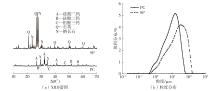
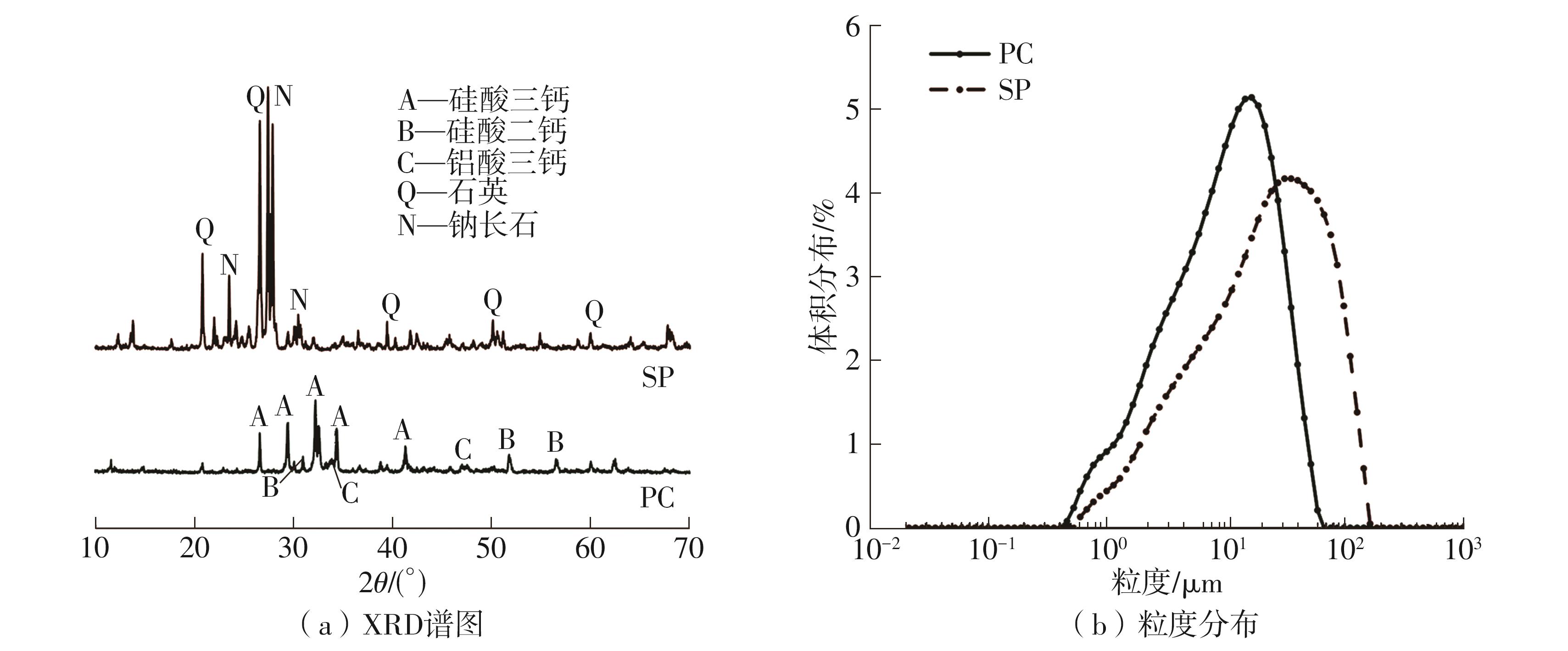
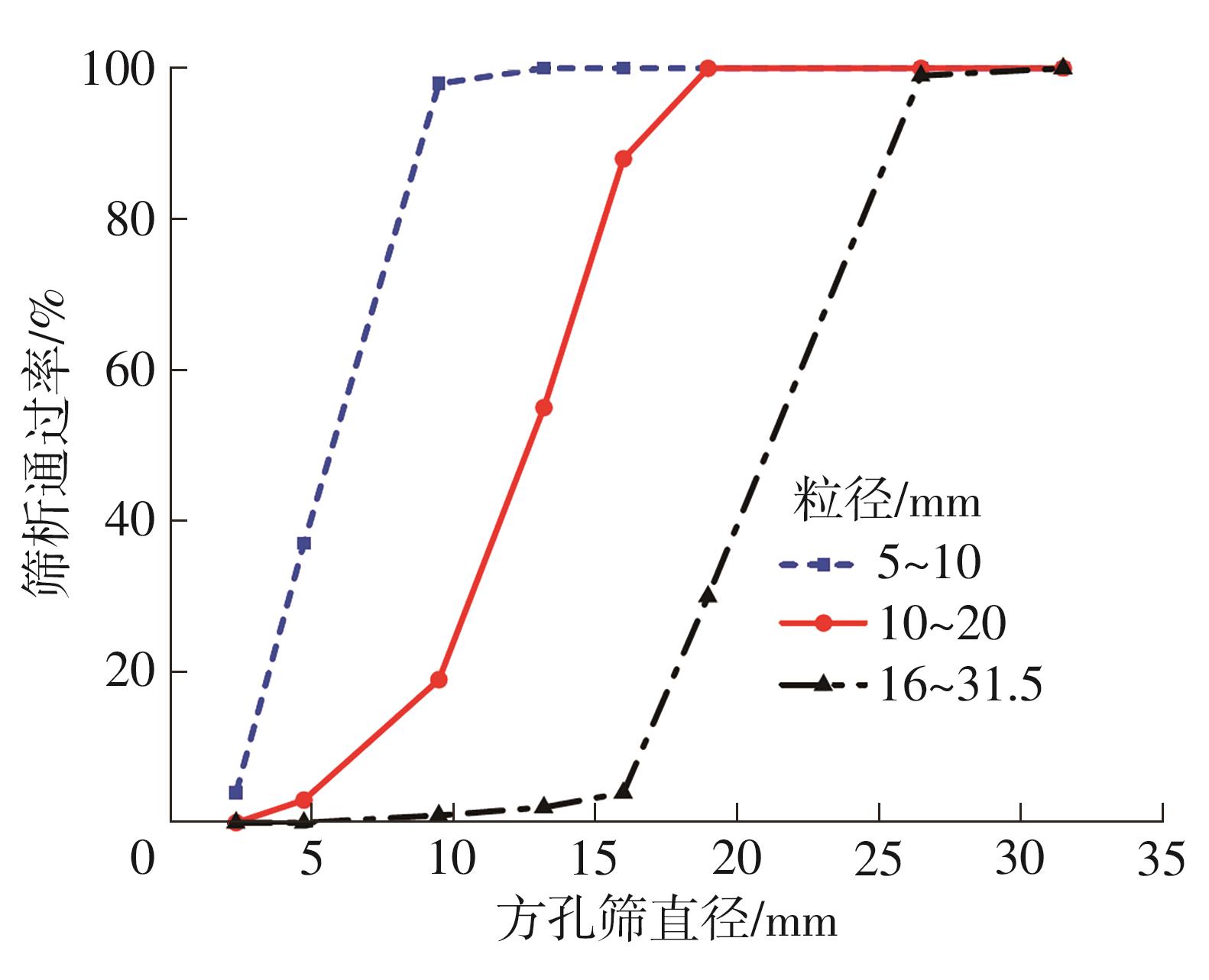
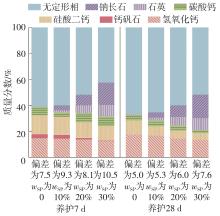
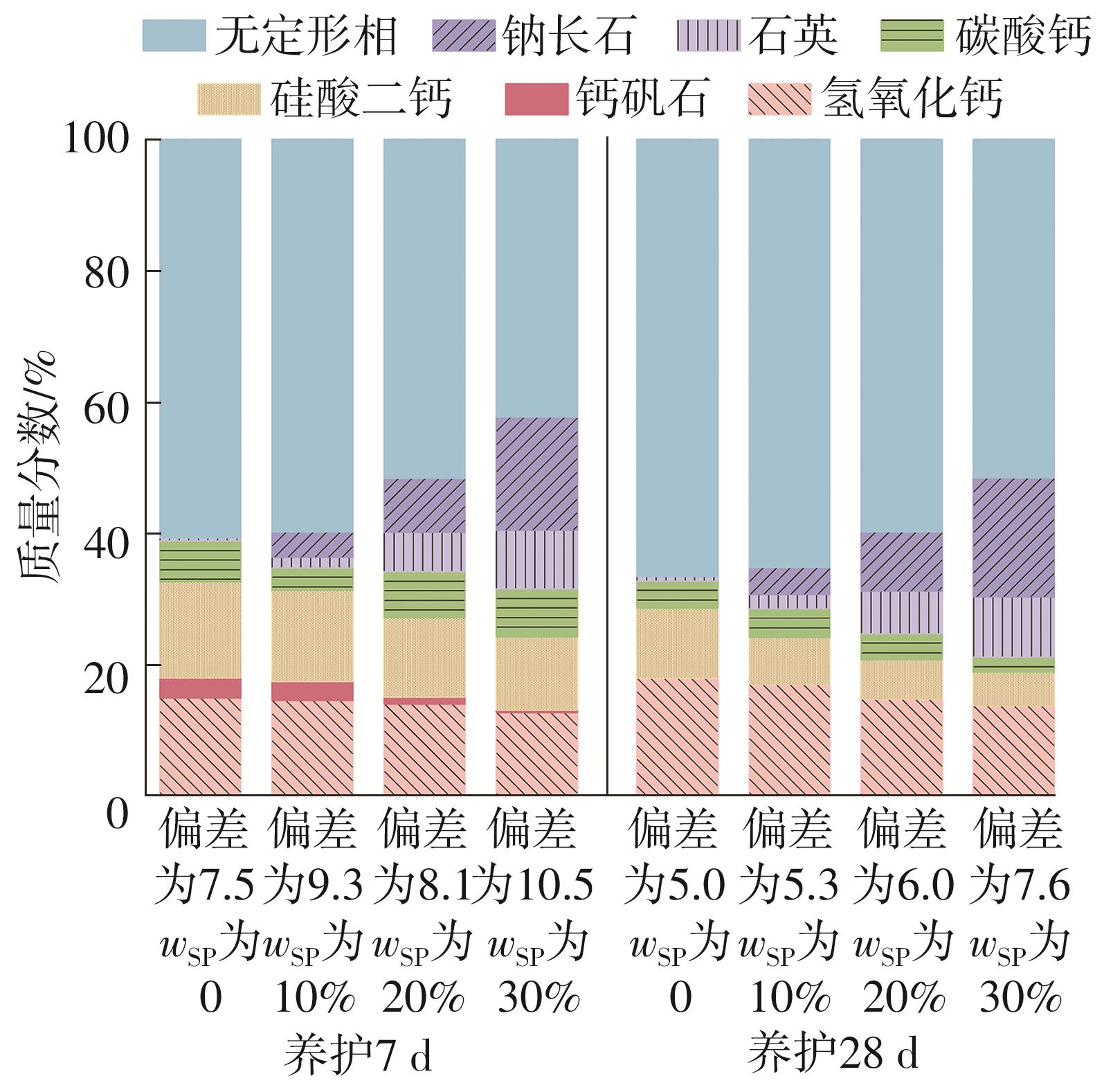
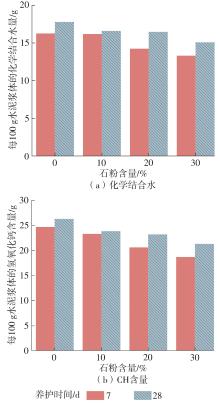
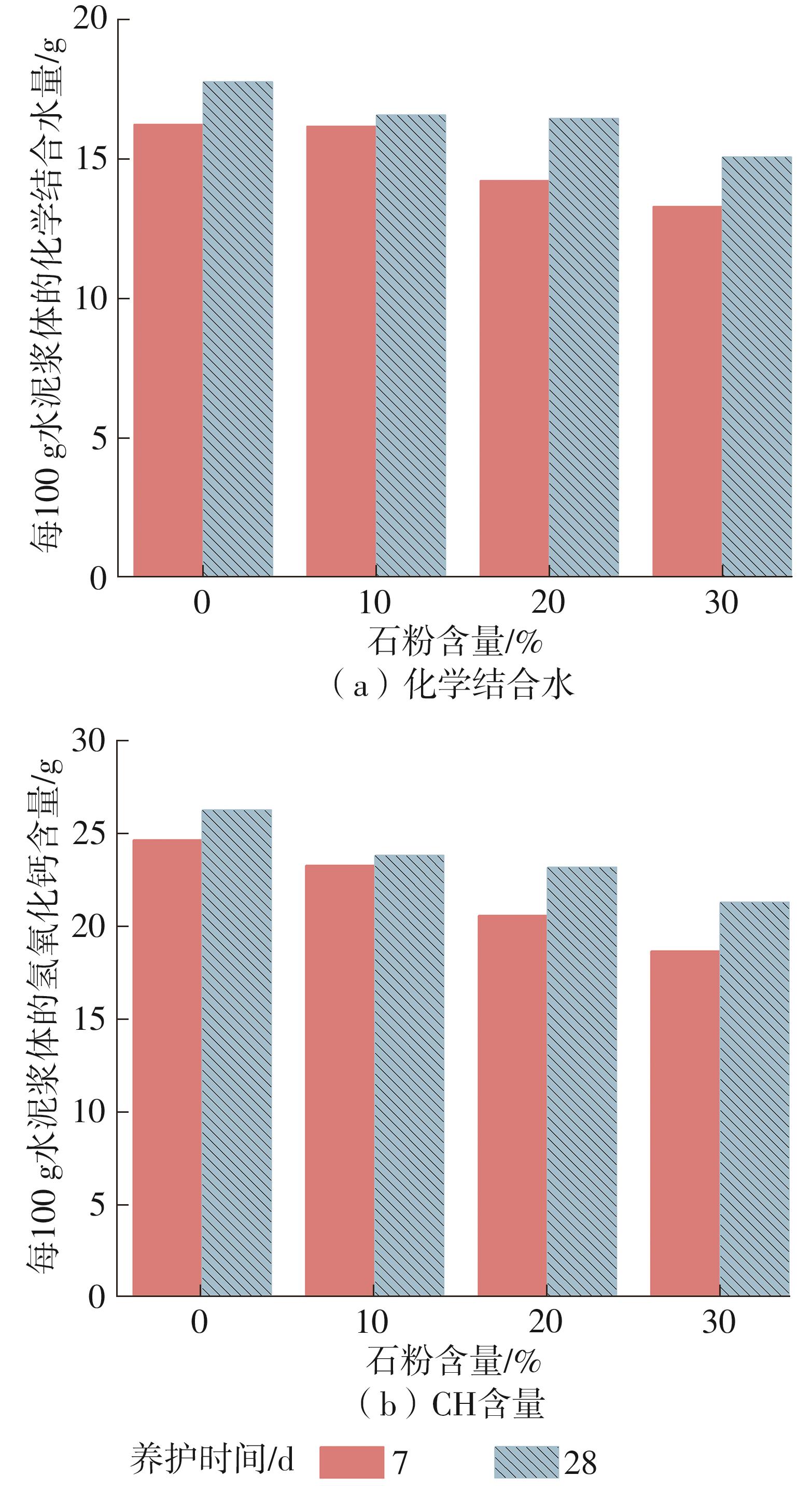
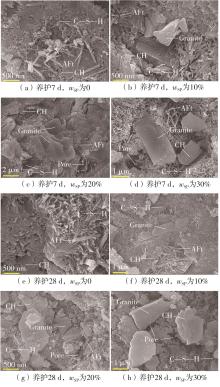
