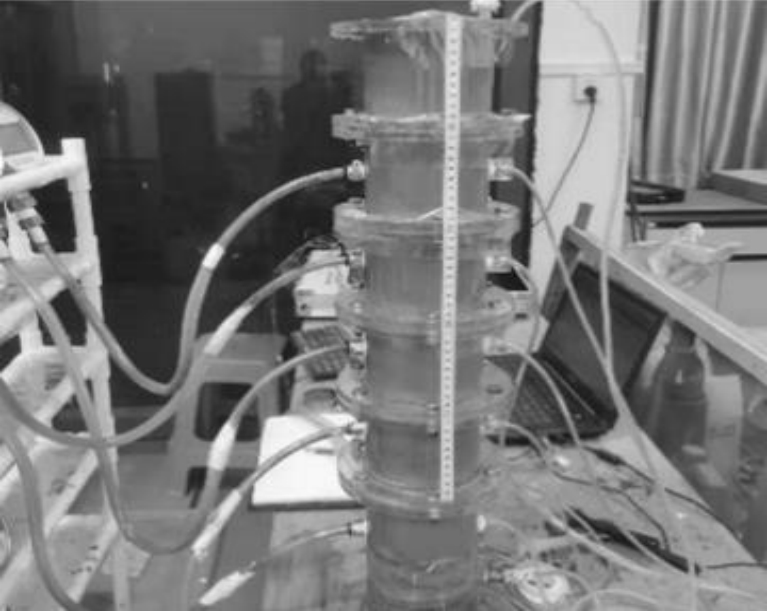
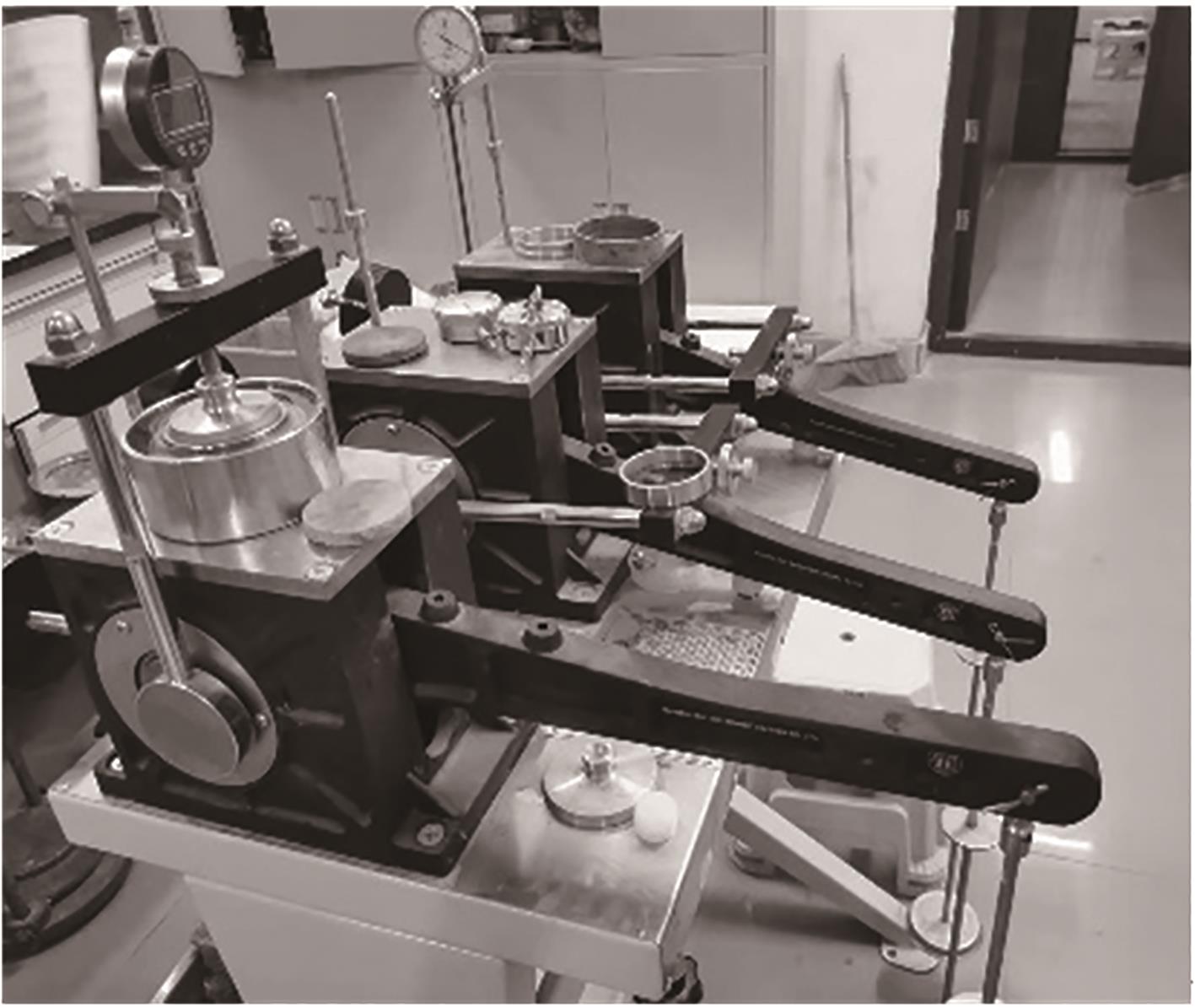
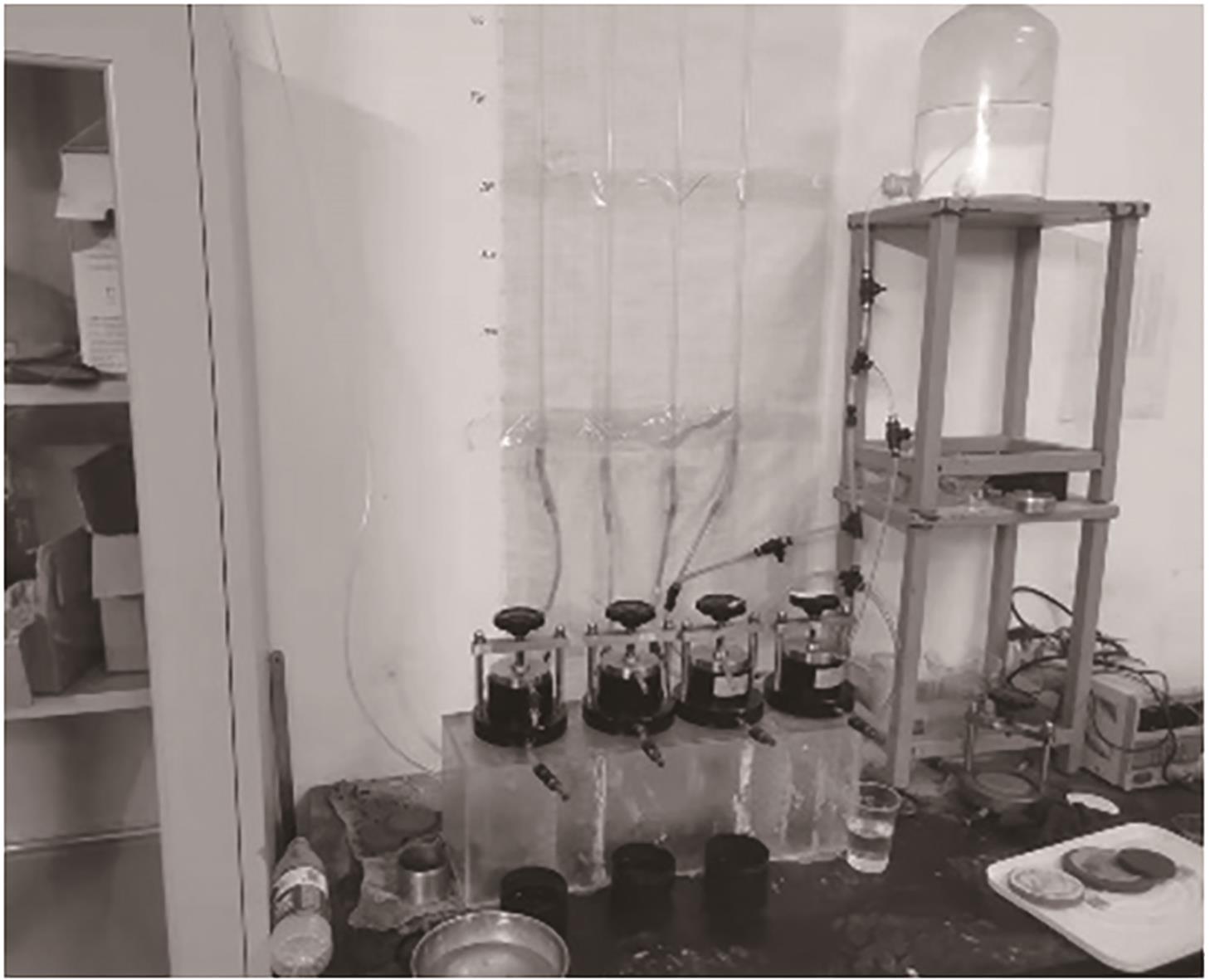
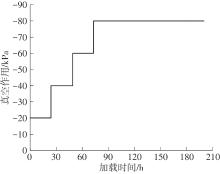
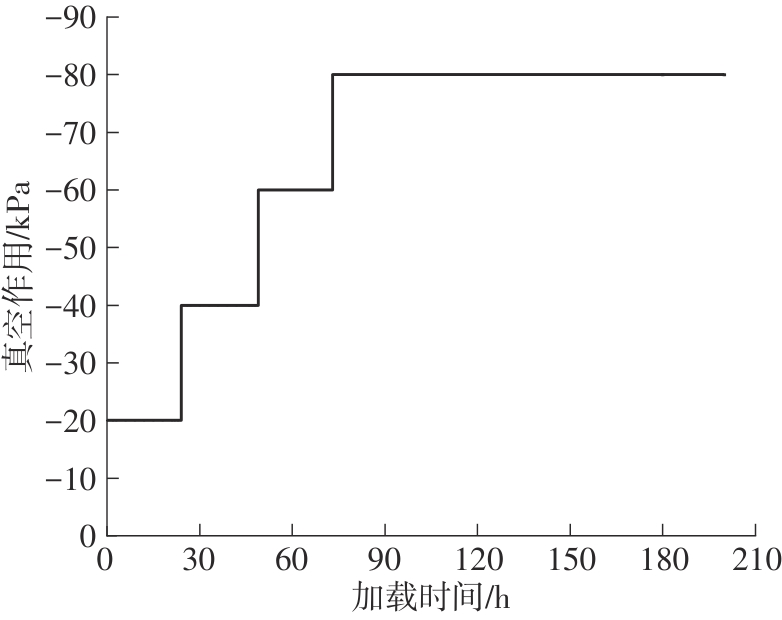
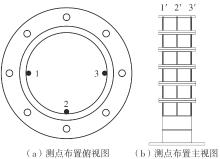
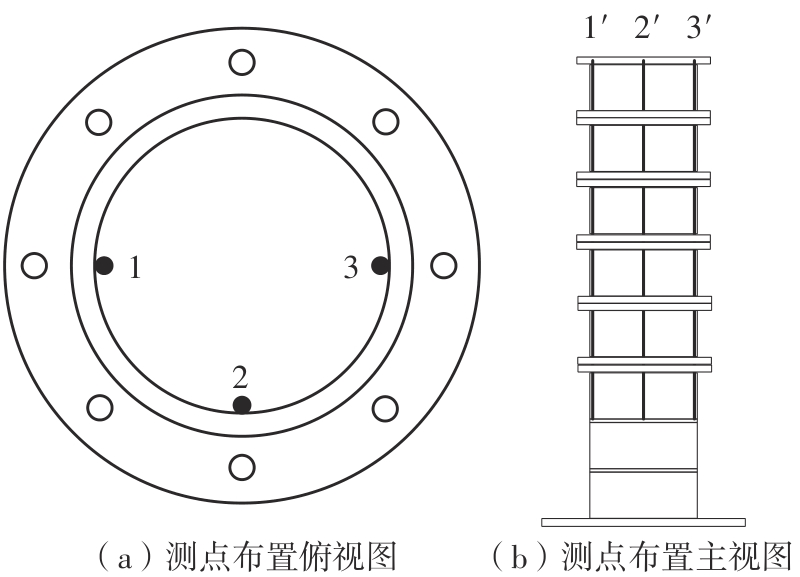
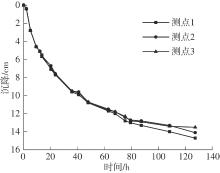
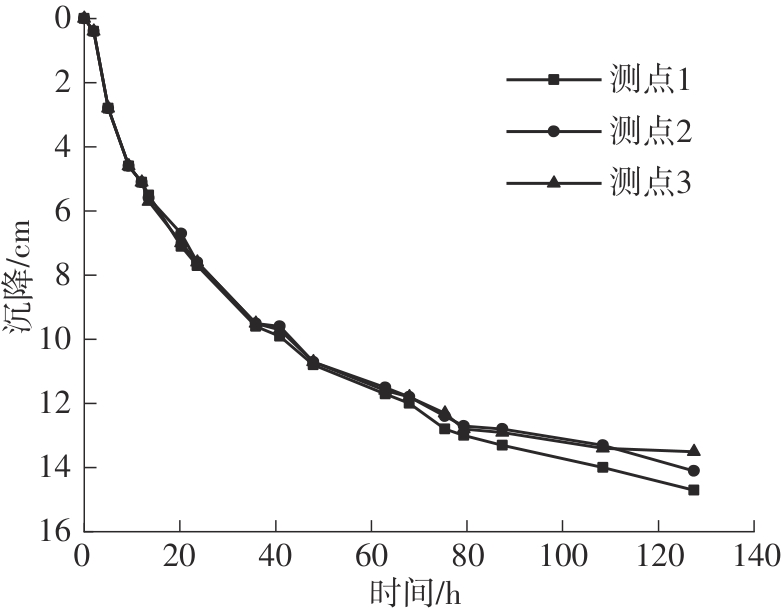
