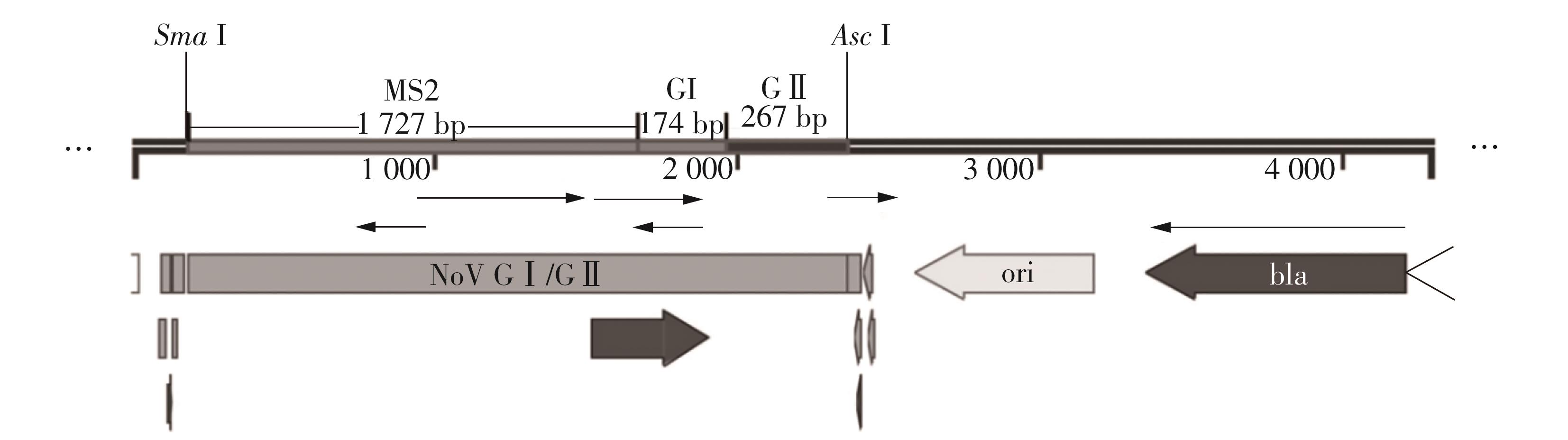
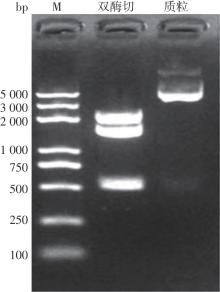
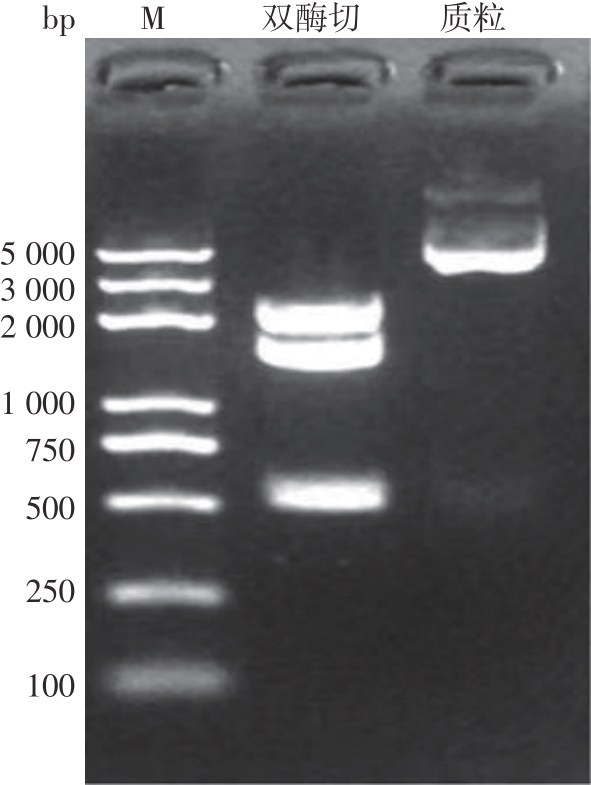
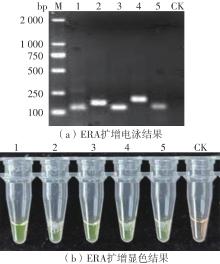
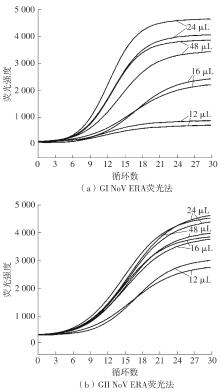
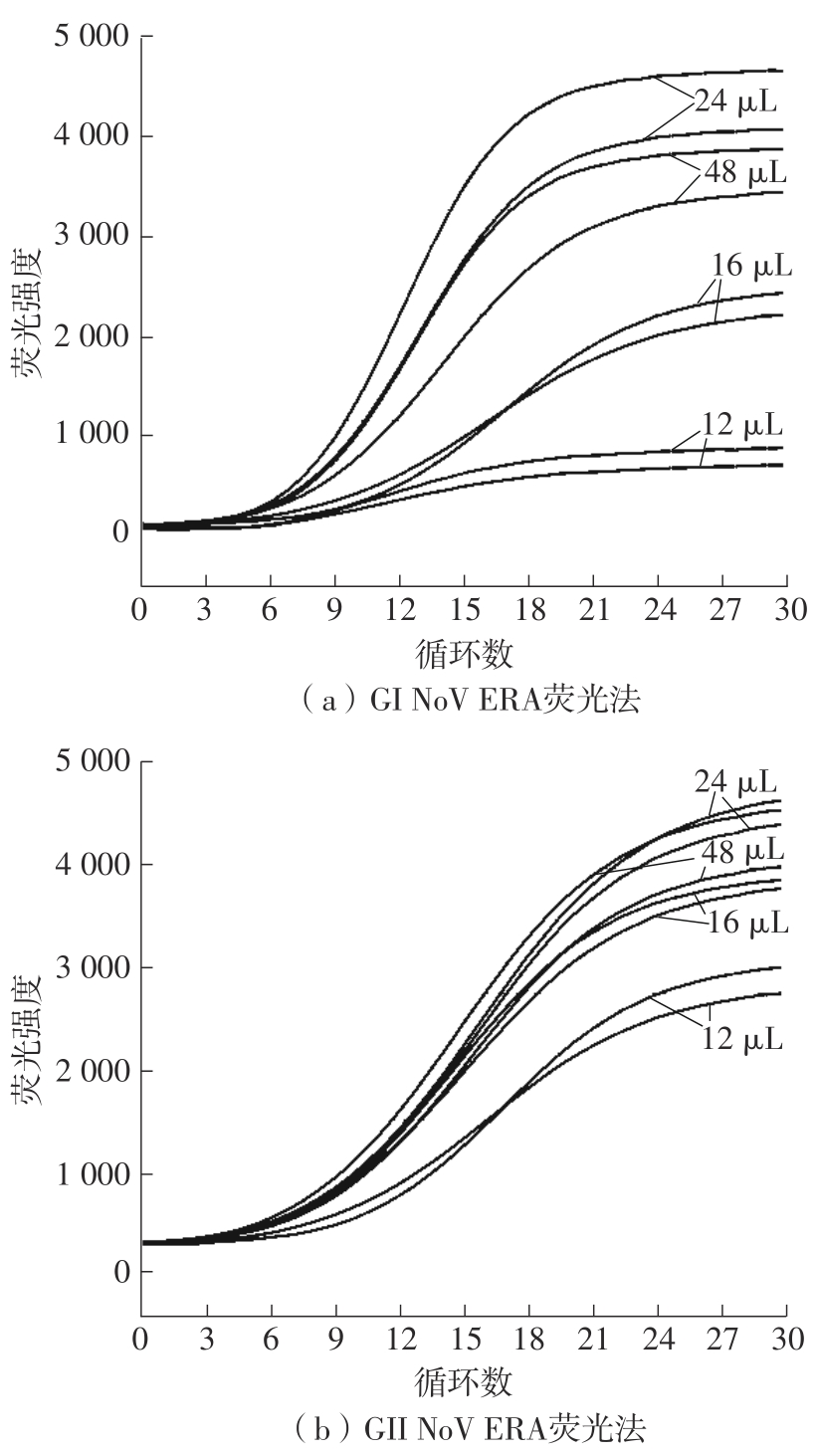
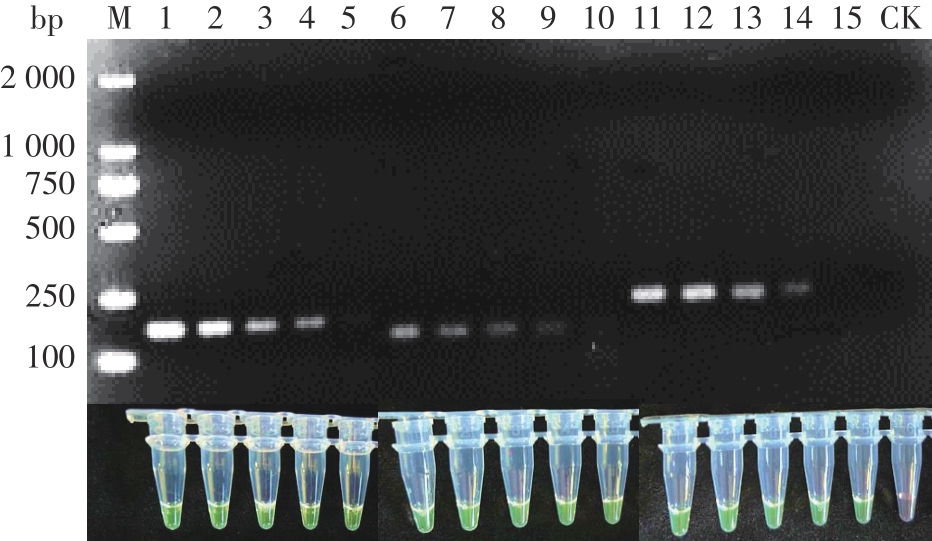
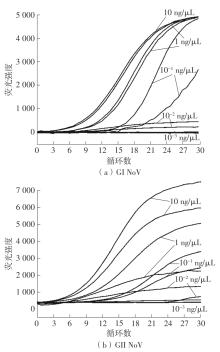
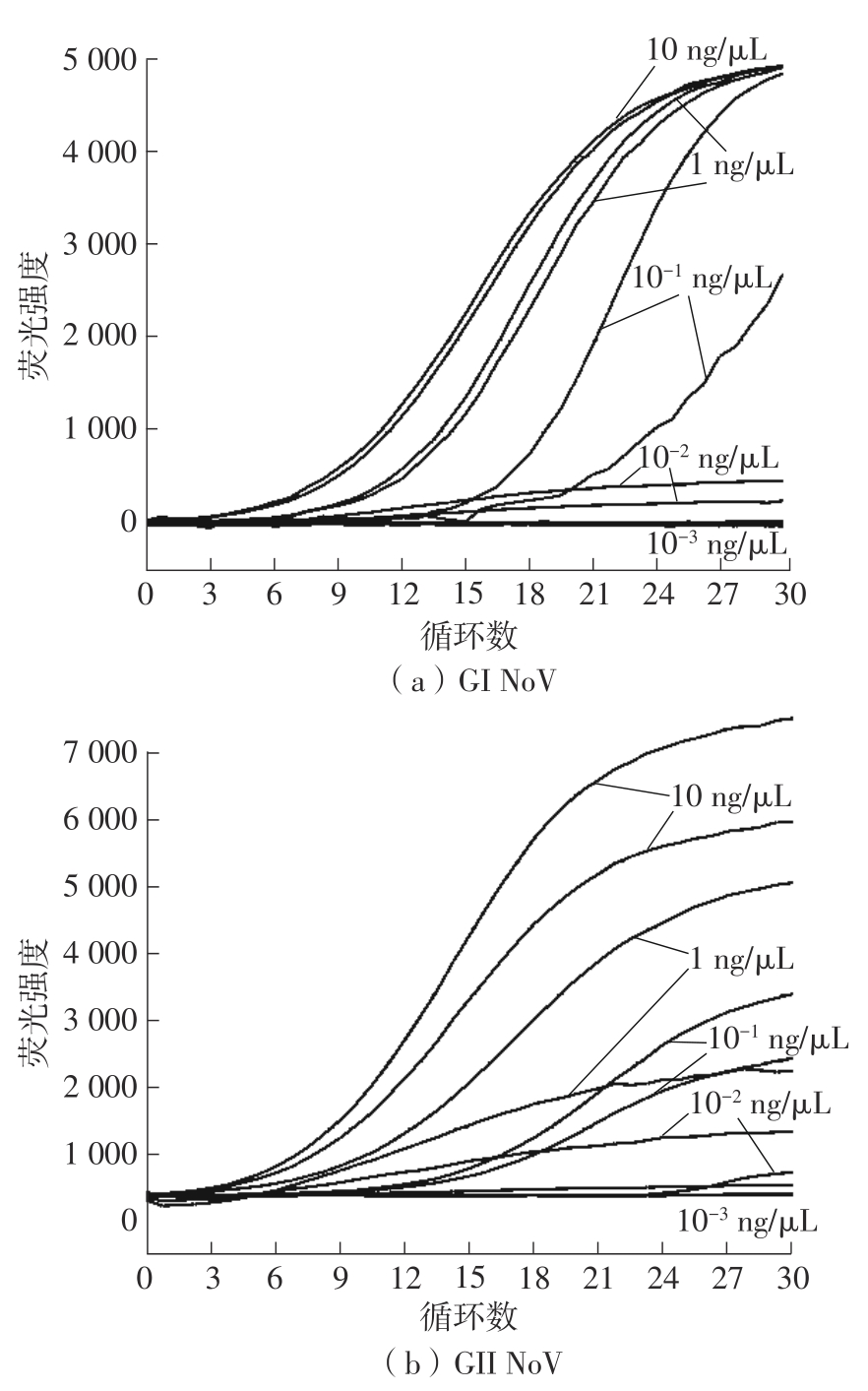
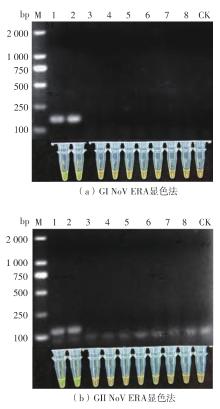
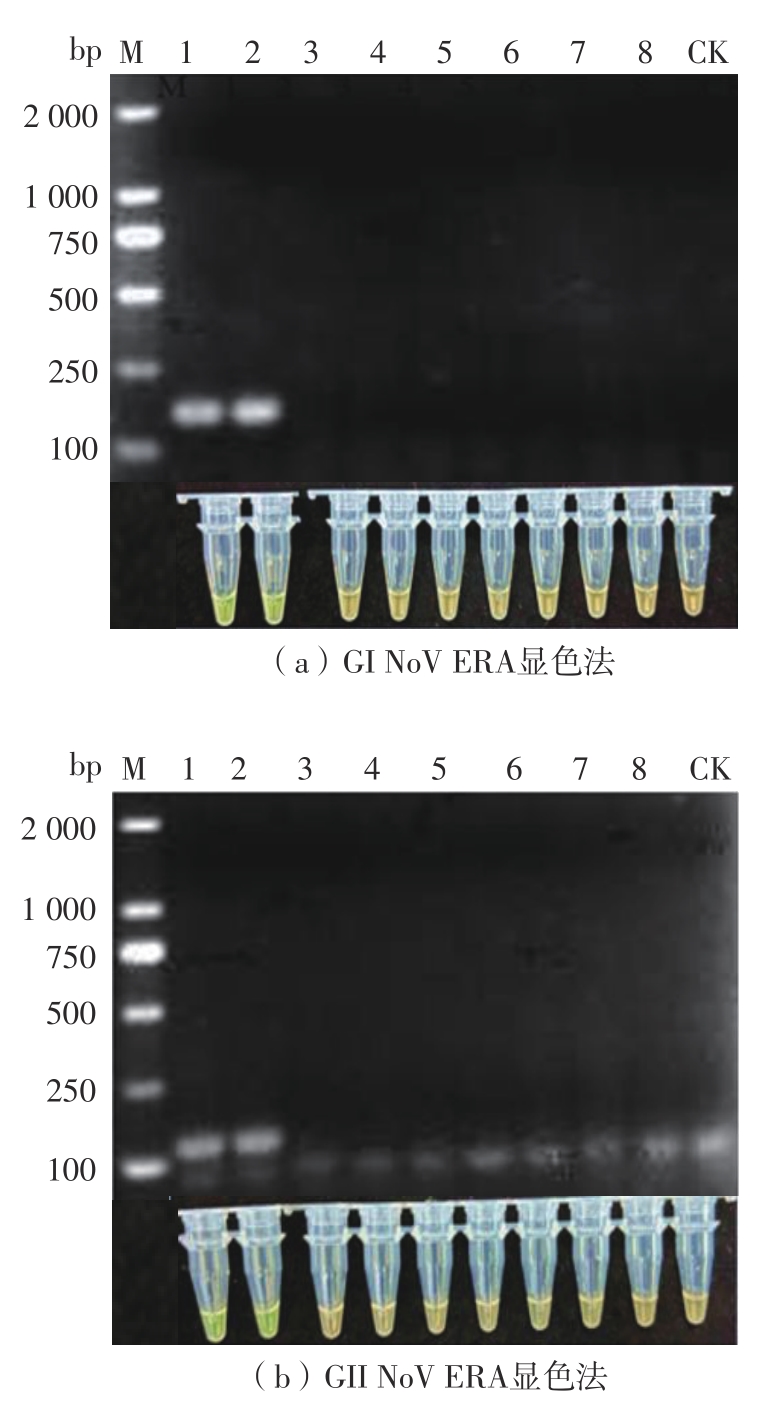
