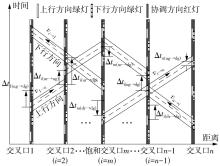
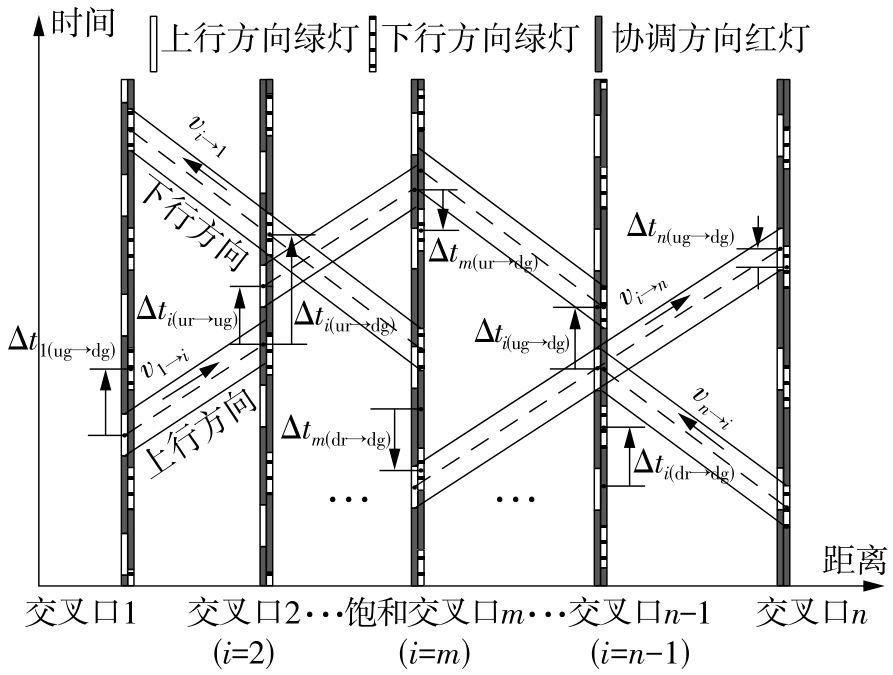
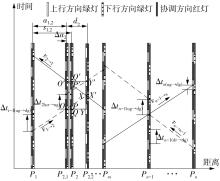
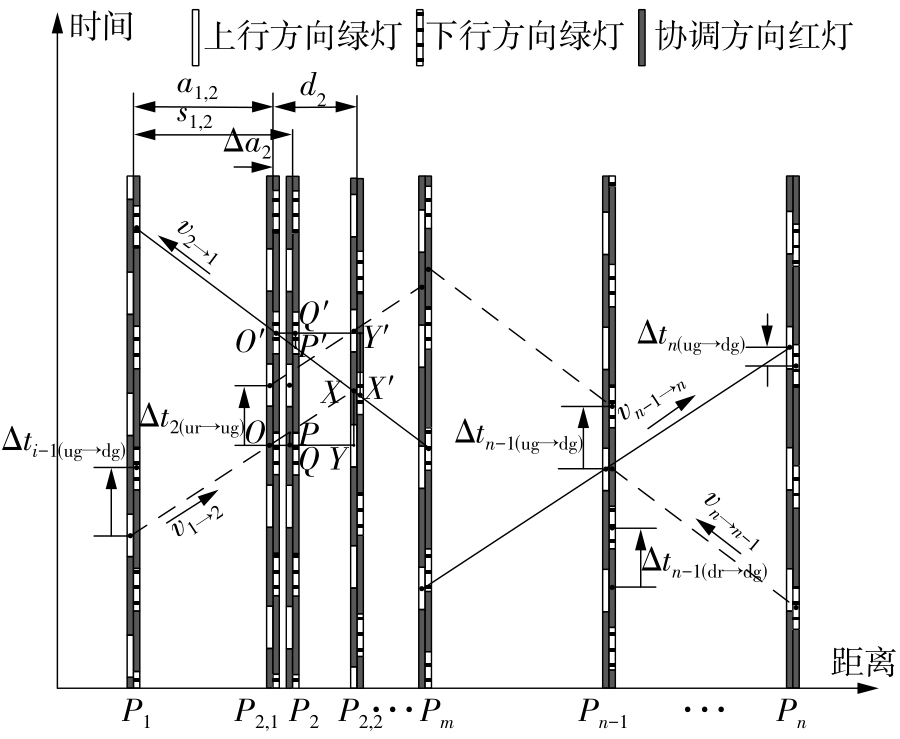
Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition) ›› 2022, Vol. 50 ›› Issue (9): 1-11.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.210809
Special Issue: 2022年交通运输工程
• Traffic & Transportation Engineering • Previous Articles Next Articles
Algebraic Method of Coordination Design for Bi-directional Red and Green Waves of Saturated Intersection
LU Kai1,2, ZHAO Shijie1, WU Huan3, et al
- 1.School of Civil Engineering and Transportation/State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Guangzhou Lab of Artificial Intelligence and Digital Economy,Guangzhou 510330,Guangdong,China
3.Shenzhen Urban Transport Planning Center Co. Ltd. ,Guangdong Transport Information Engineering Technology Research Center,Shenzhen 518021,Guangdong,China
-
Received:2021-12-21Online:2022-09-25Published:2022-04-22 -
Contact:吴焕(1991-),男,工程师,主要从事交通建模与规划研究。 E-mail:wuhuan@sutpc.com -
About author:卢凯(1979-),男,教授,博士生导师,主要从事智能交通控制研究。E-mail:kailu@scut. edu. cn -
Supported by:the National Natural Science Foundation of China(52172326);the Key Research and Development Program of Guangzhou(202103050002)
CLC Number:
Cite this article
LU Kai, ZHAO Shijie, WU Huan, et al. Algebraic Method of Coordination Design for Bi-directional Red and Green Waves of Saturated Intersection[J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(9): 1-11.
share this article
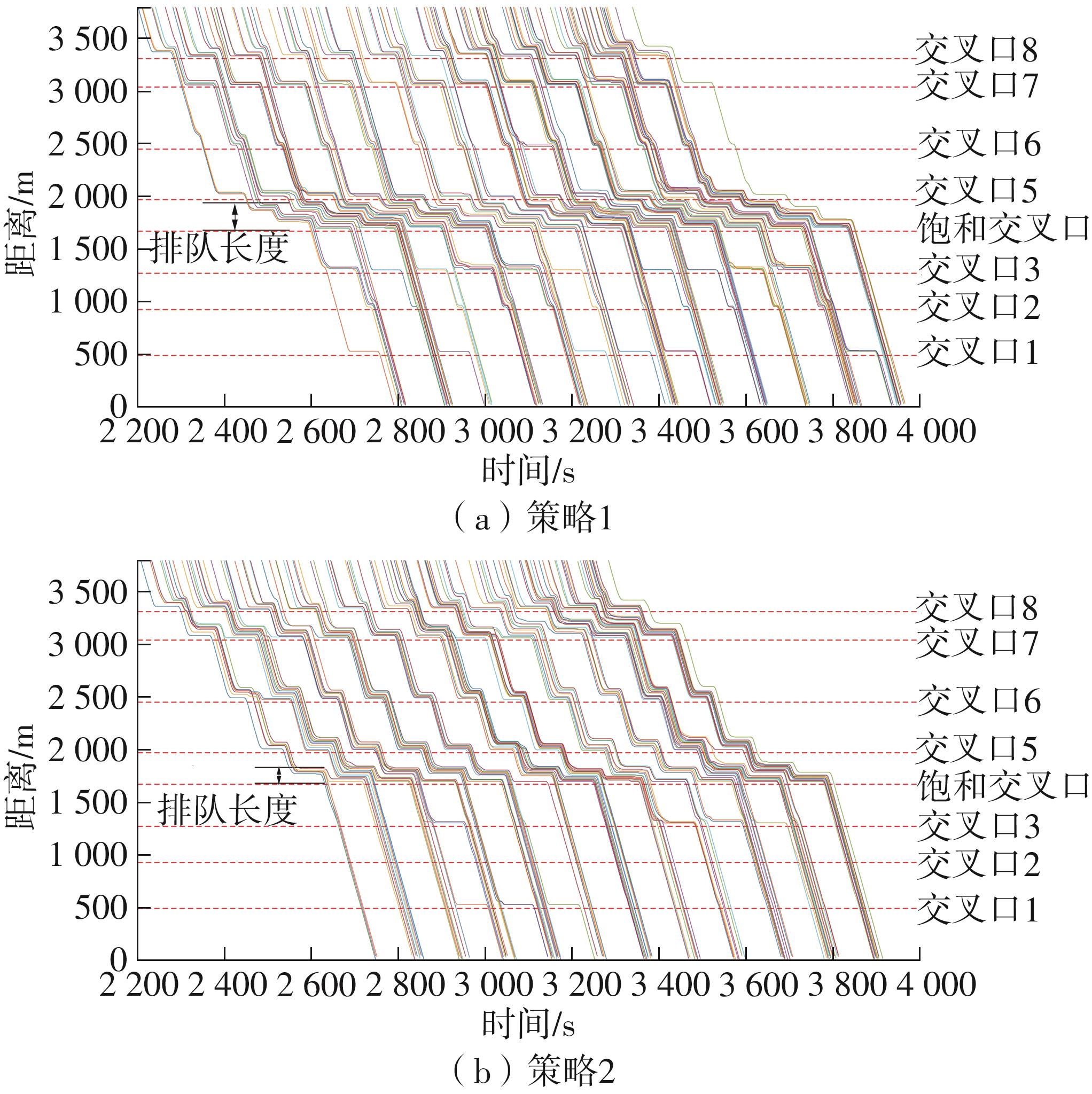
Table 1
