华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (8): 42-49.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240355
自动驾驶模块化公交服务优化研究
张积昱1, 唐春艳2
- 1.长安大学 运输工程学院,陕西 西安 710064
2.大连海事大学 交通运输工程学院,辽宁 大连 116026
A Study on the Optimization of Modular Autonomous Public Transit Services
ZHANG Jiyu1, TANG Chunyan2
- 1.School of Transportation Engineering,Chang’an University,Xi’an 710064,Shaanxi,China
2.College of Transportation Engineering,Dalian Maritime University,Dalian 116026,Liaoning,China
摘要:
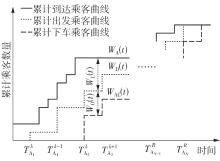
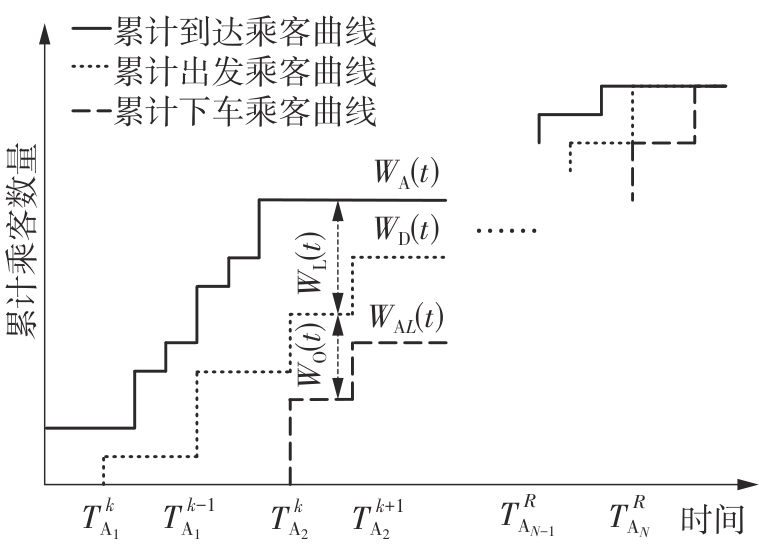
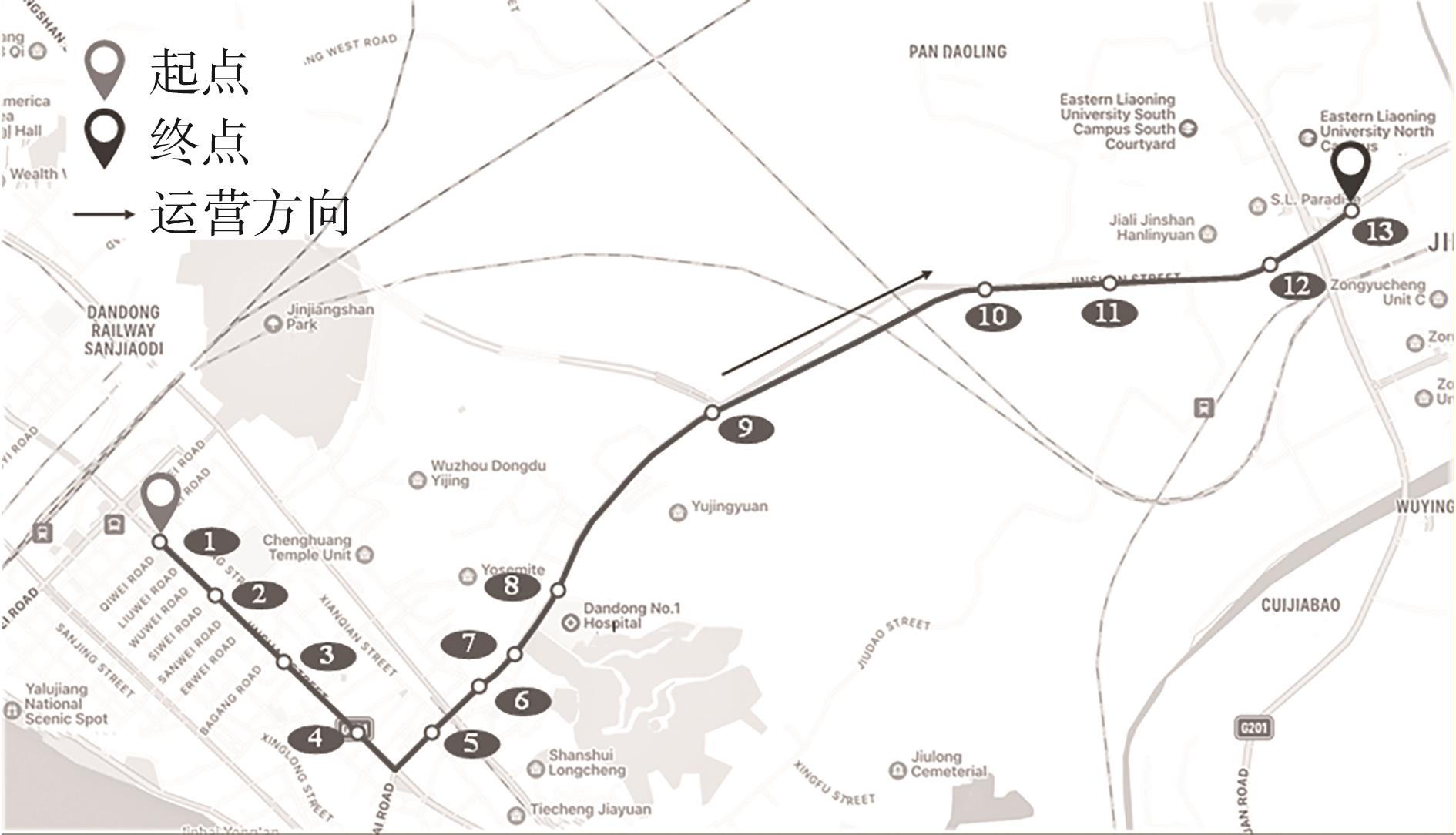
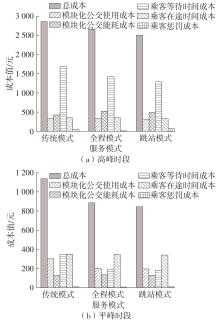
