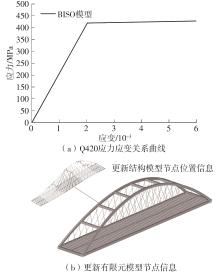
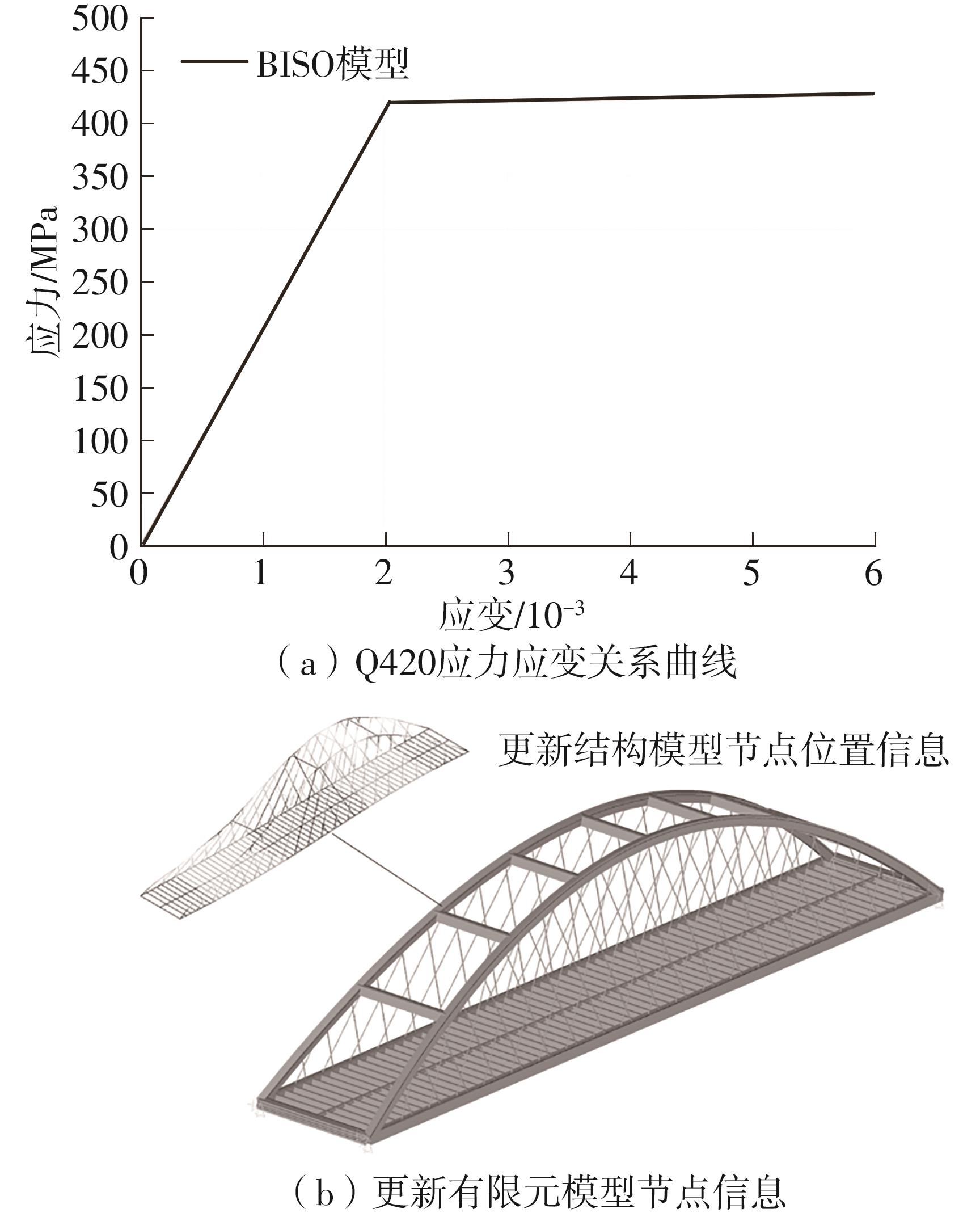
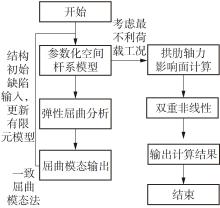
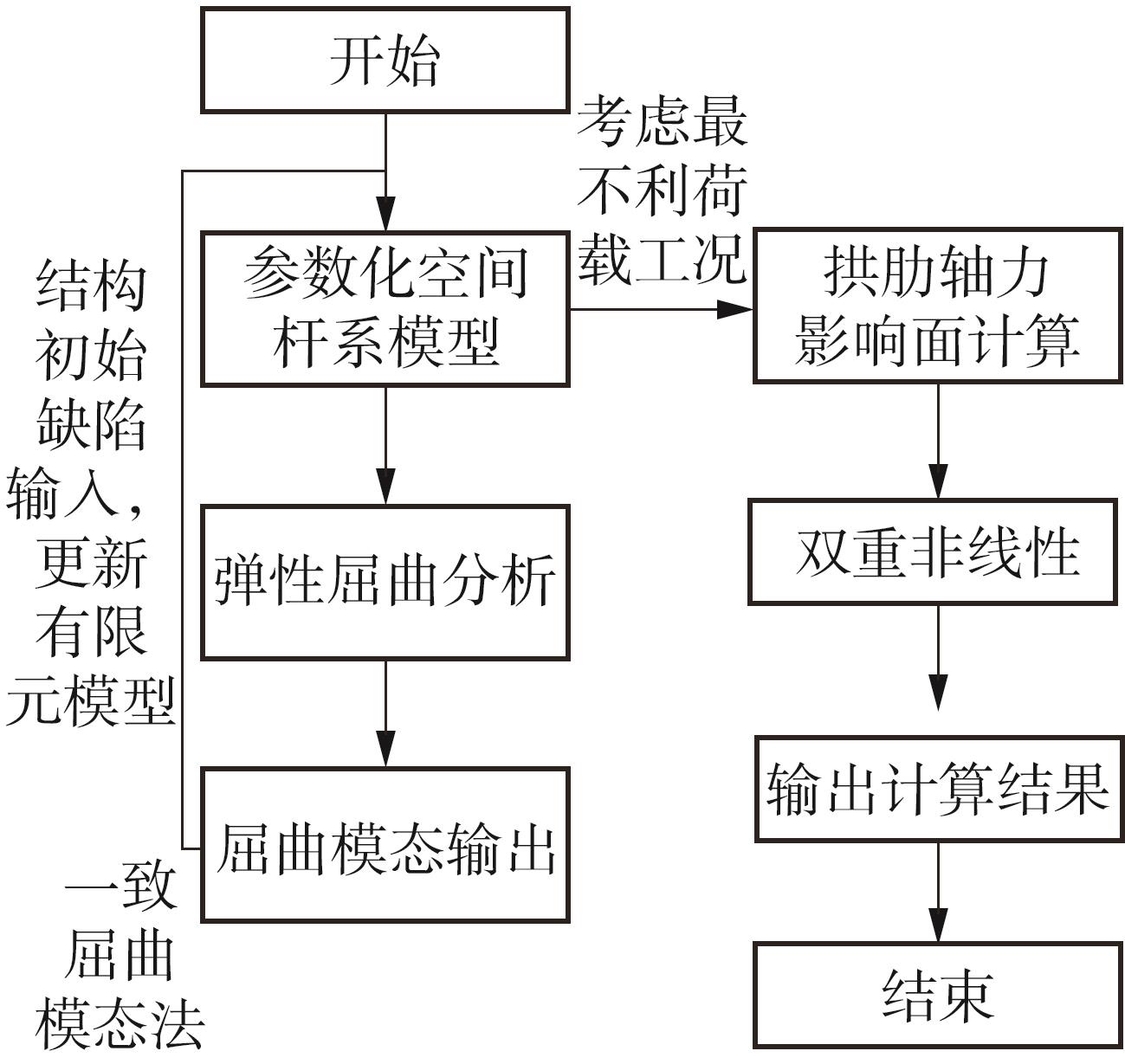