Signal timing design results of each single intersection"
交叉口 编号 | 信号周期变化范围/s | 绿信比 | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 南进口 | 北进口 | 东进口 | 西进口 | ||
| 1 | [95,125] | 0.38 | 0.34 | 0.13 | 0.15 |
| 2 | [90,125] | 0.37 | 0.39 | 0.13 | 0.11 |
| 3 | [90,135] | 0.37 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0.13 |
| 4 | [100,130] | 0.26 | 0.27 | 0.24 | 0.23 |
| 5 | [95,130] | 0.36 | 0.39 | 0.12 | 0.13 |
| 6 | [85,120] | 0.35 | 0.38 | 0.13 | 0.14 |
| 7 | [95,125] | 0.38 | 0.36 | 0.14 | 0.12 |
| 8 | [100,135] | 0.36 | 0.35 | 0.15 | 0.14 |
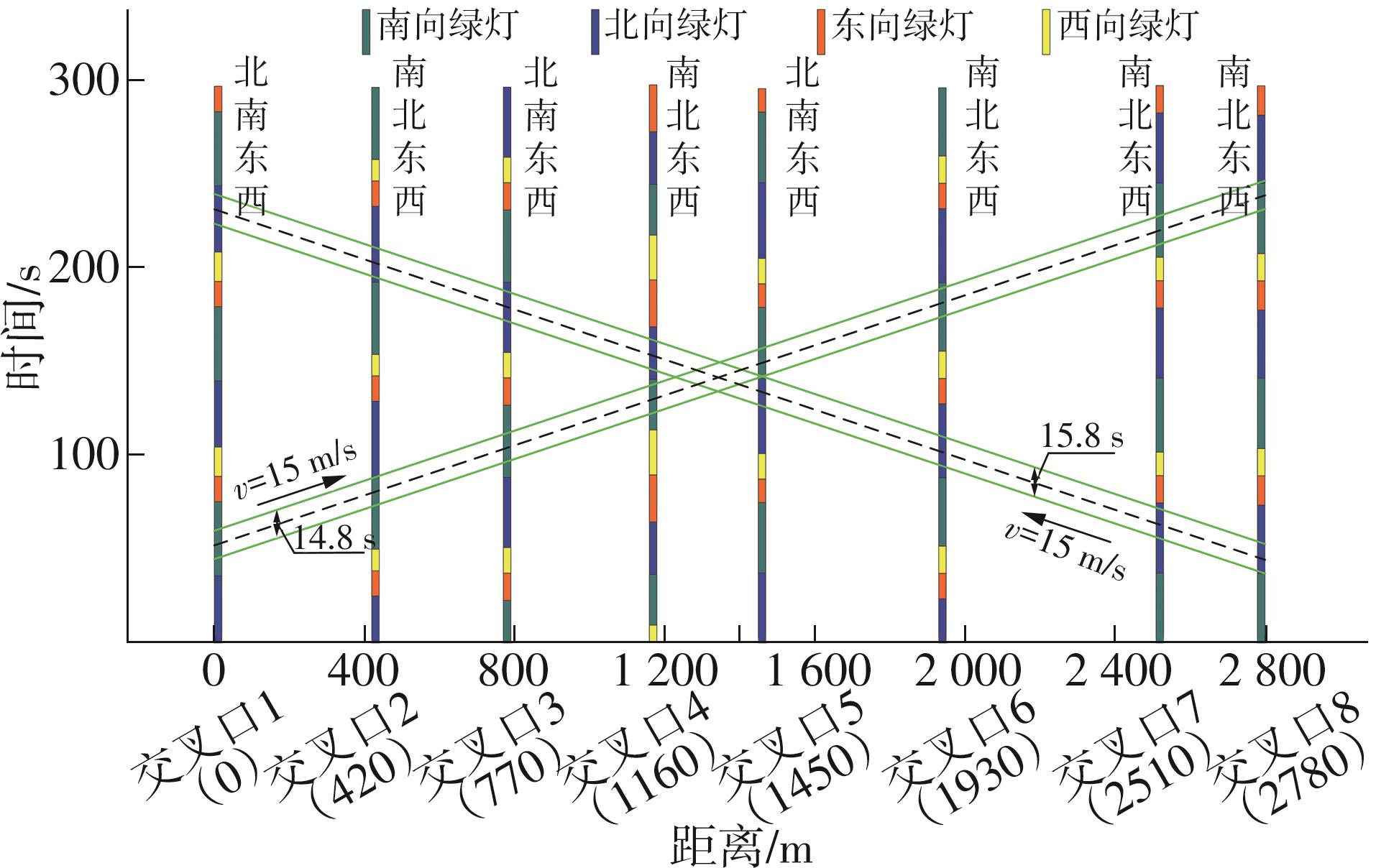
Table 2
Bias-splits and optimal phases at intersection 2 when phase sequence of intersection 1 is south-north-east-west"
| 公共信号周期/s | 理想间距/m | 中心偏移率 | 优选相位 | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 北南东西 | 南东北西 | 南西北东 | 南北东西 | 北南东西 | 南东北西 | 南西北东 | 南北东西 | ||
| 100 | 180.0 | 262.5 | 277.5 | 360.0 | 0.320 | 0.210 | 0.190 | 0.080 | 南北东西 |
| 102 | 183.6 | 267.8 | 283.1 | 367.2 | 0.309 | 0.199 | 0.179 | 0.069 | 南北东西 |
| 104 | 187.2 | 273.0 | 288.6 | 374.4 | 0.298 | 0.188 | 0.168 | 0.058 | 南北东西 |
| 106 | 190.8 | 278.3 | 294.2 | 381.6 | 0.288 | 0.178 | 0.158 | 0.048 | 南北东西 |
| 108 | 194.4 | 283.5 | 299.7 | 388.8 | 0.279 | 0.169 | 0.149 | 0.039 | 南北东西 |
| 110 | 198.0 | 288.8 | 305.3 | 396.0 | 0.269 | 0.159 | 0.139 | 0.029 | 南北东西 |
| 112 | 201.6 | 294.0 | 310.8 | 403.2 | 0.260 | 0.150 | 0.130 | 0.020 | 南北东西 |
| 114 | 205.2 | 299.3 | 316.4 | 410.4 | 0.251 | 0.141 | 0.121 | 0.011 | 南北东西 |
| 116 | 208.8 | 304.5 | 321.9 | 417.6 | 0.243 | 0.133 | 0.113 | 0.003 | 南北东西 |