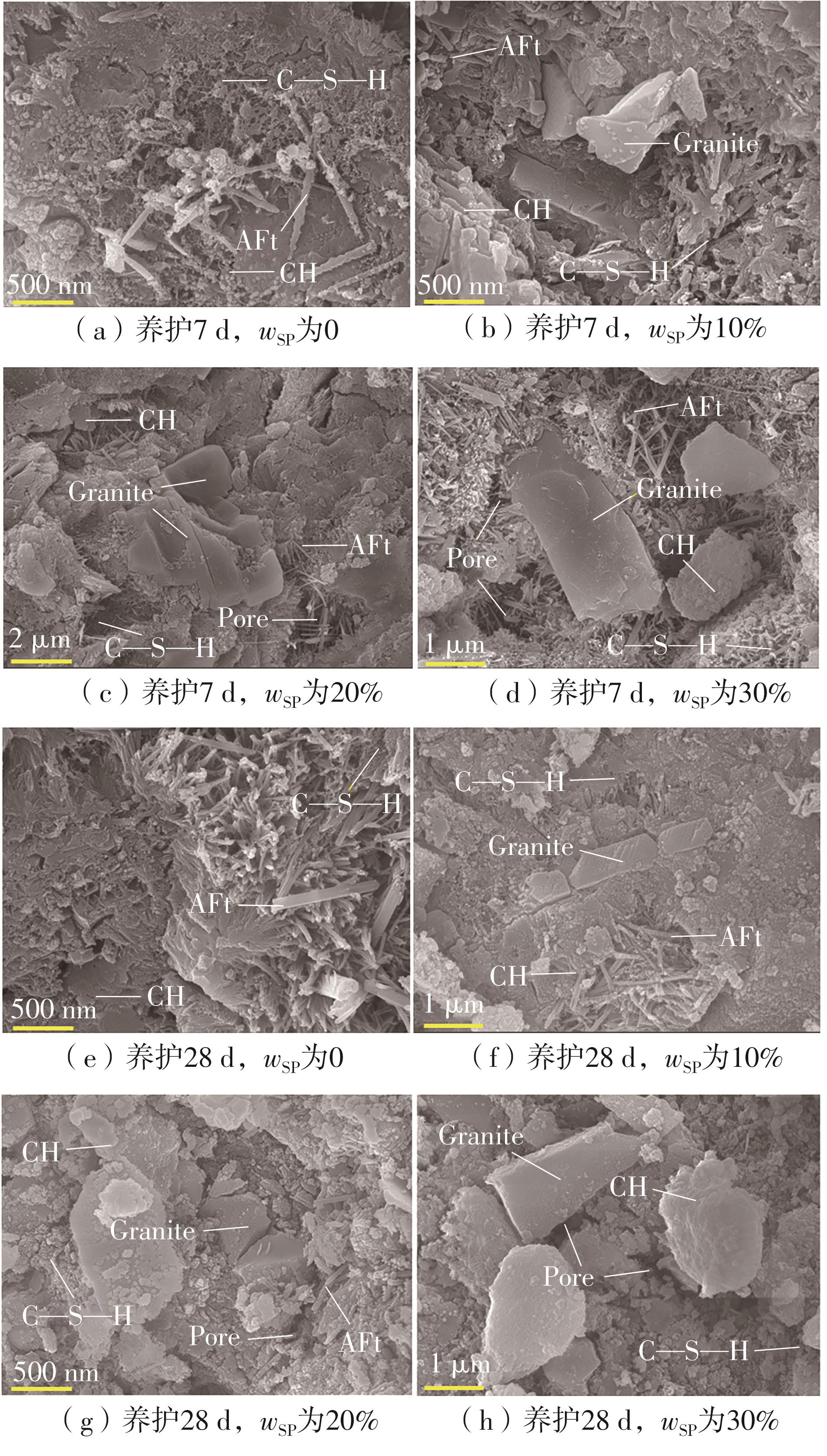
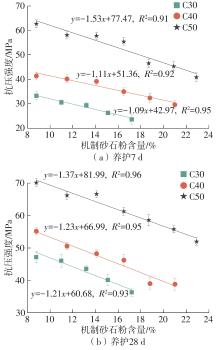
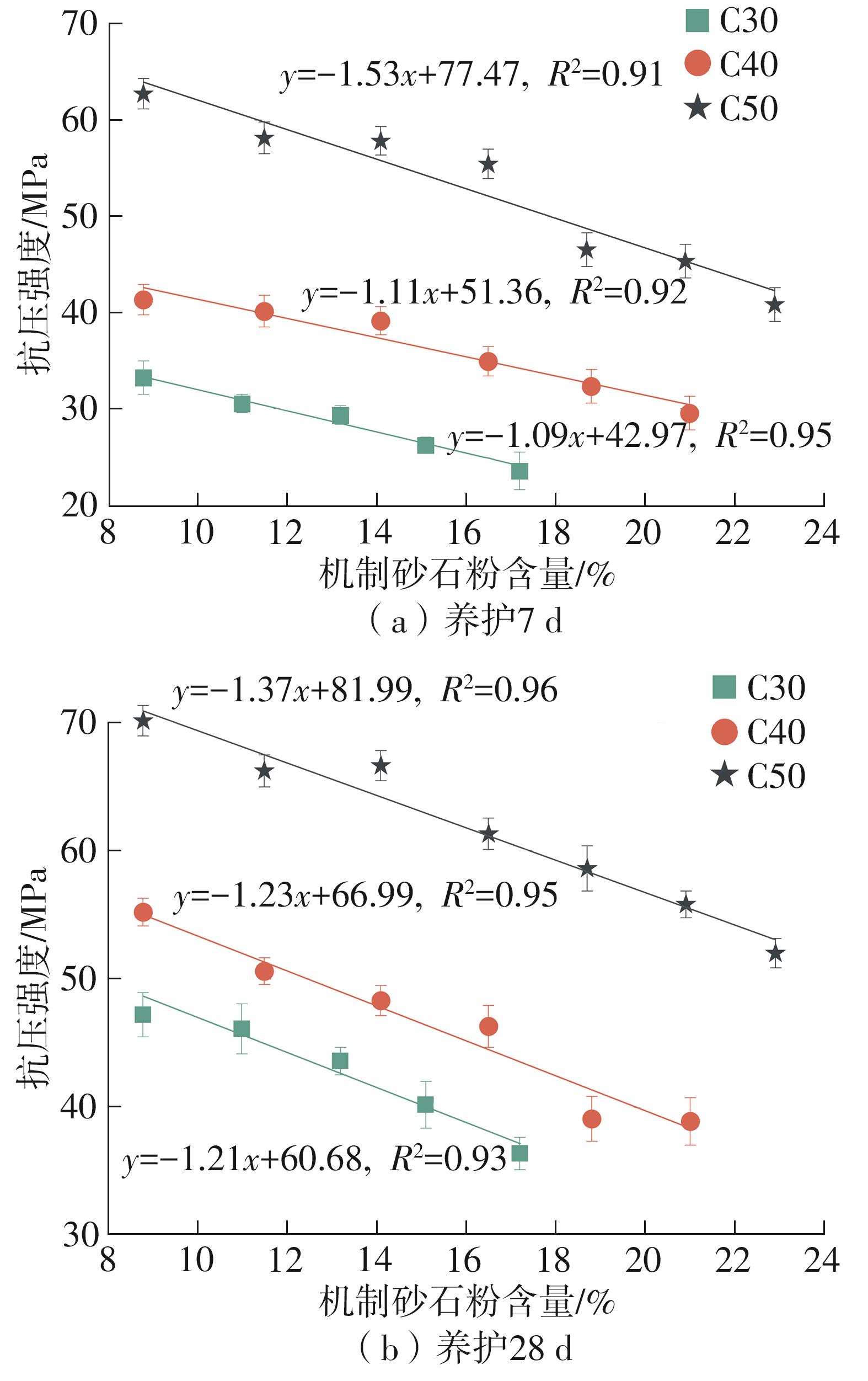
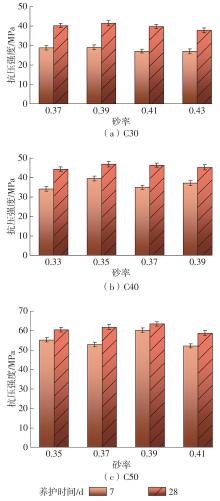
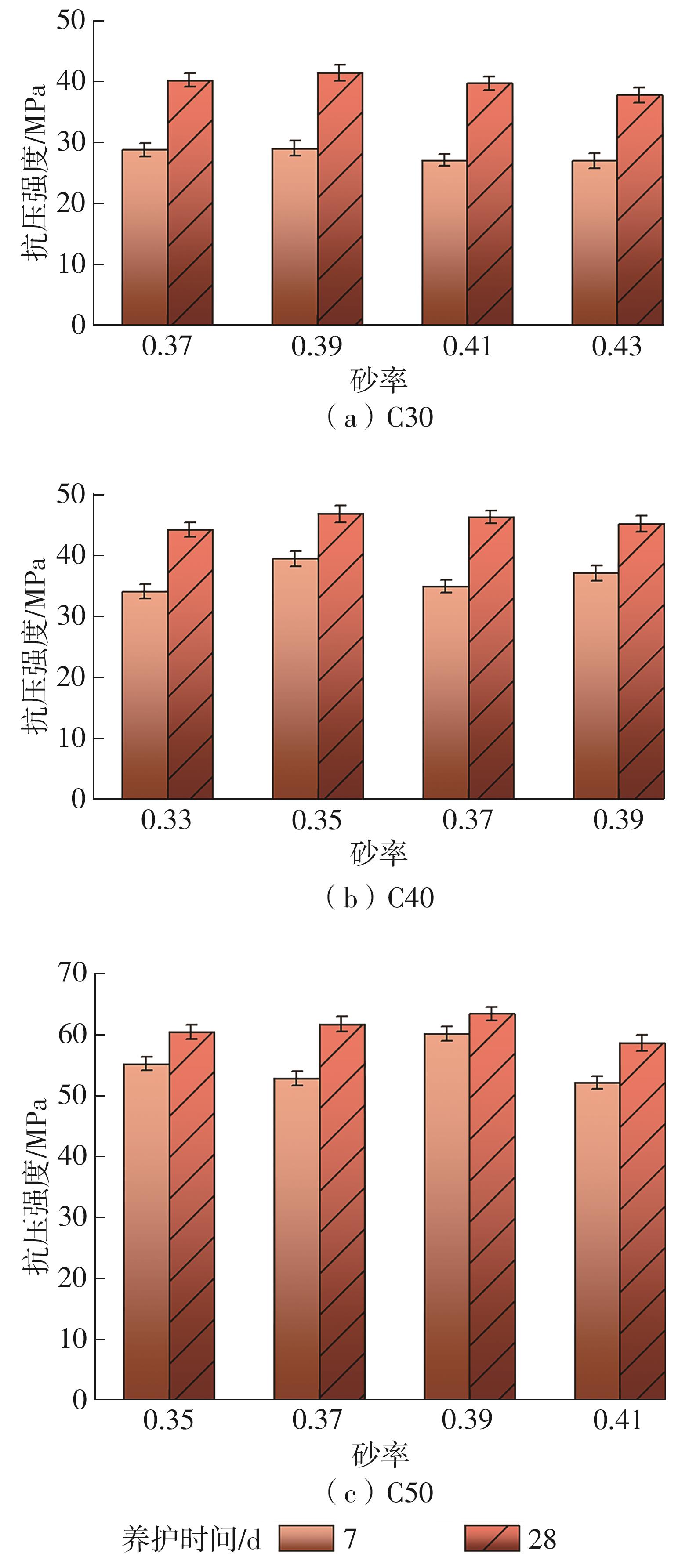
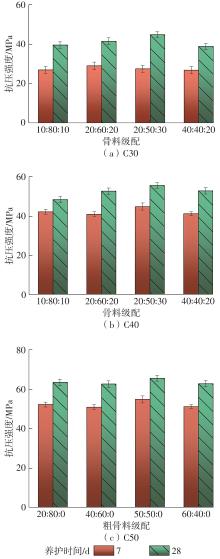
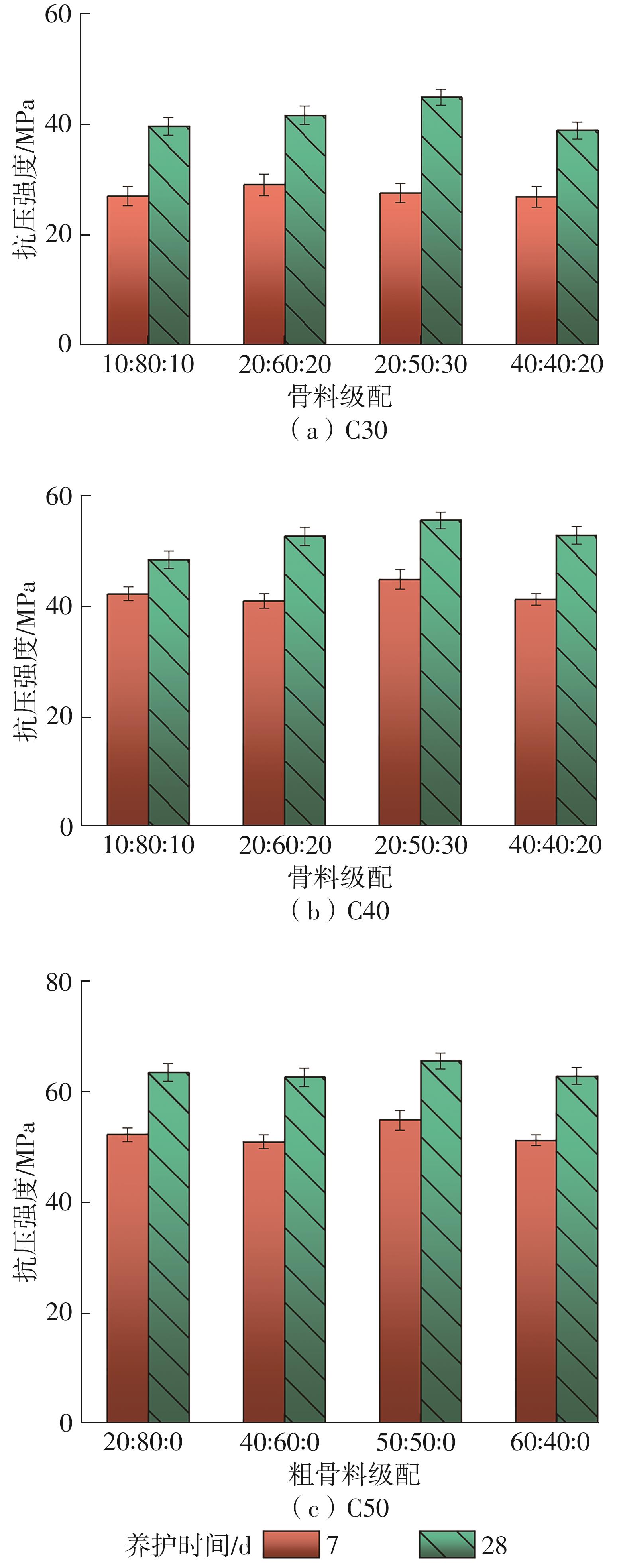
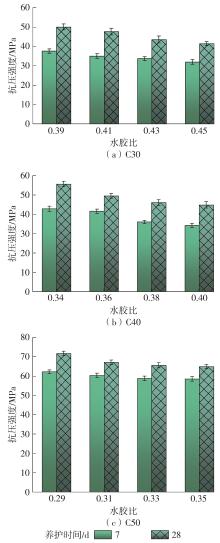
