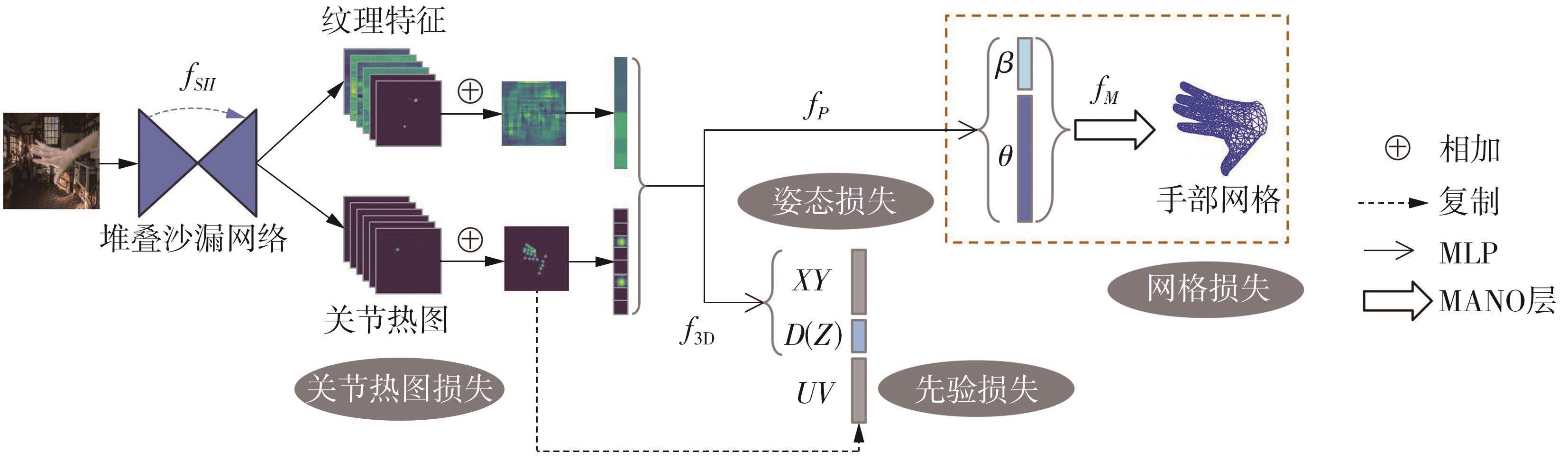
| 1 |
ZIMMERMANN C, BROX T .Learning to estimate 3D hand pose from single RGB images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Venice:IEEE,2017:4903-4911.
|
| 2 |
SPURR A, SONG J, PARK S,et al .Cross-modal deep variational hand pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:89-98.
|
| 3 |
IQBAL U, MOLCHANOV P, GALL T B J,et al .Hand pose estimation via latent 2.5D heatmap regression[C]∥Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision.Munich:Springer,2018:118-134.
|
| 4 |
MUELLER F, BERNARD F, SOTNYCHENKO O,et al .GANerated hands for real-time 3D hand tracking from monocular RGB[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Salt Lake City:IEEE,2018:49-59.
|
| 5 |
SIMON T,JOO H, MATTHEWS I,et al .Hand keypoint detection in single images using multiview bootstrapping[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Hawaii:IEEE,2017:1145-1153.
|
| 6 |
SRIDHAR S, OULASVIRTA A, THEOBALT C .Interactive markerless articulated hand motion tracking using RGB and depth data[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision.Portland:IEEE,2013:2456-2463.
|
| 7 |
ROMERO J, TZIONAS D, BLACK M J .Embodied hands:modeling and capturing hands and bodies together[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics,2017,36(6):1-17.
|
| 8 |
BOUKHAYMA A,BEM R, TORR P H S .3D hand shape and pose from images in the wild[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:10843-10852.
|
| 9 |
ZHANG X, HUANG H, TAN J,et al .Hand image understanding via deep multi-task learning[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:11281-11292.
|
| 10 |
CHEN P, CHEN Y, YANG D,et al .I2UV-HandNet:Image-to-UV prediction network for accurate and high-fidelity 3D hand mesh modeling[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:12929-12938.
|
| 11 |
GE L, REN Z, LI Y,et al .3D hand shape and pose estimation from a single RGB image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:10833-10842.
|
| 12 |
HASSON Y, TEKIN B, BOGO F,et al .Leveraging photometric consistency over time for sparsely supervised hand-object reconstruction[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Seattle:IEEE,2020:571-580.
|
| 13 |
KWON T, TEKIN B, STÜHMER J,et al .H2O:two hands manipulating objects for first person interaction recognition[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Montreal:IEEE,2021:10138-10148.
|
| 14 |
ZHANG X, LI Q, MO H,et al .End-to-end hand mesh recovery from a monocular RGB image[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:2354-2364.
|
| 15 |
WAN C, PROBST T, GOOL L V,et al .Self-supervised 3D hand pose estimation through training by fitting[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:10853-10862.
|
| 16 |
SPURR A, IQBAL U, MOLCHANOV P,et al .Weakly supervised 3D hand pose estimation via biomechanical constraints[C]∥Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:211-228.
|
| 17 |
ZHANG J, JIAO J, CHEN M,et al .A hand pose tracking benchmark from stereo matching[C]∥Proceedings of 2017 IEEE International Conference on Ima-ge Processing.Beijing:IEEE,2017:982-986.
|
| 18 |
ZIMMERMANN C, CEYLAN D, YANG J,et al .Freihand:a dataset for markerless capture of hand pose and shape from single RGB images[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision.Seoul:IEEE,2019:813-822.
|
| 19 |
HASSON Y, VAROL G, TZIONAS D,et al .Learning joint reconstruction of hands and manipulated objects[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:11807-11816.
|
| 20 |
NEWELL A, YANG K, DENG J .Stacked hourglass networks for human pose estimation[C]∥Proceedings of the 14th European Conference on Computer Vision.Amsterdam:Springer,2016:483-499.
|
| 21 |
KARRAS T, LAINE S, AILA T .A style-based generator architecture for generative adversarial networks[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition.Long Beach:IEEE,2019:4401-4410.
|
| 22 |
WU Z, CHE W .3D human pose lifting:from joint position to joint rotation[C]∥Proceedings of the 14th Conference on Image and Graphics Technologies and Applications.Singapore:Springer,2019:228-237.
|
| 23 |
GOYAL P, DOLLÁR P, GIRSHICK R,et al .Accurate,large minibatch SGD:training ImageNet in 1 hour[EB/OL].(2017-06-08)[2023-05-20]. .
|
| 24 |
MOON G, YU S I, WEN H,et al .InterHand2.6M:a dataset and baseline for 3d interacting hand pose estimation from a single RGB image[C]∥Proceedings of the 16th European Conference on Computer Vision.Glasgow:Springer,2020:548-564.
|
| 25 |
CAI Y, GE L, CAI J,et al .3D hand pose estimation using synthetic data and weakly labeled RGB images[J].IEEE Transactions on Pattern Analysis and Machine Intelligence,2020,43(11):3739-3753.
|