华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2025, Vol. 53 ›› Issue (4): 1-12.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.240260
基于空间活力的轨道交通枢纽上盖商业空间设计
蒋涛1,2,3, 王静1,3, 王永娣1
- 1.华南理工大学 建筑学院,广东 广州 510640
2.华南理工大学 建筑设计研究院有限公司,广东 广州 510640
3.华南理工大学 亚热带建筑与城市科学全国重点实验室,广东 广州 510640
Commercial Space Design Above Rail Transit Hub on Spatial Vitality
JIANG Tao1,2,3, WANG Jing1,3, WANG Yongdi1
- 1.School of Architecture,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
2.Architecture Design & Research Institute of SCUT Co. ,Ltd. ,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
3.State Key Laboratory of Subtropical Building and Urban Science,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
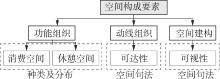
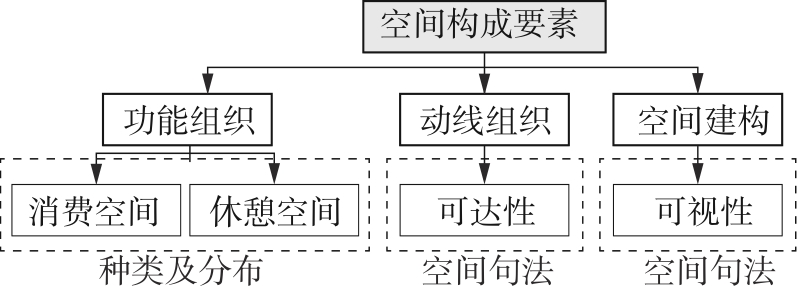
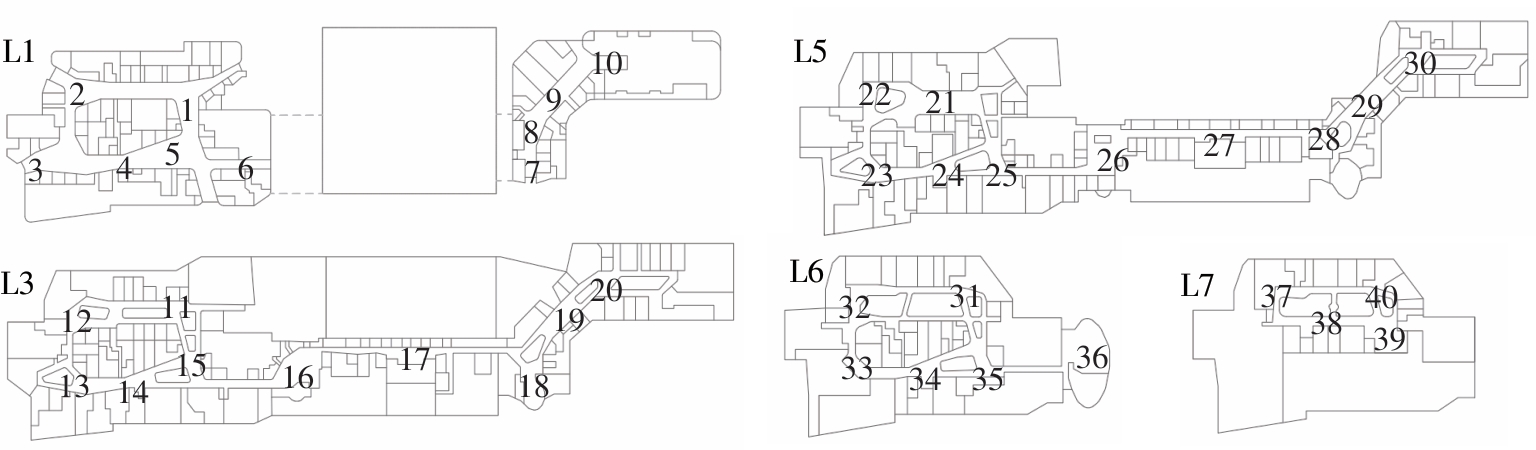