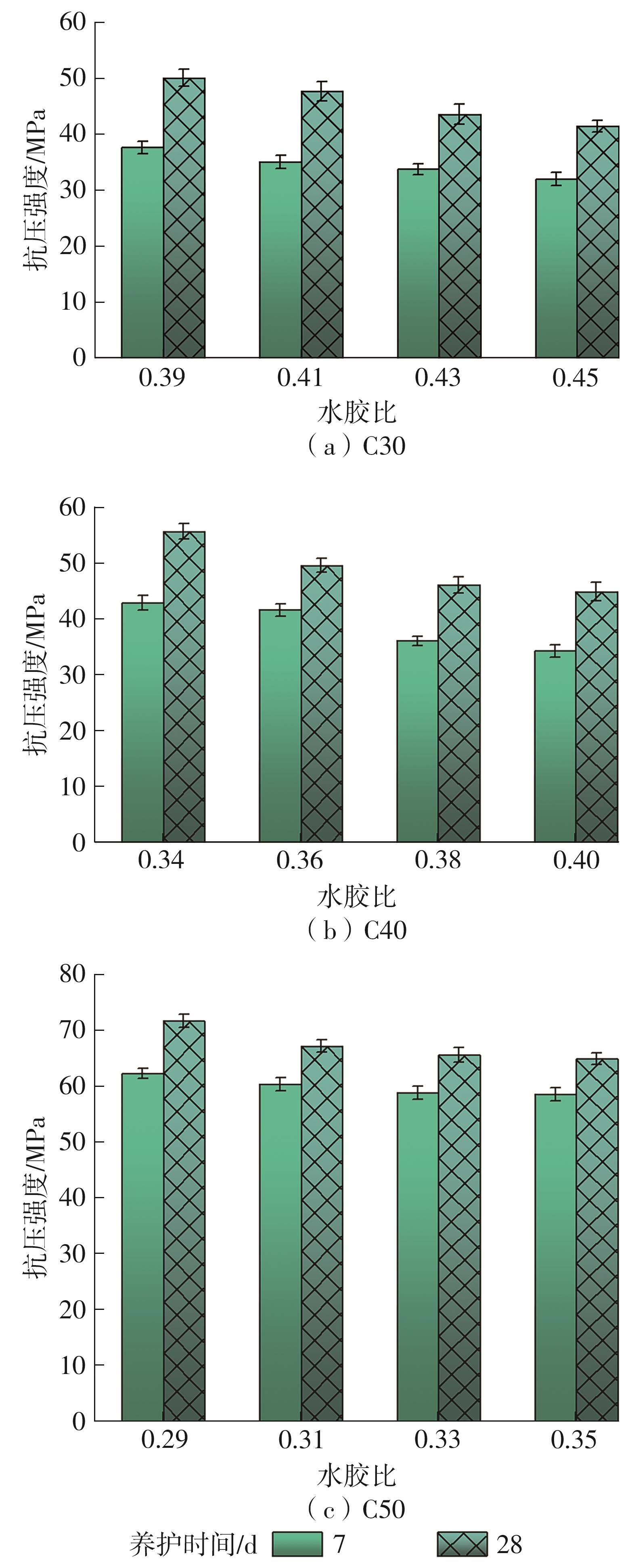
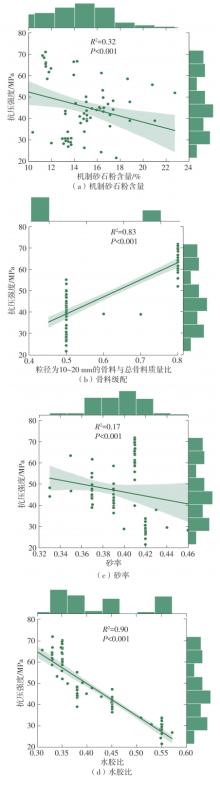
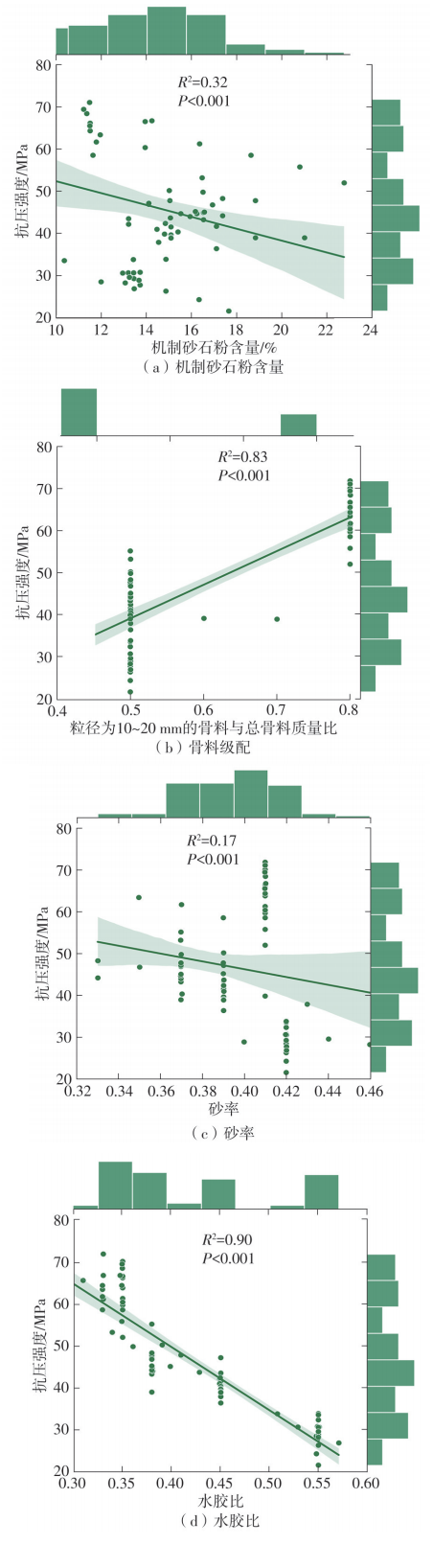
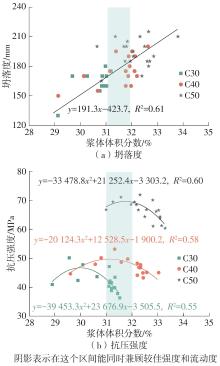
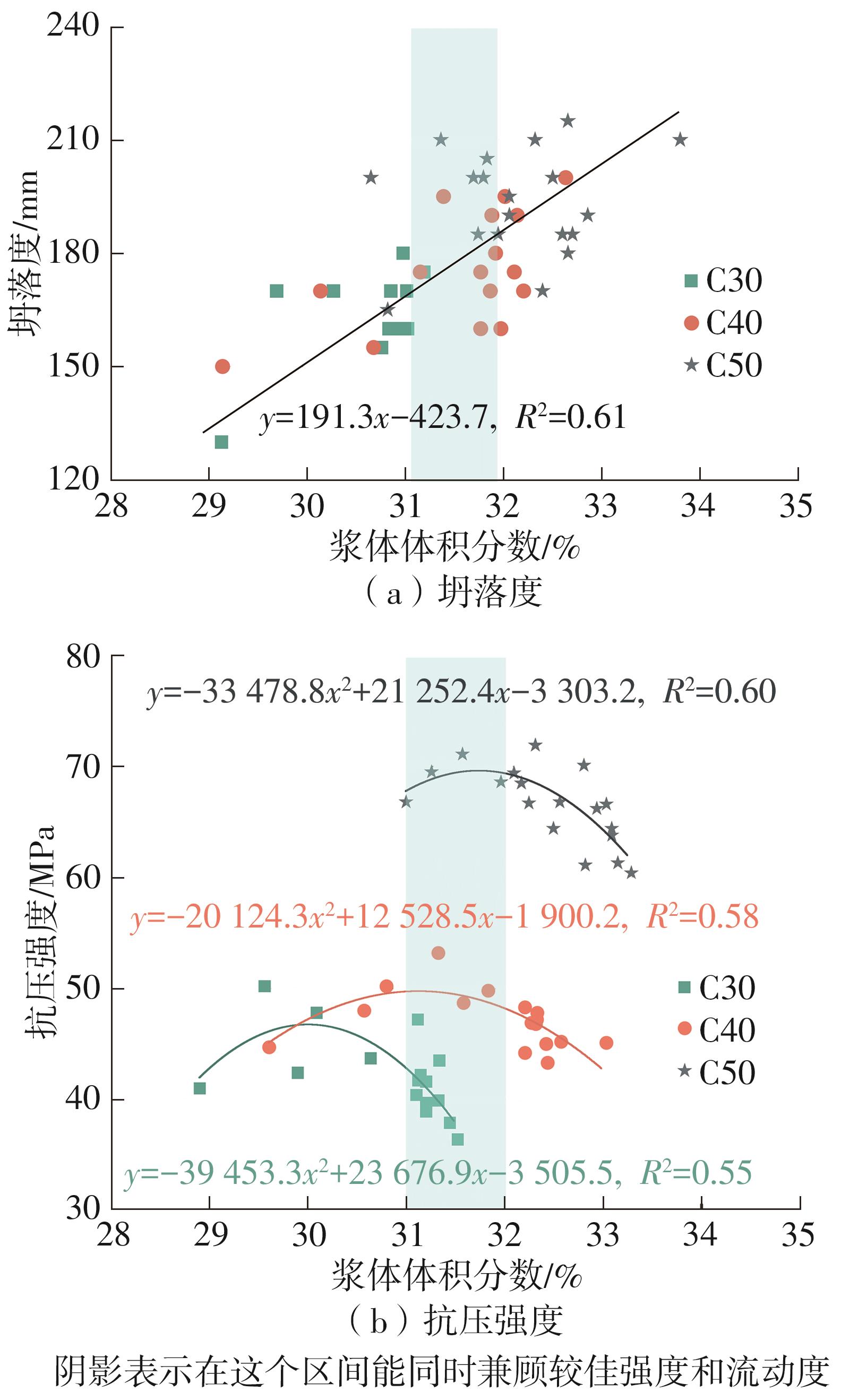
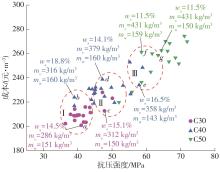
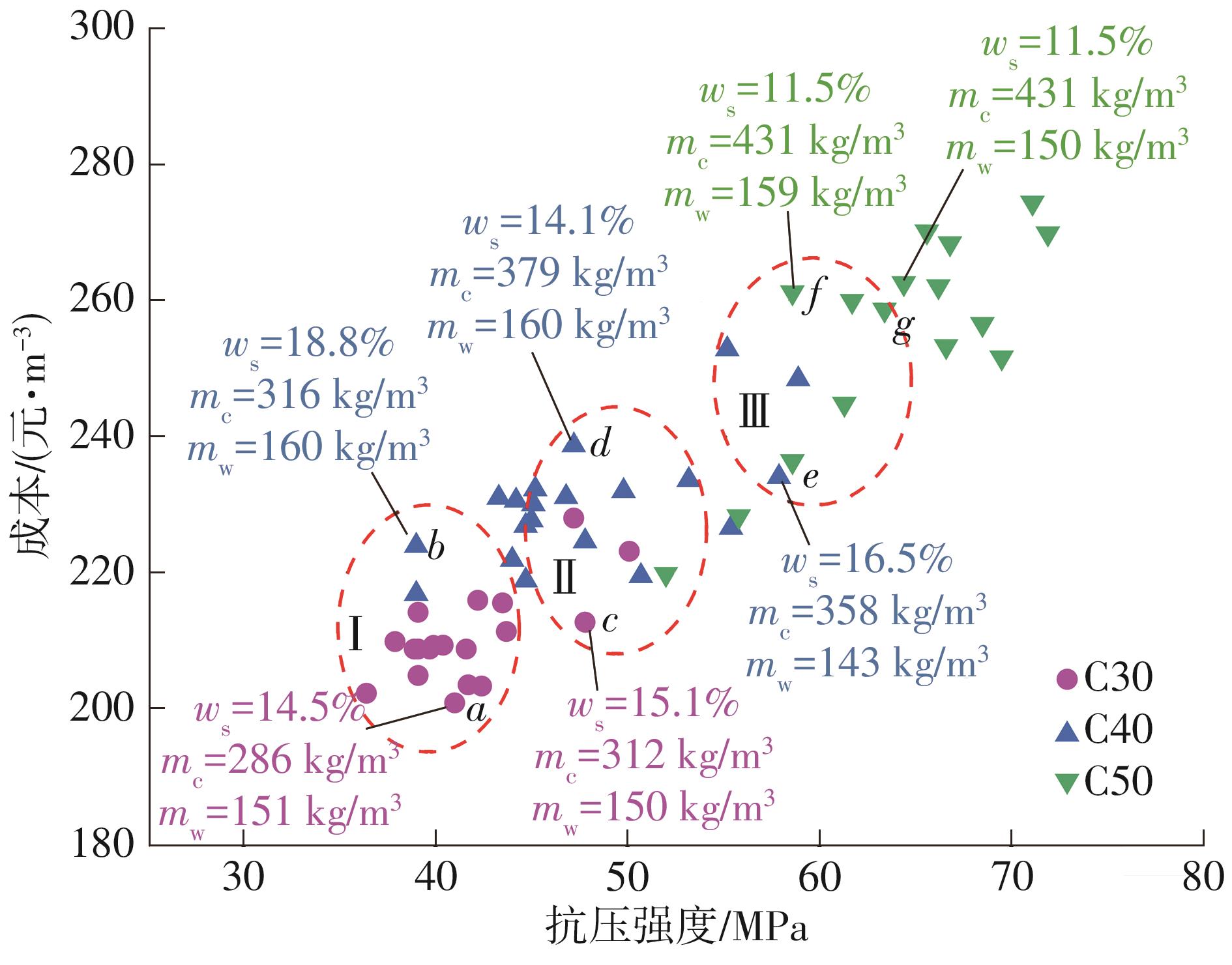
