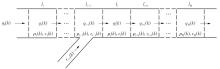
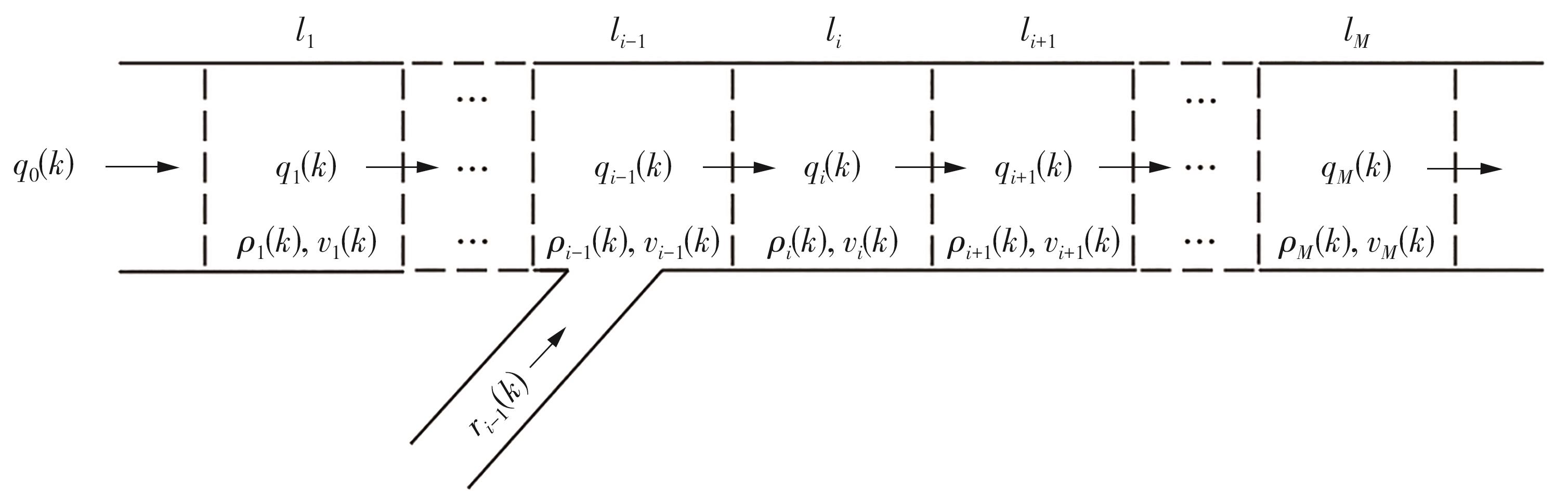
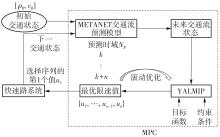
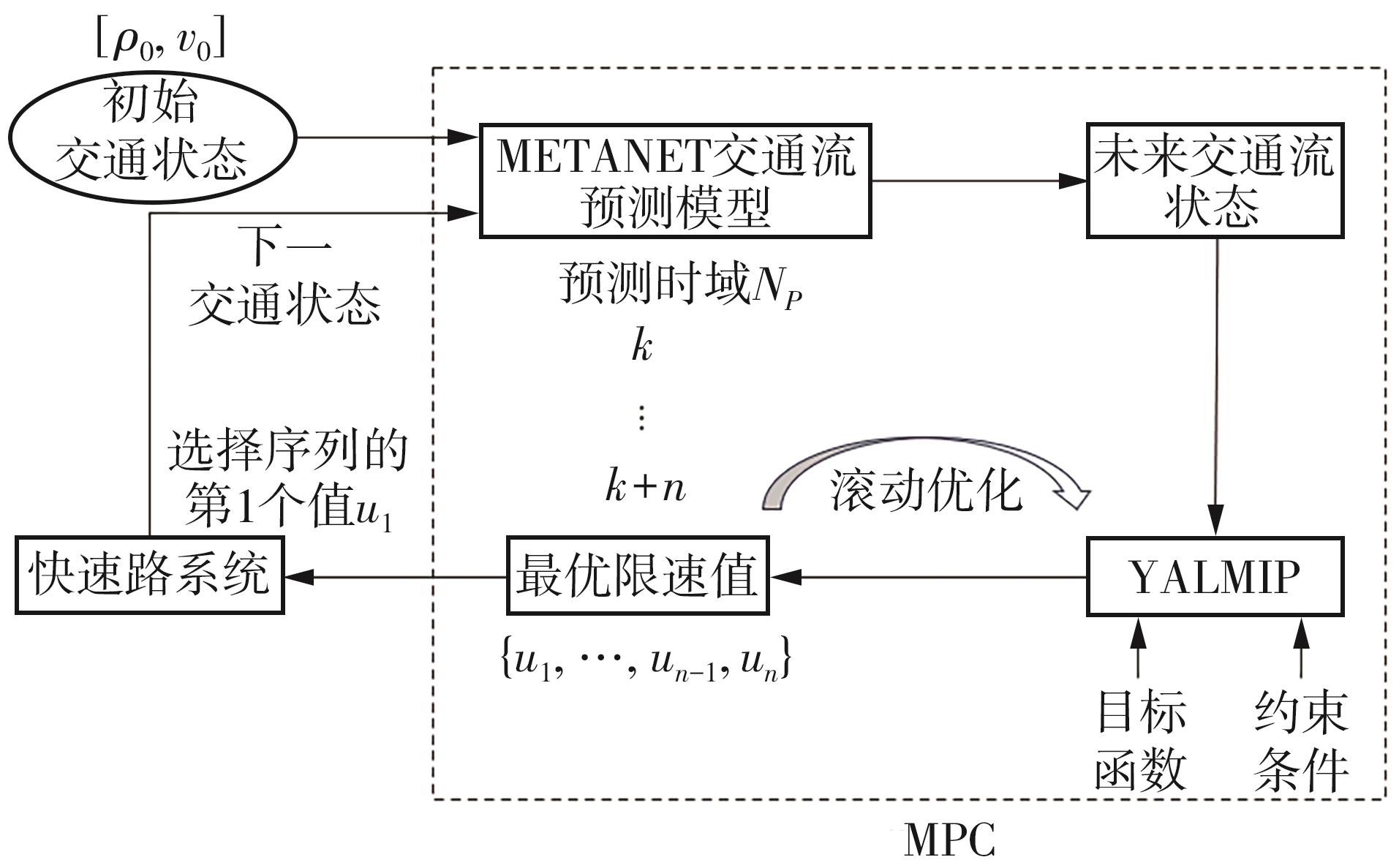
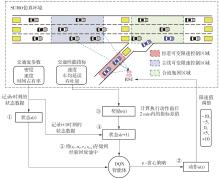
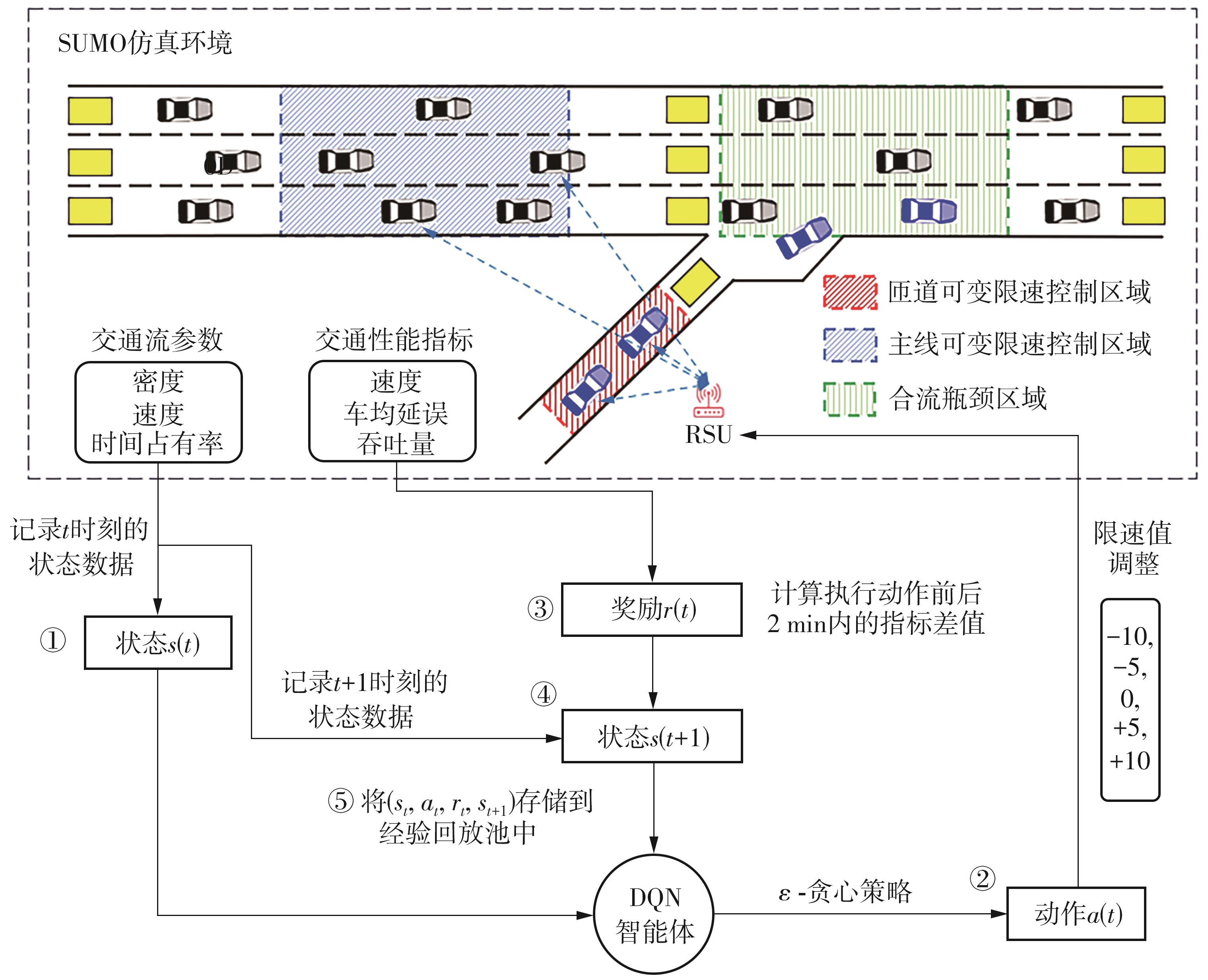
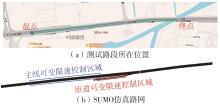
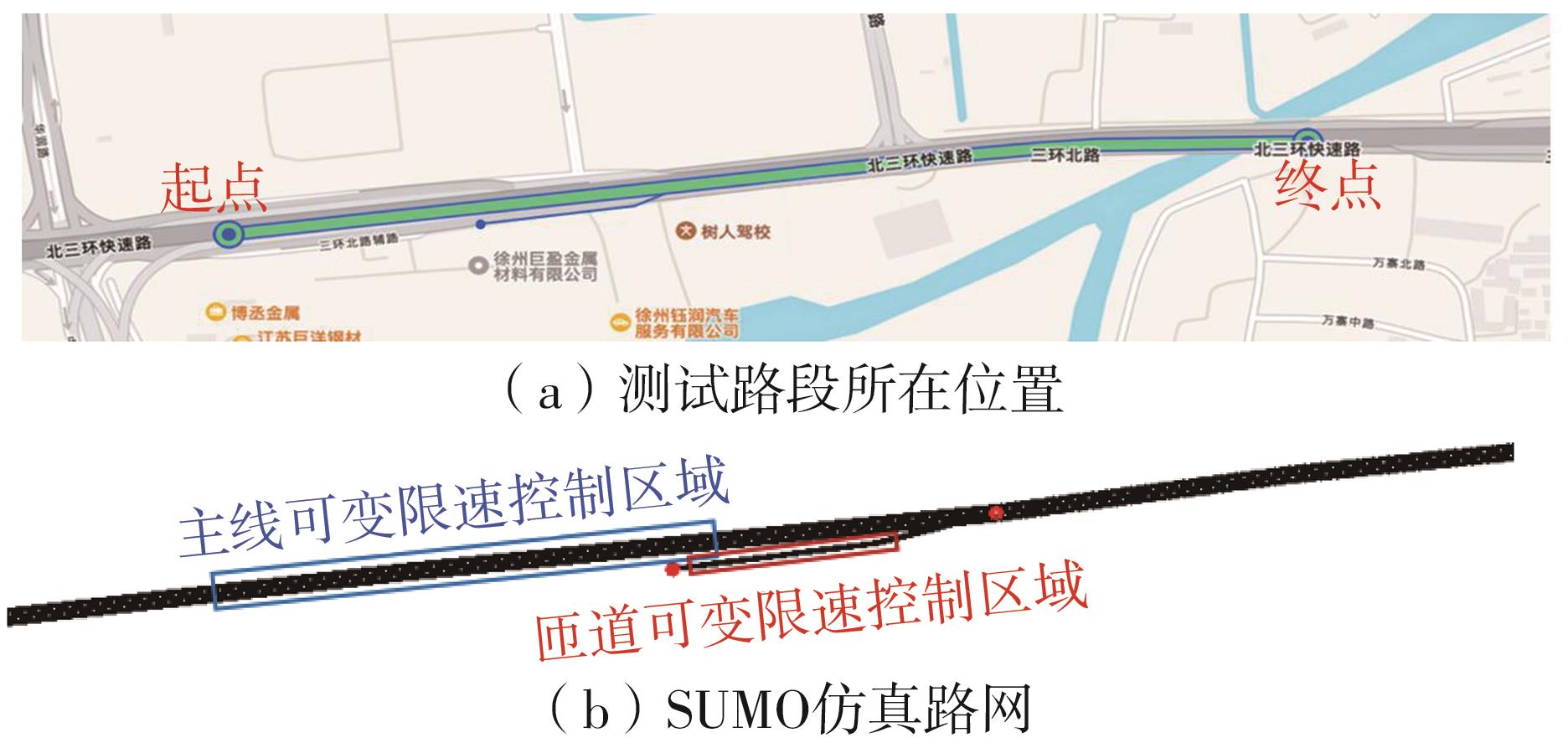
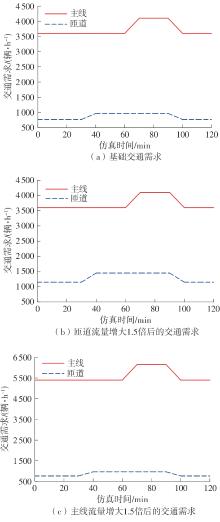
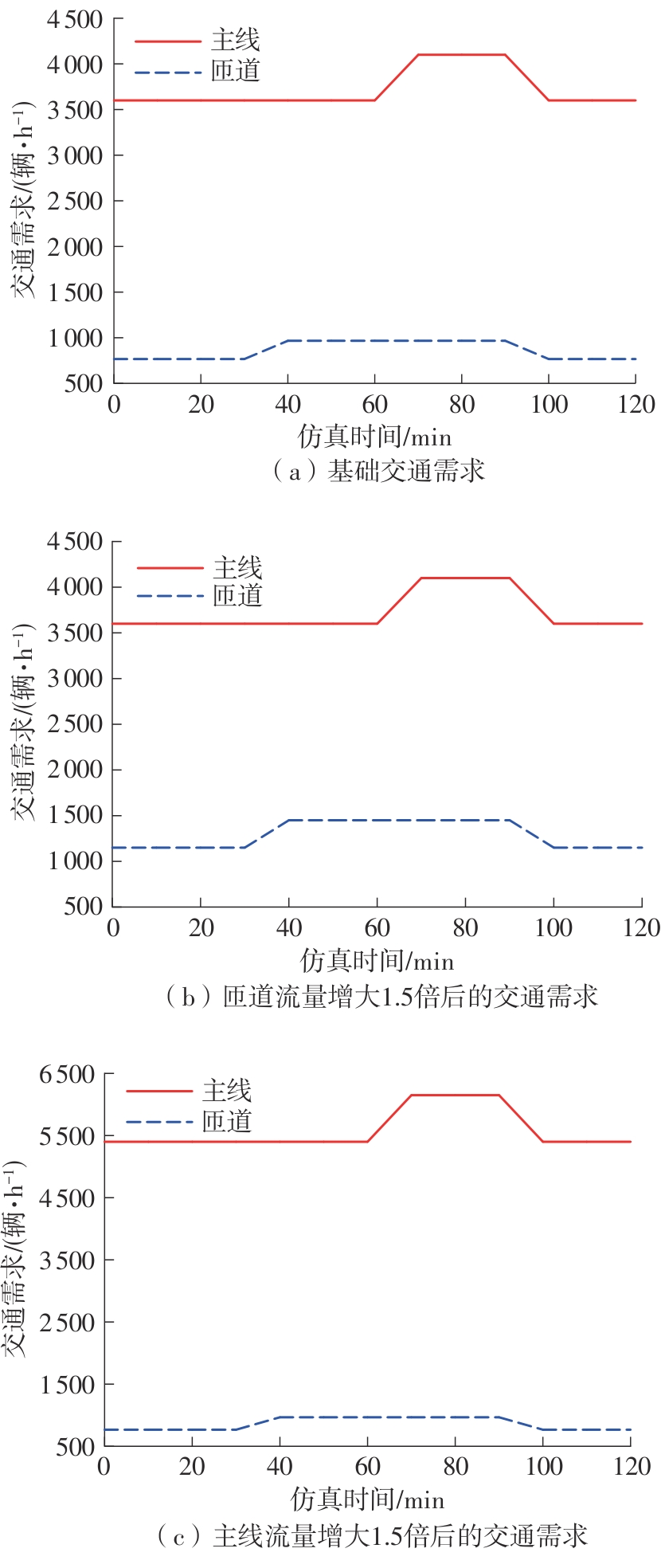
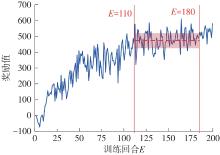
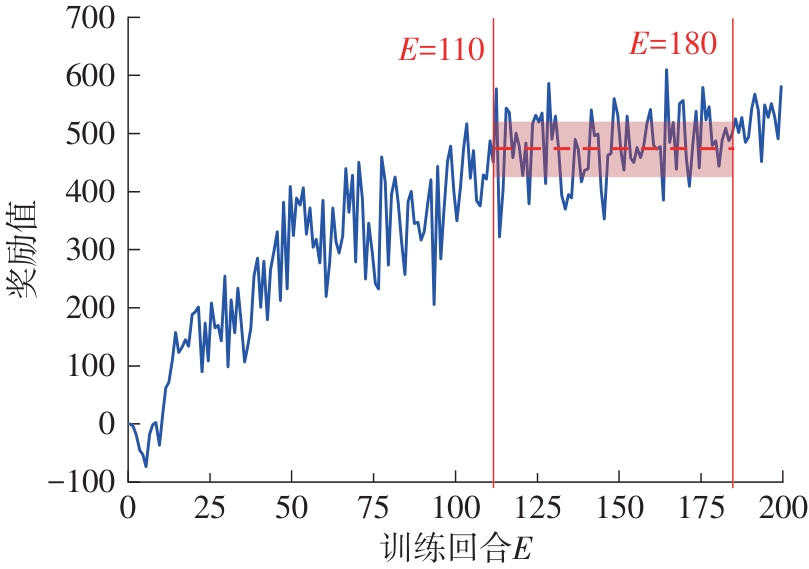