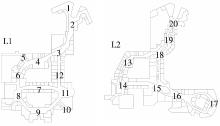
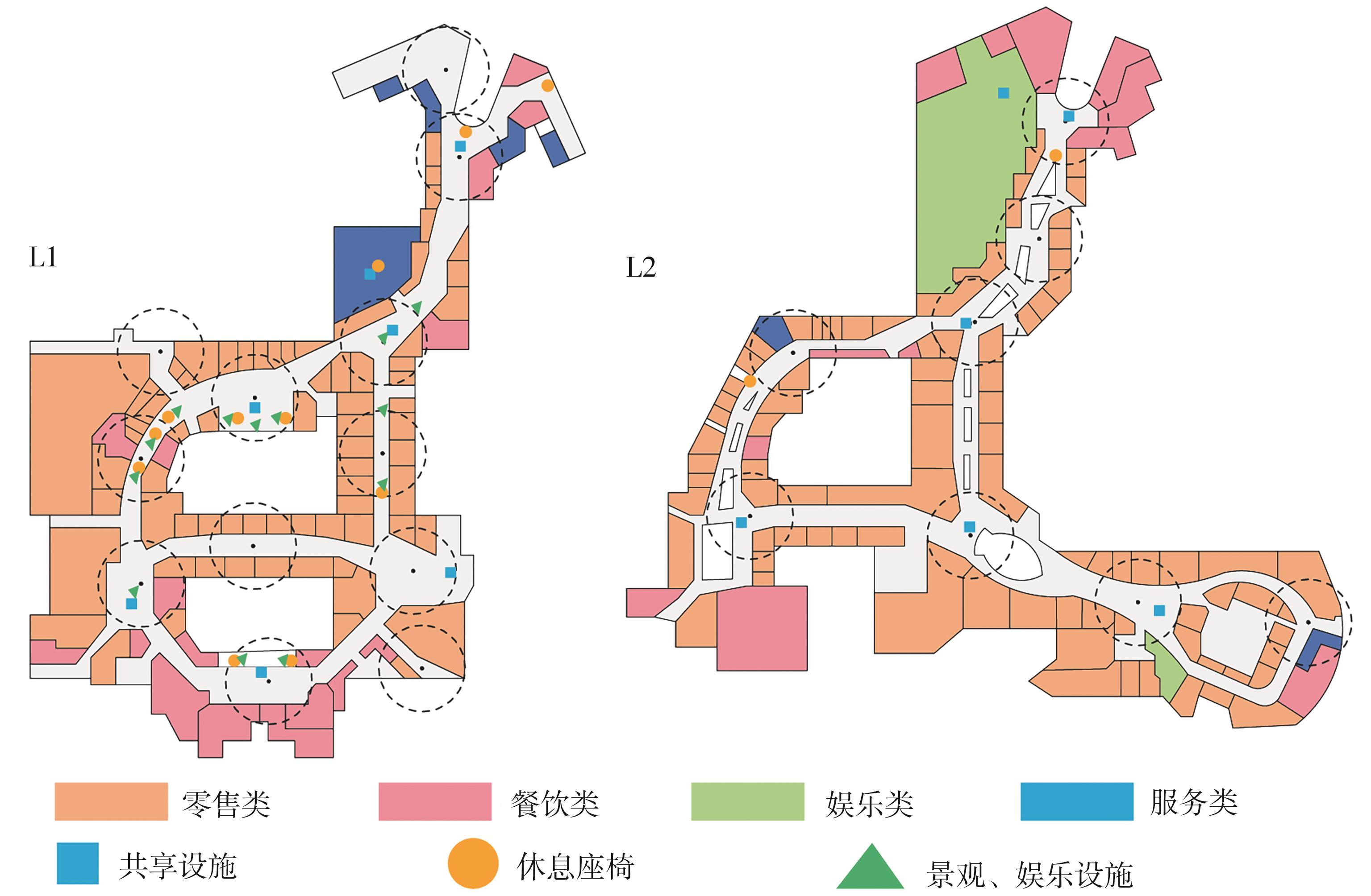
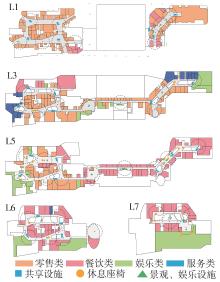
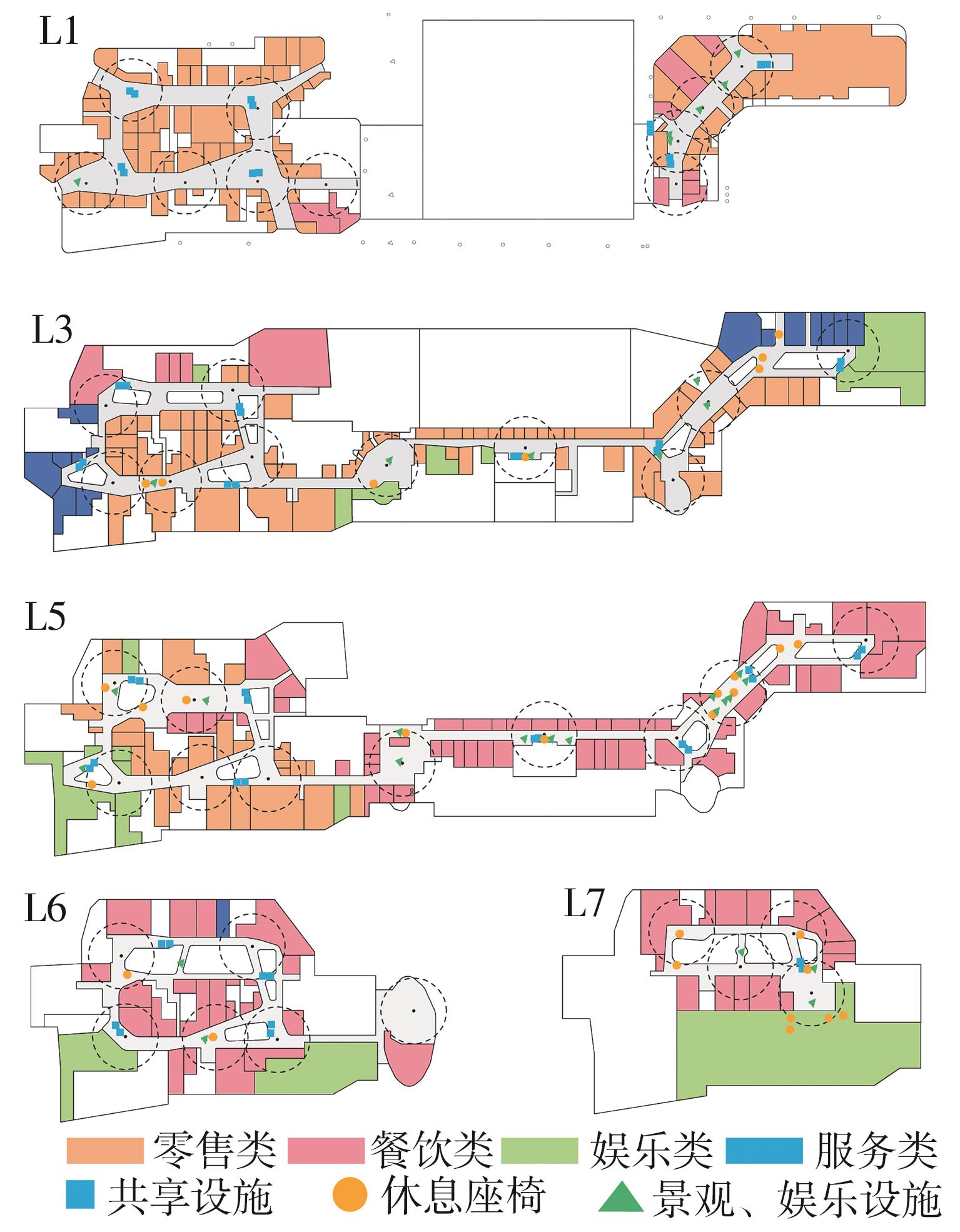
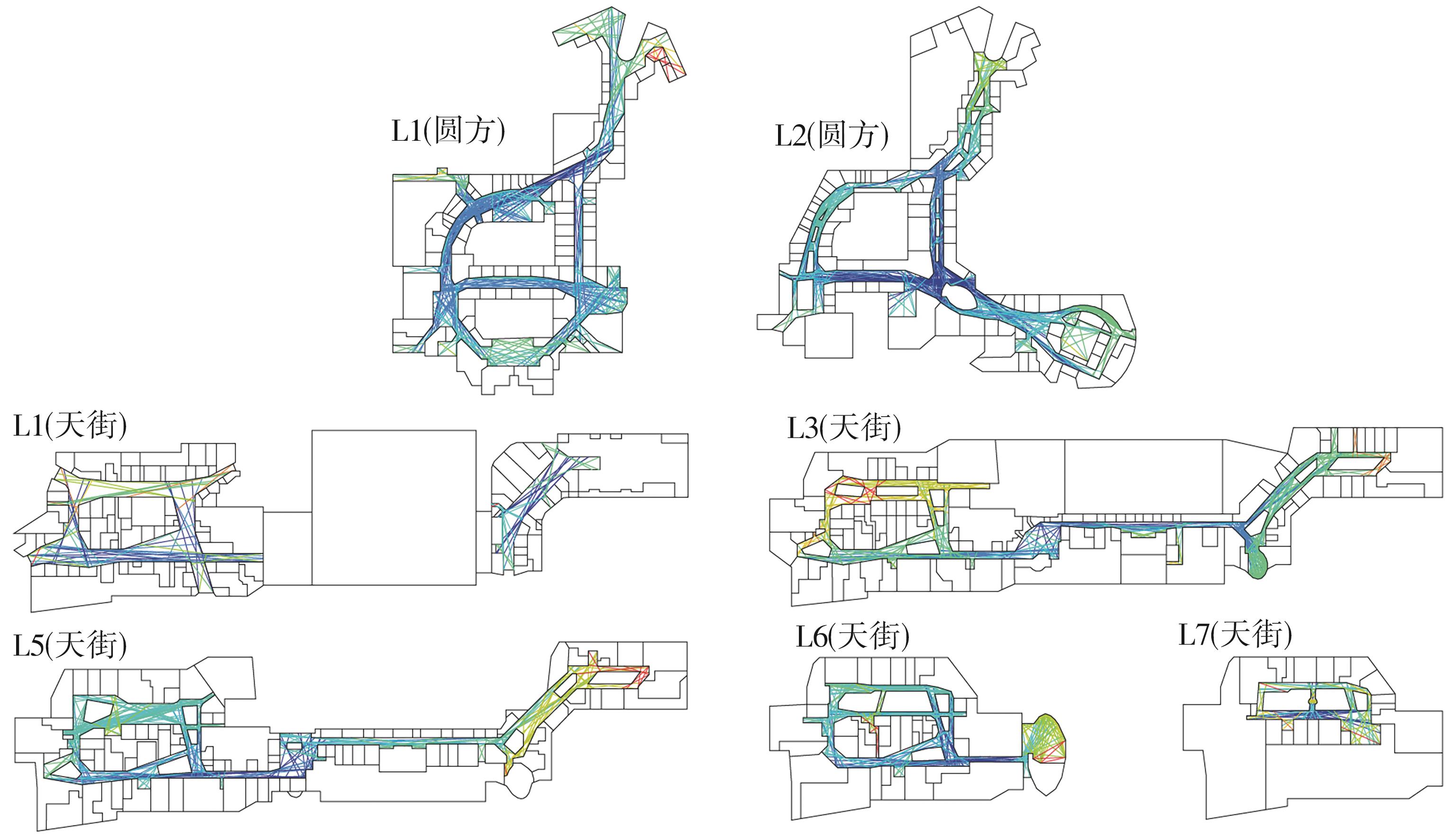