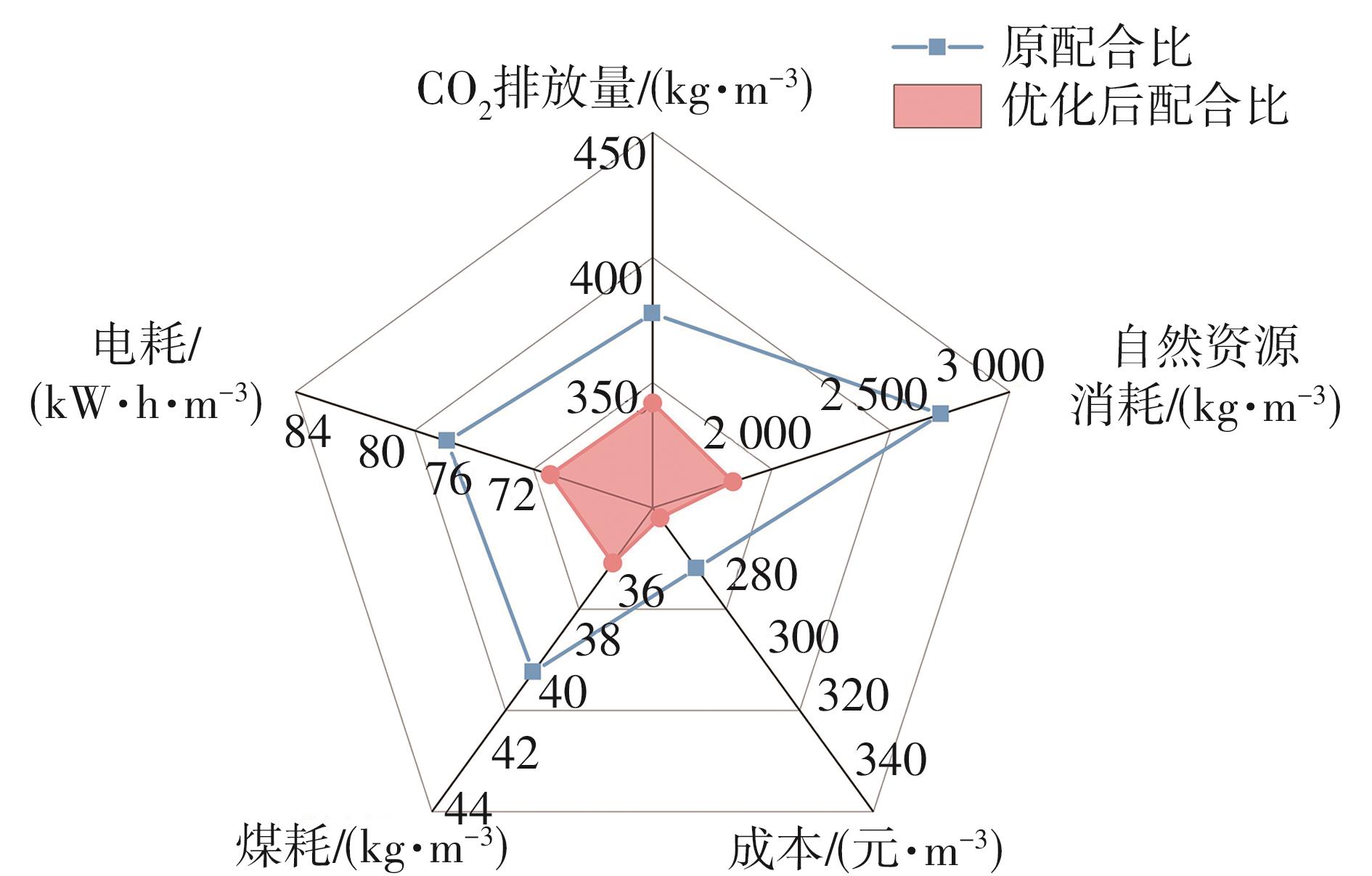
| [1] |
DOBISZEWSKA M, BAGCAL O, BEYCIOĞLU A,et al .Utilization of rock dust as cement replacement in cement composites:an alternative approach to sustainable mortar and concrete productions[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2023,69:106180/1-12.
|
| [2] |
ALI M B, SAIDUR R, HOSSAIN M S .A review on emission analysis in cement industries[J].Renewable and Sustainable Energy Reviews,2011,15(5):2252-2261.
|
| [3] |
DAMTOFT J S, LUKASIK J, HERFORT D,et al .Sustainable development and climate change initiatives[J].Cement and Concrete Research,2008,38(2):115-127.
|
| [4] |
刘战鳌,周明凯,姚楚康 .机制砂中细粉的危害性及评价研究[J].建筑材料学报,2015,18(1):150-155.
|
|
LIU Zhan-ao, ZHOU Ming-kai, YAO Chu-kang .Research on harmfulness and evaluation of various microfines in manufactured sand[J].Journal of Building Materials,2015,18(1):150-155.
|
| [5] |
ALIABDO A A, ELMOATY M ABD, AUDA E M .Re-use of waste marble dust in the production of cement and concrete[J].Construction and Building Materials,2014,50(4):28-41.
|
| [6] |
建设用砂: [S].
|
| [7] |
JEKNAVORIAN A A, KOEHLER E .Use of chemical admixtures to modify the rheological behavior of cementitious systems containing manufactured aggregates[J].Journal of Civil Engineering and Architecture,2012,6(10):1263-1272.