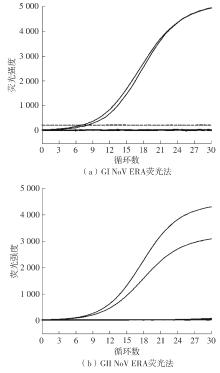
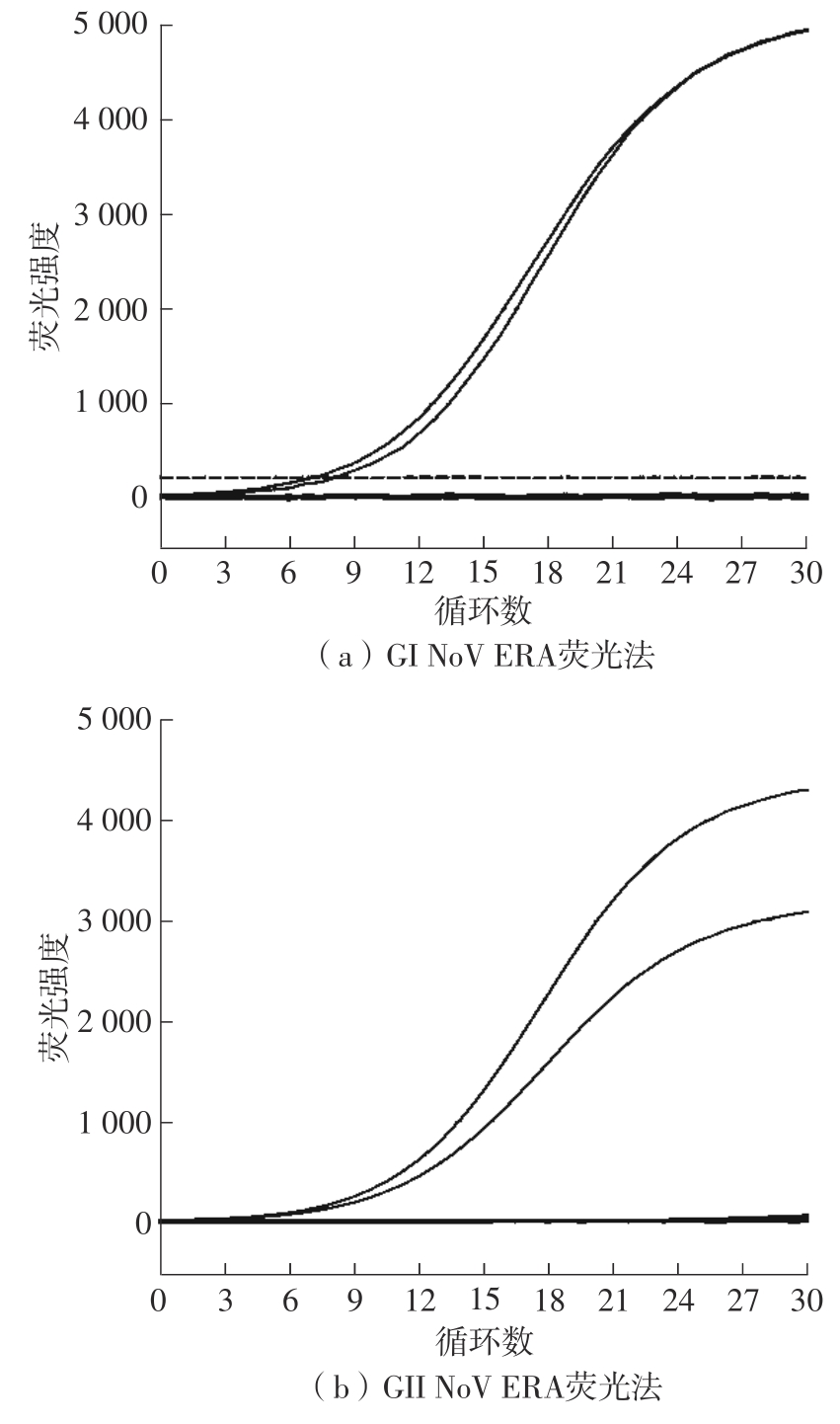
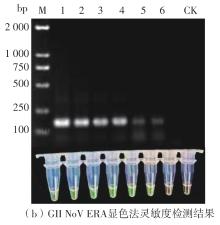
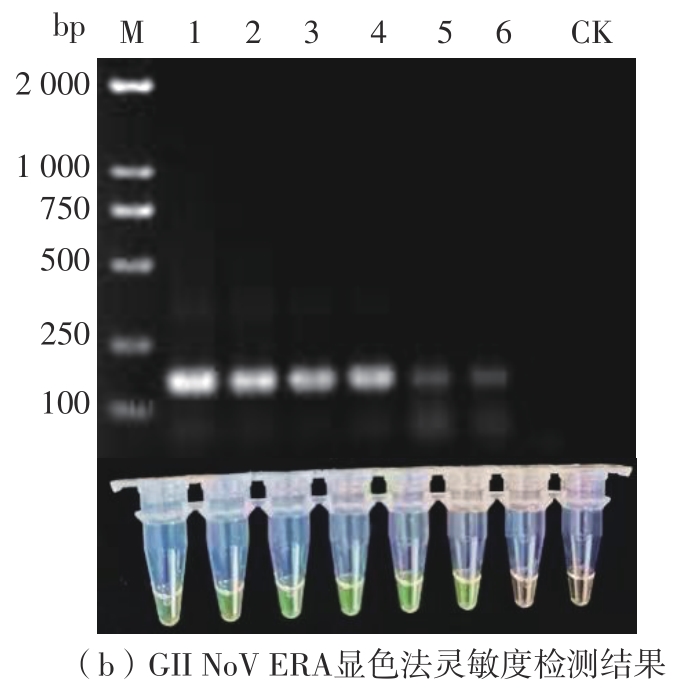
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2023, Vol. 51 ›› Issue (12): 140-151.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220529
• Food Science & Technology • Previous Articles Next Articles
Two Visual and Rapid Enzymatic Recombinase Amplification Methods for GI and GII Noroviruses Detection
YANG Yange1 WU Zhanwen1,2 LI Tao1 WANG Shuai1,2 LI Hongna1 SUN Dongmei2 YUAN Fei1
- 1.Key Laboratory of Food Quality and Safety for State Market Regulation,Chinese Academy of Inspection and Quarantine,Beijing 100176,China
2.College of Life Science and Technology,Heilongjiang Bayi Agricultural University,Daqing 163000,Heilongjiang,China
-
Received:2022-08-17Online:2023-12-25Published:2023-07-12 -
Contact:袁飞(1974-),女,博士,研究员,主要从事食源性病原微生物研究。 E-mail:feyyuan@163.com -
About author:杨艳歌(1986-),女,副研究员,主要从事分子生物学研究。E-mail: yange8602@126.com -
Supported by:the Chinese Academy of Inspection and Quarantine Project(2022JK36);the National Key Research and Development Program of China(2022YFF0607900)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
YANG Yange, WU Zhanwen, LI Tao, et al. Two Visual and Rapid Enzymatic Recombinase Amplification Methods for GI and GII Noroviruses Detection[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(12): 140-151.