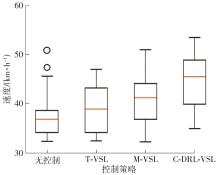
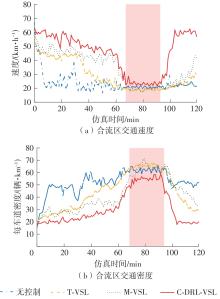
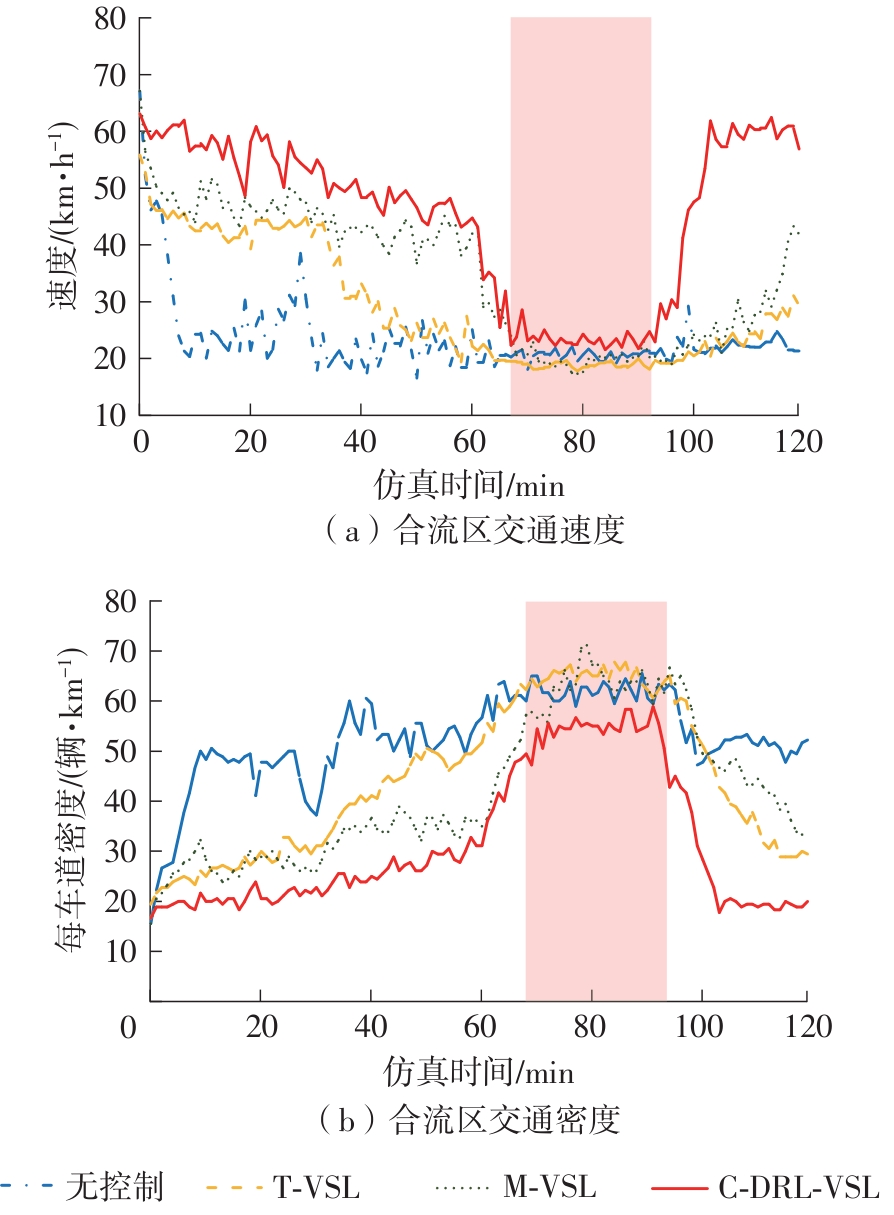
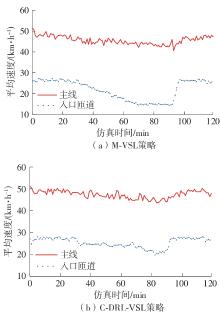
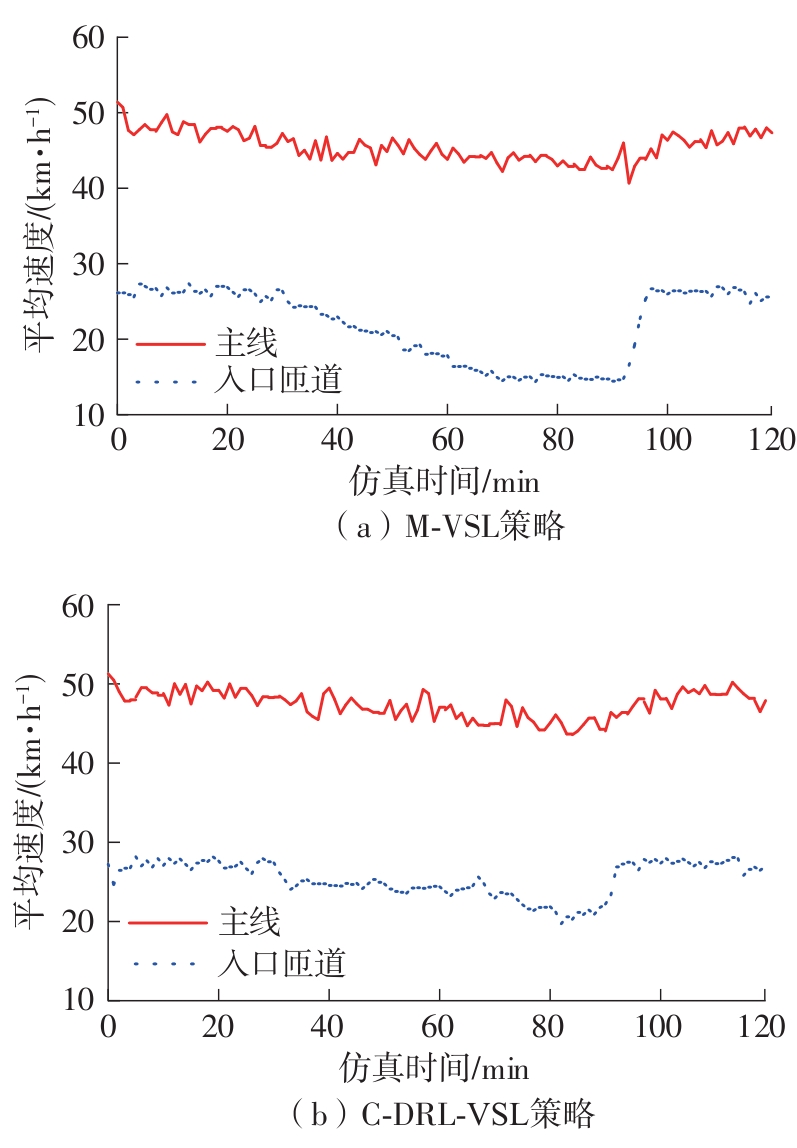
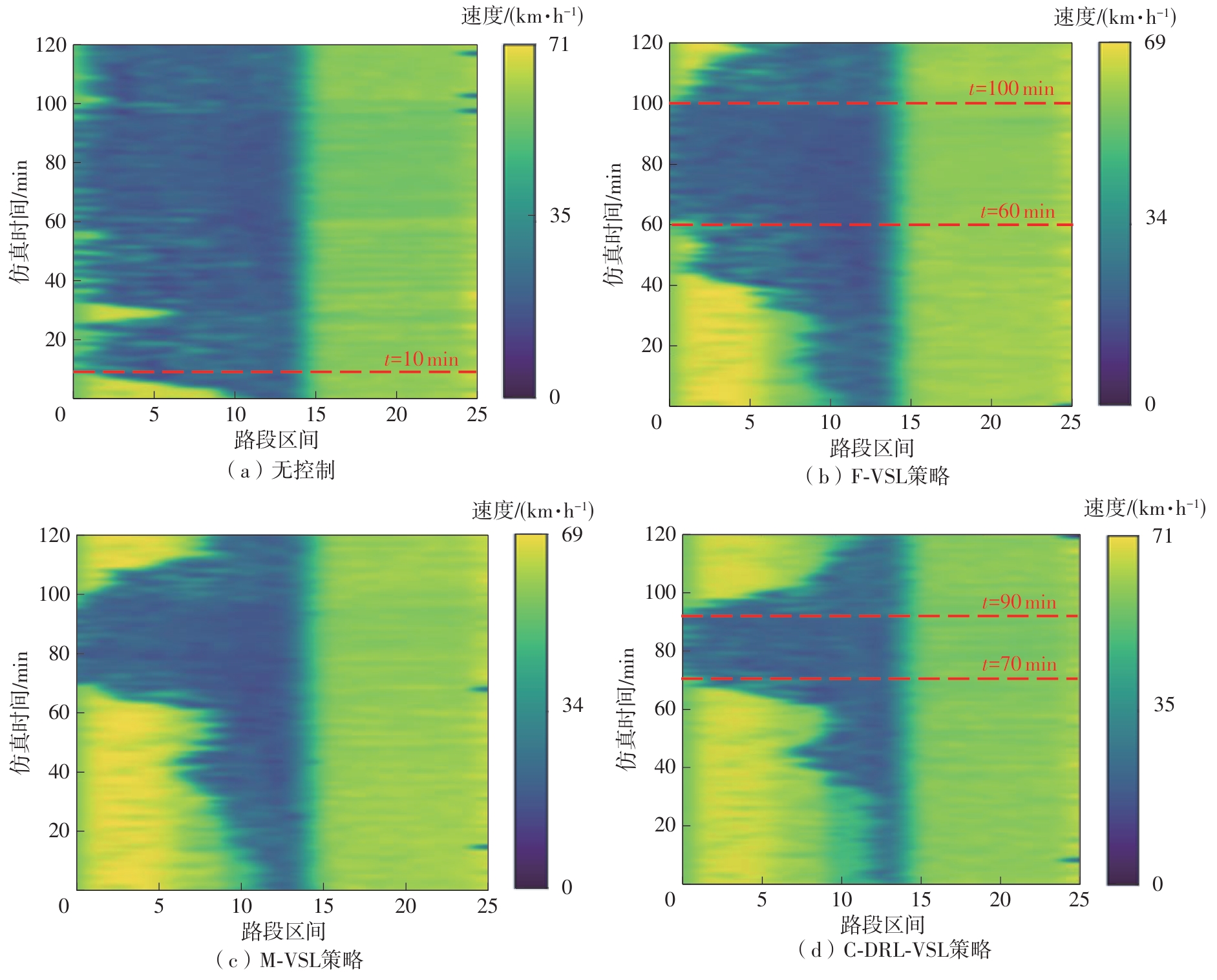
| [1] |
ZHAO J, MA W, XU H .Increasing the capacity of the intersection downstream of the freeway off-ramp using presignals[J].Computer-Aided Civil and Infrastructure Engineering,2017,32(8):674-690.
|
| [2] |