|
| [8] |
LI J .Study on different factors for working performance and strength of concrete with machined-sand[J].New Building Materials,2020,47(5):13-21.
|
| [9] |
王将华,薛翠真,张宇,等 .花岗岩石粉对砂浆干燥收缩性能的影响[J].材料导报,2023,37(22):111-116.
|
|
WANG Jianghua, XUE Cuizhen, ZHANG Yu,et al .Effect of granite powder on drying shrinkage[J].Materials Reports,2023,37(22):111-116.
|
| [10] |
JADHAV P A, KULKARNI D K .An experimental investigation on the properties of concrete containing manufactured sand[J].International Journal of Advanced Engineering Technology,2012,3(2):101-104.
|
| [11] |
李化建,赵国堂,谢永江,等 .石灰石粉作为混凝土矿物掺合料的研究[J].铁道建筑,2012,458(4):135-138.
|
|
LI Hua-jian, ZHAO Guo-tang, XIE Yong-jiang,et al .Study on limestone powder as mineral admixture in concrete[J].Railway Engineering,2012,458(4):135-138.
|
| [12] |
刘战鳌,周明凯,李北星 .石粉对机制砂混凝土性能影响的研究进展[J].材料导报,2014,28(19):100-103.
|
|
LIU Zhan-ao, ZHOU Ming-kai, LI Bei-xing .Research progress on influence of microfines on manufactured sand concrete’s performance[J].Materials Reports,2014,28(19):100-103.
|
| [13] |
TAO F, LIANG J L, LAN Y F,et al .Effect of stone powder content on mechanical properties of manufactured sand concrete[J].Iranian Journal of Science and Technology,Transactions of Civil Engineering,2022,46(6):4255-4264.
|
| [14] |
CHE D L, WANG J J, DING Z W,et al .Research on the performance of manufactured sand concrete with different stone powder content[C]∥ Proceedings of the 3rd International Conference on Civil,Architecture and Urban Engineering.Guangzhou:Academic Exchange Information Centre,2021,283:01044/1-13.
|
| [15] |
王振,李化建,黄法礼,等 .石灰岩机制砂混凝土抗冻性能研究[J].建筑材料学报,2023,26(5):516-523,537.
|
|
WANG Zhen, LI Huajian, HUANG Fali,et al .Frost resistance of limestone manufactured sand concrete[J].Journal of Building Materials,2023,26(5):516-523,537.
|
| [16] |
周翱翔,张云升,钱如胜,等 .花岗岩石粉对机制砂混凝土基本性能及气体渗透特性的影响[J].复合材料学报,2024,41(7):3704-3715.
|
|
ZHOU Aoxiang, ZHANG Yunsheng, QIAN Rusheng,et al .Influence of granite stone powder on the basic properties and gas permeability characteristics of mechanism sand concrete[J].Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2024,41(7):3704-3715.
|
| [17] |
KUMAR K P, RAMESH P S, ARAVINDA P T .Effect of fines on strength and durability of concrete with manufactured sand[J].Materials Today:Proceedings,2022,66(13):2381-2386.
|
| [18] |
ABD E M .Mechanical properties and corrosion resistance of concrete modified with granite dust[J].Construction and Building Materials,2013,47(24):743-752.
|
| [19] |
BINICI H, YARDIM Y, AKSOGAN O,et al .Durability properties of concretes made with sand and cement size basalt[J].Sustainable Materials and Technologies,2020,23:e00145/1-9.
|
| [20] |
DOBISZEWSKA M, SCHINDLER A K, PICHÓR W .Mechanical properties and interfacial transition zone microstructure of concrete with waste basalt powder addition[J].Construction and Building Materials,2018,177:222-229.
|
| [21] |
SINGH M, SRIVASTAVA A, BHUNIA D .Long term strength and durability parameters of hardened concrete on partially replacing cement by dried waste marble powder slurry[J].Construction and Building Materials,2019,198:553-569.
|
| [22] |
ÖZKILIÇ Y O, ZEYBEK Ö, BAHRAMI A,et al .Optimum usage of waste marble powder to reduce use of cement toward eco-friendly concrete[J].Journal of Materials Research And Technology,2023,25:4799-4819.
|
| [23] |
CHEN P X, WANG X H, ZHANG T S,et al .Effect of ultrafine recycled brick powder on the properties of blended cement:hydration kinetics,microstructure evolution and properties development[J].Construction and Building Materials,2023,394:132239.
|
| [24] |
普通混凝土拌合物性能试验方法标准: [S].
|
| [25] |
普通混凝土力学性能试验方法标准: [S].
|
| [26] |
DOBISZEWSKA M, BAGCAL O, BEYCIOĞLU A,et al .Utilization of rock dust as cement replacement in cement composites:an alternative approach to sustainable mortar and concrete productions[J].Journal of Building Engineering,2023,69:106180.
|
| [27] |
JAGADESH P, OYEBISI S, MUTHU A H,et al .Microscopic analyses and performance characteristics of granite powder blended cement[J].Construction and Building Materials,2024,426:136006/1-18.
|
| [28] |
BARRA B, MOMM L, GUERRERO Y,et al .Characterization of granite and limestone powders for use as fillers in bituminous mastics dosage[J].Anais da Academia Brasileira de Ciências,2014,86(2):995-1002.
|
| [29] |
SAPIAI N, JUMAHAT A, JAWAID M,et al .Mechanical performance of granite fine fly dust-filled basalt/glass polyurethane polymer hybrid composites[J].Polymers,2021,13(18):3032/1-8.
|
| [30] |
WANG J, XUE C, ZHANG Y,et al .Study of early-age hydration,mechanical properties development,and microstructure evolution of manufactured sand concrete mixed with granite stone powder[J].Materials,2023,16(13):48-57.
|
| [31] |
WANG D, SHI C, FARZADNIA N,et al .A review on use of limestone powder in cement-based materials:mechanism,hydration and microstructures[J].Construction and Building Materials.2018,181:659-672.
|
| [32] |
JAIN K L, SANCHETI G, GUPTA L K .Durability performance of waste granite and glass powder added concrete[J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,252:119075/1-11.
|
| [33] |
NANTHAGOPALAN P, SANTHANAM M .Fresh and hardened properties of self-compacting concrete produced with manufactured sand[J].Cement and Concrete Composites,2011,33(3):353-358.
|
| [34] |
SHEN W, LIU Y, WANG Z,et al .Influence of manufactured sand’s characteristics on its concrete performance[J].Construction and Building Materials,2018,172:574-583.
|
| [35] |
VARGAS P, RESTREPO-BAENA O, TOBÓN J I .Microstructural analysis of interfacial transition zone (ITZ) and its impact on the compressive strength of lightweight concretes[J].Construction and Building Materials,2017,137:381-389.
|
| [36] |
徐小宁 .中国水泥工业的生命周期评价[D].大连:大连理工大学,2013.
|
| [37] |
汪伟 .低品质再生砂粉与盾构泥浆制备可控低强充填材料及性能研究[D].广州:华南理工大学,2022.
|
| [38] |
BASSANI M, KHOSRAVIFAR S, GOULIAS D,et al .Long-term resilient and permanent deformation behavior of controlled low-strength materials for pavement applications[J].Journal of Transportation Geotechnics,2015,2:108-118.
|