share this article
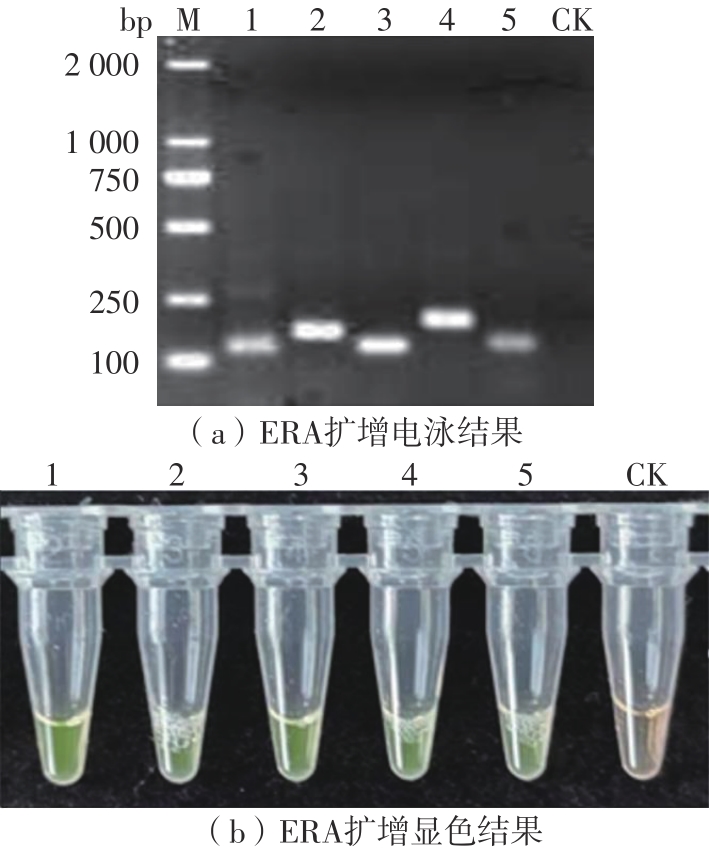
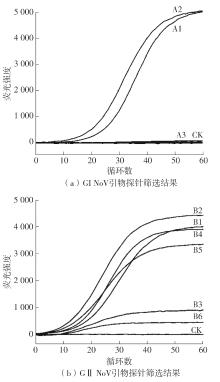
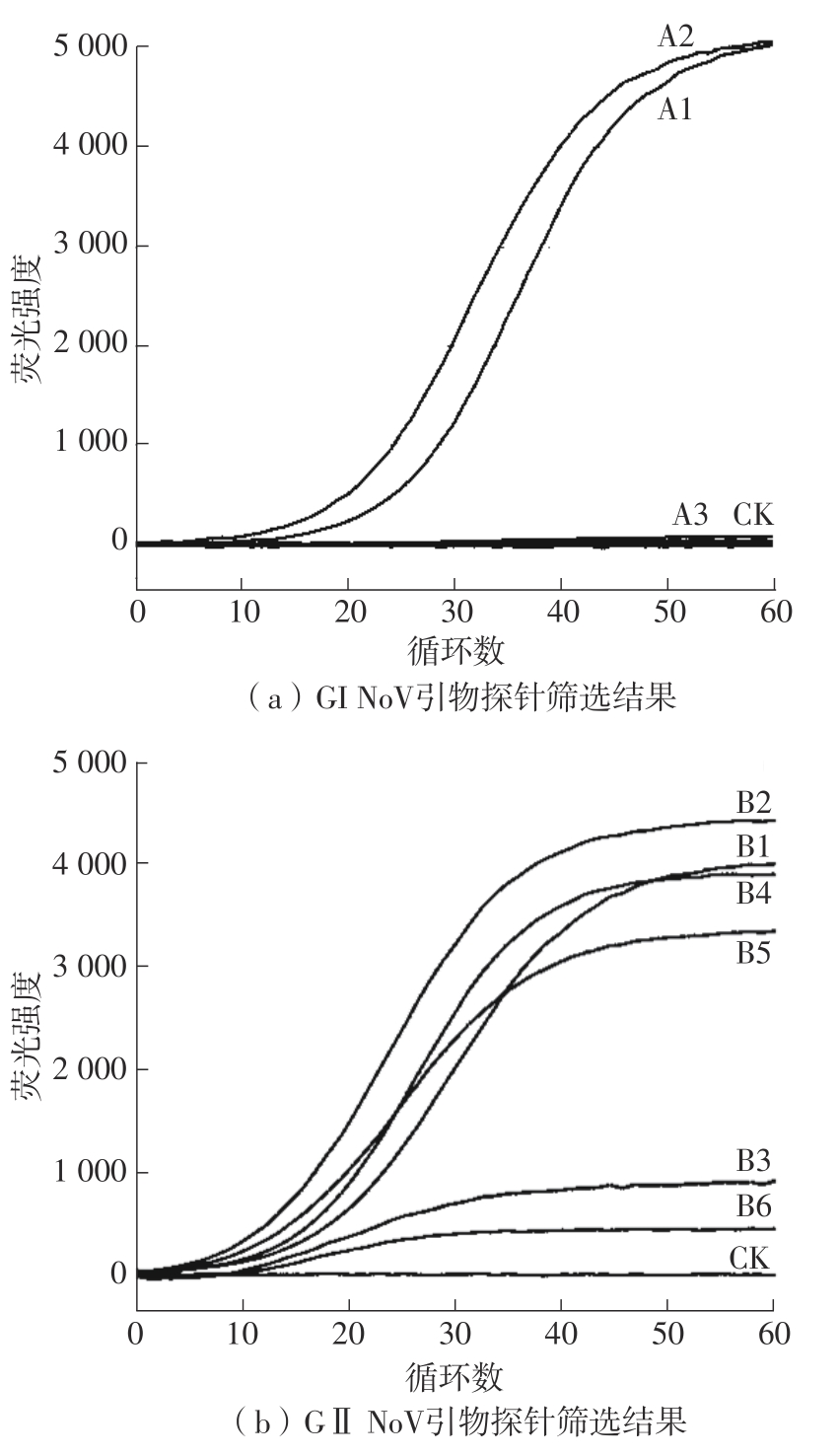
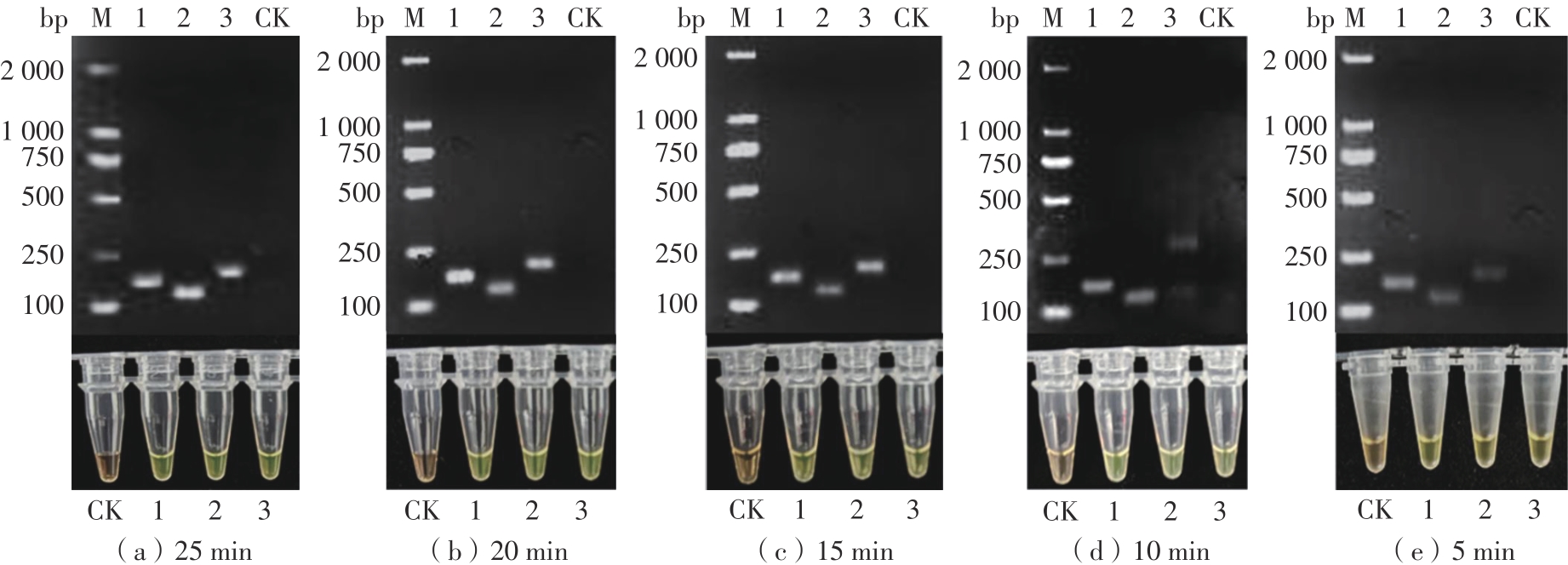
Table 1
Primers and probes sequence of GⅠ and GⅡ NoV ERA detection"
| 基因群 | 引物探针 | 序列(5′ 3′) 3′) | 片段长度/bp |
|---|---|---|---|
| GⅠ | GIF1 | GTATGTCCCAGGATGGCAGGCCATGTTC | 132 |
| GIR1 | CCACGCTTGATGTAGCGTCCTTAGACGC | ||
| GIF2 | ATGTATGTCCCAGGATGGCAGGCCATGT | 168 | |
| GIR2 | TCCGGTACCAACTGACCAGCGCCACTAG | ||
| GIP1/2 | GACCTCGGATTGTGGACAGGAGATCGCGA [FAM-dT][THF][BHQ1-dT]TCTGCCCGAATTCGT[c3-spacer] | ||
| GIP2 | TCCGCTGGATGCGCTTCCATGACCTCGGAT[FAM-dT][THF][BHQ1-dT]GGACAG[c3-spacer] | ||
| GⅡ | GIIF1 | TGAGATTCTCAGATCTGAGCACGTGGGA | 132 |
| GIIR1 | ATTATTGACCTCTGGGACGAGGTTGGCT | ||
| GIIF2 | CAGAACTGAAGGAAGGTGGCATGGATT | 194 | |
| GIIR2 | TTATTGACCTCTGGGACGAGGTTGGCTG | ||
| GIIF3 | GTTCAGATGGATGAGATTCTCAGATCTG | 140 | |
| GIIR3 | TATTGACCTCTGGGACGAGGTTGGCTGC | ||
| GIIP2 | CGTGCCCAGACAAGAGCCAATGTTCAGA[FAM-dT]G[THF]A[BHQ1-dT]GAGATTCTCAGATC[c3-spacer] | ||
| GIIP2/3 | GGAGGGCGATCGCAATCTGGCTCCCAGCTT[FAM-dT][THF][BHQ1-dT]GAATGAAGATGGCGT[c3-spacer] | ||
| GIIP1/2/3 | GGCGATCGCAATCTGGCTCCCAGCTTTG[FAM-dT]G[THF]A[BHQ1-dT]GAAGATGGCGTCGAAT[c3-spacer] |
| 1 | 廖小艳,陈丽丽,白亚龙 .食品中诺如病毒检测技术研究进展[J].食品与机械,2021,37:200-206,232. |
| LIAO Xiao-yan, CHEN Li-li, BAI Ya-long .The progress of detection methods for norovirus in foods[J].Food & Machinery,2021,37:200-206,232. | |
| 2 | 廖巧红,冉陆,靳淼,等 .诺如病毒感染暴发调查和预防控制技术指南 (2015版)[J].中国病毒病杂志,2015,5:448-458. |
| LIAO Qiao-hong, RAN Lu, JIN Miao,et al .Guidelines on outbreak investigation,prevention and control of norovirus infection (2015)[J].Chinese Journal of Viral Diseases,2015,5:448-458. | |
| 3 | PRINGLE K, LOPMAN B, VEGA E,et al .Noroviruses:epidemiology,immunity and prospects for prevention[J].Future Microbiology,2015,10(1):53-67. |
| 4 | RUMBLE C, ADDIMAN S, BALASEGARAM S,et al .Role of food handlers in norovirus outbreaks in london and South East England,2013 to 2015[J].Journal of Food Protection,2017,80(2):257-264. |
| 5 | 邵云平,郭黎 .海淀区中小学校和托幼机构诺如病毒感染疫情流行特征[J].预防医学,2021,33(12):1262-1264. |
| SHAO Yun-ping, GUO Li .Epidemiological characteristics of norovirus infection in primary and secondary schools and kindergartens in Haidian District[J].Preventive Medicine,2021,33(12):1262-1264. | |