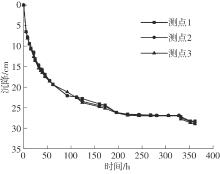
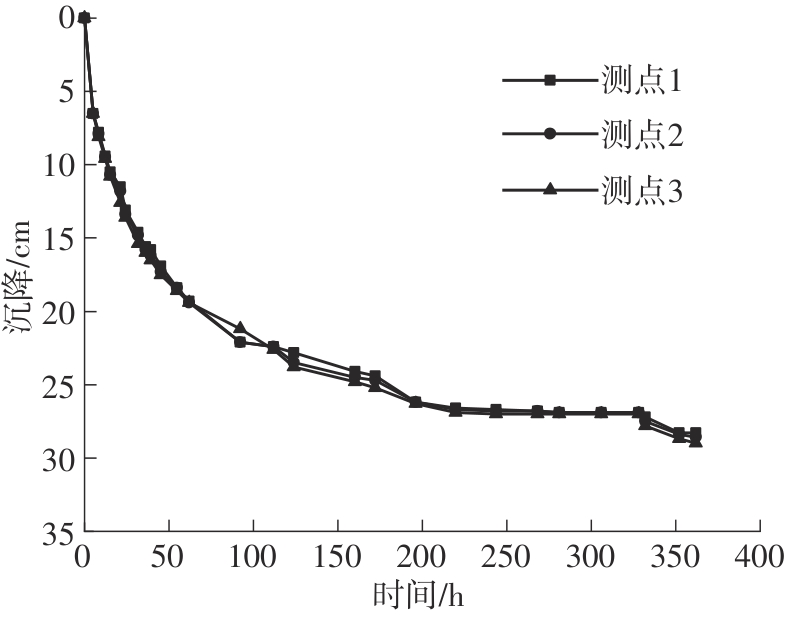
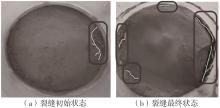
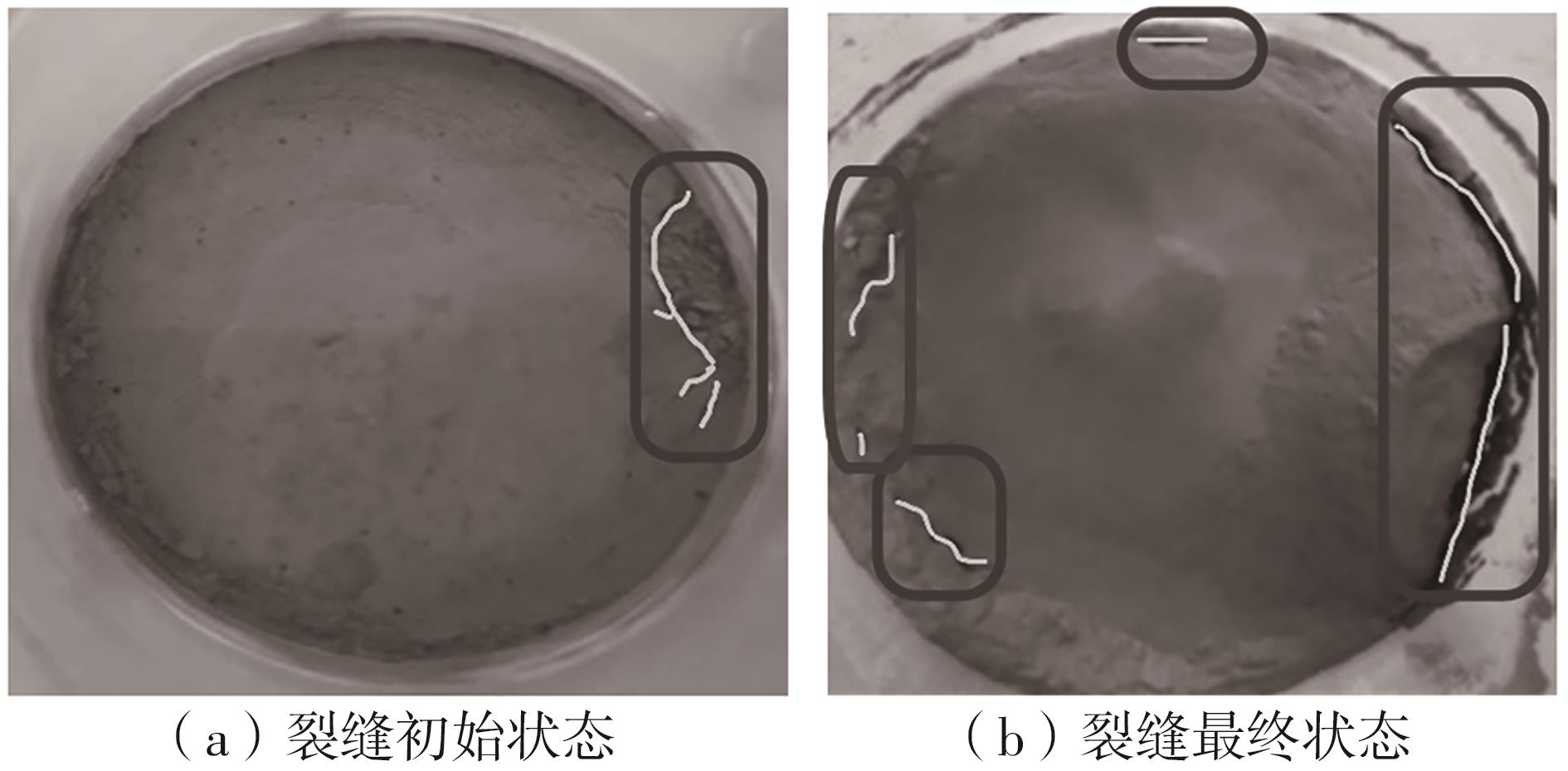
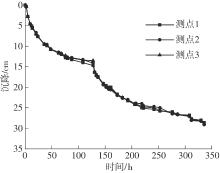
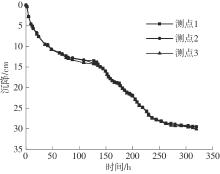
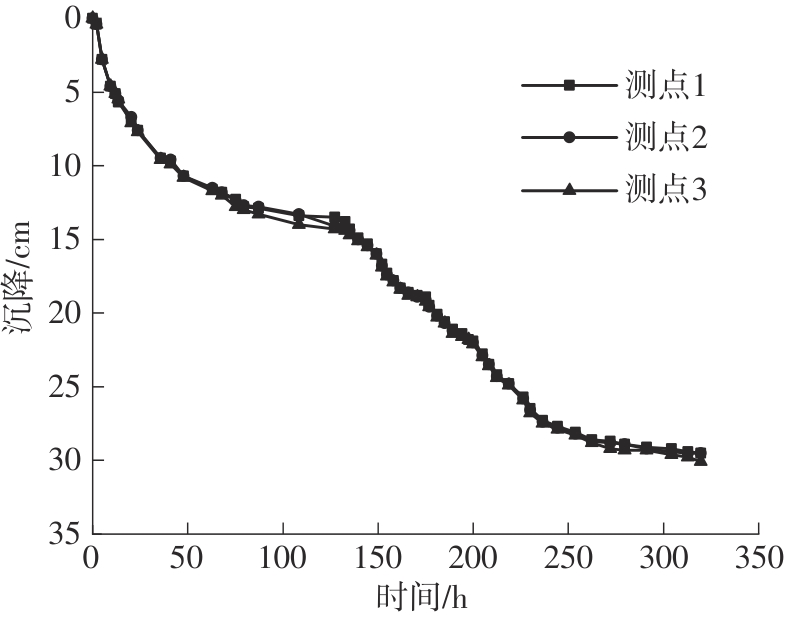
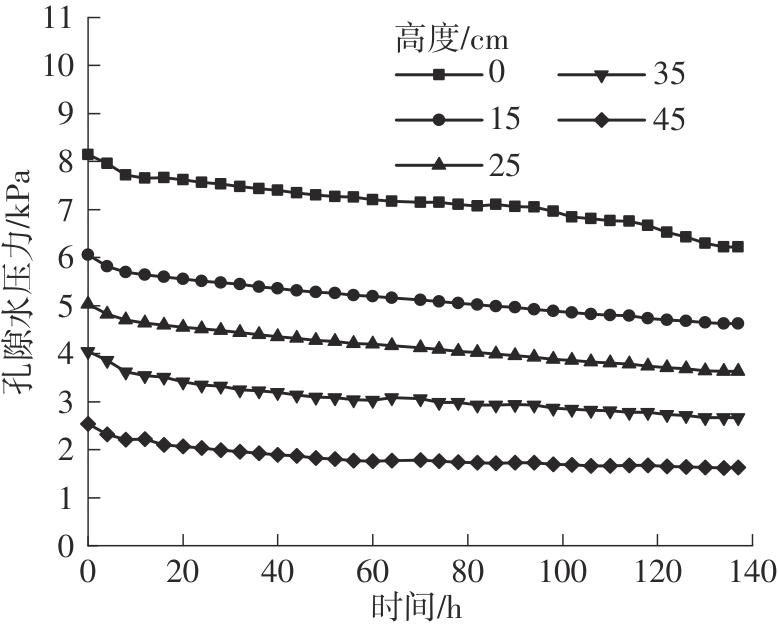
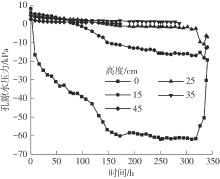
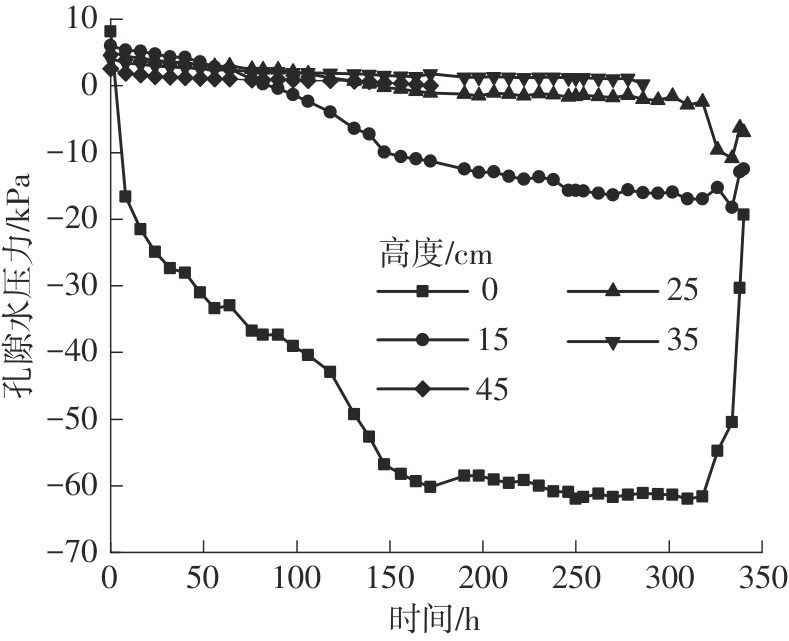