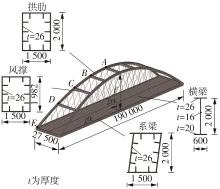
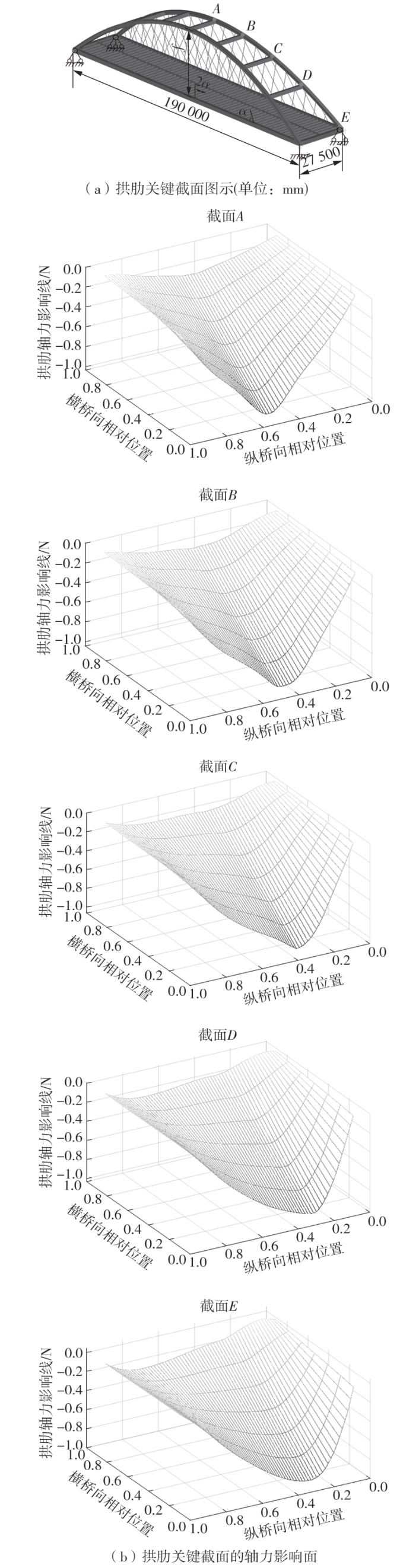
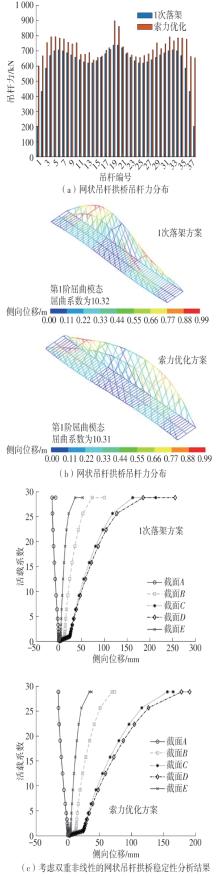