| 118 | 212.4 | 309.8 | 327.5 | 424.8 | 0.235 | 0.125 | 0.105 | -0.005 | 南北东西 |
| 120 | 216.0 | 315.0 | 333.0 | 432.0 | 0.227 | 0.117 | 0.097 | -0.013 | 南北东西 |
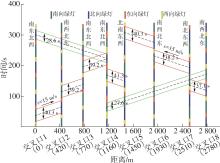
Table 4
Calculation of absolute offset of each intersection under the optimal phase scheme"
| 交叉口 | 信号相位 | 理想间距/m | 中心偏移率 | 区间行驶速度/(m?s-1) | 相位差调整率 | 绝对相位差/s |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 南东北西 | 0 | 0.000 | 15 | 0.000 | -20.1 |
| 2 | 南西北东 | 397.5 | 0.028 | 15 | -0.014 | 58.4 |
| 3 | 南东北西 | 783.1 | -0.016 | 15 | -0.008 | 33.4 |
| 4 | 南东北西 | 1 180.6 | -0.026 | 15 | -0.013 | 13.3 |
| 5 | 北南东西 | 1 482.7 | -0.041 | 15 | -0.006 | 27.3 |
| 6 | 南西北东 | 1 975.6 | -0.057 | 15 | -0.003 | 59.9 |
| 7 | 南北东西 | 2 480.4 | 0.037 | 15 | 0.045 | 96.9 |
| 8 | 南西北东 | 2 778.5 | 0.002 | 15 | 0.027 | 10.0 |
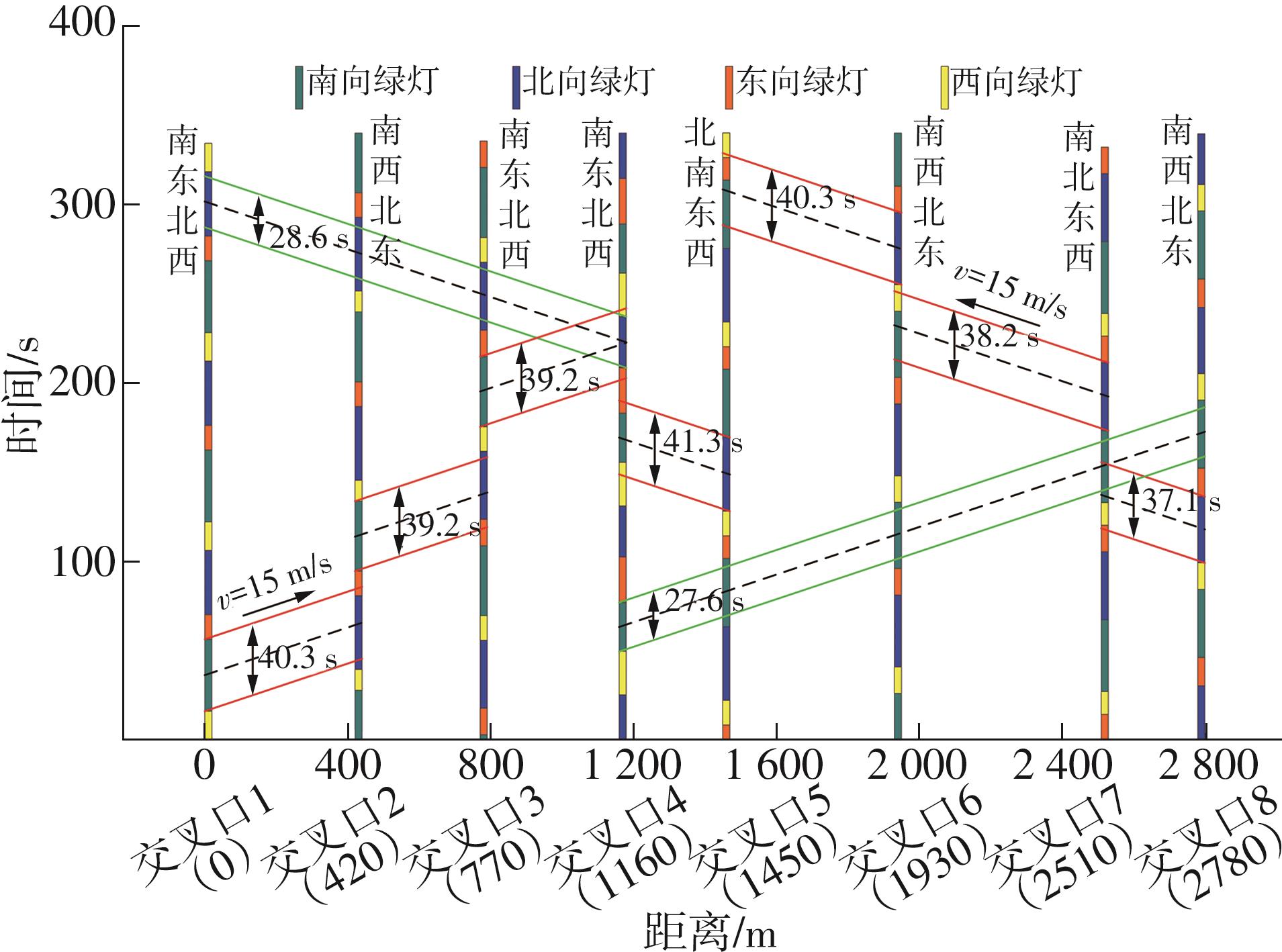
Table 6
Calculation of red wave bandwidth"
| 红波带区段 | 直行相位 绿信比 | 直行相位红灯时间比 | 中心偏移率 | 绿信比 | 红信比 | 红波带宽/% | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 中心线上方 | 中心线下方 | 中心线上方 | 中心线下方 | ||||||
| 上行方向 | 1→2 | 0.380 | 0.630 | 0.028 | 0.287 | 0.343 | 38.0 | ||
| 2→3 | 0.370 | 0.630 | -0.044 | 0.359 | 0.271 | 37.0 | |||
| 3→4 | 0.370 | 0.740 | -0.010 | 0.380 | 0.360 | 37.0 | |||
| 下行方向 | 8→7 | 0.350 | 0.640 | -0.035 | 0.355 | 0.285 | 35.0 | ||
| 7→6 | 0.360 | 0.620 | 0.094 | 0.216 | 0.404 | 36.0 | |||
| 6→5 | 0.380 | 0.610 | -0.016 | 0.321 | 0.289 | 38.0 | |||
| 5→4 | 0.390 | 0.730 | -0.015 | 0.380 | 0.350 | 39.0 | |||
Table 7
Bidirectional green wave coordinated control scheme"