| 6 | 董瑞,刘富强,张斯钰,等 .湖南省2017—2019年学校诺如病毒感染暴发疫情流行特征分析[J].现代预防医学,2021,48(21):3847-3851. |
| DONG Rui, LIU Fu-qiang, ZHANG Si-yu,et al .Study on epidemiological characteristics of norovirus outbreak at schools in Hunan Province during 2017—2019[J].Modern Preventive Medicine,2021,48(21):3847-3851. | |
| 7 | 乔雪飞,刘玲,吴健灏,等 .2017—2019年上海市松江区诺如病毒感染性腹泻疫情的病毒基因型特征分析[J].中华预防医学杂志,2021,55(11):1316-1320. |
| QIAO Xue-fei, LIU Ling, WU Jian-hao,et al .Characterization of viral genotypes of norovirus-infected diarrhea outbreaks in Songjiang District,Shanghai,2017—2019[J].Chinese Journal of Preventive Medicine,2021,55(11):1316-1320. | |
| 8 | 王竹叶,韩雪英,王国川,等 .GⅡ.17型诺如病毒样颗粒的制备及鉴定[J].微生物学通报,2022,49:483-491. |
| WANG Zhu-ye, HAN Xue-ying, WANG Guo-chuan,et al .Preparation and identification of Norovirus GII.17 virus-like particles[J].Microbiology China,2022,49:483-491. | |
| 9 | MATHIJS E, STALS A, BAERT L,et al .A review of known and hypothetical transmission routes for noroviruses[J].Food and Environmental Virology,2012,4(4):131-152. |
| 10 | 颜伟,吴杰 .一起高校直饮水被诺如病毒污染引起的急性胃肠炎暴发调查[J].热带医学杂志,2021,21:1214-1217. |
| YAN Wei, WU Jie .An outbreak of acute gastroenteritis caused by norovirus contamination associated with contamination of direct drinking water in a university[J].Journal of Tropical Medicine,2021,21:1214-1217. | |
| 11 | 朱曦,孔翔羽,章青,等 .2016-2019年我国诺如病毒暴发疫情的分子流行病学特征分析[J].疾病监测,2021,36(8):774-779. |
| ZHU Xi, KONG Xiang-yu, ZHANG Qing,et al .Molecular epidemiological characteristics of norovirus outbreaks reported to Chinese norovirus outbreak laboratory surveillance network,2016—2019[J].Disease Surveillance,2021,36(8):774-779. | |
| 12 | 赵峰,佟利惠,杨敏,等 .牡蛎中诺如病毒的感染及其防控研究进展[J].南方水产科学,2021,17:133-140. |
| ZHAO Feng, TONG Li-hui, YANG Min,et al .Progress and prospects of infection,prevention and control of norovirus in oyster[J].South China Fisheries Science,2021,17:133-140. | |
| 13 | LEE H M, KWON J, CHOI J S,et al .Rapid detection of norovirus from fresh lettuce using immunomagnetic separation and a quantum dots assay[J].Journal of Food Protection,2013,76(4):707-711. |
| 14 | PARK Y, CHO Y H,JEE Y,et al .Immunomagnetic separation combined with real-time reverse transcriptase PCR assays for detection of norovirus in contaminated food[J].Applied & Environmental Microbiology,2008,74(13):4226-4230. |
| 15 | WANG D, TIAN P .Inactivation conditions for human norovirus measured by an in situ capture-qRT-PCR method[J].International Journal of Food Microbiology,2014,172:76-82 . |
