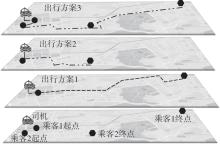
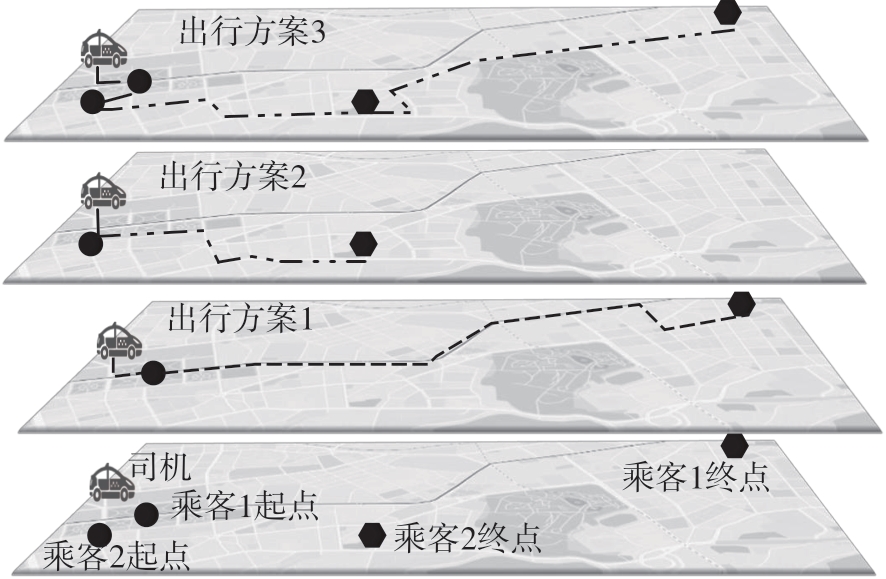
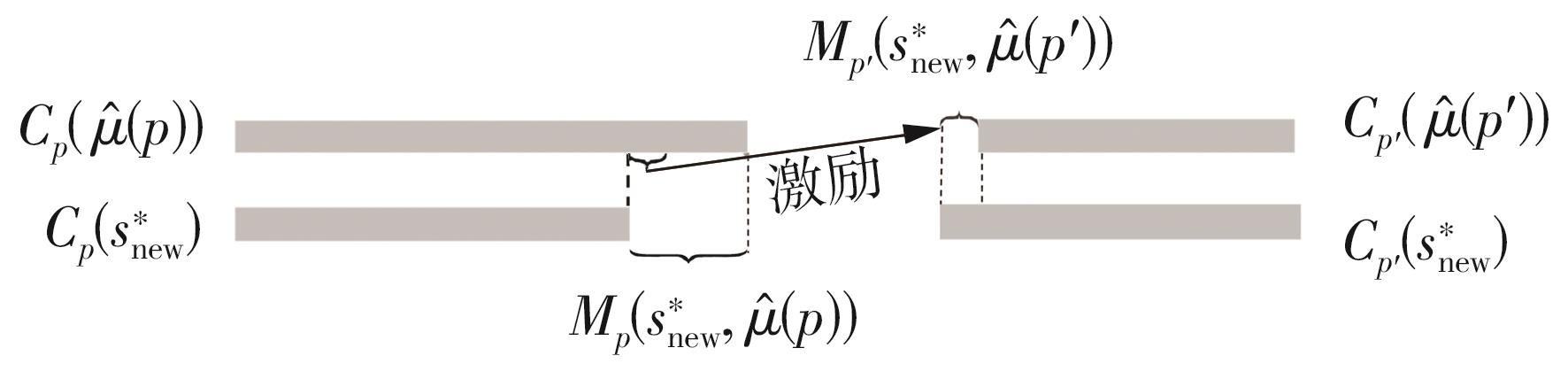
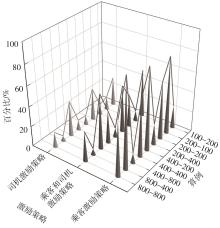
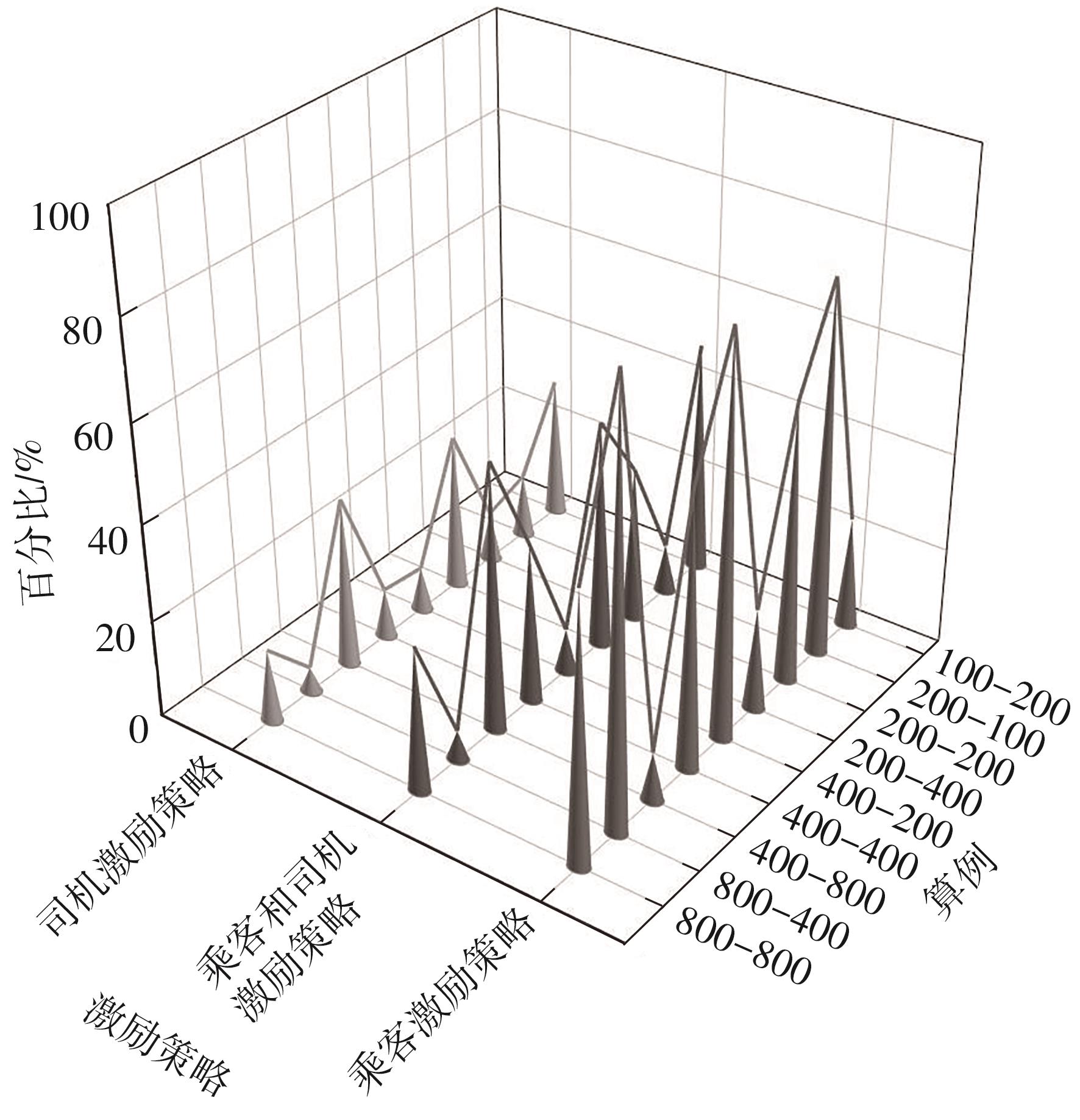
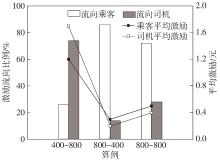
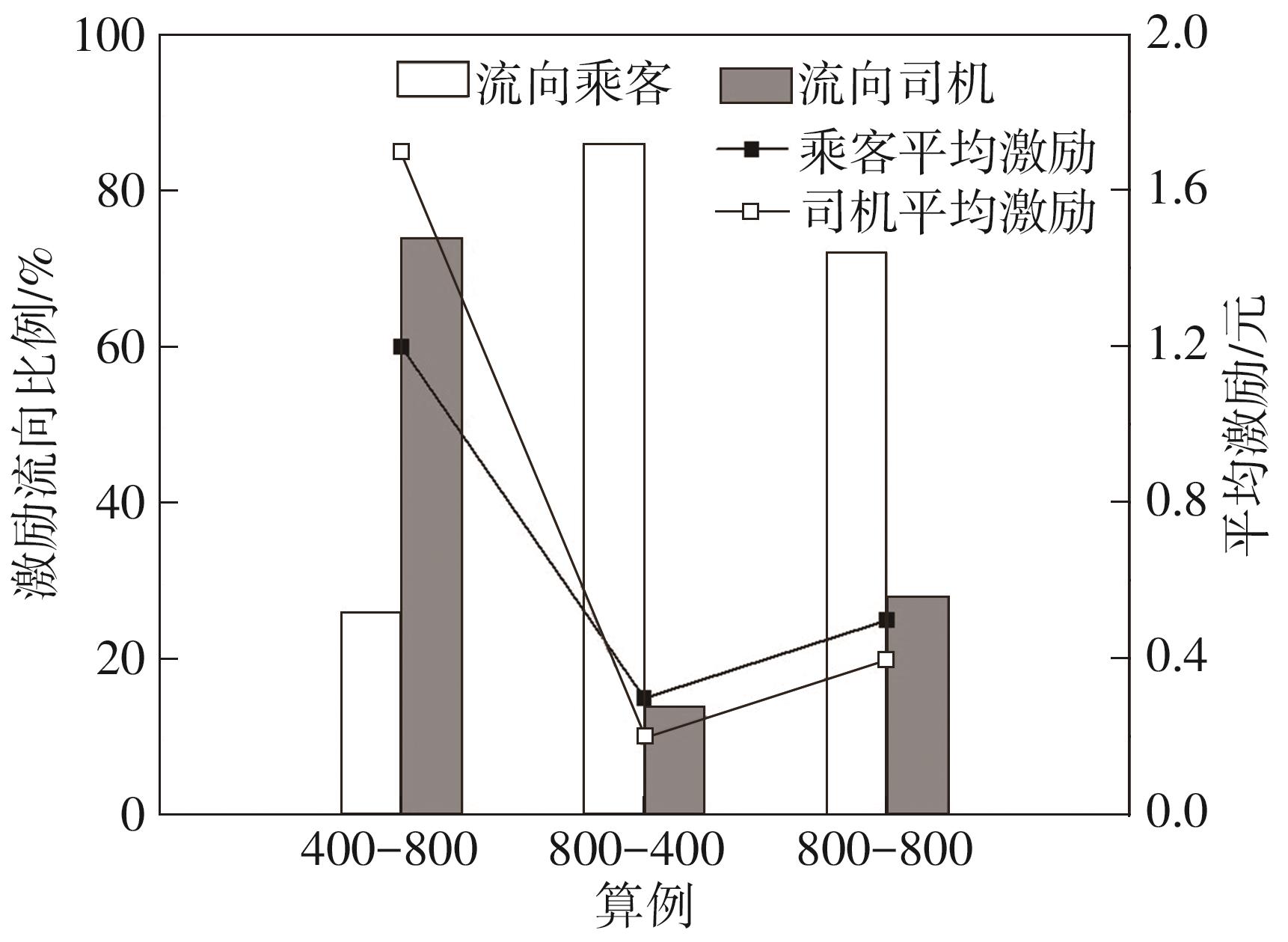
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (2): 95-103.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230158
• Green & Intelligent Transportation • Previous Articles Next Articles
Taxi-Sharing Matching Equilibrium Under Peer-Passenger Incentive Mechanism
PENG Zixuan1 CUI Lin1 GUO Zhiwei1 CHEN Hanyang2 WEI Liying1
- 1.School of Traffic and Transportation,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China
2.School of Computer and Information Technology,Beijing Jiaotong University,Beijing 100044,China