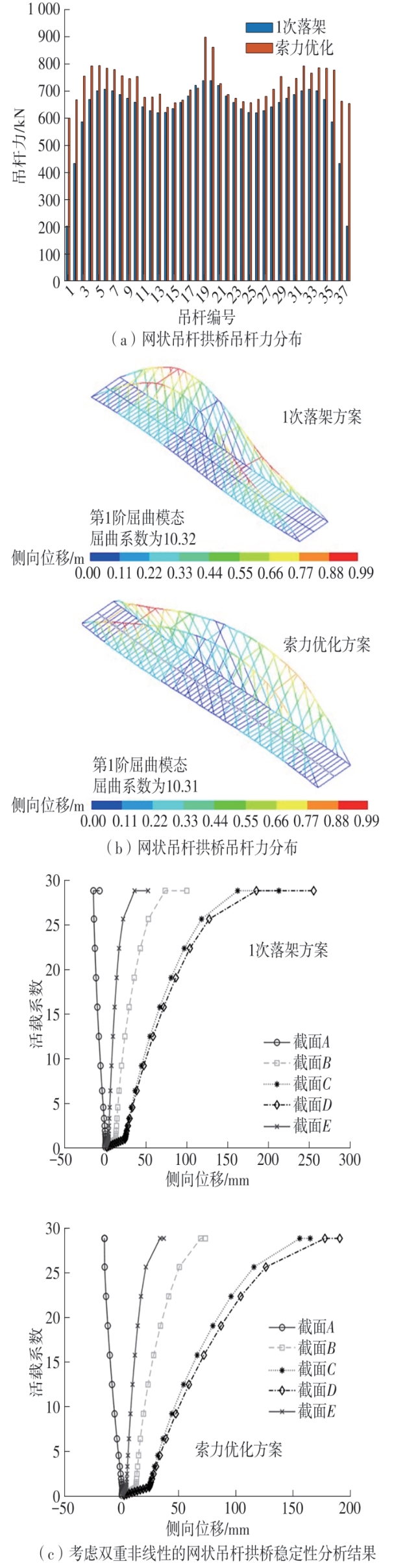
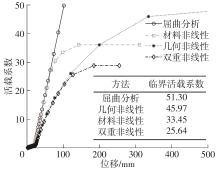
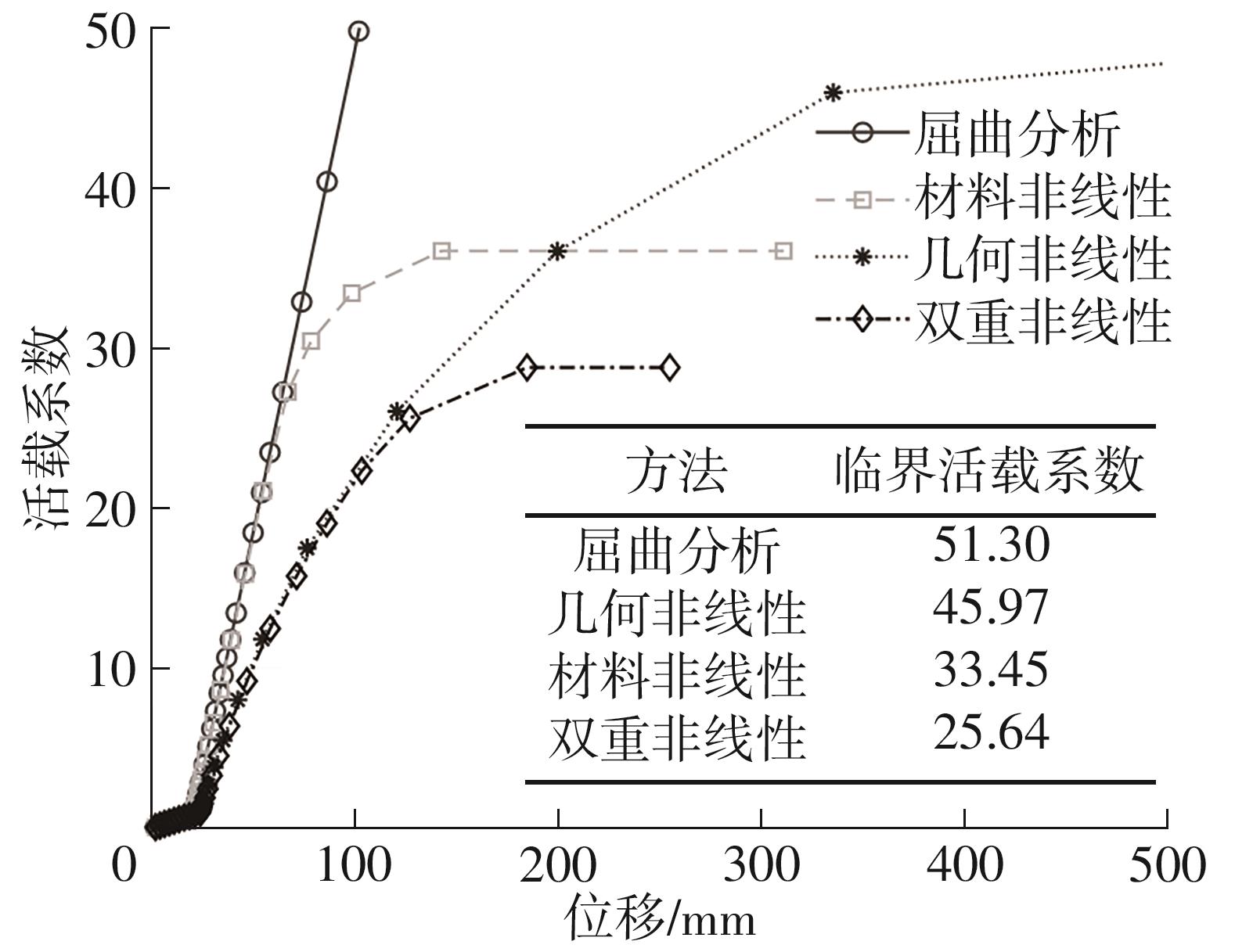
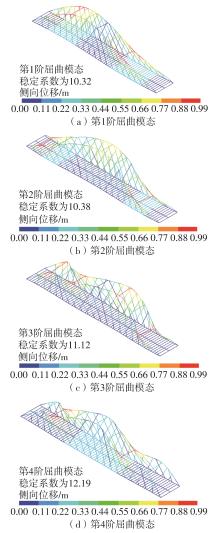