| 交叉口编号 | 相位相序组合 | 中心偏移率 | 绿信比 | 绿信比 | 绝对相位差/s | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 上行中心线上方 | 上行中心线下方 | 下行中心线上方 | 下行中心线下方 | ||||
| 1 | 北南东西 | 0.000 | 0.190 | 0.190 | 0.170 | 0.170 | -19.8 |
| 2 | 南北东西 | 0.278 | 0.046 | 0.324 | 0.334 | 0.056 | 98.3 |
| 3 | 北南东西 | -0.018 | 0.194 | 0.176 | 0.171 | 0.189 | 33.0 |
| 4 | 南北东西 | 0.112 | 0.074 | 0.186 | 0.191 | 0.079 | 58.0 |
| 5 | 北南东西 | -0.156 | 0.258 | 0.102 | 0.117 | 0.273 | 86.1 |
| 6 | 南北东西 | 0.199 | 0.075 | 0.275 | 0.290 | 0.090 | 100.1 |
| 7 | 南北东西 | -0.052 | 0.216 | 0.164 | 0.154 | 0.206 | 46.3 |
| 8 | 南北东西 | 0.279 | 0.040 | 0.320 | 0.315 | 0.035 | 48.1 |
| 1 | 中国公路学会《交通工程手册》编委会 .交通工程手册[M].北京:人民交通出版社,1988. |
| 2 | 姬利娜,宋清华 .非对称放行方式下的干道双向绿波协调控制[J].公路交通科技,2011,28(10):96-101. |
| JI Li-na, SONG Qing-hua .Bidirectional green wave coordinate control for arterial road under asymmetric signal mode[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2011,28(10):96-101. | |
| 3 | WANG J X, ZHAI R P, LIU D,et al .An algorithm for maximum bi-direction green wave band based on boundary conditions[C]∥CICTP 2014:Safe,Smart,and Sustainable Multimodal Transportation Systems.Changsha:ASCE,2014:1840-1848. |
| 4 | GUO L, YANG R, ZHANG M .Arterial traffic two-direction green wave coordination control based on MATLAB graphical method[C]∥2015 2nd International Conference on Information Science and Control Engineering.Shanghai:IEEE,2015:632-635. |
| 5 | 卢凯,徐建闽,叶瑞敏 .经典干道协调控制信号配时数解算法的改进[J].公路交通科技,2009,26(1):120-124,129. |
| LU Kai, XU Jian-min, YE Rui-min. Improvement of classical algebraic method of signal timing for arterial road coordinate control[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2009,26(1):120-124,129. | |