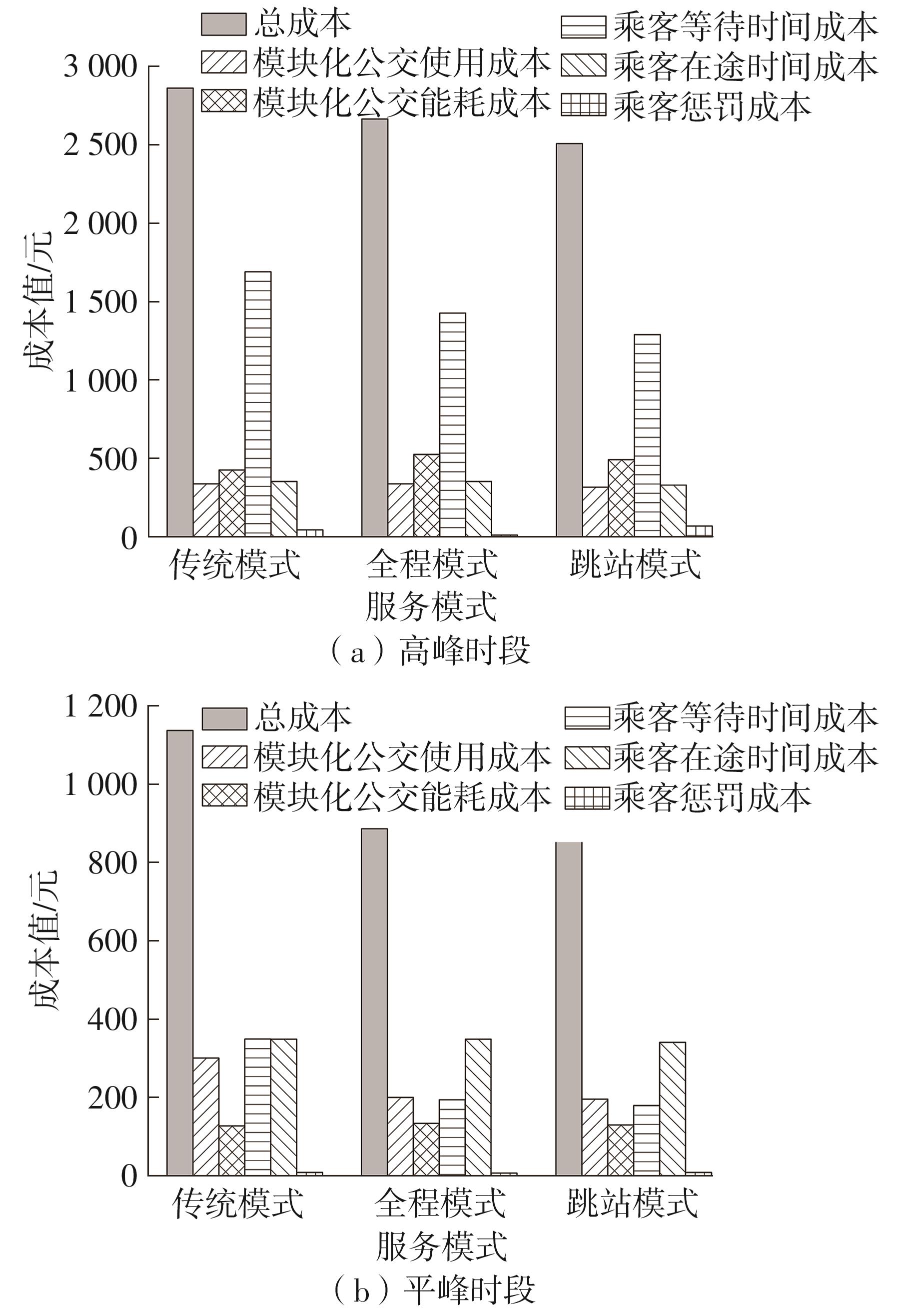
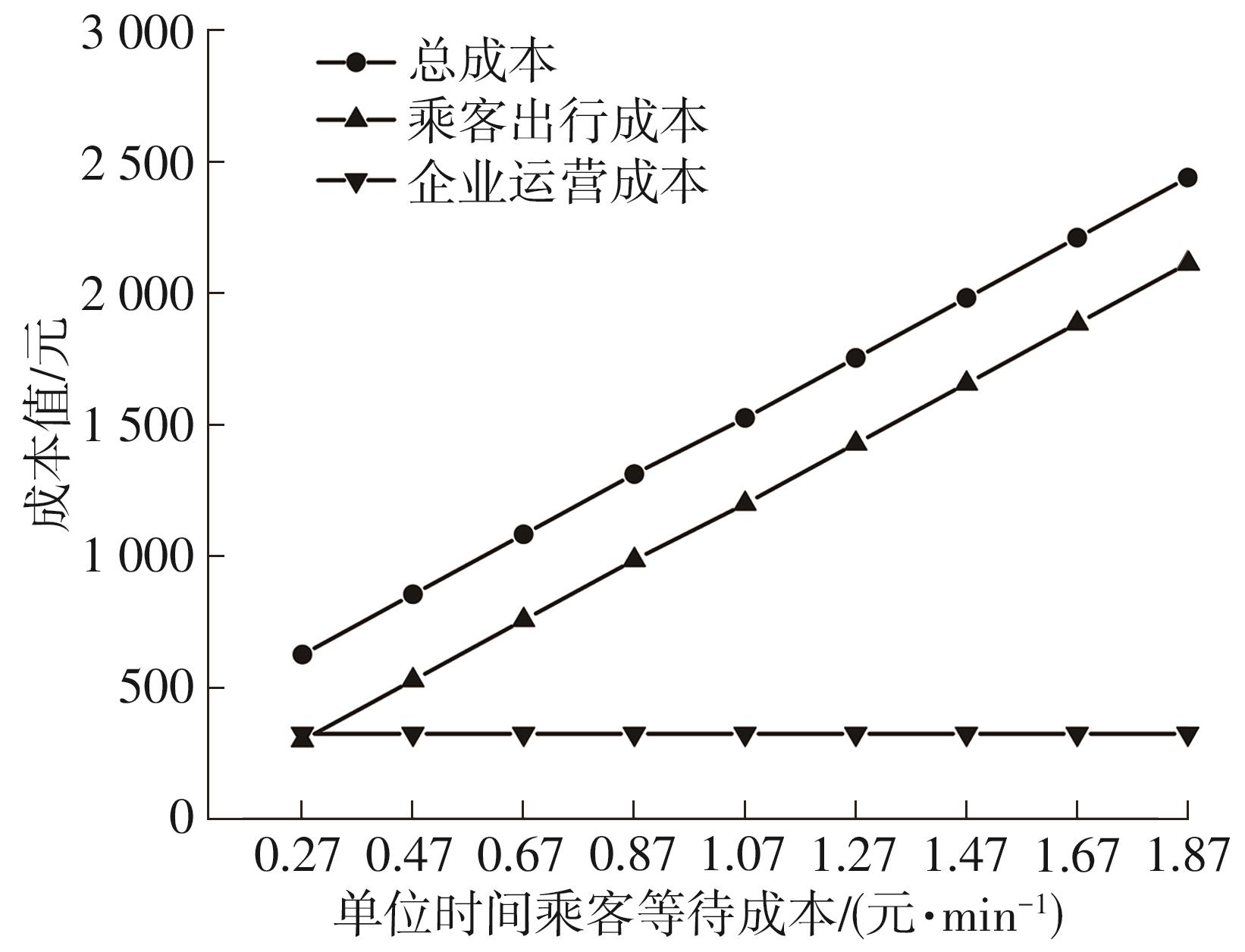
随着智能网联技术和自动驾驶技术的快速发展,新兴的自动驾驶模块化公交在公共交通领域受到极大的关注。它可通过车辆间的自由组合/分离操作,实现公交容量的灵活设计,以适应客流时空分布不均的需求。然而既有的全程式服务模式,难以充分发挥模块化公交的灵活运营特性以高效满足乘客的差异化需求。因此,提出一种面向自动驾驶模块化公交的新服务模式,该模式充分结合模块化公交车的自由组合/分离特性以及跳站策略的差异化服务优势,实现公交线路供给的高效化、差异化服务设计。首先采用离散时间建模方法和拓展的Newell理论,以乘客出行成本和企业运营成本最小为优化目标,构建自动驾驶模块化公交跳站服务优化模型,实现发车间隔、发车编组及跳站计划的同时优化;其中,通过对Newell理论进行拓展,使其由计算单个站点的乘客等待时间和在途时间,拓展为从整个系统角度高效计算乘客等待时间和在途时间,极大地降低了建模的复杂度。其次,以丹东市公交110路线路为例,给出优化后的运营方案,并在平峰和高峰时段与传统固定容量公交服务模式和模块化公交全程式服务模式进行比较。结果表明:该研究提出的模块化公交跳站服务模式极大地降低系统总成本,节约3.34%~24.65%,其中,乘客等待时间成本和在途时间成本分别节约7.49%~48.52%和2.31%~6.28%;此外,在高峰时段,模块化公交发车频率较平峰时段更加密集,且倾向于采用低容量编组和跳站服务策略。
中图分类号: