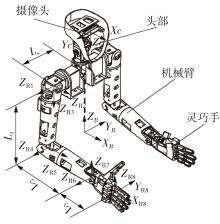
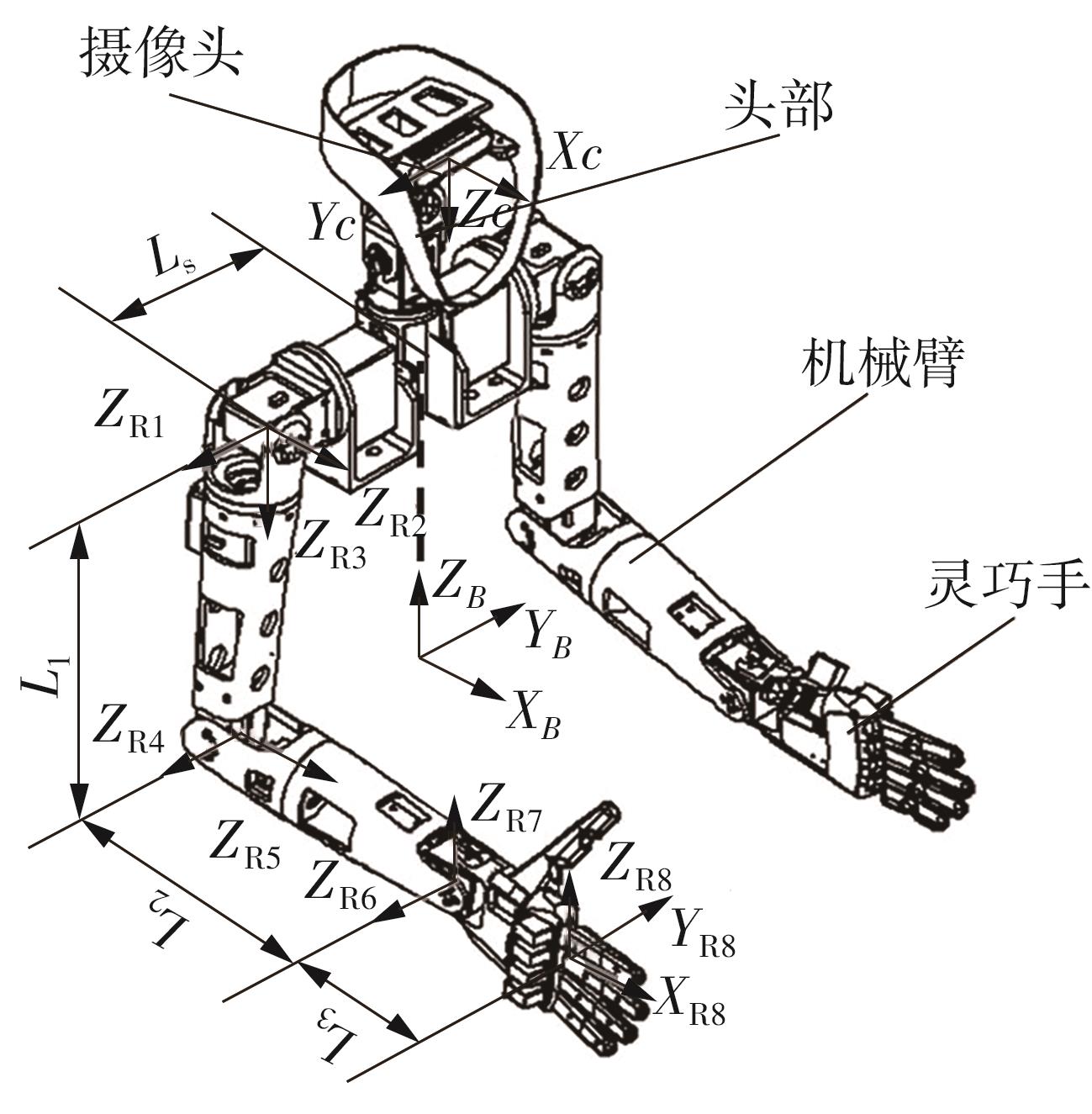
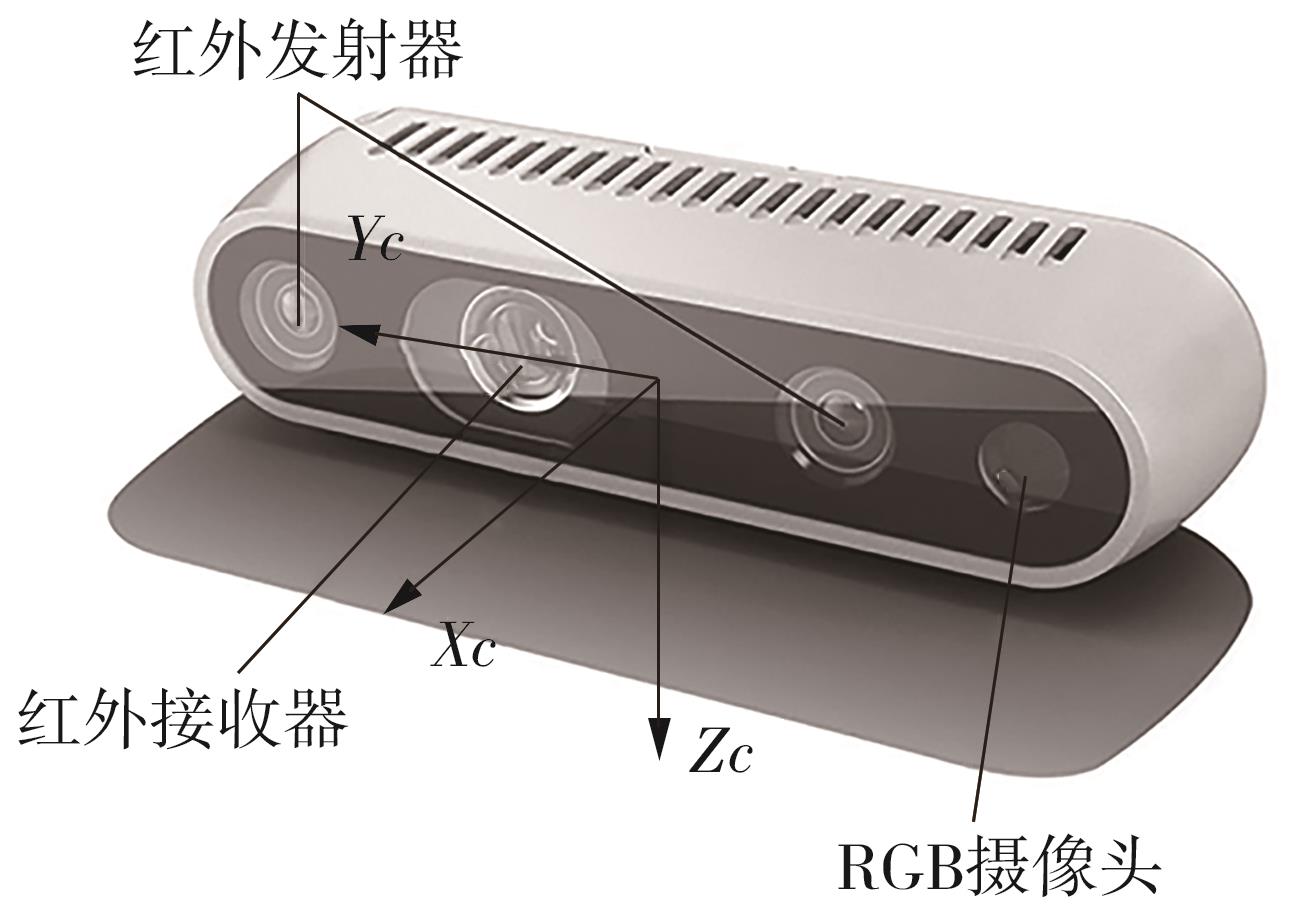
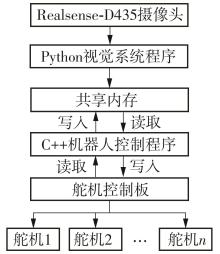
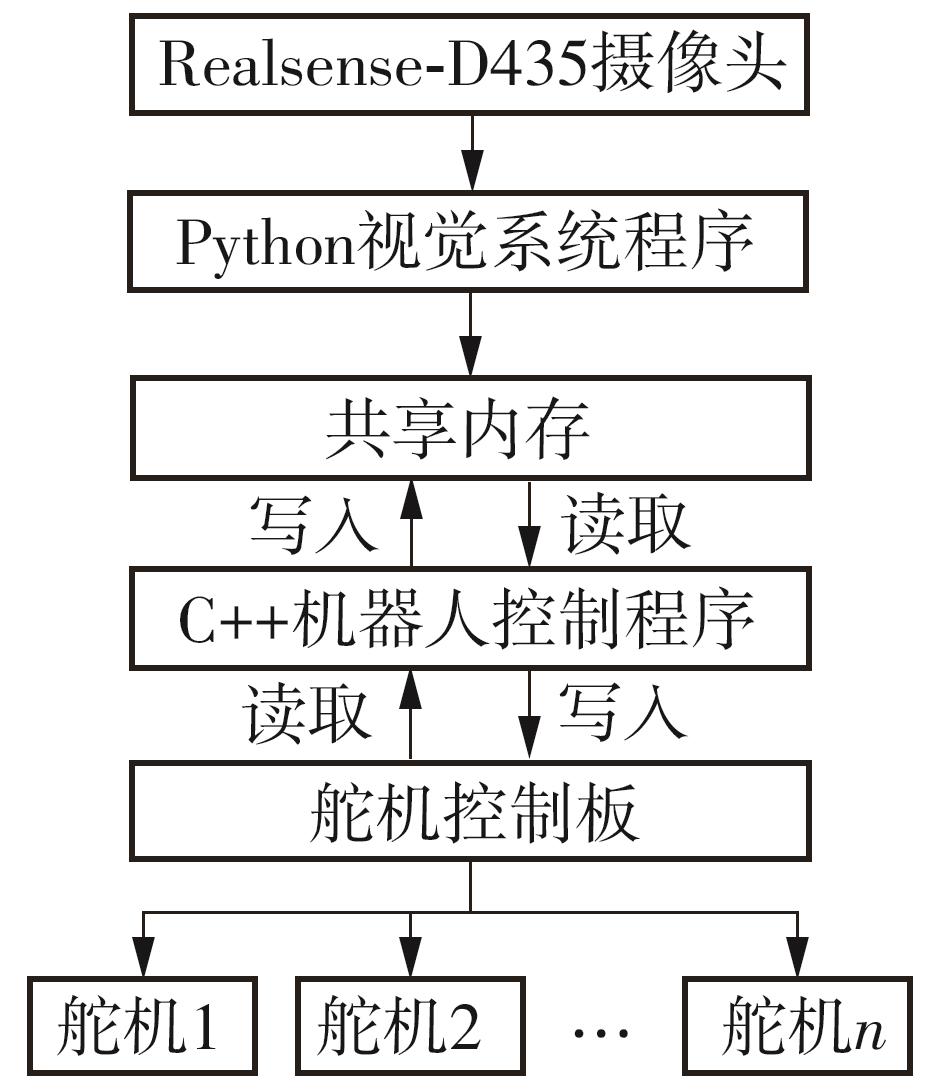
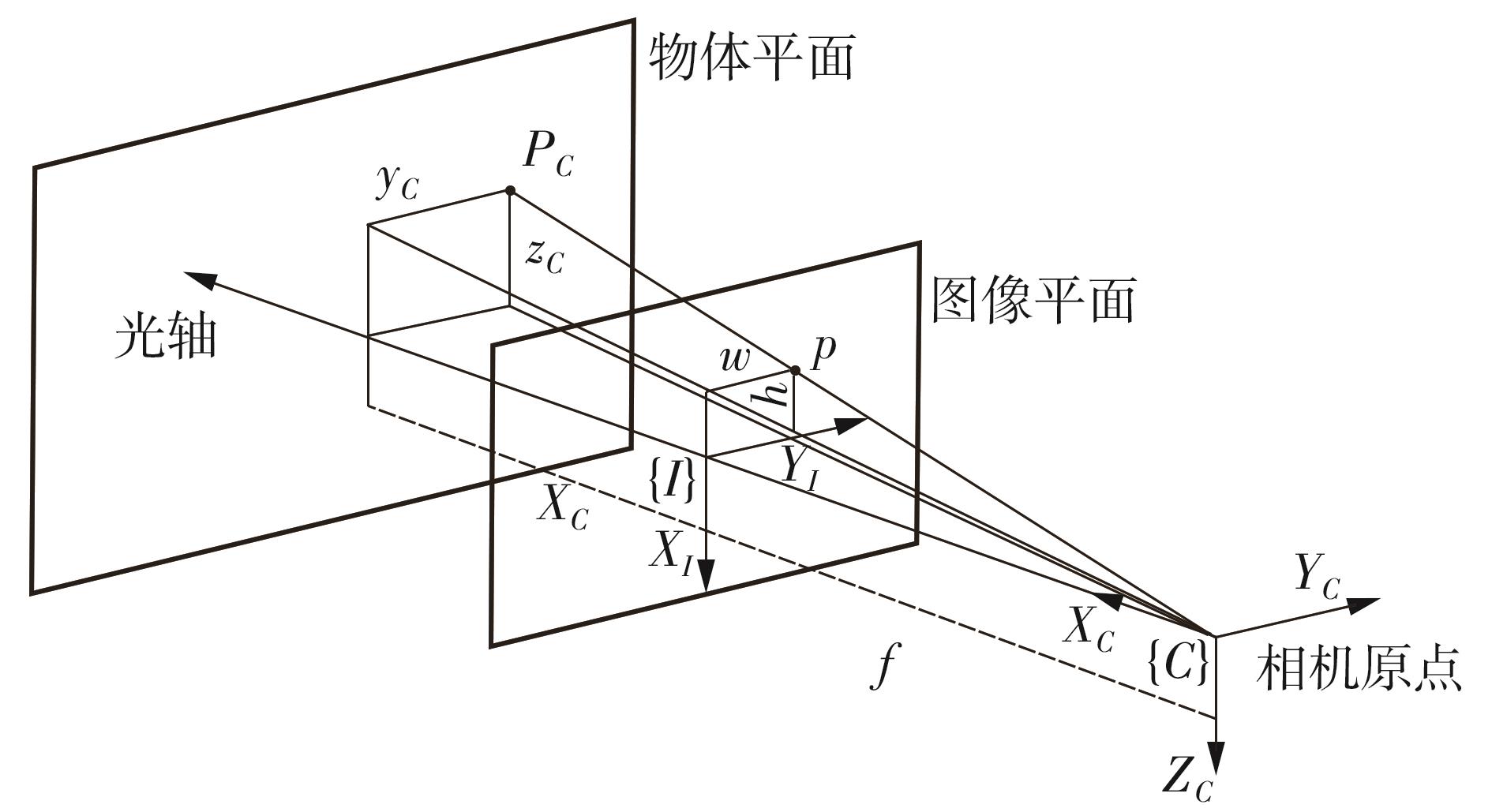
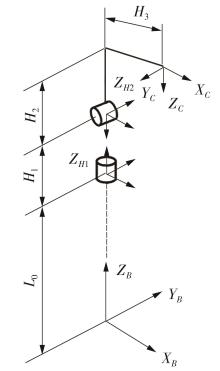
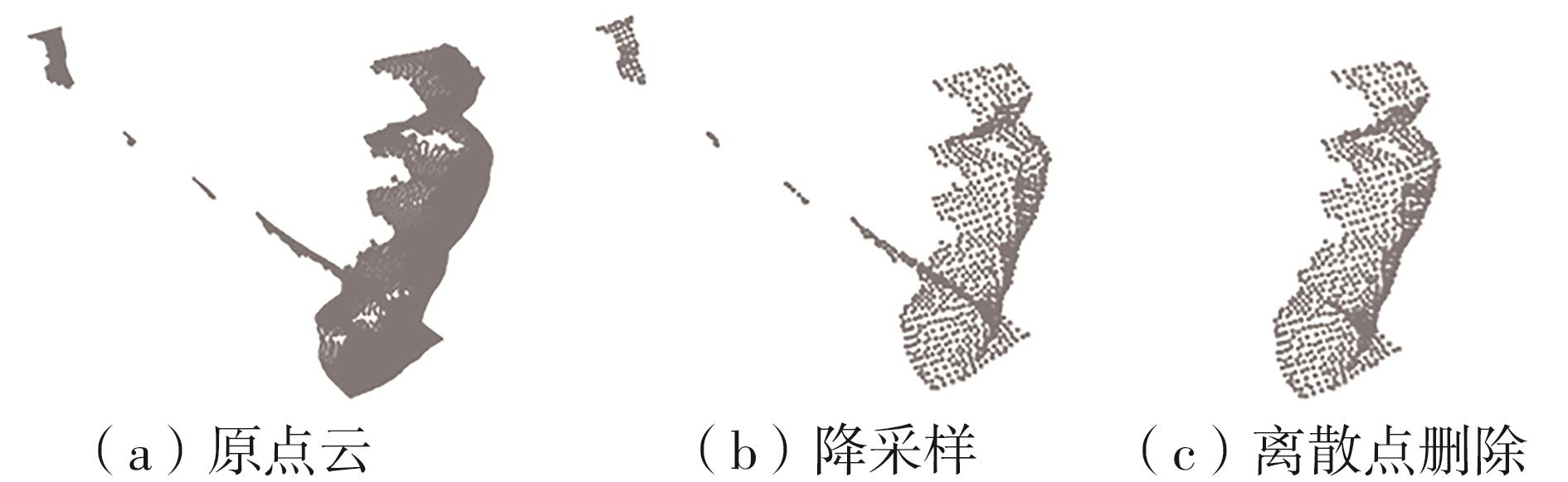
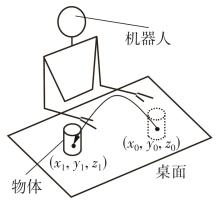
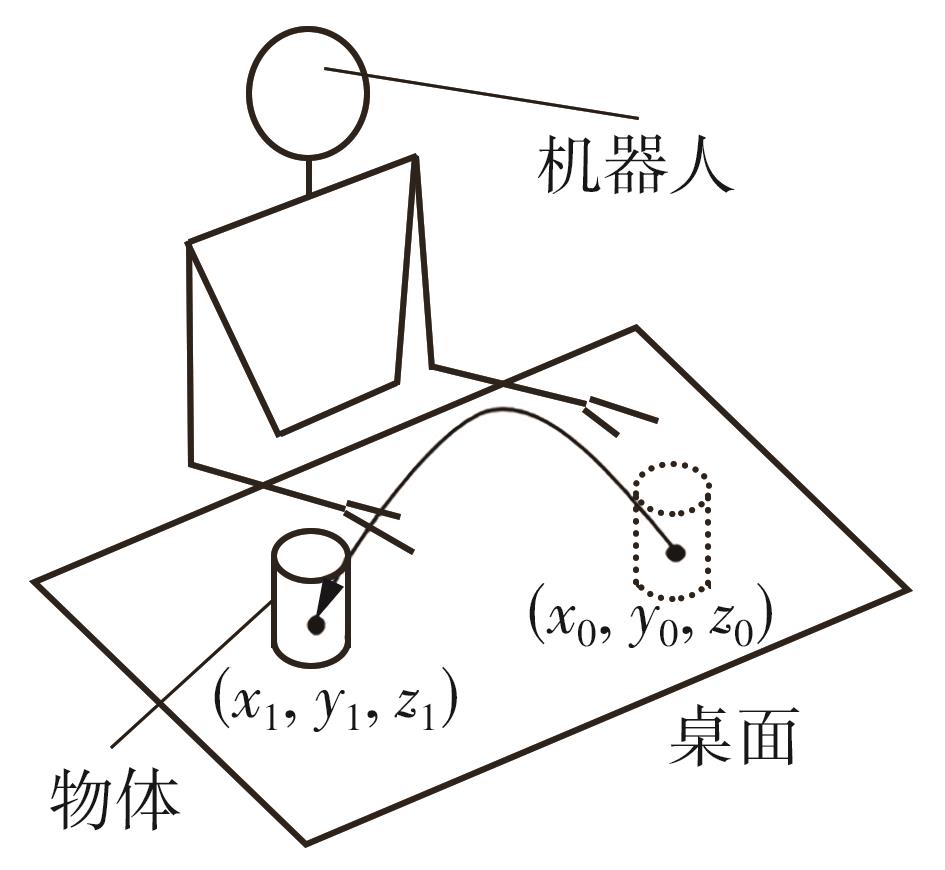
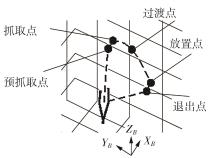
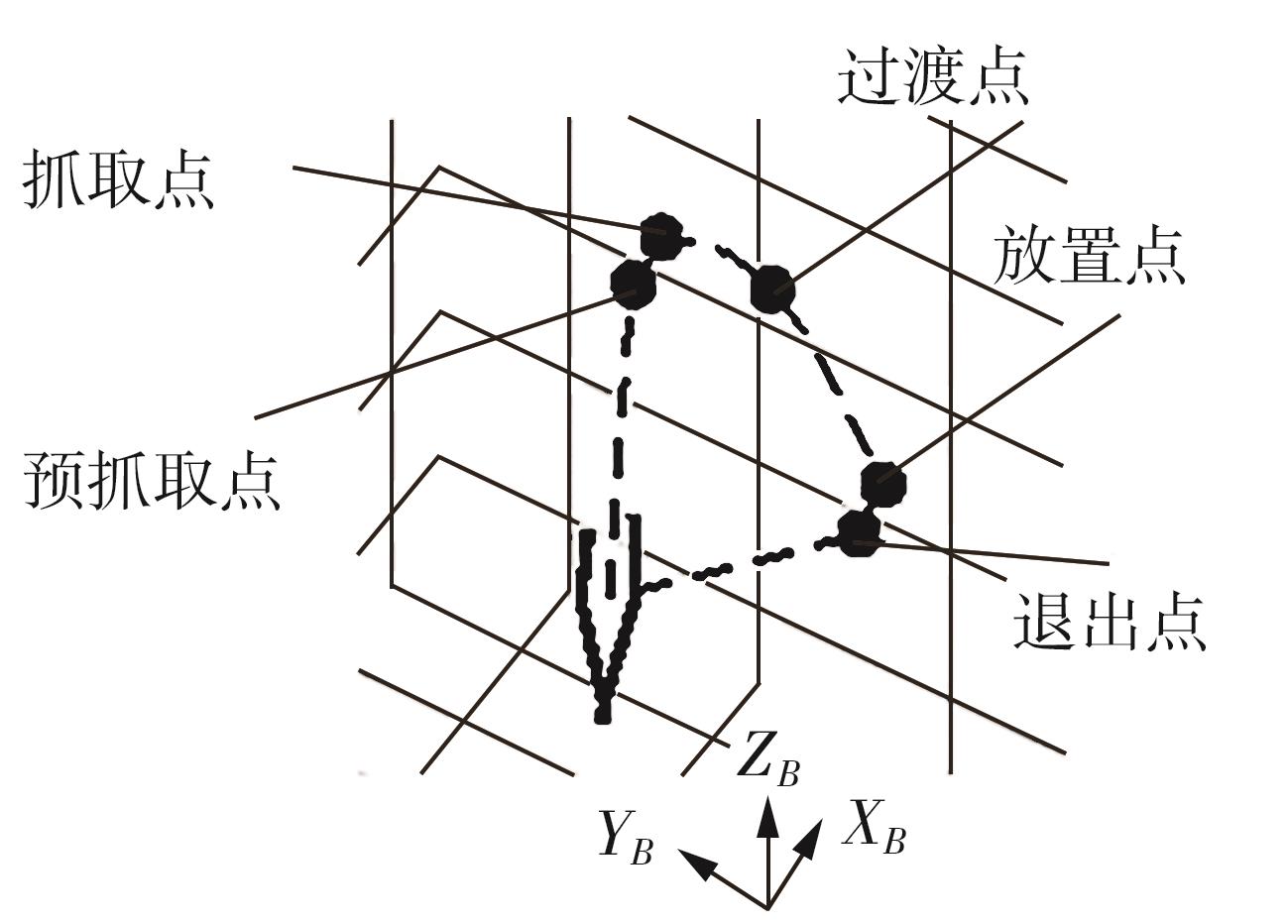
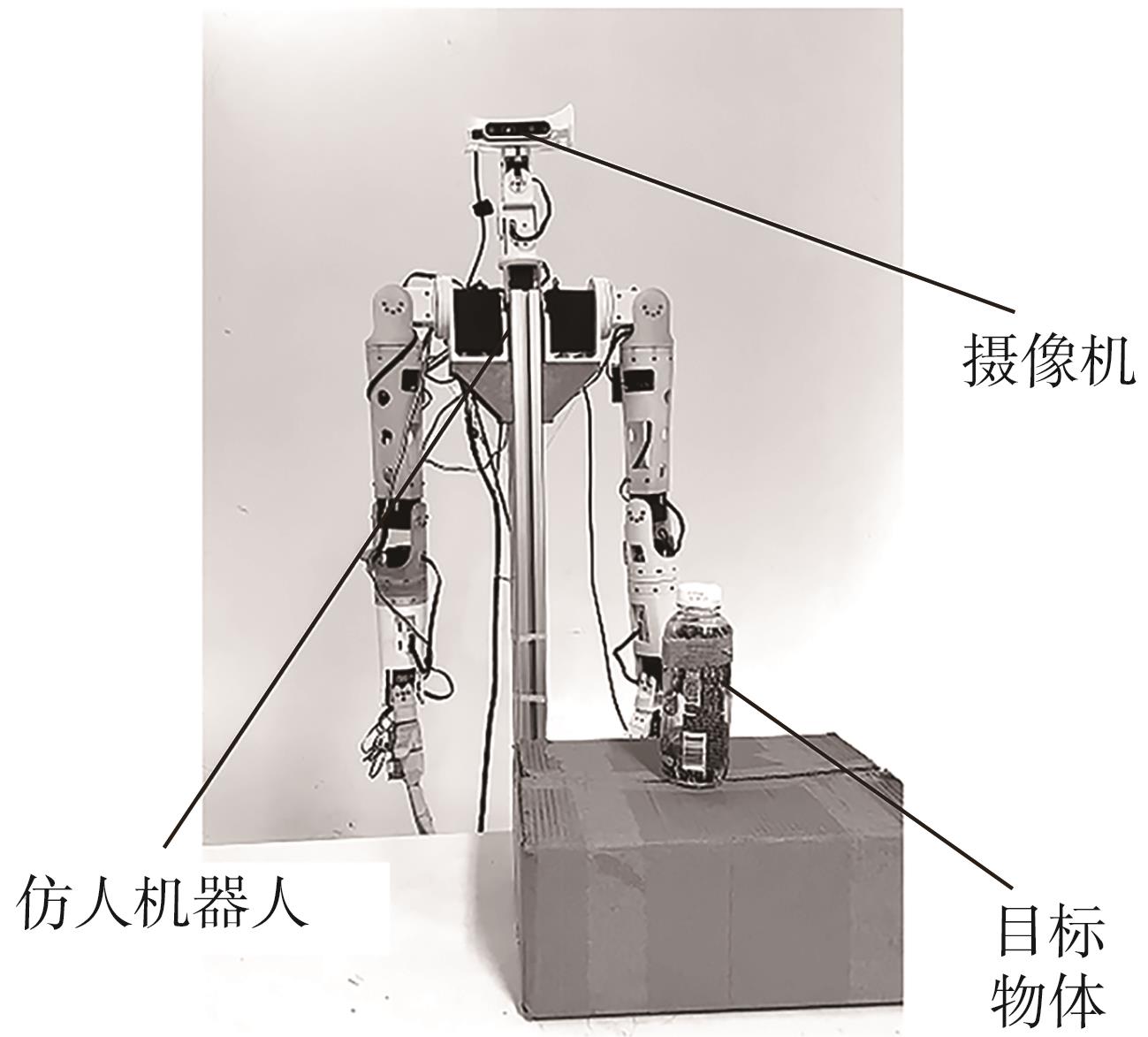
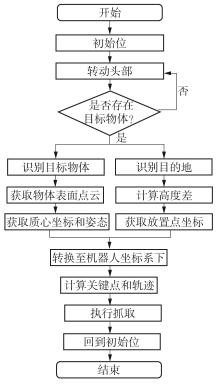
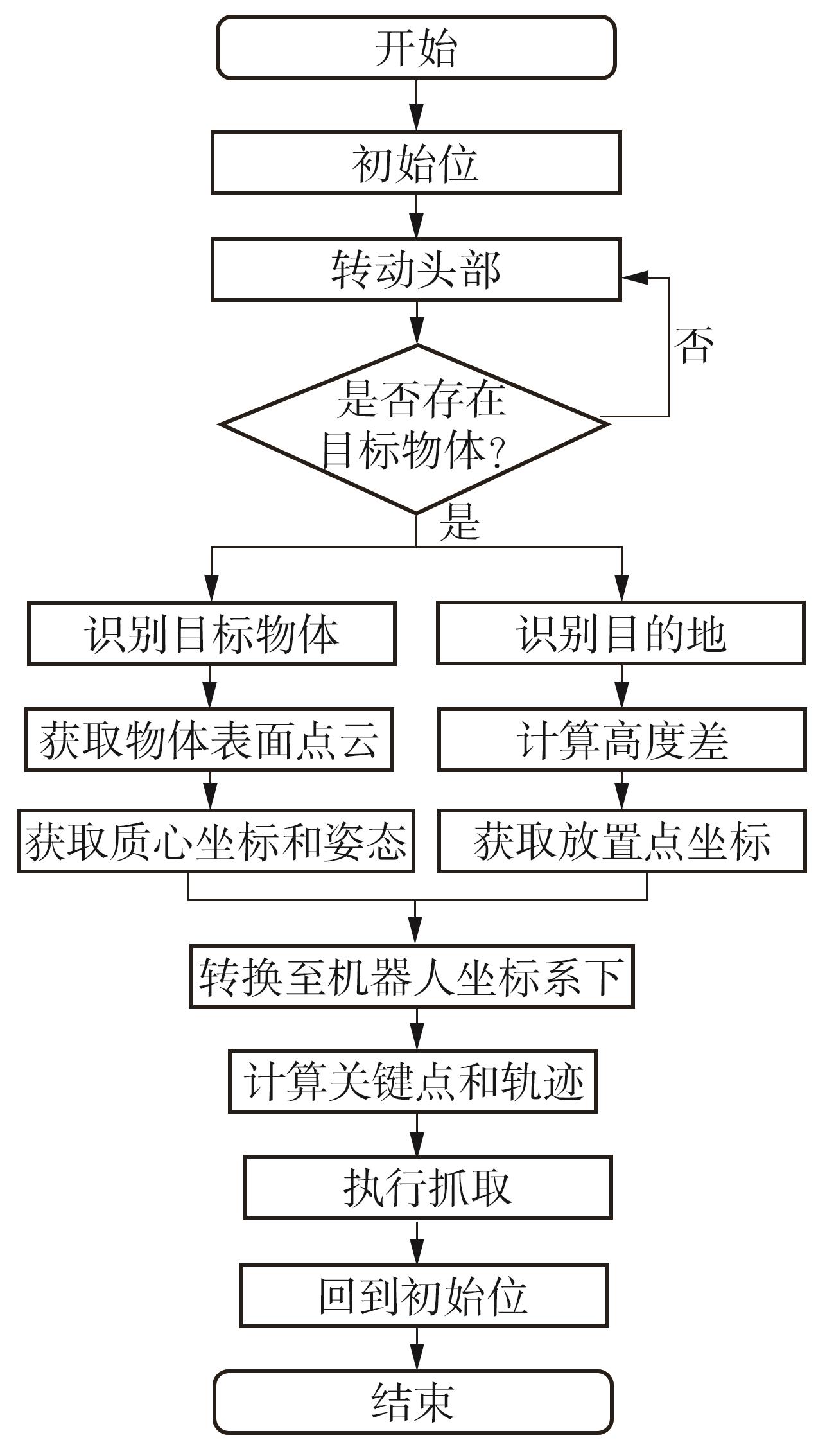
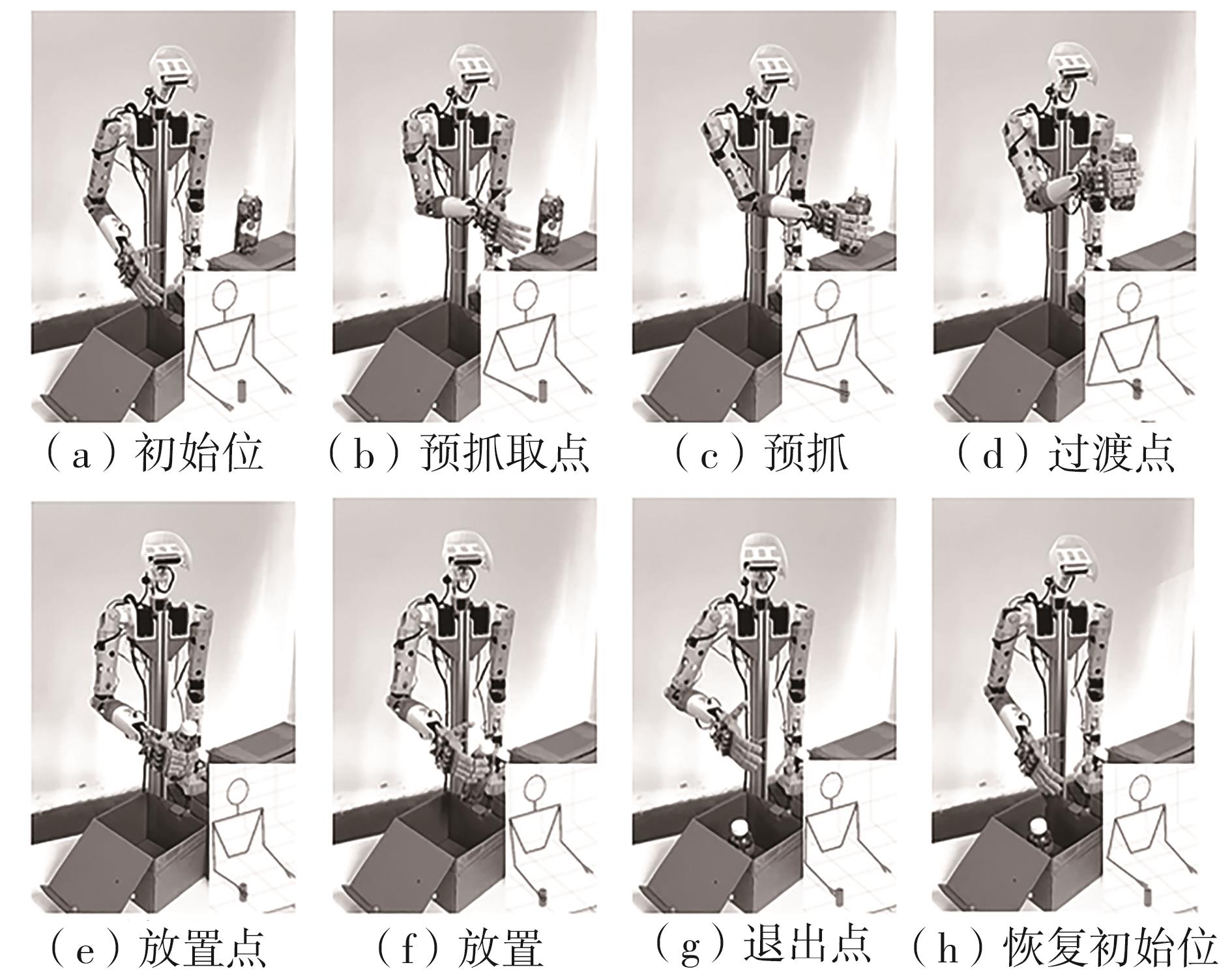
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (7): 53-61.