KHONDAKER B, KATTAN L .Variable speed limit:an overview[J].Transportation Letters,2015,7(5):264-278.
|
| [3] |
余向华 .快速路瓶颈通行能力陡降动态建模与交通控制机理解析[D].杭州:浙江大学,2023.
|
| [4] |
PAPAGEORGIOU M, KOSMATOPOULOS E, PAPAMICHAIL I .Effects of variable speed limits on motorway traffic flow[J].Transportation Research Record,2008,2047(1):37-48.
|
| [5] |
HEGYI A, DE SCHUTTER B, HELLENDOORN H .Model predictive control for optimal coordination of ramp metering and variable speed limits[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2005,13(3):185-209.
|
| [6] |
LIU H, ZHANG L, SUN D,et al .Optimize the se-ttings of variable speed limit system to improve the performance of freeway traffic[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2015,16(6):3249-3257.
|
| [7] |
周浩,胡坚明,张毅,等 .快速路可变限速与匝道控制协同优化策略[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2017,17(2):68-75.
|
|
ZHOU Hao, HU Jianming, ZHANG Yi,et al .A coordinated optimization strategy of variable speed limit and ramp metering for expressway[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2017,17(2):68-75.
|
| [8] |
ARORA K, KATTAN L .Operational and safety impacts of integrated variable speed limit with dynamic hard shoulder running[J].Journal of Intelligent Transportation Systems,2023,27(6):769-798.
|
| [9] |
MCCARTT A T, NORTHRUP V S, RETTING R A .Types and characteristics of ramp-related motor vehicle crashes on urban interstate roadways in Northern Virginia[J].Journal of Safety Research,2004,35(1):107-114.
|
| [10] |
GUO Y, LI Z, SAYED T .Analysis of crash rates at freeway diverge areas using Bayesian Tobit modeling framework[J].Journal of The Transportation Research Board,2019,2673(4):652-662.
|
| [11] |
CHENG M, ZHANG C H, JIN H,et al .Adaptive coordinated variable speed limit between highway mainline and on-ramp with deep reinforcement learning[J].Journal of Advanced Transportation,2022(1): 2435643/1-11.
|
| [12] |
WALRAVEN E, SPAAN M T J, BAKKER B .Traffic flow optimization:a reinforcement learning approach[J].Engineering Applications of Artificial Intelligence,2016,52:203-212.
|
| [13] |
ZHU F, UKKUSURI S V .Accounting for dynamic speed limit control in a stochastic traffic environment:a reinforcement learning approach[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2014,41:30-47.
|
| [14] |
GREGURIĆ M, KUŠIĆ K, VRBANIĆ F,et al .Variable speed limit control based on deep reinforcement learning:A possible implementation[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 International Symposium ELMAR.[S.l.]:IEEE, 2020:67-72.