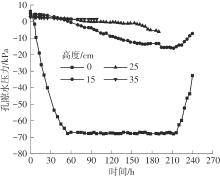
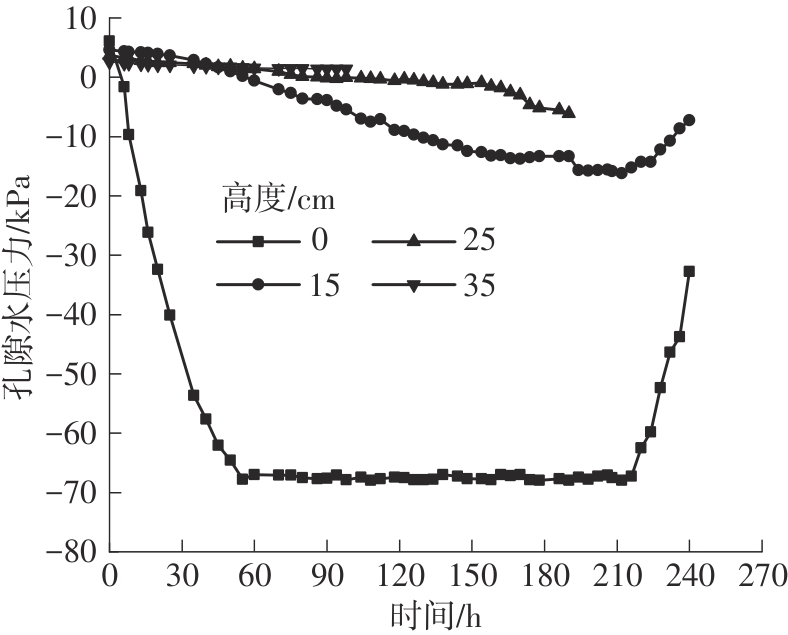
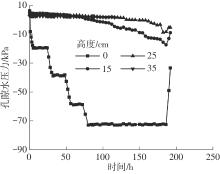
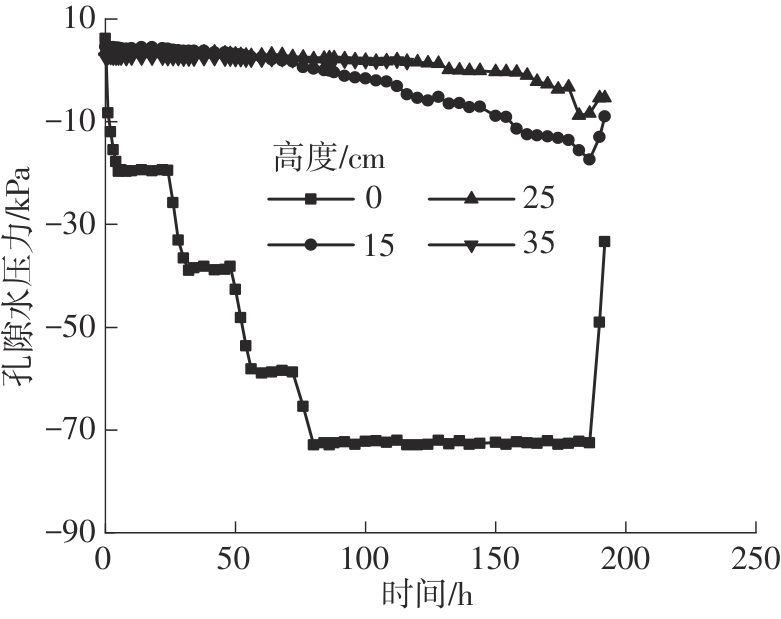
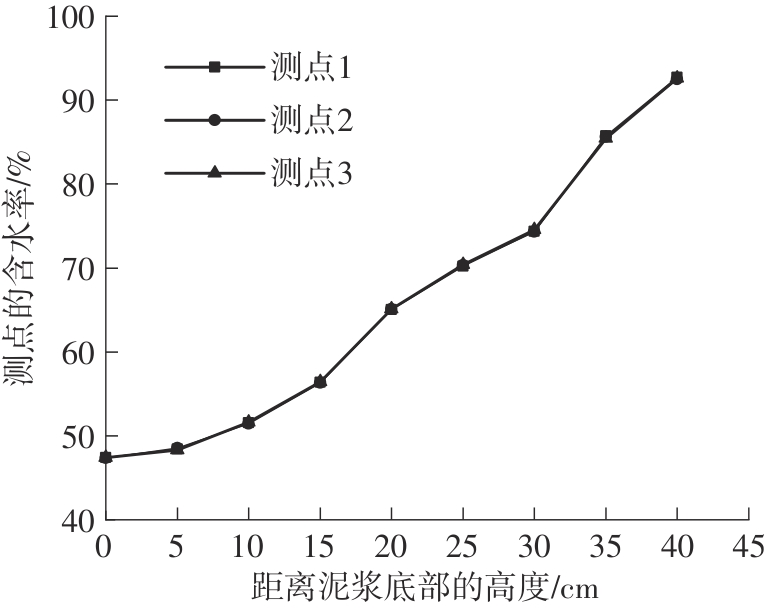
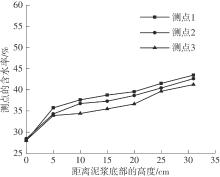
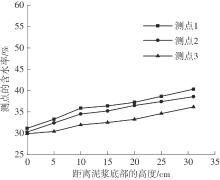
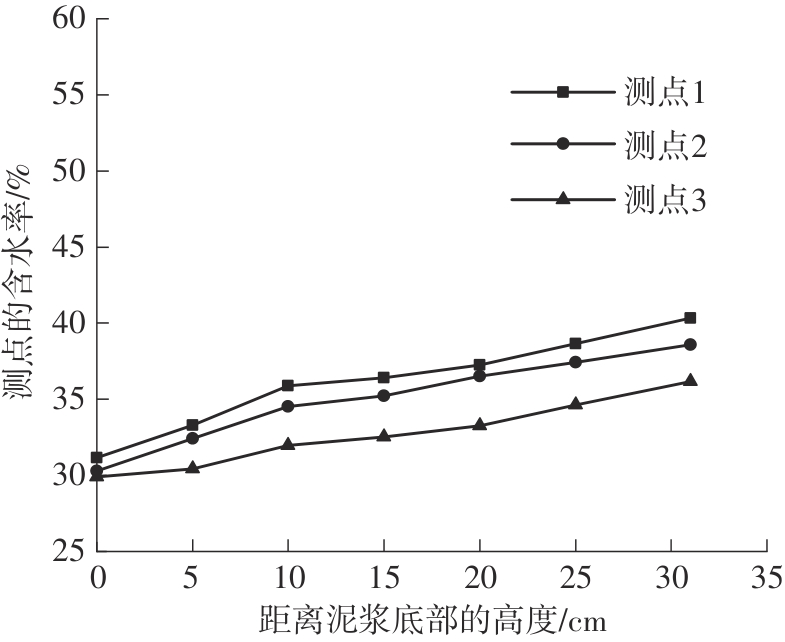
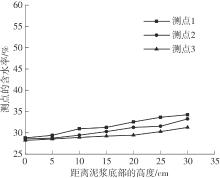
