

收稿日期: 2023-06-20
网络出版日期: 2023-12-27
基金资助
广东省重点领域研发计划项目(2019B090915002);广州市科技计划项目(202206030008)
Hand Pose Estimation Based on Prior Knowledge and Mesh Supervision
Received date: 2023-06-20
Online published: 2023-12-27
Supported by
the Key-Area Research and Development Program of Guangdong Province(2019B090915002)
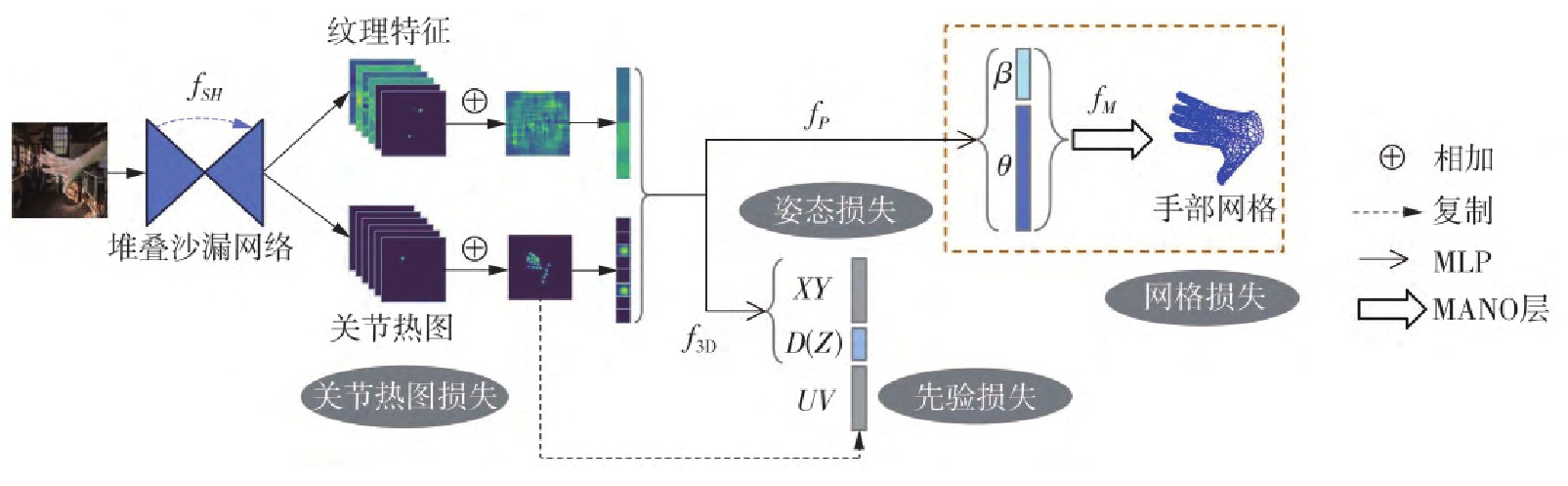
手部自遮挡和深度信息缺失使得由单目RGB图像进行三维手部姿态估计存在关节相对深度估计不够准确、生成的姿态违背手部生物力学约束等问题。为解决此问题,文中结合手部结构中蕴含的先验知识以及手部网格信息,提出一种基于先验知识和网格监督的深度神经网络。手部骨架的铰链式结构意味着关节三维位置在二维图像平面和深度方向的投影之间存在着特定关系,但个体之间的手部结构差异导致难以对其进行直观的形式化描述,为此文中提出通过学习来对其进行拟合。同一手指的关节位置和骨骼长度、同一手指的不同分段以及不同手指的弯曲方向之间也存在特定关系,文中将其设计为损失函数,用于监督网络训练。所提出的神经网络在估计手部姿态的同时并行生成手部网格,通过网格标注监督网络训练,优化姿态估计,且不增加网络复杂度。使用混合数据集对神经网络进行了训练,以进一步提高其泛化能力。实验结果表明,所提方法在多个数据集的内部交叉验证精度、跨数据集验证精度、模型的时间和空间复杂度等方面都优于其他方法,手部结构先验知识和网格监督在提升姿态估计精度的同时保持了神经网络结构的紧凑性。
孙迪钢 , 张平 . 基于先验知识和网格监督的手部姿态估计[J]. 华南理工大学学报(自然科学版), 2024 , 52(6) : 138 -147 . DOI: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.230420
Due to the hand self-occlusion and the lack of depth information, the estimation of 3D hand pose based on monocular RGB images is not accurate enough in estimating relative depth of joints, and the generated hand pose violates the biomechanical constraints of the hand. To solve this problem, by combining the prior knowledge contained in the hand structure and the hand grid information, a deep neural network based on prior knowledge and mesh supervision is proposed. The articulated structure of the hand skeleton implies that there exists a specific relationship between the projections of the 3D hand pose in the 2D image plane and the depth direction, but the differences in hand structure between individuals make it difficult to describe this relationship intuitively and formally. Therefore, this paper proposes to fit it through learning. Specific relationships also exist between joint positions and bone lengths of the same finger, bending directions of different segments of the same finger, and bending directions of different fingers, which are designed as loss functions to supervise network training. The proposed neural network generates hand meshes in parallel with hand poses, supervises the network training through mesh annotation, and optimizes the pose estimation without increasing the network complexity. Furthermore, the neural network is trained using a mixed dataset to further improve its generalization capability. Experimental results show that the proposed method outperforms other methods in terms of internal cross-validation accuracy in multiple datasets, cross-dataset validation accuracy, and time and space complexity of the model. As a result, the prior knowledge of hand skeleton and the mesh supervision improve the accuracy of pose estimation while keeping the neural network compact.