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230528
Special Issue: 2024年电子、通信与自动控制技术
• Electronics, Communication & Automation Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
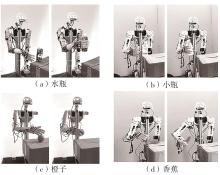
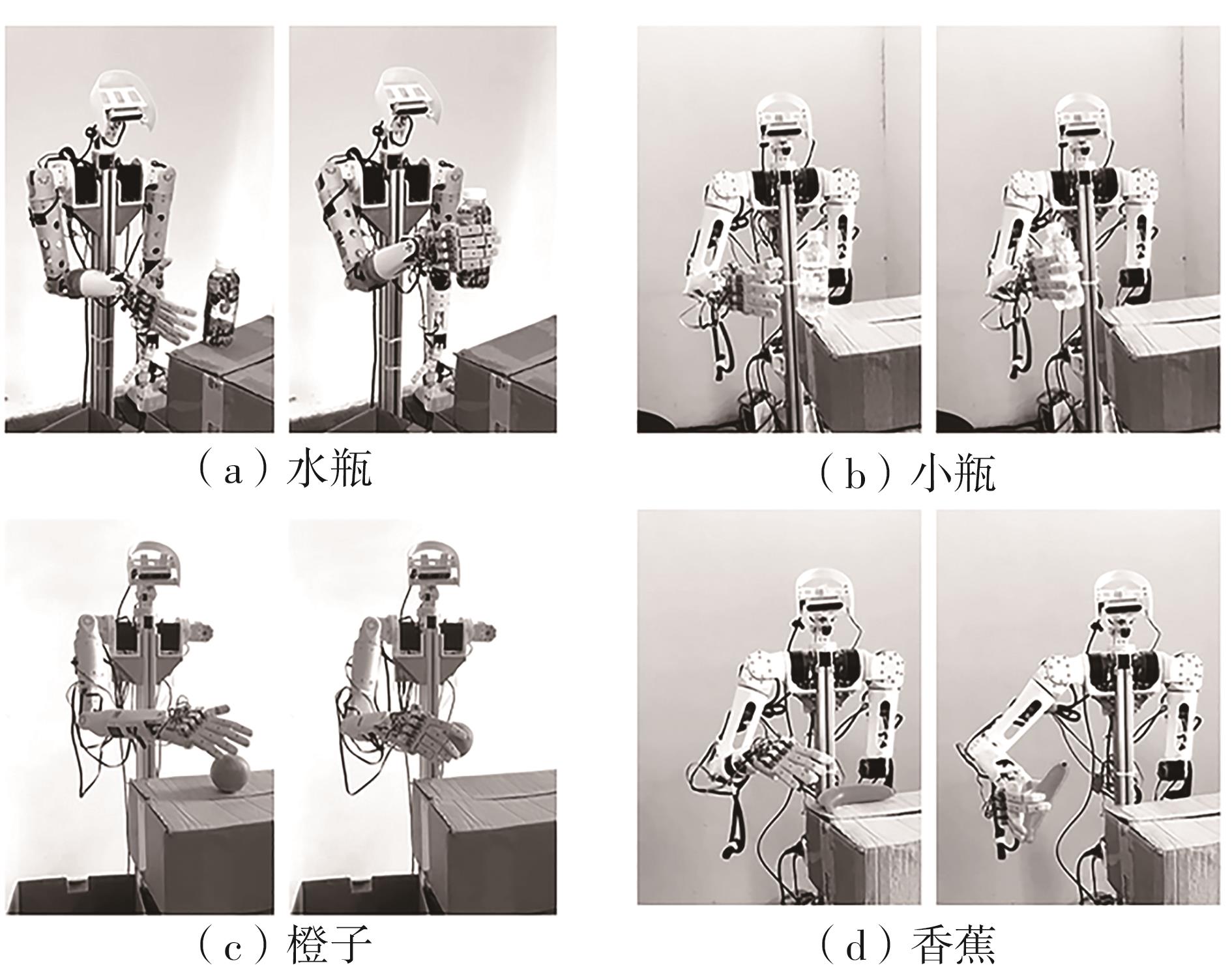
Research on Autonomous Grasping of a Humanoid Robot Based on Vision
- School of Design,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510006,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2024-02-06Online:2024-07-25Published:2024-02-09 -
About author:张续冲(1989—),男,博士,副教授,主要从事仿人机器人设计、运动规划研究。E-mail: sdxczhang@scut.edu.cn -
Supported by:the Natural Science Foundation of Guangdong Province(2020A1515010397)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
ZHANG Xuchong, YANG Jun. Research on Autonomous Grasping of a Humanoid Robot Based on Vision[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2024, 52(7): 53-61.