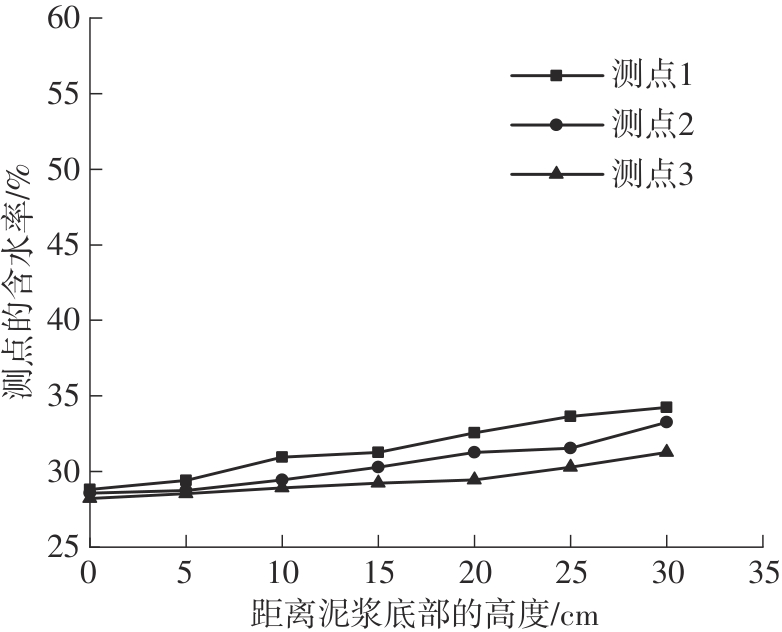
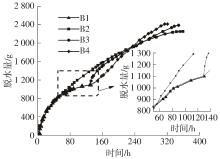
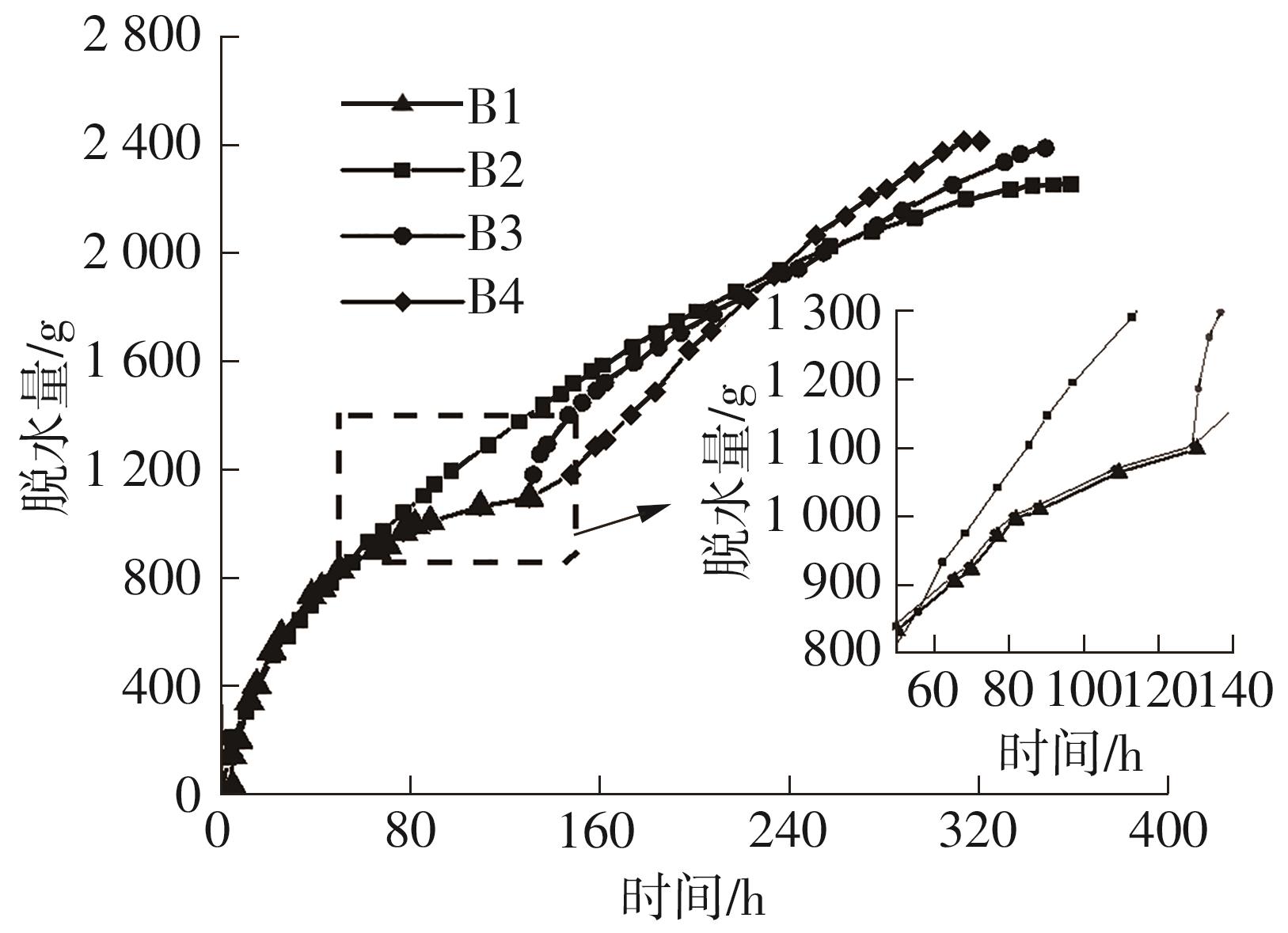
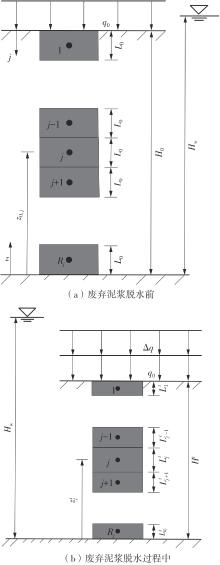
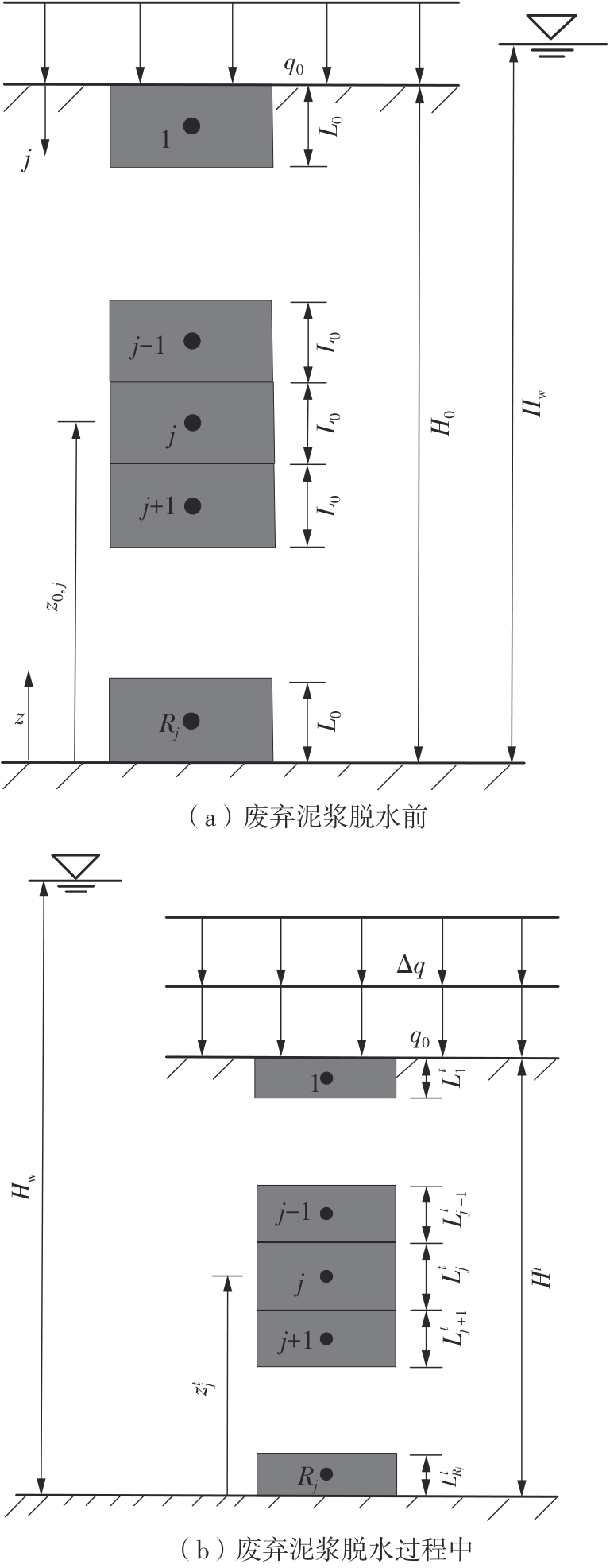
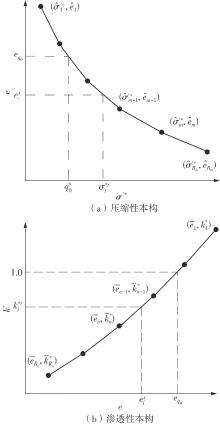
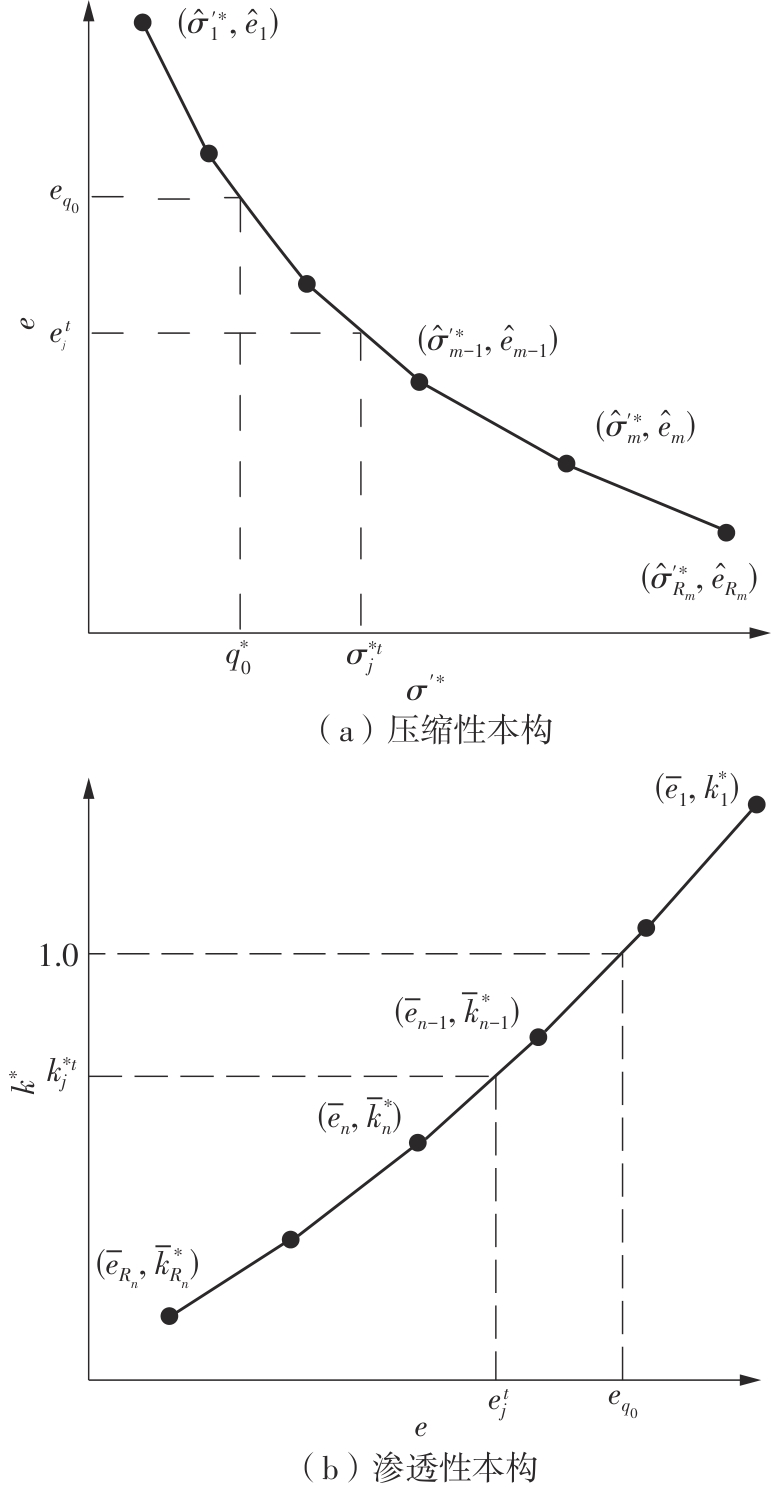
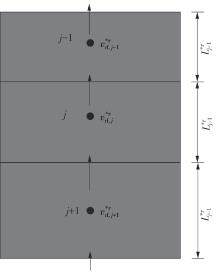
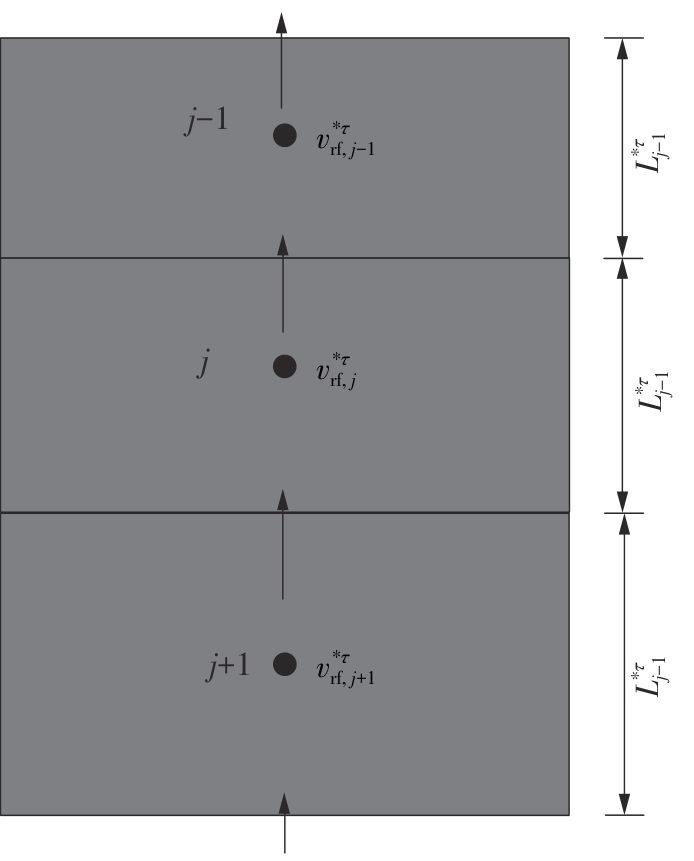
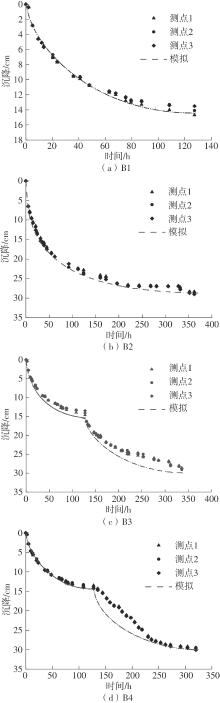