| 6 | 王殿海,杨希锐,宋现敏 .交通信号干线协调控制经典数值计算法的改进[J].吉林大学学报(工学版),2011,41(1):29-34. |
| WANG Dian-hai, YANG Xi-rui, SONG Xian-min. Improvement of classical numerical method for arterial road signal coordinate control[J].Journal of Jilin University(Engineering and Technology Edition),2011,41(1):29-34. | |
| 7 | 卢凯,徐建闽,李轶舜 .进口单独放行方式下的干道双向绿波协调控制数解算法[J].中国公路学报,2010,23(3):95-101. |
| LU Kai, XU Jian-min, LI Yi-shun .Algebraic method of arterial road coordinate control for bidirectional green wave under signal design mode of one-phase-one-approach[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2010,23(3):95-101. | |
| 8 | LITTLE J D C .The synchronization of traffic signals by mixed-integer linear programming[J].Operations Research,1966,14(4):568-594. |
| 9 | LITTLE J D C, KELSON M D, GARTNER N H .MAXBAND:a versatile program for setting signals on arteries and triangular networks[J].Transportation Research Record,1981,795:40-46. |
| 10 | GARTNER N H, ASSMANN S F, LASAGA F,et al .A multi-band approach to arterial traffic signal optimization[J].Transportation Research Part B,1991,25(1):55-74. |
| 11 | GARTNER N H, STAMATIADIS C .Arterial-based control of traffic flow in urban grid networks[J].Mathematical and Computer Modelling,2002,35(5):657-671. |
| 12 | 李轶舜,徐建闽,王琳虹 .过饱和交通网络的多层边界主动控制方法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2012,40(7):27-32. |
| LI Yi-shun, XU Jian-min, WANG Lin-hong .Active multi-layer perimeter control strategy of oversaturated traffic networks[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2012,40(7):27-32. | |
