| 1 |
SONG Y, DEMIRDJIAN D, DAVIS R .Continuous body and hand gesture recognition for natural human-computer interaction[J].ACM Transactions on Interactive Intelligent Systems,2012,2(1):1-28.
|
| 2 |
CHEN C, YANG Y, NIE F,et al .3D human pose recovery from image by efficient visual feature selection[J].Computer Vision and Image Understanding,2011,115(3):290-299.
|
| 3 |
SEDAI S, BENNAMOUN M, HUYNH D .Context-based appearance descriptor for 3D human pose estimation from monocular images[C]∥Proceedings of the 2009 Digital Image Computing:Techniques and Applications.Melbourne:IEEE,2009:484-491.
|
| 4 |
SHOTTON J, GIRSHICK R, FITZGIBBON A,et al .Efficient human pose estimation from single depth images[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2012,35(12):2821-2840.
|
| 5 |
SUMA E A, LANGE B, RIZZO A S,et al .Faast:the flexible action and articulated skeleton toolkit[C]∥Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE Virtual Reality Conference.Singapore:IEEE,2011:247-248.
|
| 6 |
FASTOVETS M, GUILLEMAUT J Y, HILTON A. Athlete pose estimation from monocular tv sports footage[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops.Portland:IEEE,2013:1048-1054.
|
| 7 |
KRIZHEVSKY A, SUTSKEVER I, HINTON G E .Imagenet classification with deep convolutional neural networks[J].Communications of the ACM,2017,60(6):84-90.
|
| 8 |
REN S, HE K, GIRSHICK R,et al .Faster r-cnn:towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks[J].Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems,2016,38(6):1137-1149.
|
| 9 |
LONG J, SHELHAMER E, DARRELL T. Fully convolutional networks for semantic segmentation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Boston:IEEE,2015:3431-3440.
|
| 10 |
LIN T Y, MAIRE M, BELONGIE S,et al .Microsoft coco:common objects in context[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin:Springer International Publishing,2014:740-755.
|
| 11 |
MEHTA D, RHODIN H, CASAS D,et al .Monocular 3d human pose estimation in the wild using improved cnn supervision[C]∥Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on 3D Vision.Qingdao:IEEE,2017:506-516.
|
| 12 |
LIN K, WANG L, LIU Z .End-to-end human pose and mesh reconstruction with transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Nashville:IEEE,2021:1954-1963.
|
| 13 |
VAROL G, CEYLAN D, RUSSELL B,et al .Bodynet:volumetric inference of 3d human body shapes[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV).Berlin:Springer International Publishing,2018:20-36.
|
| 14 |
KOCABAS M, ATHANASIOU N, BLACK M J .Vibe:video inference for human body pose and shape estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Seattle:IEEE,2020:5253-5263.
|
| 15 |
MAHMOOD N, GHORBANI N, TROJE N F,et al .AMASS:archive of motion capture as surface shapes[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Seoul:IEEE,2019:5442-5451.
|
| 16 |
KIPF T N, WELLING M. Semi-supervised classification with graph convolutional networks[J].arXiv preprint arXiv:,2016.
|
| 17 |
WANG N, ZHANG Y, LI Z,et al .Pixel2mesh:generating 3d mesh models from single rgb images[C]∥Proceedings of the European conference on computer vision (ECCV).Berlin:Springer International Publishing,2018:52-67.
|
| 18 |
KOLOTOUROS N, PAVLAKOS G, JAYARAMAN D,et al .Probabilistic modeling for human mesh recovery[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:11605-11614.
|
| 19 |
ZHANG Q, FU B, YE M,et al .Quality dynamic human body modeling using a single low-cost depth camera[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Columbus:IEEE,2014:676-683.
|
| 20 |
ANGUELOV D, SRINIVASAN P, KOLLER D,et al .Scape:shape completion and animation of people[A]∥ACM SIGGRAPH 2005 Papers Association for Computing Machinery[M].New York:ACM States,2005:408-416.