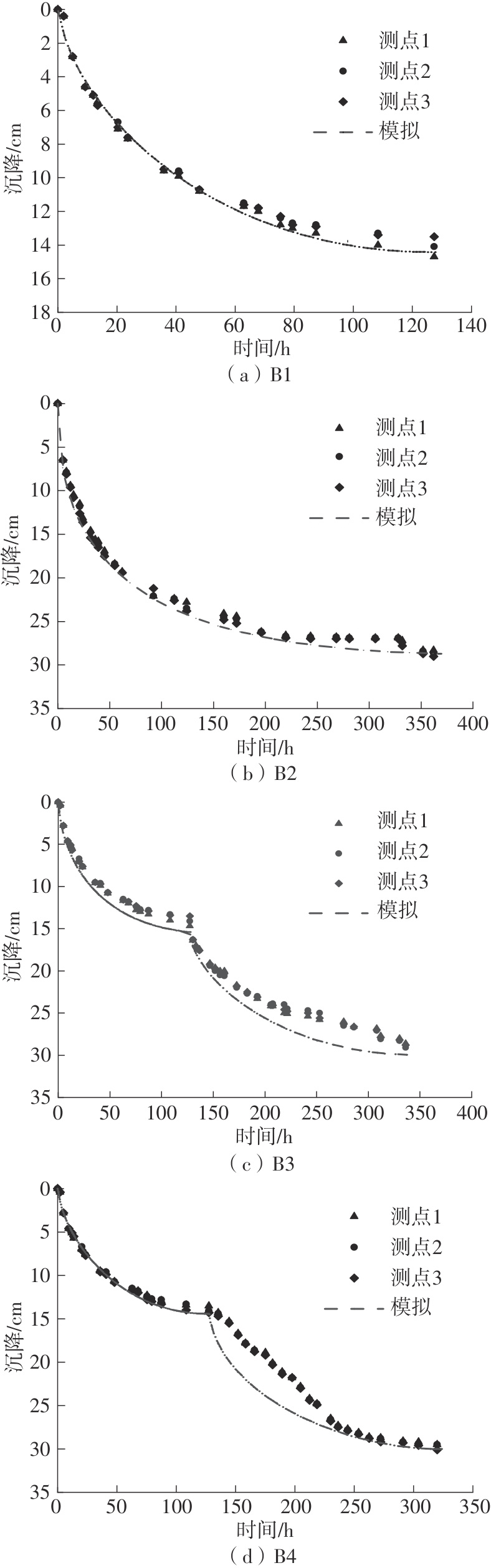
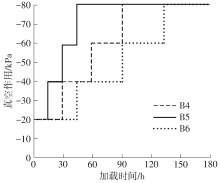
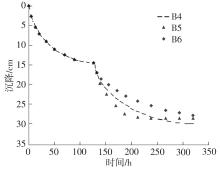
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (11): 69-82.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230736
Special Issue: 2024年土木建筑工程
• Architecture & Civil Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Experimental Study on Vacuum Dehydration of Waste Silty Clay Slurry in Shield Tunneling
GAO Xinjun( ), WANG Jianbo, SU Qinghui, LIU Zhongyu, WANG Lei, ZHOU Tonghe
), WANG Jianbo, SU Qinghui, LIU Zhongyu, WANG Lei, ZHOU Tonghe
- School of Civil Engineering,Zhengzhou University,Zhengzhou 450001,Henan,China
-
Received:2023-11-26Online:2024-11-25Published:2024-06-07 -
About author:郜新军(1981—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事岩土工程及城市地下工程研究。E-mail:gxjun@zzu.edu.cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(51578511)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
GAO Xinjun, WANG Jianbo, SU Qinghui, et al. Experimental Study on Vacuum Dehydration of Waste Silty Clay Slurry in Shield Tunneling[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(11): 69-82.
