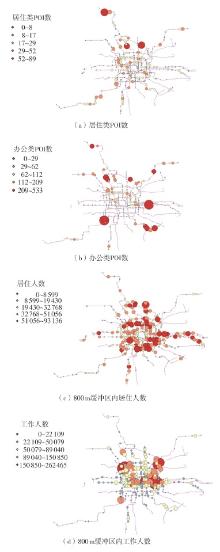
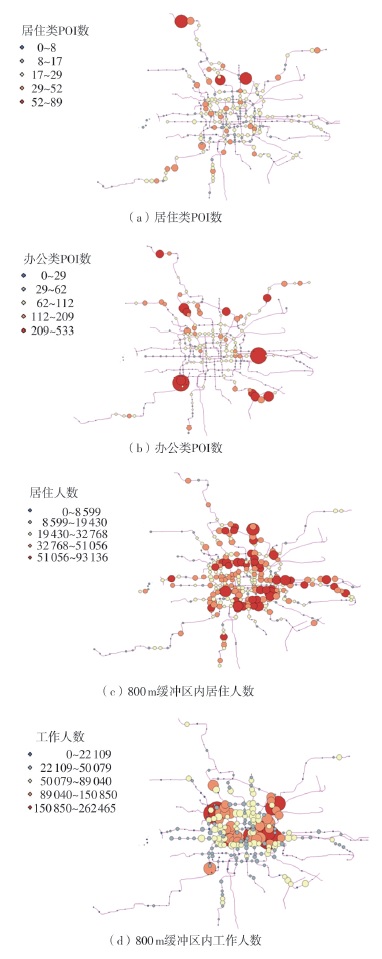
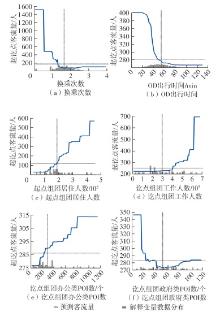
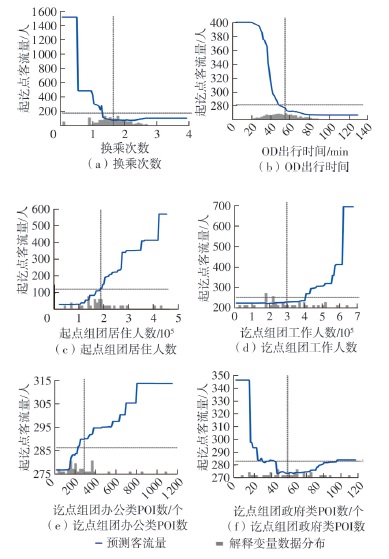
| [1] |
彭诗尧,陈绍宽,许奇,等 .基于POI的土地利用与轨道交通客流的空间特征[J].地理学报,2021,76(2):459-470.
|
|
PENG Shiyao, CHEN Shaokuan, XU Qi,et al .Spatial characteristics of land use based on POI and urban rail transit passenger flow[J].Acta Geographica Sinica,2021,76(2):459-470.
|
| [2] |
DEMISSIE M G, KATTAN L .Understanding thetemporal and spatial interactions between transit ridership and urban land-use patterns:an exploratory study[J].Public Transport,2022,14(2):385-417.
|
| [3] |
马壮林,杨兴,谭晓伟,等 .基于客流时间序列的城市轨道交通车站分类[J].长安大学学报(自然科学版),2021,41(6):113-126.
|
|
MA Zhuanglin, YANG Xing, TAN Xiaowei,et al .Classification of urban rail transit stations based on flow time series[J].Journal of Chang’ an Passenger University(Natural Science Edition),2021,41(6):113-126.
|
| [4] |
ZHANG Jinlei, CHE Hongshu, CHEN Feng,et al. Short-term origin-destination demand prediction in urban rail transit systems:a channel-wise attentive split-convolutional neural network method[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2021,124:102928/1-20.
|
| [5] |
许心越,孔庆雪,李建民,等 .建成环境对轨道交通客流的时空异质性影响分析[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2023,23(4):194-202.
|
|
XU Xinyue, KONG Qinxue, LI Jianmin,et al .Analysis of spatio-temporal heterogeneity impact of built environment on rail transit passenger flown[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2023,23(4):194-202.