|
| 21 |
LOPER M, MAHMOOD N, ROMERO J,et al .SMPL:a skinned multi-person linear model[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics,2015,34(6):1-16.
|
| 22 |
DIBRA E, JAIN H, ÖZTIRELI C,et al .Hs-nets:estimating human body shape from silhouettes with convolutional neural networks[C]∥Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision.Stanford:IEEE,2016:108-117.
|
| 23 |
KANAZAWA A, BLACK M J, JACOBS D W,et al .End-to-end recovery of human shape and pose[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Lake City:IEEE,2018:7122-7131.
|
| 24 |
GOODFELLOW I, POUGET-ABADIE J, MIRZA M,et al .Generative adversarial networks[J].Communications of the ACM,2020,63(11):139-144.
|
| 25 |
ZIMMERMANN C, BROX T .Learning to estimate 3d hand pose from single rgb images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision. Venice:IEEE,2017:4903-4911.
|
| 26 |
SUN Y, BAO Q, LIU W,et al .Monocular,one-stage,regression of multiple 3d people[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision. Montreal:IEEE,2021:11179-11188.
|
| 27 |
SUN Y, LIU W, BAO Q,et al .Putting people in their place:monocular regression of 3d people in depth[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.New Orleans:IEEE,2022:13243-13252.
|
| 28 |
LI J, XU C, CHEN Z,et al .Hybrik:a hybrid analytical-neural inverse kinematics solution for 3d human pose and shape estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Nashville:IEEE,2021:3383-3393.
|
| 29 |
WOO S, PARK J, LEE J Y,et al .Cbam:convolutional block attention module[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin:Springer International Publishing,2018:3-19.
|
| 30 |
VASWANI A, SHAZEER N, PARMAR N,et al .Attention is all you need[C]∥Proceedings of the 31st Conference on Advances in Neural Information Processing Systems.Long Beach:[s.n.],2017:5998-6008.
|
| 31 |
KIM J, GWON M G, PARK H,et al .Sampling is matter:point-guided 3D human mesh reconstruction[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vancouver:IEEE,2023:12880-12889.
|
| 32 |
IONESCU C, PAPAVA D, OLARU V,et al .Human3.6m:large scale datasets and predictive methods for 3d human sensing in natural environments[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2013,36(7):1325-1339.
|
| 33 |
KOLOTOUROS N, PAVLAKOS G, DANIILIDIS K .Convolutional mesh regression for single-image human shape reconstruction[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:4501-4510.
|
| 34 |
KOLOTOUROS N, PAVLAKOS G, BLACK M J,et al .Learning to reconstruct 3D human pose and shape via model-fitting in the loop[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Seoul:IEEE,2019:2252-2261.
|
| 35 |
CHOI H, MOON G, LEE K M .Pose2mesh:graph convolutional network for 3d human pose and mesh recovery from a 2d human pose[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin:Springer,2020:769-787.
|
| 36 |
KOCABAS M, ATHANASIOU N, BLACK M J .Vibe:video inference for human body pose and shape estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Seattle:[s.n.],2020:5253-5263.
|
| 37 |
MOON G, LEE K M .I2l-meshnet:Image-to-lixel prediction network for accurate 3d human pose and mesh estimation from a single rgb image[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin:Springer International Publishing,2020:752-768.
|
| 38 |
CHOI H, MOON G, CHANG J Y,et al .Beyond static features for temporally consistent 3d human pose and shape from a video[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Nashville:IEEE,2021:1964-1973.
|
| 39 |
ZHANG H, TIAN Y, ZHOU X,et al .Pymaf:3d human pose and shape regression with pyramidal mesh alignment feedback loop[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:11446-11456.
|
| 40 |
LIN K, WANG L, LIU Z .End-to-end human pose and mesh reconstruction with transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. Nashville:IEEE,2021:1954-1963.
|
| 41 |
CHO J, YOUWANG K, OH T H .Cross-attention of disentangled modalities for 3d human mesh recovery with transformers[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Berlin:Springer International Publishing,2022:342-359.