share this article
| 1 | QI Y, THAPA K B, HOADLEY A F A .Application of filtration aids for improving sludge dewatering properities-a review[J].Chemical Engineering Journal,2011,171(2):373-384. |
| 2 | 孙晓辉,郭柯雨,姬凤玲,等 .盾构泥浆絮凝-固化联合作用试验研究及宏细观探析[J].隧道建设(中英文),2022,42(4):602-610. |
| SUN Xiaohui, GUO Keyu, JI Fengling,et al .Macro-and meso-coupling effect of flocculation-solidification of waste shield slurry[J].Tunnel Construction,2022,42(4):602-610. | |
| 3 | 李悦,李俊才,汪效祖,等 .废弃钻孔泥浆快速泥水分离试验研究[J].科学技术与工程,2020,20(25):10366-10371. |
| LI Yue, LI Juncai, WANG Xiaozu,et al .Experimental study of rapid water separation from slurry of drilling mud[J].Science Technology and Engineering,2020,20(25):10366-10371. | |
| 4 | 王东星,伍林峰,唐弈锴,等 .建筑废弃泥浆泥水分离过程与效果评价[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2020,54(6):1049-1057. |
| WANG Dong-xing, WU Lin-feng, TANG Yi-kai,et al .Mud-water separation process and performance evaluation of waste slurry from construction engineering[J].Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2020,54(6):1049-1057. | |
| 5 | HE J, CHU J .Sedimentation behavior of flocculant-treated soil slurry[J].Marine Georesources and Geotech-nology,2017,35(5):593-602. |
| 6 | 李旭 .泥水盾构废弃泥浆絮凝脱水试验研究[J].铁道建筑,2018,58(5):144-147. |
| LI Xu .Flocculation and dehydration experimental study of waste mud in slurry shield[J].Railway Engineering,2018,58(5):144-147. | |
| 7 | 孙肖 .改性壳聚糖絮凝剂改善污泥脱水性能的研究[D].哈尔滨:哈尔滨工业大学,2009. |
| 8 | 冯源,詹良通,陈云敏 .城市污泥电渗脱水实验研究[J].环境科学学报,2012,32(5):1081-1087. |
| FENG Yuan, ZHAN Liangtong, CHEN Yunmin .Laboratory study on electroosmosis dewatering of sewage sludge[J].Acta Scientiae Circumstantiae,2012,32(5):1081-1087. | |
| 9 | CHIEN S C, OU C Y .A novel technique of harmonic waves applied electro-osmotic chemical treatment for soil improvement[J].Applied Clay Science,2011,52(3):235-244. |
| 10 | 梁嘉林 .氧化-絮凝调理对市政污泥超高压压滤深度脱水的影响及其机理研究[D].广州:广东工业大学,2020. |
| 11 | FENG S, LEI H, WANG L,et al .The reinforcement analysis of soft ground treated by thermal consolidation vacuum preloading[J].Transportation Geotechnics,2021,31:100672/1-8. |
| 12 | 蒋楚生,司文明,曾惜,等 .电渗联合真空预压技术处理高速铁路软土地基[J].铁道工程学报,2019,36(6):28-32,96. |
| JIANG Chusheng, SI Wenming, ZENG Xi,et al .Research on the treatment of soft soil foundation of a high speed railway by electric-osmosis combined with vacuum preloading technology[J].Journal of Railway Engineering Society,2019,36(6):28-32,96. | |
| 13 | 曹杰,郑建国,刘智,等 .真空预压法处理软土地基的工程应用[J].岩土工程学报,2017,39(S2):124-127. |
| CAO Jie, ZHENG Jianguo, LIU Zhi,et al .Application of vacuum preloading method in consolidating soft soil foundation[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(S2):124-127. | |
| 14 | BERGADO D T, JAMSAWANG P, JONGPRADIST P,et al .Case study and numerical simulation of PVD improved soft Bangkok clay with surcharge and vacuum preloading using a modified air-water separation system[J].Geotextiles and Geomembranes,2022,50(1):137-153. |
| 15 | LIN S, FU D F, ZHOU Z F,et al .Numerical investigation to the effect of suction-induced seepage on the settlement in the underwater vacuum preloading with prefabricated vertical drains[J].Journal of Marine Science and Engineering,2021,9(8):797/1-26. |
| 16 | TER-MARTIROSYAN Z G, TER-MARTIROSYAN A Z, STRUNIN P V,et al .Stress-strain state of thick-walled soil cylinder with sand core and grillage view of elastoplastic properties of the soil[J].Procedia Engineering,2014,91:286-291. |
| 17 | 武亚军,顾赛帅,强小兵,等 .基于骨架构建药剂真空预压法加固超软土试验[J].浙江大学学报(工学版),2018,52(4):735-743. |
| WU Ya-jun, GU Sai-shuai, QIANG Xiao-bing,et al .Experimental study on ultra-soft soil reinforced by vacuum preloading with flocculation based on skeleton construction[J].Journal of Zhejiang University (Engineering Science),2018,52(4):735-743. | |
| 18 | 魏雁冰,范明桥,林生法,等 .建筑废弃泥浆真空预压方法处理试验研究[J].郑州大学学报(工学版),2016,37(1):65-69. |
| WEI Yanbing, FAN Mingqiao, LIN Shengfa,et al .Experimental study on construction waste slurry treatment by vacuum preloading[J].Journal of Zhengzhou University (Engineering Science),2016,37(1):65-69. | |
| 19 | 胡圣祥 .真空压力加载方式对泥浆固结效果的影响[J].水电能源科学,2014,32(1):125-127. |
| HU Shengxiang .Impacts of vacuum loading methods on consolidation of slurry[J].Water Resources and Power,2014,32(1):125-127. | |
| 20 | 吴思麟,朱伟,闵凡路,等 .泥浆真空抽滤泥水分离中堵塞机理及规律性研究[J].岩土工程学报,2017,39(8):1530-1537. |
| WU Si-lin, ZHU Wei, MIN Fan-lu,et al .Clogging mechanism and effect of cake permeability in soil-water separation using vacuum filtration[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2017,39(8):1530-1537. | |
| 21 | 土工试验方法标准: [S]. |
| 22 | 詹良通,张斌,郭晓刚,等 .废弃泥浆底部真空—上部堆载预压模型试验研究[J].岩土力学,2020,41(10):3245-3254. |
| ZHAN Liangtong, ZHANG Bin, GUO Xiaogang,et al .Physical modeling study on treatment of waste slurry with vacuum preloading at bottom combined with upper surcharge loading[J].Rock and Soil Mechanics,2020,41(10):3245-3254. | |
| 23 | 王海波,王树英,胡钦鑫,等 .盾构砂性渣土—泡沫混合物渗透性影响因素研究[J].隧道建设(中英文),2018,38(5):833-838. |
| WANG Haibo, WANG Shuying, HU Qinxin,et al .Study on influencing factors of permeability of sand-foam mixture for shield tunneling[J].Tunnel Construction,2018,38(5):833-838. | |
| 24 | 魏康林 .土压平衡式盾构施工用泡沫混和土透水性试验研究[J].现代隧道技术,2005,42(5):17-21. |
| WEI Kanglin .Research on the permeability of the foamed soil adopted in EPB shield tunneling[J].Modern Tunnel Technology,2005,42(5):17-21. | |
| 25 | FOX P J, BERLES J D .CS2:a piecewise-linear model for large strain consolidation[J].International Journal for Numerical and Analytical Methods in Geomechanics,1997,21(7):453-475. |
| 26 | 江辉煌,刘国楠,赵有明 .Gibson一维固结方程的一种求解方法[J].岩土工程学报,2010,32(5):745-750. |
| JIANG Hui-huang, LIU Guo-nan, ZHAO You-ming .A solution of Gibson’s governing equation of one-dimensional consolidation[J].Chinese Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2010,32(5):745-750. |
| [1] | WEI Haibin, WEI Dongsheng, JIANG Boyu, et al. Prediction Analysis of Settlement of Existing Road Under Shield Tunneling Based on IPSO-SVR [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 62-71. |
| [2] | XIE Jiehui, NIU Fujun, PENG Zhiyu, et al. Deformation Law and Settlement Prediction Application of Soft Soil Subgrade in Coastal Expressway [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(4): 97-107. |
| [3] | Li Heng-zhen Yao Si-hai Yang Kun-sheng Yang Ying Liu Gang Li Li-cheng. Force Analysis and Kinematic Analysis of Polluted Particles Before Their Adsorption on Electrical Insulator Surface [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2013, 41(4): 21-26. |
| [4] | Wang Yi-min Li Qing-zhen Gao Shui-qin. Experimental Investigation into Effect of Differential Settlement on Working Performance of Geogrid Reinforced Embankment [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(9): 68-74. |
| [5] | Pan Jian Hu Wei-wei. Negative Effect of Horizontal Ground Movement on Raked Piles [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(6): 6-9. |
| [6] | Zhang Li-juan, Wang Yi-min, Chen Ye-kai, et al. Compactibility of Ionic Soil Stabilizer Strengthening Soil [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2004, 32(3): 83-87. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||