| 13 | 张勇,白玉,杨晓光 .城市道路交通网络死锁控制策略[J].中国公路学报,2010,23(6):96-102. |
| ZHANG Yong, BAI Yu, YANG Xiao-guang .Strategy of traffic gridlock control for urban road network[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2010,23(6):96-102. | |
| 14 | 李瑞敏,唐瑾 .过饱和交叉口交通信号控制动态规划优化模型[J].交通运输工程学报,2015,15(6):101-109. |
| LI Rui-min, TANG Jin .Traffic signal control optimization model of over-saturated intersection based on dynamic programming[J].Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2015,15(6):101-109. | |
| 15 | LIU Y, CHANG G L .An arterial signal optimization model for intersections experiencing queue spillback and lane blockage[J].Transportation Research Part C,2010,19(1):130-144. |
| 16 | PUTHA R, QUADRIFOGLIO L, ZECHMAN E .Comparing ant colony optimization and genetic algorithm approaches for solving traffic signal coordination under oversaturation conditions[J].Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering,2012,27(1):14-28. |
| 17 | ZHENG S J, XU J M .Research on red wave and green wave coordinated control model in arterial road for different traffic demands[C]∥2011 International Conference on Multimedia Technology.Hangzhou:IEEE,2011:1661-1664. |
| 18 | 李华,徐建闽 .干道交通瓶颈交叉口的红波双向协调控制模型[J].交通信息与安全,2014,32(6):72-76,119. |
| LI Hua, XU Jian-min .A red wave two way coordination control model for bottleneck intersections of arterial roads[J].Journal of Transport Information and Safety,2014,32(6):72-76,119. |