|
| 42 |
ZHENG C, LIU X, QI G J,et al .POTTER:pooling attention transformer for efficient human mesh recovery[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Vancouver:IEEE,2023:1611-1620.
|
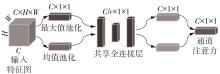
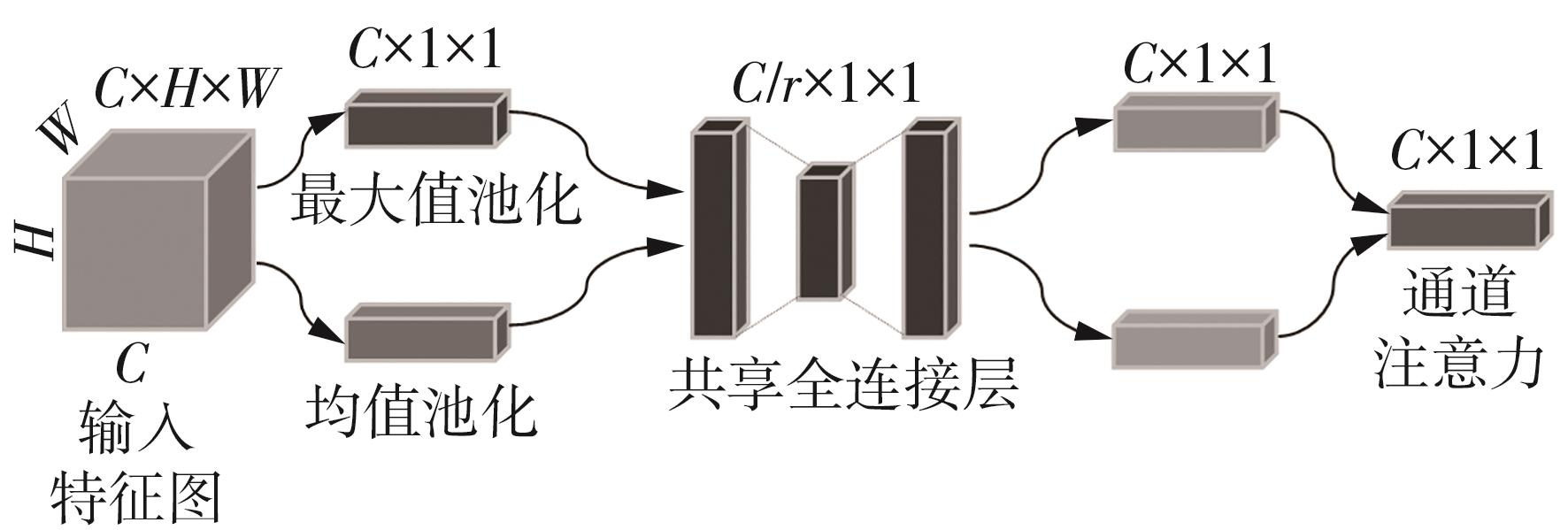
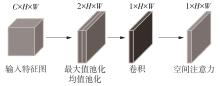
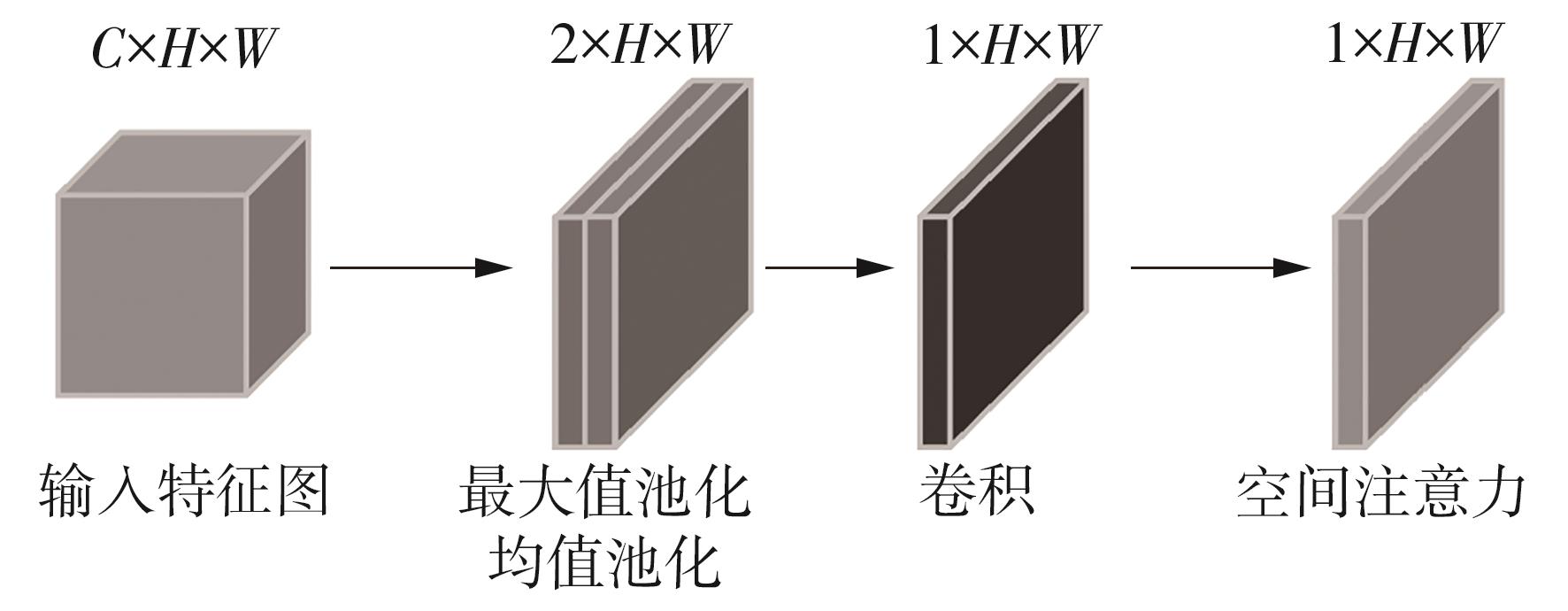
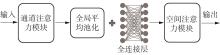
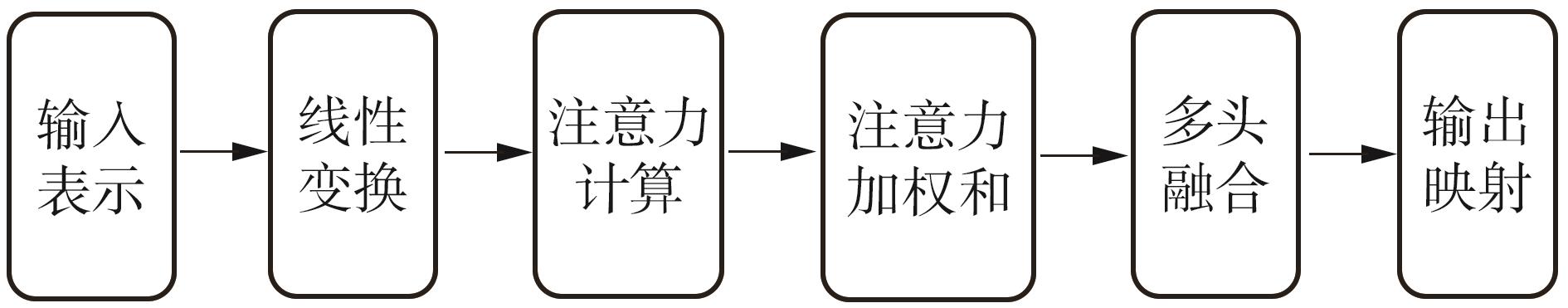


 1)/mm
1)/mm /mm
/mm / mm
/ mm / mm
/ mm /mm
/mm /mm
/mm