| 16 | XU D, WU X, HAN J,et al .Detection of GI and GII noroviruses in drinking water and vegetables using filtration and real-time RT-PCR[J].European Food Research and Technology,2014,239(5):795-801. |
| 17 | 孙志强,黄志成,王修,等 .诺如病毒检测技术的研究进展[J].中国实验诊断学,2020,24(10):1750-1752. |
| SUN Zhi-qiang, HUANG Zhi-cheng, WANG Xiu,et al .Research progress of norovirus detection technology[J].Chinese Journal of Laboratory Diagnosis,2020,24(10):1750-1752. | |
| 18 | SAYLAN Y, ERDEM Z,NAL S,et al .An alternative medical diagnosis method:biosensors for virus detection[J].Biosensors,2019,9(2):65/1-22. |
| 19 | 施奕,徐昌平,余蓓蓓,等 .重组酶聚合酶扩增技术研究进展[J].病毒学报,2020,36(3):522-532. |
| SHI Yi, XU Chang-ping, YU Bei-bei,et al .Research progress in recombinase polymerase amplification (RPA)[J].Chinese Journal of Virology,2020,36(3):522-532. | |
| 20 | 杜亚楠,赵笑,范小瑞,等 .重组酶聚合酶扩增技术的研究进展及其应用[J].上海农业学报,2018,34(6):117-122. |
| DU Ya-nan, ZHAO Xiao, FAN Xiao-rui,et al .Advances and applications of recombinase polymerase amplification[J].Acta Agriculturae Shanghai,2018,34(6):117-122. | |
| 21 | 胡海洋,应婉琴,何军,等 .酶促重组等温扩增实时荧光法快速检测肺炎支原体方法的建立及应用[J].生物技术通报,2022,38(9):264-270. |
| HU Hai-yang, YING Wan-qin, HE Jun,et al .Establishment and application of ERA real-time fluorescence method for rapid detection of mycoplasma pneumoniae[J].Biotechnology Bulletin,2022,38(9):264-270. | |
| 22 | 曾宇晨,龚浪,王京煜,等 .基于B646L、EP402R、MGF360/505基因的非洲猪瘟病毒ERA检测方法的建立[J].华南农业大学学报,2021,42(5):33-40. |
| ZENG Yu-chen, GONG Lang, WANG Jing-yu,et al .Development of ERA detection method for African swine fever virus based on B646L,EP402R and MGF360/505 genes[J].Journal of South China Agricultural University,2021,42(5):33-40. | |
| 23 | 刘迪,许鑫燕,郑亚婷,等 .猫疱疹病毒ERA-LFD检测技术的建立与应用[J].中国兽医科学,2022,52:11-18. |
| LIU Di, XU Xin-yan, ZHENG Ya-ting,et al .Establishment and application of ERA-LFD method for rapid detection of feline calicivirus[J].Chinese Veterinary Science,2022,52:11-18. | |
| 24 | DREIER J, STORMER M, KLEESIEK K .Use of bacteriophage MS2 as an internal control in viral reverse transcription-PCR assays[J].Journal of Clinical Microbiology,2005,43(9):4551-4557. |
| 25 | PASLOSKE B L, WALKERPEACH C R, OBERMOELLER R D,et al .Armored RNA technology for production of ribonuclease-resistant viral RNA controls and standards[J].Journal of Clinical Microbiology,1999,36(12):3590-3594. |
