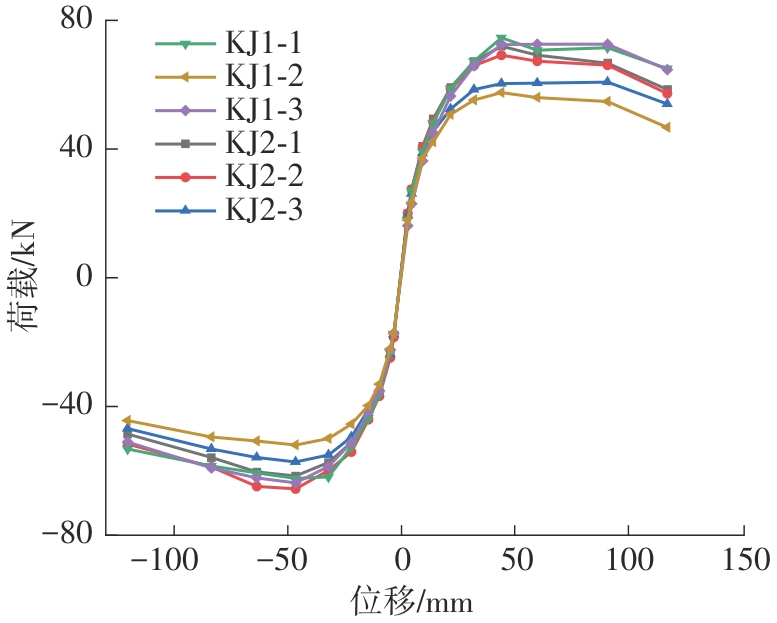
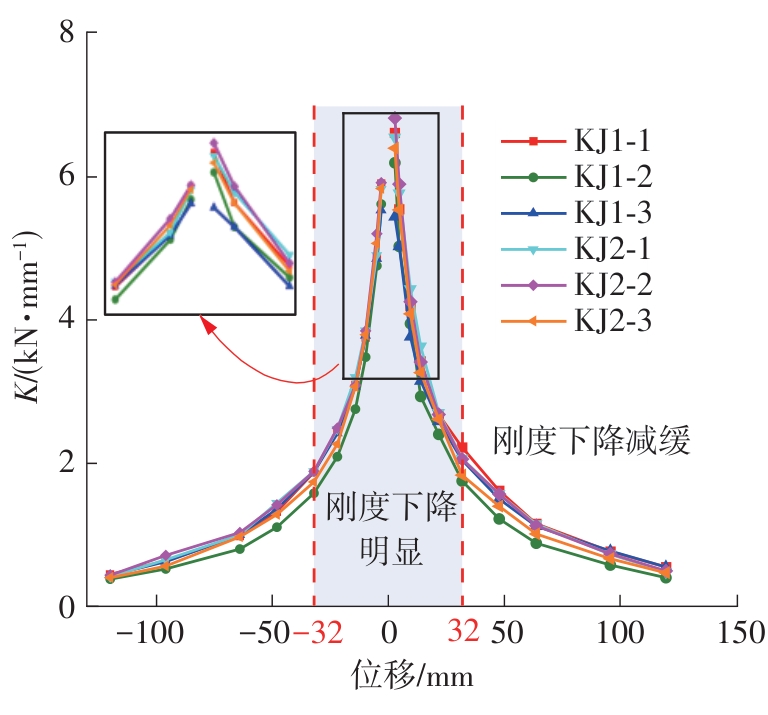
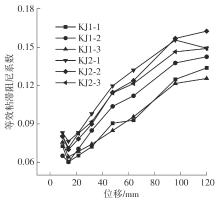
| 1 |
高层建筑混凝土结构技术规程: [S].
|
| 2 |
建筑抗震设计规范: [S].
|
| 3 |
方小丹 .DBJ/T 15-92—2021《高层建筑混凝土结构技术规程》的修订依据及相关问题说明[J].建筑结构学报,2021,42(9):172-188.
|
|
FANG Xiaodan .Basis and background of revision of DBJ/T 15-92—2021 “Technical specification for concrete structures of tall buildings”[J].Journal of Building Structures,2021,42(9):172-188.
|
| 4 |
叶列平,方鄂华 .关于建筑结构地震作用计算方法的讨论[J].建筑结构,2009,39(2):1-7.
|
|
YE Lieping, FANG Ehua .Discussion on calculation method of earthquake force for building structures[J].Buidling Structure,2009,39(2):1-7.
|
| 5 |
张宇,李宏男,李钢 .既有钢筋混凝土结构抗震设防目标与性能评估[J].建筑结构学报,2013,34(7):29-39.