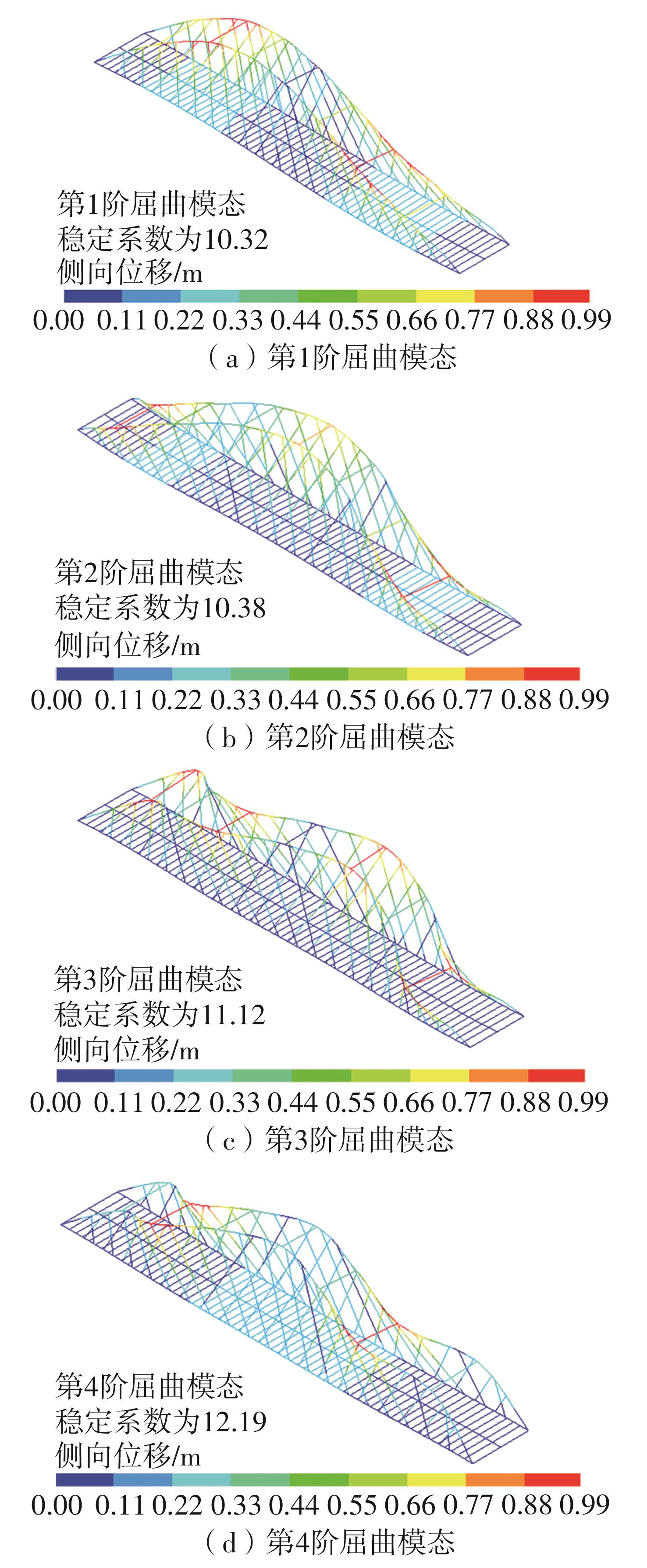
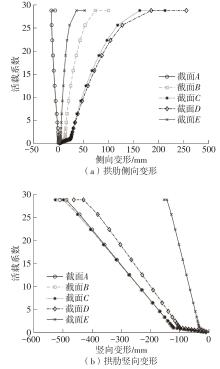
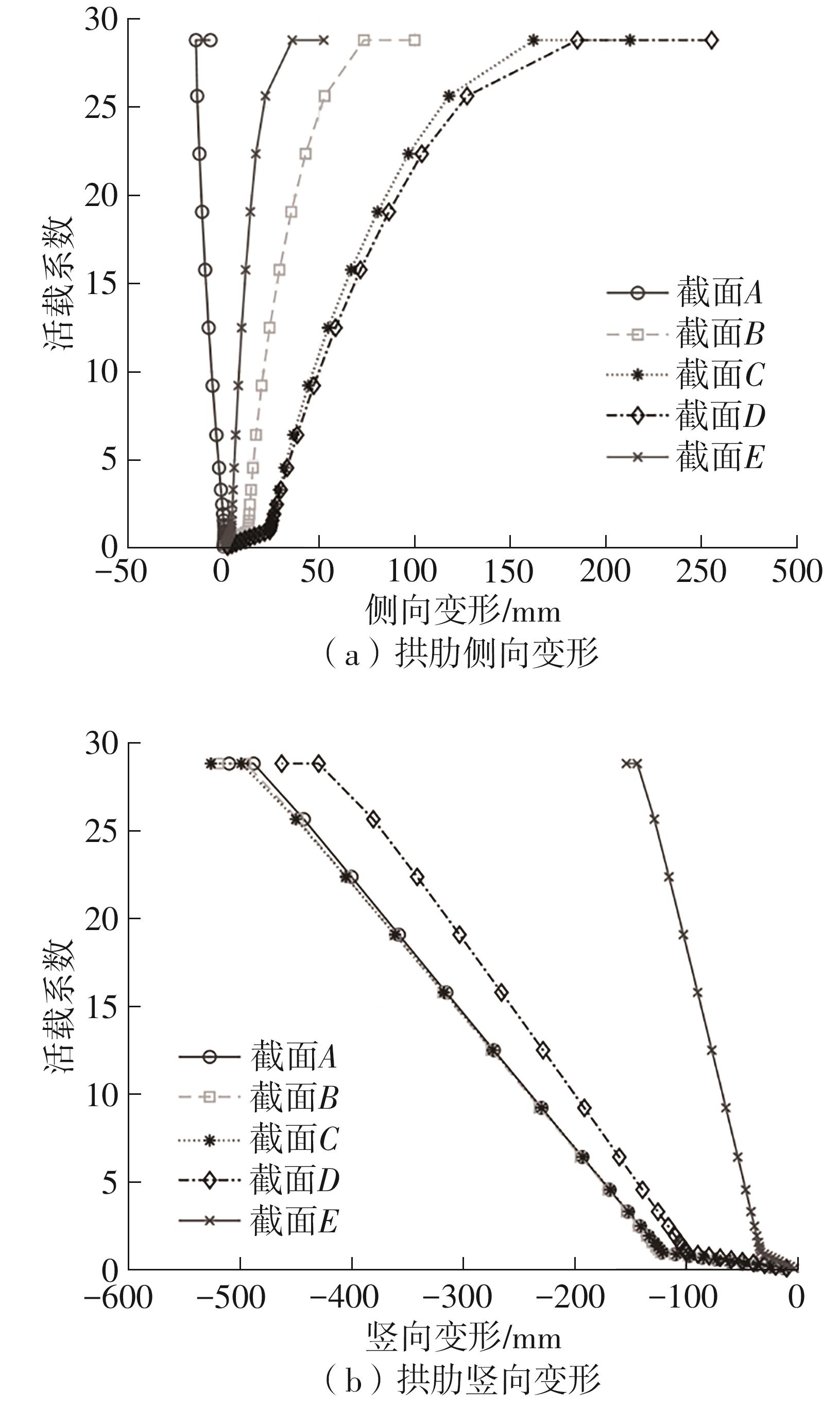
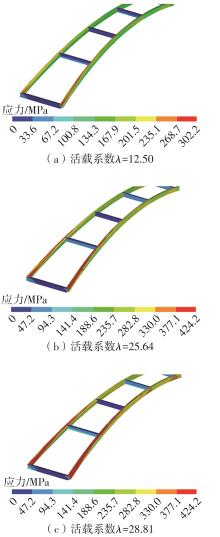