| [1] | YANG Yange, WU Zhanwen, LIU Tong, et al. Establishment of a Triple ERA Rapid Detection Method for Pathogens in Refrigerated Meat Products [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2025, 53(4): 135-146. |
| [2] | LIU Xiumei, WU Su, LI Beibei, et al.. Study on 3D Flow Field Characteristics of Control Valve Based on 2D-PIV [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(11): 110-118. |
| [3] | FU Xinsha, ZENG Yanjie, MA Li, et al. Weather Recognition of Highway Surveillance Scenes Based on Light-Weight Deep Neural Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 1-8. |
| [4] | CHAI Bosen, WANG Guangyi, ZHU Guoren, et al. Large Eddy Simulation Flow Field Analysis and Visualization Test Verification of Hydraulic Torque Converter Under Braking Condition [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(3): 95-105. |
| [5] | XIA Qinxiang, ZHANG Yilong, XIAO Gangfeng, et al. Automatic Measurement Method of Wall Thickness of Spun Workpieces Based on Abaqus [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(6): 1-7. |
| [6] | Liu Huan-yu Zhang Gui-zhen Chen Jia-jia Qu Jin-ping. Visualization of Solid Polymer Deformation in Vane Extruder and Its Influence Factors [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(7): 8-13. |
| [7] | Zhang Gui- zhen Liu Huan- yu Chen Jia- jia Qu Jin- ping. Visualization Research on Polypropylene Melting Process in Vane Extruder [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2014, 42(6): 32-39. |
| [8] | Liu Jie Yang Yong-qiang Song Chang-hui. SLM-Based Direct Manufacturing of Metal Bas-Relief from Images [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2011, 39(6): 13-17. |
| [9] | Tian He-qiang Wu Dong-mei Du Zhi-jiang Sun Li-ning. Registration Technology Based on ICP Algorithm for Spinal Surgical Navigation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2010, 38(11): 141-147. |
| [10] | Li Bin Tian Lian-fang Wang Li-fei Mao Zong-yuan . 3D Visualization System for 3D Conformal Radiotherapy Treatment Planning [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(9): 122-127. |
| [11] | Fan Ming-hui Chen Chong-cheng. Interactive Visualization Technology Based on Map [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2008, 36(5): 48-52. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||