Key words: hand pose estimation; hand shape estimation; prior knowledge; hand mesh
| 1 | ZIMMERMANN C, BROX T .Learning to estimate 3D hand pose from single RGB images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:4903-4911. |
| 2 | SPURR A, SONG J, PARK S,et al .Cross-modal deep variational hand pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:89-98. |
| 3 | IQBAL U, MOLCHANOV P, GALL T B J,et al .Hand pose estimation via latent 2.5D heatmap regression[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich:Springer,2018:118-134. |
| 4 | MUELLER F, BERNARD F, SOTNYCHENKO O,et al .GANerated hands for real-time 3D hand tracking from monocular RGB[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:49-59. |
| 5 | SIMON T,JOO H, MATTHEWS I,et al .Hand keypoint detection in single images using multiview bootstrapping[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Hawaii:IEEE,2017:1145-1153. |
| 6 | SRIDHAR S, OULASVIRTA A, THEOBALT C .Interactive markerless articulated hand motion tracking using RGB and depth data[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Portland:IEEE,2013:2456-2463. |
| 7 | ROMERO J, TZIONAS D, BLACK M J .Embodied hands:modeling and capturing hands and bodies together[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics,2017,36(6):1-17. |
| 8 | BOUKHAYMA A,BEM R, TORR P H S .3D hand shape and pose from images in the wild[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:10843-10852. |
| 9 | ZHANG X, HUANG H, TAN J,et al .Hand image understanding via deep multi-task learning[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:11281-11292. |
| 10 | CHEN P, CHEN Y, YANG D,et al .I2UV-HandNet:Image-to-UV prediction network for accurate and high-fidelity 3D hand mesh modeling[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:12929-12938. |
| 11 | GE L, REN Z, LI Y,et al .3D hand shape and pose estimation from a single RGB image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:10833-10842. |
| 12 | HASSON Y, TEKIN B, BOGO F,et al .Leveraging photometric consistency over time for sparsely supervised hand-object reconstruction[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Seattle:IEEE,2020:571-580. |
| 13 | KWON T, TEKIN B, STüHMER J,et al .H2O:two hands manipulating objects for first person interaction recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:10138-10148. |
| 14 | ZHANG X, LI Q, MO H,et al .End-to-end hand mesh recovery from a monocular RGB image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:2354-2364. |
| 15 | WAN C, PROBST T, GOOL L V,et al .Self-supervised 3D hand pose estimation through training by fitting[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:10853-10862. |
| 16 | SPURR A, IQBAL U, MOLCHANOV P,et al .Weakly supervised 3D hand pose estimation via biomechanical constraints[C]∥Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:211-228. |
| 17 | ZHANG J, JIAO J, CHEN M,et al .A hand pose tracking benchmark from stereo matching[C]∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Ima-ge Processing.Beijing:IEEE,2017:982-986. |
| 18 | ZIMMERMANN C, CEYLAN D, YANG J,et al .Freihand:a dataset for markerless capture of hand pose and shape from single RGB images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Seoul:IEEE,2019:813-822. |
| 19 | HASSON Y, VAROL G, TZIONAS D,et al .Learning joint reconstruction of hands and manipulated objects[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:11807-11816. |
| 20 | NEWELL A, YANG K, DENG J .Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam:Springer,2016:483-499. |
| 21 | KARRAS T, LAINE S, AILA T .A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:4401-4410. |
| 22 | WU Z, CHE W .3D human pose lifting:from joint position to joint rotation[C]∥Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Image and Graphics Technologies and Applications.Singapore:Springer,2019:228-237. |
| 23 | GOYAL P, DOLLáR P, GIRSHICK R,et al .Accurate,large minibatch SGD:training ImageNet in 1 hour[EB/OL].(2017-06-08)[2023-05-20]. . |
| 24 | MOON G, YU S I, WEN H,et al .InterHand2.6M:a dataset and baseline for 3d interacting hand pose estimation from a single RGB image[C]∥Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:548-564. |
| 25 | CAI Y, GE L, CAI J,et al .3D hand pose estimation using synthetic data and weakly labeled RGB images[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2020,43(11):3739-3753. |
/
| 〈 |
|
〉 |