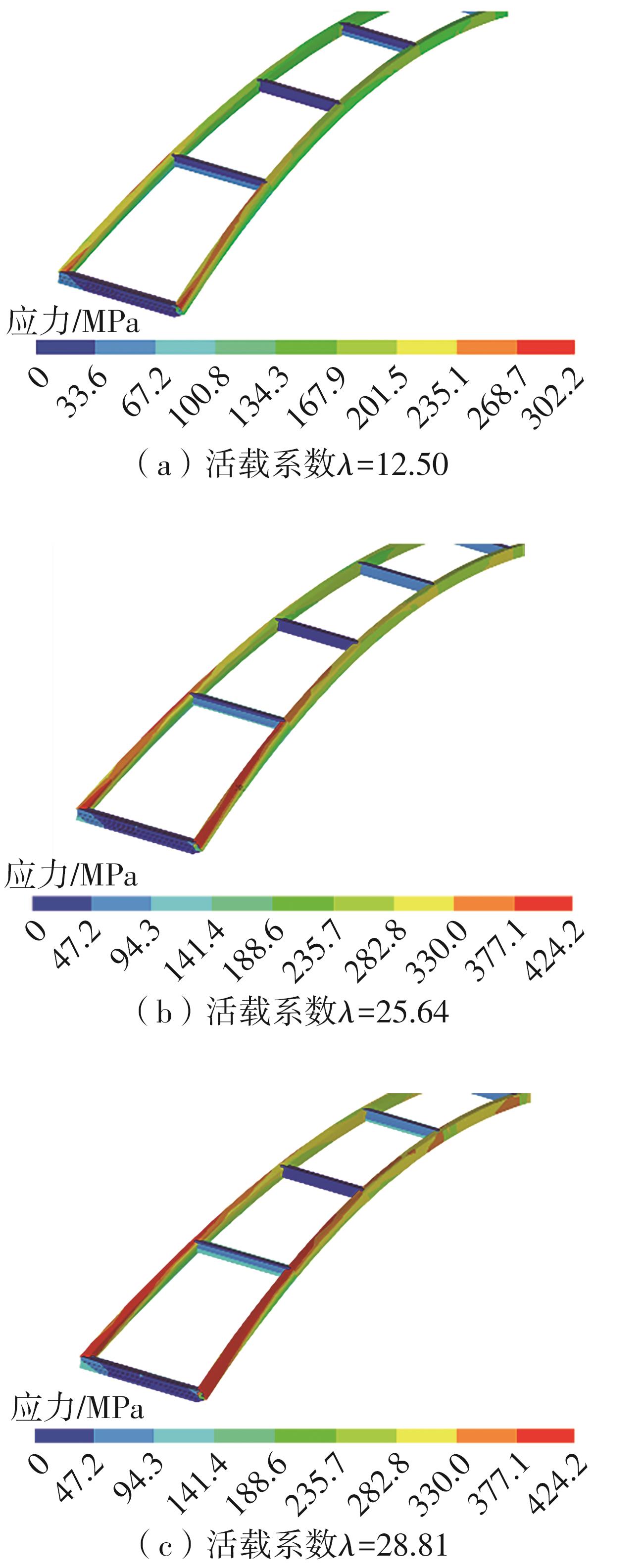
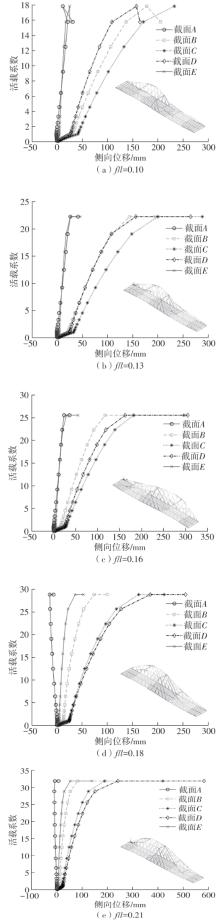
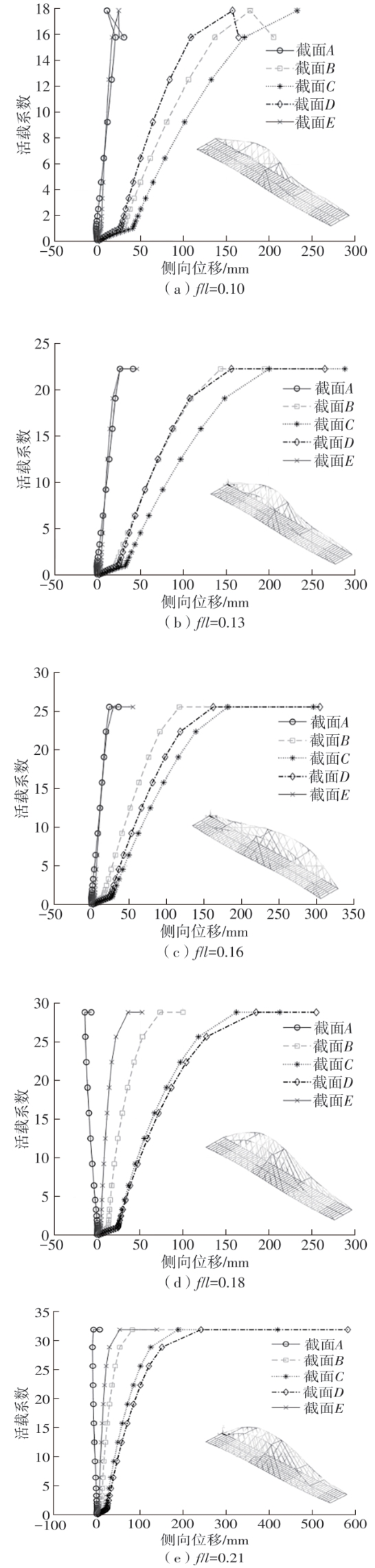
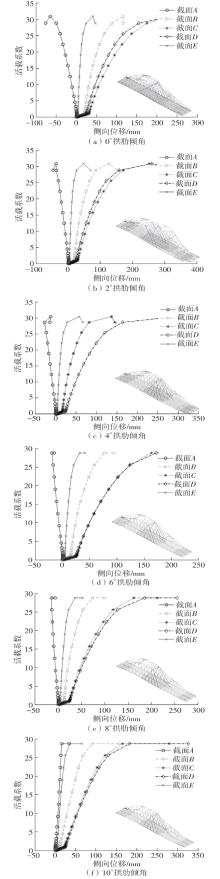