| [1] | WANG Linhong, LI Hongtao, LI Ruonan. Design of Speed Limit at Expressway in Rainy Day Considering Drivers’ Visual Search Ability [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 20-29. |
| [2] | MA Shuhong, YANG Lei, CHEN Xifang. Resilience Evolution of Multi-mode Transportation Network in Urban Agglomeration Based on Risk Diffusion [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(6): 42-51. |
| [3] | HU Yucong, WEI Hu, ZENG Qiang . Analysis of Freeway Crash Severity Based on Spatial Generalized Ordered Probit Model [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2023, 51(1): 114-122. |
| [4] | LU Kai, WU Wei, DENG Xingdong, et al. Composition and Optimization Method of Coordination Path Set in Control Subarea [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2022, 50(2): 1-14. |
| [5] | MA Xinlu, FAN Bo, CHEN Shiao, et al. Evaluation and Analysis Model for Freeways Crash Risk Based on Real-Time Traffic Flow [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition), 2021, 49(8): 19-25,34. |
| [6] | CHANG Xin, LI Haijian, RONG Jian, et al. Effect of the Tunnel Warning System on Traffic Capacity Based on Aggregated Spatiotemporal Characteristics of Vehicles [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(9): 107-115,123. |
| [7] | HU Baoyu PANG Yu PEI Yulong . Multi-type Bus Timetable Optimization Considering Unbalanced Passenger Flow in Time and Space [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2020, 48(11): 38-48. |
| [8] | YAN Hai LIU Runkun. Short-Turn Vehicles Departure Strategy Considering Reliability of Bus Operation [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2019, 47(11): 25-32,43. |