|
| [6] |
CHEN Long, LU Yi, LIU Yanfang,et al .Association between built environment characteristics and metro usa-ge at station level with a big data approach[J].Travel Behaviour and Society,2022,28:38-49.
|
| [7] |
SOHN K, SHIM H .Factors generating boardings at metro stations in the Seoul metropolitan area[J].Ci-ties,2010,27(5):358-368.
|
| [8] |
LI Xiangyu, SINNIAH G K, LI Ruiwei .Identify impacting factor for urban rail ridership from built environment spatial heterogeneity[J].Case Studies on Transport Policy,2022,10(2):1159-1171.
|
| [9] |
魏杰,余丽洁,任璐,等 .城市轨道交通车站高峰时段与高峰客流预测模型[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2023,20(3):867-877.
|
|
WEI Jie, YU Lijie, REN Lu,et al .Prediction model of station-level peak time and peak ridership in urban rail transit[J].Journal of Railway Science and Enginee-ring,2023,20(3):867-877.
|
| [10] |
SHAO Qifan, ZHANG Wenjia, CAO Xinyu,et al .Threshold and moderating effects of land use on metro ridership in Shenzhen:implications for TOD planning[J].Journal of Transport Geography,2020,89(12):102878/1-12.
|
| [11] |
李培坤,陈旭梅,鲁文博,等 .基于XGBOOST-SHAP的地铁建成环境与站点出行距离的非线性关系研究[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2024,21(4):1624-1633.
|
|
LI Peikun, CHEN Xumei, LU Wenbo,et al .Research on nonlinear relationship between subway built environment and travel distance of stations based on XGBOOST-SHAP[J].Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2024,21(4):1624-1633.
|
| [12] |
YANG Linchuan, YU Bingjie, LIANG Yuan,et al .Time-varying and non-linear associations between metro ridership and the built environment[J].Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2023,132(2):104931/1-16.
|
| [13] |
GAN Zuoxian, YANG Min, FENG Tao,et al .Exa-mining the relationship between built environment and metro ridership at station-to-station level[J].Transportation Research Part D:Transport and Environment,2020,82:102332/1-19.
|
| [14] |
DANTSUJI T, HOANG N H, ZHENG Nan,et al .A novel metamodel-based framework for large-scale dynamic origin-destination demand calibration[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2022,136:103545/1-24.
|
| [15] |
雷方舒 .2022北京市通勤特征年度报告[R].北京:北京交通发展研究院,2023.
|
| [16] |
张鹏羽 .考虑时空异质性的城市轨道交通新线运营初期进出站客流量预测研究[D].北京:北京交通大学,2023.
|
| [17] |
王潇然,许心越,潘保霏,等 .基于地铁客流与建成环境映射关系的新线车站分类方法[J].铁道科学与工程学报.2024,21(3):980-993.
|
|
WANG Xiaoran, XU Xinyue, PAN Baofei,et al .A classification method for new line stations based on the mapping relationship between subway passenger flow and built environment[J].Journal of Railway Science and Engineer,2024,21(3):980-993.
|
| [18] |
李浩然,许心越,李建民,等 .考虑稀疏特性的城市轨道交通短时OD时空预测方法[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2023,20(10):3685-3695.
|
|
LI Haoran, XU Xinyue, LI Jianmin,et al .A spatio-temporal prediction method of short-term OD in urban rail transit with sparse data[J].Journal of Railway Science and Engineering,2023,20(10):3685-3695.
|
| [19] |
JAYAWEERA I, PERERA K, MUNASINGHE J .Centrality measures to identify traffic congestion on road networks:a case study of sri lanka[J].IOSR Journal of Mathematics,2017,13(2):13-19.
|
| [20] |
许奇,李雯茜,陈越,等 .建成环境对城市轨道交通起讫点客流的非线性影响及阈值效应[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2023,23(4):290-297.
|
|
XU Qi, LI Wenqian, CHEN Yue,et al .Nonlinear and threshold effects of built environment on origin-destination flows of urban rail transit[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2023,23(4):290-297.
|
| [21] |
LIANG Jian, TANG Jinjun, GAO Fan,et al .On region-level travel demand forecasting using multi-task adaptive graph attention network[J].Information Sciences,2023,622:161-177.
|