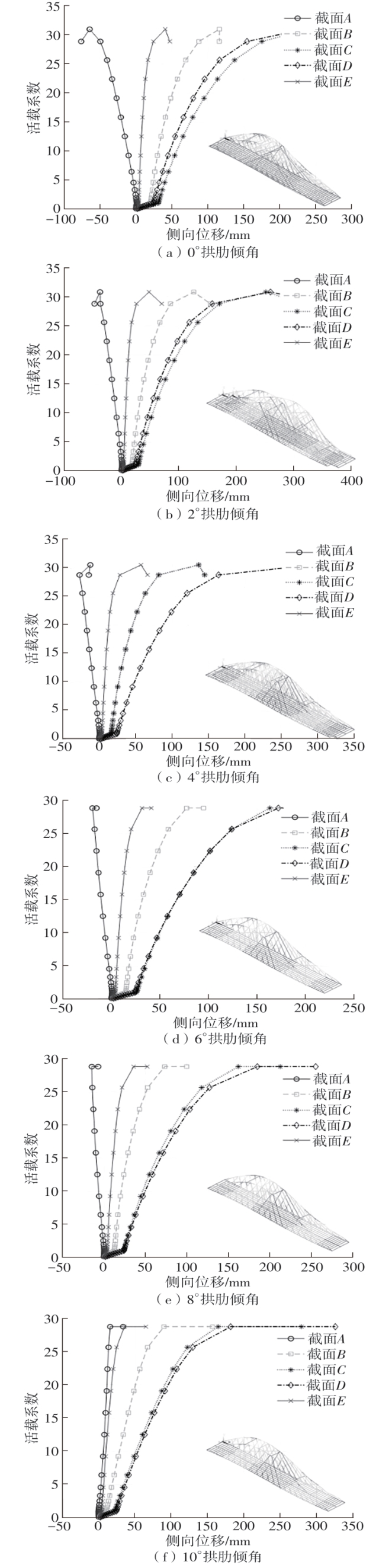
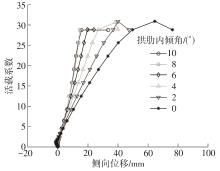
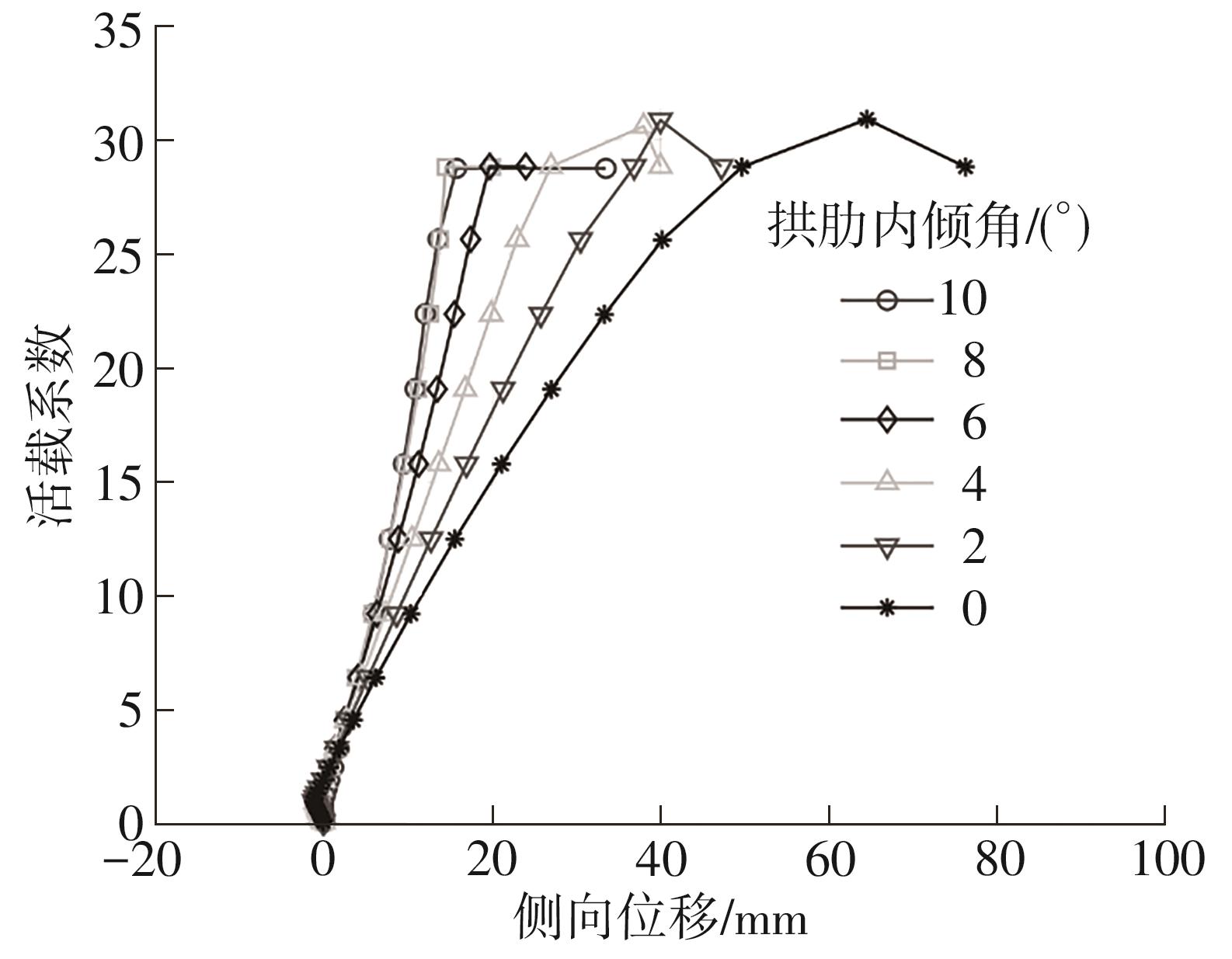