| [9] | ZHU Jia ZUO Jian LI Yinhong. Commutation Failure Suppression Strategy Based on Multi-Angle Prediction in Hybrid Dual-Infeed HVDC System [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2018, 46(10): 24-31. |
| [10] | SHANG Qiang LIN Ci-yun YANG Zhao-sheng BING Qi-chun TIAN Xiu-juan WANG Shu-xing. Traffic State Identification for Urban Expressway Based on Spectral Clustering and RS-KNN [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2017, 45(6): 52-58. |
| [11] | ZHOU Xi-yang YANG Zhao-sheng ZHANG Wei BING Qi-chun SHANG Qiang. Optimal Route Planning Algorithm Considering Movement Type at Signal Intersections [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(4): 101-108. |
| [12] | YE Jie HUANG Xiang-dong ZHAO Ke-gang HE Xiao-peng LIU Yan-wei . Control of Positive-Torque Downshifting Process of Automatic Transmission with State Variable Constraints [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2016, 44(3): 60-67. |
| [13] | Deng Ya-juan Wang Huan Du Ruo Hu Shao-rong. Division of Highway Network Hierarchy Based on Weighted Complex Network [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(4): 33-40. |
| [14] | . Estimationof Expressway Section Travel Time Based on Correction Algorithm [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(4): 20-27. |
| [15] | Lin Pei-qun Gu Yu-mu Zhuo Fu-qing Ran Bin Xu Jian-min . Delay Models for Two Kinds of Left-Turn Traffic Flow Organizations at Intersection [J]. Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 43(12): 119-126. |
| Viewed | ||||||
|
Full text |
|
|||||
|
Abstract |
|
|||||