|
|
ZHANG Yu, LI Hongnan, LI Gang .Seismic performance objectives and evalution of existing reinforced concrete structures[J].Journal of Building Structures,2013,34(7):29-39.
|
| 6 |
门进杰,史庆轩,周琦 .框架结构基于性能的抗震设防目标和性能指标的量化[J].土木工程学报,2008,41(9):76-82.
|
|
Jinjie MEN, SHI Qingxuan, ZHOU Qi .Performance-based seismic fortification criterion and quantified performance index for reinforced concrete frame structures[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2008,41(9):76-82.
|
| 7 |
袁健,易伟建 .钢筋混凝土梁受剪承载力可靠度分析[J].建筑结构学报,2017,38(4):109-128.
|
|
YUAN Jian, YI Weijian .Reliability analysis of shear capacity of reinforced concrete beams[J].Journal of Building Structures,2017,38(4):109-128.
|
| 8 |
韩小雷,王雨,张一璐,等 .RC剪力墙结构小震与中震设计对比及其抗震性能研究[J].地震工程与工程振动,2021,41(1):9-15.
|
|
HAN Xiaolei, WANG Yu, ZHANG Yilu,et al .Comparative study on seismic design under frequent earthquake and moderate earthquake and seismic performance of RC shear wall structures[J].Earth Quake Engineering and Engineering Dynamics,2021,41(1):9-15.
|
| 9 |
汪小林,顾祥林,印小晶,等 .现浇楼板对钢筋混凝土框架结构倒塌模式的影响[J].建筑结构学报,2013,34(4):23-31,42.
|
|
WANG Xiaolin, GU Xianglin, YIN Xiaojing,et al .Effect of cast-in-situ floor slab on collapse modes of RC frame structures under earthquake[J].Journal of Building Structures,2013,34(4):23-31,42.
|
| 10 |
WANG Y, ZHANG B, GU X L,et al .Experimental and numerical investigation on progressive collapse resistance of RC frame structures considering transverse beam and slab effects[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2022,47:103908/1-20.
|
| 11 |
周颖,吕西林 .建筑结构振动台模型试验方法与技术[M].2版.北京:科学出版社,2016.
|
| 12 |
建筑抗震试验规程: [S].
|
| 13 |
SHA H, CHONG X, XIE L,et al .Seismic performance of precast concrete frame with energy dissipative cladding panel system:half-scale test and numerical analysis[J].Soil Dynamics and Earthquake Engineering,2023,165:107712/1-13.
|
| 14 |
WANG W, MA J, WANG X .Seismic behavior of a precast RC frame-shear wall structure using full/half grout sleeve connections[J].Engineering Structures,2023,280:115685/1-22.
|
| 15 |
徐云扉,胡庆昌,陈玉峰,等 .低周反复荷载下两跨三层钢筋混凝土框架受力性能的试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,1986,2(1):1-16.
|
|
XU Yunfei, HU Qingchang, Chen Yufeng,et al .The experimental study of the behavior of a two-bay three-story R. C. frame under cyclic loading[J].Journal of Building Structures,1986,2(1):1-16.
|
| 16 |
冯鹏,强翰霖,叶列平 .材料、构件、结构的“屈服点”定义与讨论[J].工程力学,2017,34(3):36-46.
|
|
FENG Peng, QIANG Han-lin, YE Lie-ping .Discussion and definition on yield points of materials,members and strucures[J].Engineering Mechanics,2017,34(3):36-46.
|
| 17 |
陈圣刚,高峰,耿娇,等 .预应力型钢混凝土双坡框架抗震性能试验研究[J].建筑结构学报,2023, 44(2):100-108.
|
|
CHEN Shenggang, GAO Feng, GENG Jiao,et al .Experimental study on seismic behavior of prestressed steel reinforced concrete frame with double-pitches[J].Journal of Building Structures,2023,44(2):100-108.
|
| 18 |
叶列平,曲哲,马千里,等 .从汶川地震框架结构震害谈“强柱弱梁”屈服机制的实现[J].建筑结构,2008,38(11):52-59,67.
|
|
YE Lieping, QU Zhe, MA Qianli,et al .Study on ensuring the strong column-weak beam mechanism for RC frames based on the damage analysis in the Wenchuan earthquake[J].Building Structure,2008,38(11):52-59,67.
|
| 19 |
薛伟辰,程斌,李杰 .双层双跨高性能混凝土框架抗震性能研究[J].土木工程学报,2004,37(3):58-65.
|
|
XUE Weichen, CHENG Bin, LI Jie .Studies on seismic performance of double-story and double-span HPC frames[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2004,37(3):58-65.
|
 ), HUANG Qianyi2,4, ZHOU Jing1,2,3(
), HUANG Qianyi2,4, ZHOU Jing1,2,3( ), WU Shan2
), WU Shan2