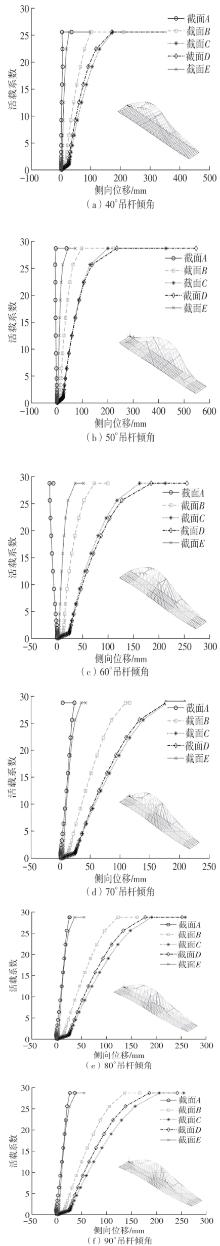
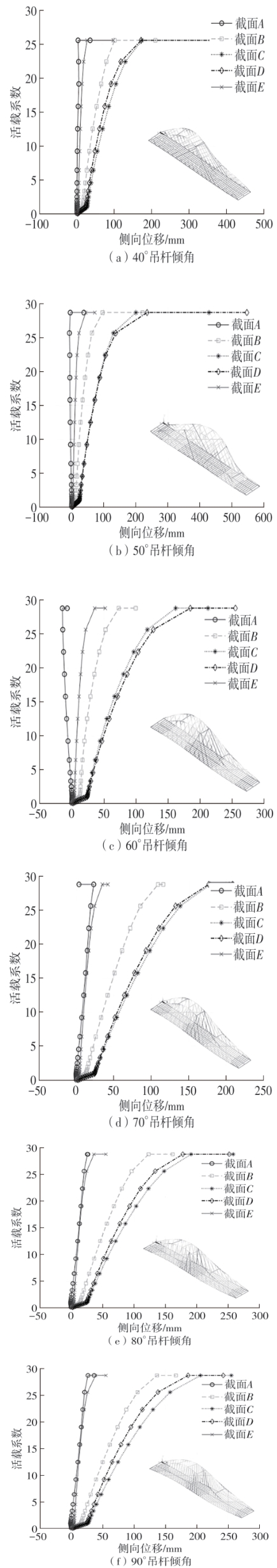
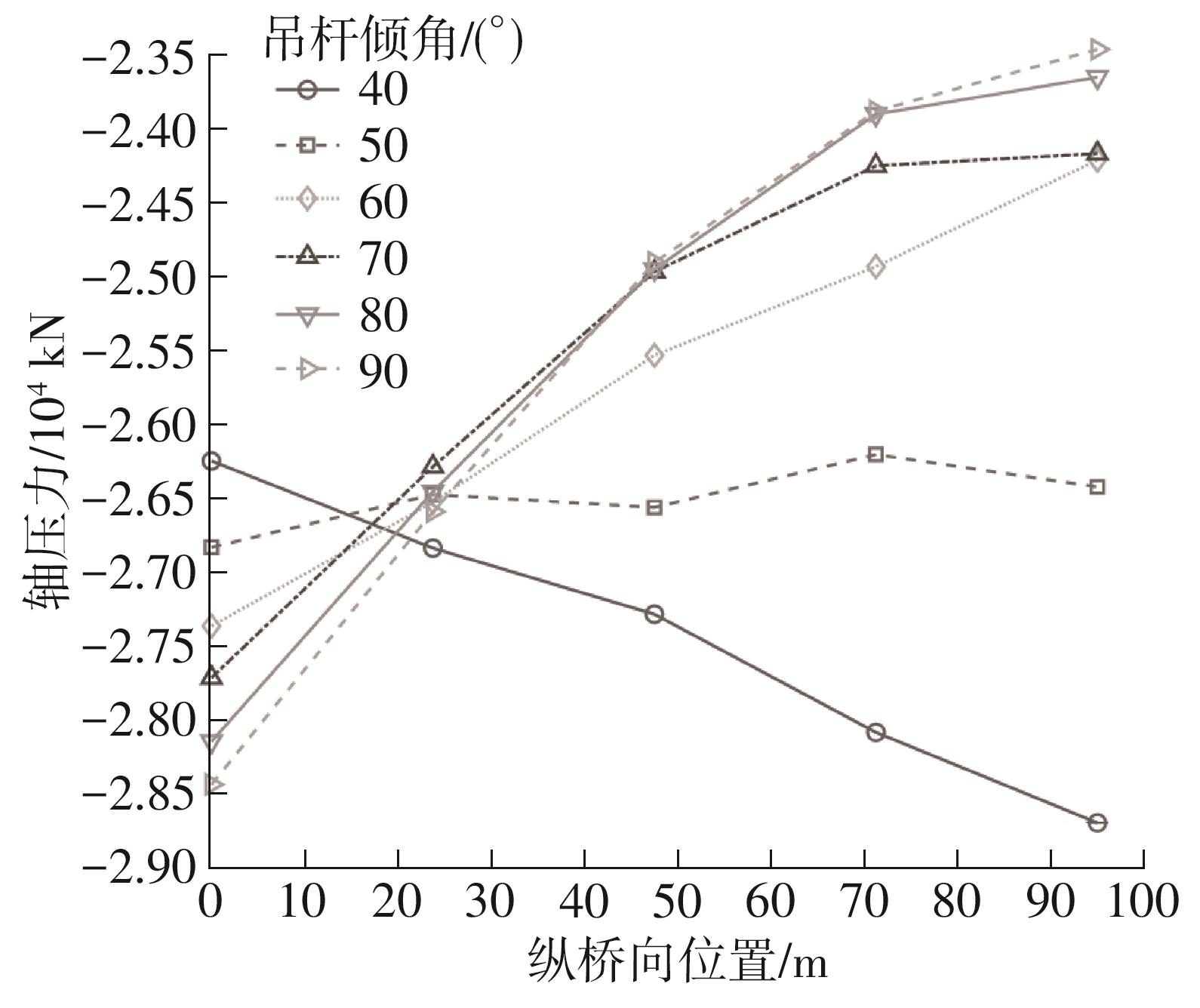
| [1] |
肖汝诚 .桥梁结构体系[M].北京:人民交通出版社,2013.