|
| [15] |
白如玉,焦朋朋,陈越,等 .基于强化学习的车道级可变限速控制策略[J].交通信息与安全,2024,42(1):105-114.
|
|
BAI Ruyu, JIAO Pengpeng, CHEN Yue,et al .Di-fferential variable speed limit control strategy based on reinforcement learning[J].Journal of Transport Information and Safety,2024,42(1):105-114.
|
| [16] |
韩磊,张轮,郭为安 .混合交通流环境下基于改进强化学习的可变限速控制策略[J].交通运输系统工程与信息,2023,23(3):110-122.
|
|
HAN Lei, ZHANG Lun, GUO Weian .Variable speed limit control based on improved dueling double deep Q network under mixed traffic environment[J].Journal of Transportation Systems Engineering and Information Technology,2023,23(3):110-122.
|
| [17] |
WU J, QU X .Intersection control with connected and automated vehicles: a review[J].Journal of Intelligent and Connected Vehicles,2022,5(3):260-269.
|
| [18] |
VRBANIĆ F, TIŠLJARIĆ L, MAJSTOROVIĆ Ž,et al .Reinforcement learning-based dynamic zone placement variable speed limit control for mixed traffic flows using speed transition matrices for state estimation[J].Machines,2023,11(4):479-494.
|
| [19] |
WANG X, ZHANG R, GOU Y,et al .Variable speed limit control method of freeway mainline in intelligent connected environment[J].Journal of Advanced Transportation,2021(1):8863487/1-12.
|
| [20] |
邵敬波,黄轲,张兆磊,等 .高速公路连续瓶颈混合交通流可变限速与换道协同控制方法[J].交通信息与安全,2023,41(3):59-68,79.
|
|
SHAO Jingbo, HUANG Ke, ZHANG Zhaolei,et al .A cooperative control method of variable speed limit and lane change for mixed traffic flow on continuous bottlenecks of freeway[J].Journal of Transport Information and Safety,2023,41(3):59-68,79.
|
| [21] |
KONTORINAKI M, SPILIOPOULOU A, RONCOLI C,et al .First-order traffic flow models incorporating capacity drop:overview and real-data validation[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2017,106:52-75.
|
| [22] |
PAPAGEORGIOU M, PAPAMICHAIL I, SPILIOPOULOU A D,et al .Real-time merging traffic control with app-lications to toll plaza and work zone management[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2008,16(5):535-553.
|
| [23] |
HADIUZZAMAN M, QIU T Z, LU X Y .Variable speed limit control design for relieving congestion caused by active bottlenecks[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering,2013,139(4):358-370.
|
| [24] |
DERVISOGLU G, GOMES G, KWON J,et al .Automatic calibration of the fundamental diagram and empirical observations on capacity[C]∥Proceedings of the Transportation Research Board 88th Annual Meeting. Washington D C:TRB,2009:31-59.
|
| [25] |
GAO H, JIA H, WU R,et al .Variable speed limit control for mixed traffic flow on highways based on deep-reinforcement learning[J].Journal of Transportation Engineering,Part A:Systems,2024,150(3):04023147/1-19.
|
| [26] |
AHMIC K, TAHIRBEGOVIC A, TAHIROVIC A,et al .Simulation framework for platooning based on gazebo and SUMO[C]∥Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE 3rd Connected and Automated Vehicles Symposium (CAVS). Victoria:IEEE,2020:1-7.
|
| [27] |
姚志洪,顾秋凡,徐桃让,等 .考虑时延的智能网联汽车混合交通流稳定性分析[J].控制与决策,2022,37(6):1505-1512.
|
|
YAO Zhihong, GU Qiufan, XU Taorang,et al .Stability of mixed traffic flow with intelligent connected vehicles considering time delay[J].Control and Decision,2022,37(6):1505-1512.
|
| [28] |
JIA D, NGODUY D, VU H L .A multiclass microscopic model for heterogeneous platoon with vehicle-to-vehicle communication[J].Transportmetrica B:Transport Dynamics,2019,7(1):311-335.
|
| [29] |
秦严严,王昊,王炜,等 .混有协同自适应巡航控制车辆的异质交通流稳定性解析与基本图模型[J].物理学报,2017,66(9):094502/1-9.
|
|
QIN Yanyan, WANG Hao, WANG Wei,et al .Stability analysis and fundamental diagram of heterogeneous traffic flow mixed with cooperative adaptive cruise control vehicles[J].Acta Physica Sinica,2017,66(9):094502/1-9.
|
| [30] |
孙健,宋茂星,邱果,等 .基于电动汽车大数据的多等级充电站选址与服务能力研究[J].中国公路学报,2024,37(4):48-60.
|
|
SUN Jian, SONG Maoxing, QIU Guo,et al .Location and service capability of multilevel charging stations based on electric vehicle big data[J].China Journal of Highway and Transport,2024,37(4):48-60.
|