share this article
| 1 | 林义忠,陈旭 .基于机器视觉的机器人定位抓取的研究进展[J].自动化与仪器仪表,2021,257(3):9-12. |
| LIN Yizhong, CHEN Xun .Research progress of robot positioning and grasping based on machine vision[J].Automation & Instrumentation,2021,257(3):9-12. | |
| 2 | WANG J, LI S .Grasp detection via visual rotation object detection and point cloud spatial feature scoring[J].International Journal of Advanced Robotic Systems,2021,18(6):1459-1475. |
| 3 | SUN J, INFORMATION V F A, ZHANG K,et al .A model-free 6-DOF grasp detection method based on point clouds of local sphere area[J].Advanced Robotics,2023,37(11):679-690. |
| 4 | 刘汉伟,曹雏清,王永娟 .基于非结构基本组成分析的自主抓取方法[J].机器人,2019,41(5):583-590. |
| LIU Hanwei, CAO Chuqing, WANG Yongjuan .Autonomous grasping method based on non-structural basic composition analysis[J].Robot,2019,41(5):583-590. | |
| 5 | HUANG L, WANG H, LU Y,et al .Research on intelligent grasping system for general objects based on deep learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 2nd International Conference on Computer,Control and Robotics.Shanghai:ICCR,2022:103-108. |
| 6 | WU Y, FU Y, WANG S .Information-theoretic exploration for adaptive robotic grasping in clutter based on real-time pixel-level grasp detection[J]2023 IEEE Transactions on Industrial Electronics,2023,71(3):2683-2693. |
| 7 | 仵沛宸,帅威,陈小平,等 .抓取任务中的融差控制方法[J].机器人,2022,44(5):589-600. |
| WU Peichen, SHUAI Wei, CHEN Xiaoping,et al .The rong-cha based control method in grasping task[J].Robot,2022,44(5):589-600. | |
| 8 | CHEN H, WANG J, MENG M Q H .Kinova gemini:interactive robot grasping with visual reasoning and conversational AI[C]∥Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Biomimetics.Jinghong:IEEE,2022:129-134. |
| 9 | HUNDHAUSEN F, GRIMM G, STIEBER L,et al .Fast reactive grasping with in-finger vision and in-hand FPGA-accelerated CNNs[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems.Prague:IROS,2021:6825-6832. |
| 10 | 王高,陈晓鸿,柳宁,等 .一种基于视角选择经验增强算法的机器人抓取策略[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(9):126-137. |
| WANG Gao, CHEN Xiaohong, LIU Ning,et al .A robot grasping policy based on viewpoint selection experience enhancement algorithm[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(9):126-137. | |
| 11 | 陈佳盼,郑敏华 .基于深度强化学习的机器人操作行为研究综述[J].机器人,2022,44(2):236-256. |
| CHEN Jiapan, ZHENG Minhua .A survey of robot manipulation behavior research based on deep reinforcement learning[J].Robot,2022,44(2):236-256. | |
| 12 | XU L, ZHOU Z, WANG C .An robot vision grasping network based on inception-lite[J].Journal of Physics:Conference Series,2021,1748(2):022041/1-7. |
| 13 | LIANG P, HUANG C, FAN Z,et al .3D eye-to-hand coordination for uninstructed robot grasp planning [C]∥Proceedings of the 2022 12th International Conference on CYBER Technology in Automation,Control,and Intelligent Systems.Baishan:CYBER,2022:537-542. |
| 14 | 于旭,陶先童,宁丹阳,等 .RGB-D图像引导的机器人操作任务模仿学习[J].组合机床与自动化加工技术,2023,590(4):165-168,173. |
| YU Xu, TAO Xiantong, NING Danyang,et al .Imitation learning of robot operation task based on RGB-D image[J]Modular Machine Tool & Automatic Manufacturing Technique,2023,590(4):165-168,173. | |
| 15 | 史步海,欧华海,郭清达 .基于位置跟踪器的机器人快速示教方法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2022,50(10):62-69. |
| SHI Buhai, Huahai OU, GUO Qingda .A fast teaching method of robot based on position tracker[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2022,50(10):62-69. | |
| 16 | ZHOU R, ZHANG Z, PENG K,et al .Humanoid action imitation learning via boosting sample DQN in virtual demonstrator environment[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 23rd International Conference on Mechatronics and Machine Vision in Practice.Nanjing:M2VIP,2016:1-9. |
| 17 | KAYUKAWA Y, TAKAHASHI Y, TSUJIMOTO T,et al .Influence of emotional expression of real humanoid robot to human decision-making[C]∥Proceeding of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Fuzzy Systems.Naples:IEEE,2017:1-6. |
| 18 | KIM B, BRUCE M, BROWN L,et al .A comprehensive approach to validating the uncanny valley using the anthropomorphic RoBOT (ABOT) database[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 Systems and Information Engineering Design Symposium.Charlottesville:SIEDS,2020:1-6. |
| 19 | 张续冲,张瑞秋,陈亮,等 .仿人机械双臂的运动学建模及实验[J].机械设计与研究,2020,36(6):24-28,34. |
| ZHANG Xuchong, ZHANG Ruiqiu, CHEN Liang,et al .Kinematical modeling and experimental research of a humanoid dual-manipulator[J].Machine Design and Research,2020,36(6):24-28,34. | |
| 20 | ZHOU Q, PARK J, KOLTUN V .Open 3D:modern library fora 3D data processing[EB/OL].(2018-01-30)[2023-08-17].. |
| 21 | WU X, QU W, ZHANG T,et al .Object pose estimation with point cloud data for robot grasping[C]∥Proceeding of the 2022 IEEE International Conference on Mechatronics and Automation.Guilin:ICMA,2022:1069-1074. |
| 22 | ZHANG X, YANG P, LI W .Research on humanoid movements of a 7-DOF manipulator for planar grasping[C]∥Proceeding of the 2022 2nd International Conference on Robotics and Control Engineering.New York:RobCE,2022:67-72. |
| 23 | LIN Yuquan, ZHANG Xuchong, LI Wenfan,et al .Human-like motion planning of anthropomorphic arms based on hierarchical strategy[C]∥Proceeding of the 2023 3nd International Conference on Robotics and Control Engineering. ACM International Conference Proceeding Series.New York:ACM,2023:55-59. |
| 24 | THOMAS T, JAVIER R, HEINZ-BODO S,et al .The GRASP taxonomy of human grasp types[J].IEEE Transactions on Human-Machine Systems,2016,46(1):66-77. |
| [1] | BI Sheng LIU Hao-xi MIN Hua-qing DONG Min HUANG Xin-long. Falling Detection and Control of Humanoid Robots Based on Multi-Sensor Information Fusion [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(1): 95-101. |
| [2] | ZHANG Qin FAN Chang-xiang. Motion Planning of Robot on the Basis of Task Decomposition and Speed Distribution [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(3): 44-50. |
| [3] | Bi Sheng Zhuang Zhong-jie Min Hua-qing. Gait Planning of Biped Robots Based on Strength Pareto Evolutionary Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(10): 68-73. |
| [4] | Zou Yan-biao Zhang Tie Chen Wei-hua . Motion Planning and Path Optimization of Manipulator for Holes Machining [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(8): 56-60. |
| [5] | Bi Sheng Min Hua-qing Chen Qiang Zhuang Zhong-jie Liu Qi-feng. Gait Planning of Humanoid Robots Walking on Slope [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(11): 148-154,160. |
| [6] | Shen Jin-hua Yang Jian-guo. Thermal Variation Analysis of Spatial Positioning Error of Machine Tool Based on Diagonal Measurement [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(10): 125-128,139. |
| [7] | Gan Zhi-gang Xiao Nan-feng. Design and Implementation of Virtual Teaching System for Humanoid Robot [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(1): 18-24. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||