|
| [2] |
DANCIU A D, GUTIU S I, MOGA C,et al .A review of the network arch bridge[J].Applied Sciences-Basel,2023,13(19):10966/1-27.
|
| [3] |
FEDIN K V, GRITSENKO A A, GROMYKO P V .Diagnostics of the stability state of the bugrinsky bridge by acoustic noise method[J].Processes in GeoMedia,2023,6:33-41.
|
| [4] |
汤虎,王伟,路辉,等 .济南齐鲁黄河大桥420 m网状吊杆系杆拱桥主拱设计[J].桥梁建设,2022,52(4):117-124.
|
|
TANG Hu, WANG Wei, LU Hui,et al .Design of arch ribs of 420 m-span network arch main bridge of qilu huanghe river bridge in Jinan[J].Bridge Construction,2022,52(4):117-124.
|
| [5] |
吴丽丽,于雅倩,吕步凡 .波形钢腹板支架拱结构的局部稳定性能[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(10):93-104.
|
|
WU Lili, YU Yaqian, Bufan LÜ .Local stability performance of arch components of underground supporting structure with corrugated steel webs[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2019,47(10):93-104.
|
| [6] |
张毅,李正良,刘红军,等 .特高压输电塔不等边角钢交叉斜材的承载力[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(7):19-31.
|
|
ZHANG Yi, LI Zhengliang, LIU Hongjun,et al .Study on the stability bearing capacity of unequal angle cross bracing of ultra-high voltage transmission tower[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2019,47(7):19-31.
|
| [7] |
薛峰,荆克林,段书龙,等 .公路网状吊杆拱桥极限承载力研究[J].公路,2022,67(6):164-168.
|
|
XUE Feng, JING Kelin, DUAN Shulong,et al .Research on the ultimate bearing capacity of highway mesh suspension arch bridge[J].Highway,2022,67(6):164-168.
|
| [8] |
PAN W H, ZHAO C H, WANG C M,et al .Optimal bracing system design for funicular twin arches against out-of-plane buckling[J].Engineering Structures,2024,301:1-12.
|
| [9] |
JIANG Z, XIAO R, SONG C,et al .An analytical method for out-of-plane stability assessment of network arch bridges[J].Thin-Walled Structures,2024,204:1-17.
|
| [10] |
郝天之,李春华,杨涛,等 .索-悬链线拱联合结构的受力机理与力学特征[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2024,52(8):89-102.
|
|
HAO Tianzhi, LI Chunhua, YANG Tao,et al .Mechanism and mechanical characteristics of cable-catenary arch combined structure[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2024,52(8):89-102.
|
| [11] |
LAI Y, Li Y, HUANG M,et al .Conceptual design of long span steel-UHPC composite network arch bridge[J].Engineering structures,2023,277:1-19.
|
| [12] |
WERONIKA O A, ARNE M K .Network arch timber bridges with light timber decks and spoked configuration of hangers-parametric study[J].Engineering Structures,2022,253:1-10.
|
| [13] |
曹鑫科 .大跨度网状吊杆拱桥力学性能及结构参数优化研究[D].西安:长安大学,2022.
|
| [14] |
钢结构设计标准: [S].
|
| [15] |
公路钢筋混凝土及预应力混凝土桥涵设计规范: [S].
|
| [16] |
Eurocode 3:Design of steel structures (Part 2:Steel bridges):UNE—EN 1993-2-2013 [S].
|
| [17] |
刘星星 .网状吊杆拱桥力学行为及极限承载能力研究[D].武汉:华中科技大学,2019.
|
| [18] |
曾顺得 .700m跨钢管混凝土拱桥稳定性研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学,2023.
|
| [19] |
康洪滔 .大跨径提篮式钢桁架拱桥非线性稳定研究[D].重庆:重庆交通大学,2024.
|
| [20] |
LONETTI P, PASCUZZO A .A practical method for the elastic buckling design of network arch bridges[J].International Journal of Steel Structures,2020,20(1):311-329.
|
| [21] |
黄云,张清华,叶华文,等 .钢管混凝土系杆拱桥空间稳定性分析[J].桥梁建设,2014,44(4):50-56.
|
|
HUANG Yun, ZHANG Qinghua, YE Huawen,et al .Analysis of spatial stability of a CFST tied arch bridge[J].Bridge Construction,2014,44(4):50-56.
|
| [22] |
卜一之,赵雷,李乔 .苏通长江大桥结构非线性稳定性研究[J].土木工程学报,2013,46(1):84-91.
|
|
PU Yizhi, ZHAO Lei, LI Qiao .Structural nonlinear stability analysis of Sutong Yangtze river bridge[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2013,46(1):84-91.
|
| [23] |
程进,江见鲸,肖汝诚,等 .大跨度拱桥极限承载力的参数研究[J].中国公路学报,2003,16(2):45-47.
|
|
CHENG Jin, JIANG Jianjing, XIAO Rucheng,et al .Parametric study of ultimate capacity of long-span arch bridges[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2003,16(2):45-47.
|
| [24] |
梁岩,罗小勇,欧娅 .大跨径拱桥轴线横向偏差对结构的影响[J].公路交通科技,2013,30(8):92-95.
|
|
LIANG Yan, LUO Xiaoyong, Ya OU .Impact of transverse axis deviation on structure of long-span arch bridge[J].Journal of Highway and Transportation Research and Development,2013,30(8):92-95.
|
| [25] |
TVEIT P .How to design economical network arches[J].IOP Conference Series:Materials Science and Engineering,2019,471(5):052078/1-11.
|
| [26] |
WANG W, LIN Y, CHEN K .Evaluation of criteria for out-of-plane stability of steel arch bridges in major design codes by FE analysis[J].Applied Sciences-Basel,2022,12(24):12632/1-21.
|
| [27] |
COSTA B M .Design and analysis of a network arch bridge[D].Lisboa:Instituto Superior Técnico,University of Lisbon,2013.
|