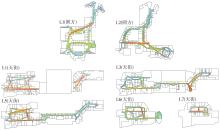
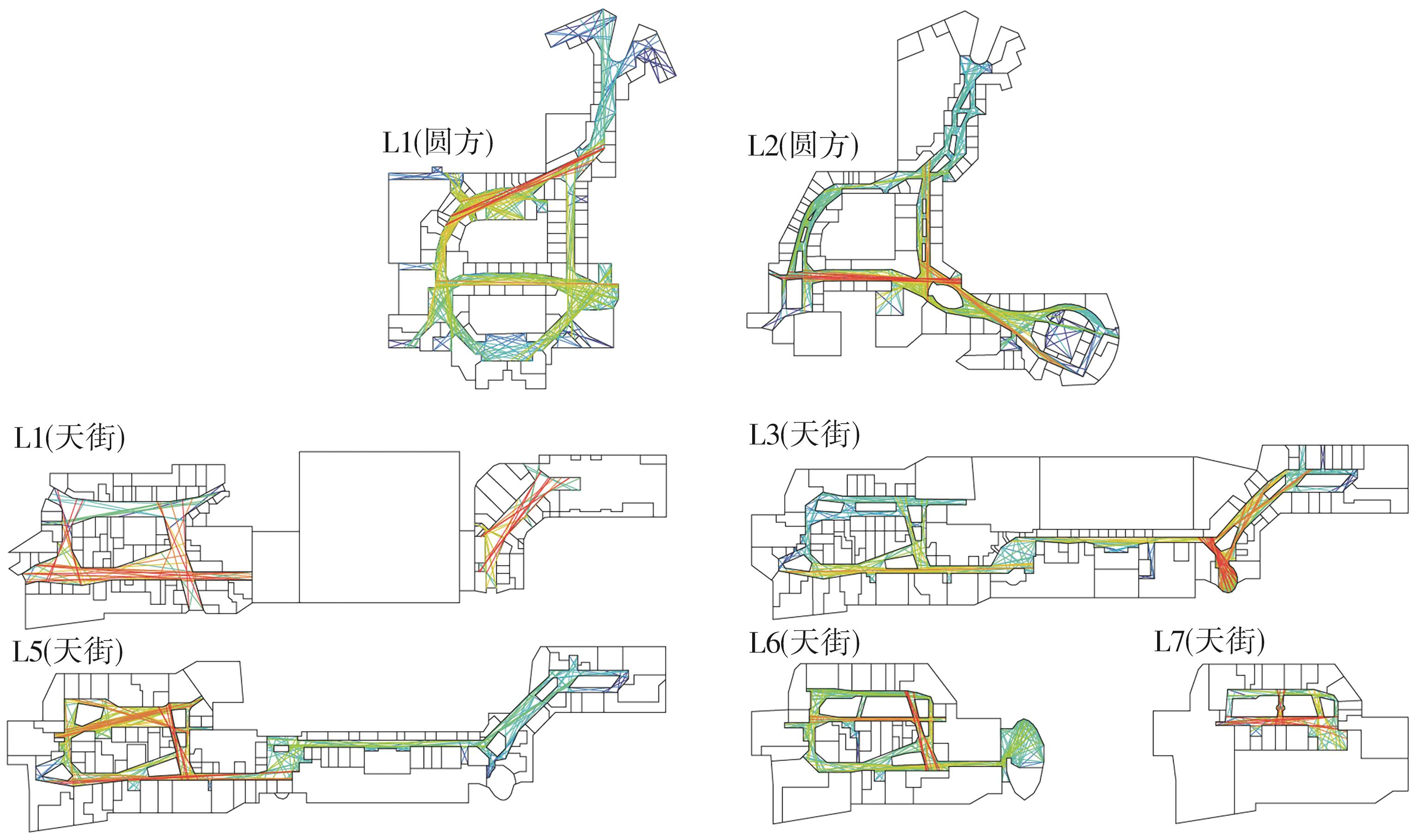
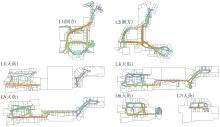
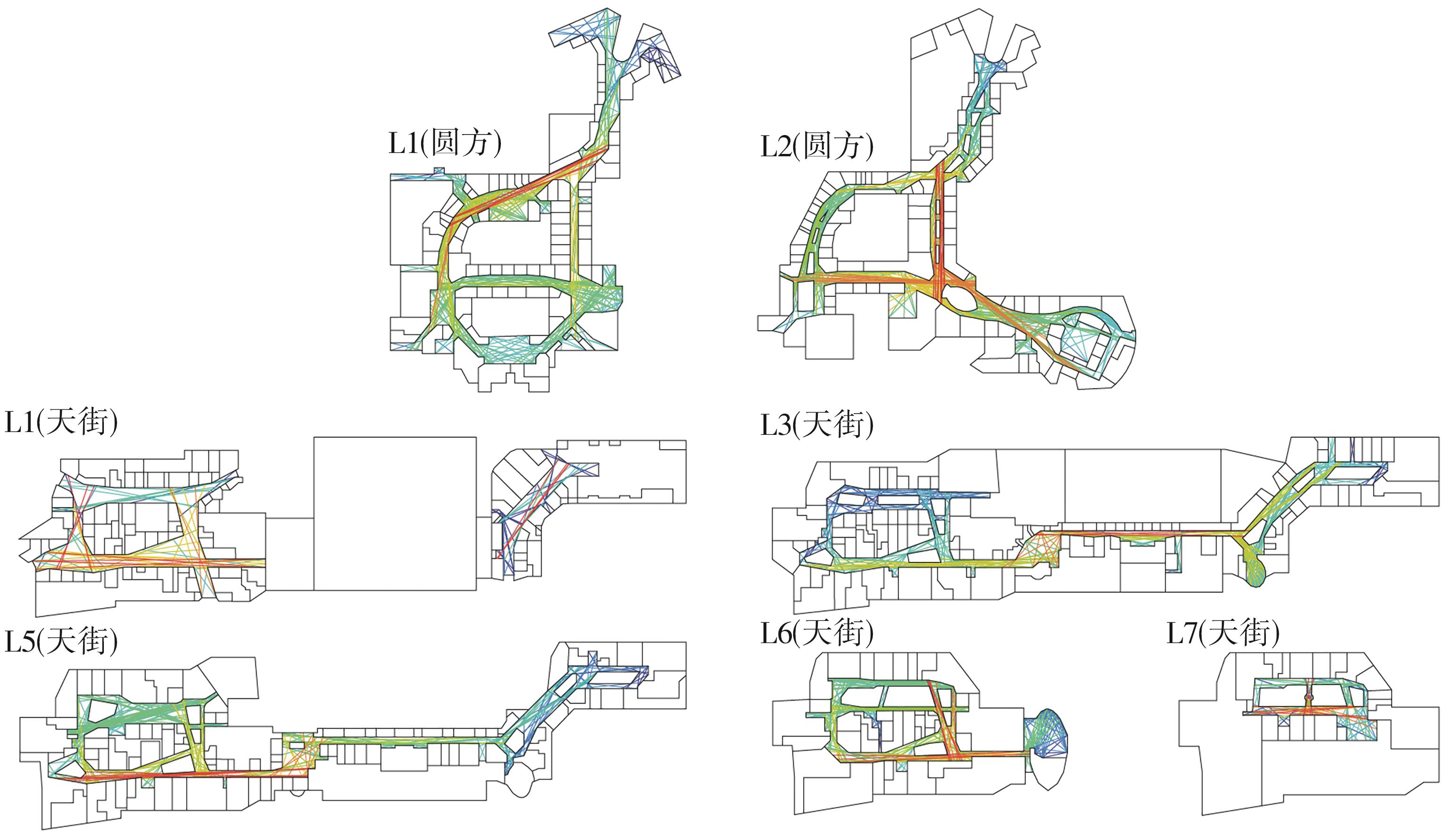
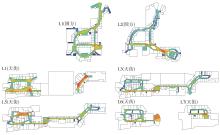
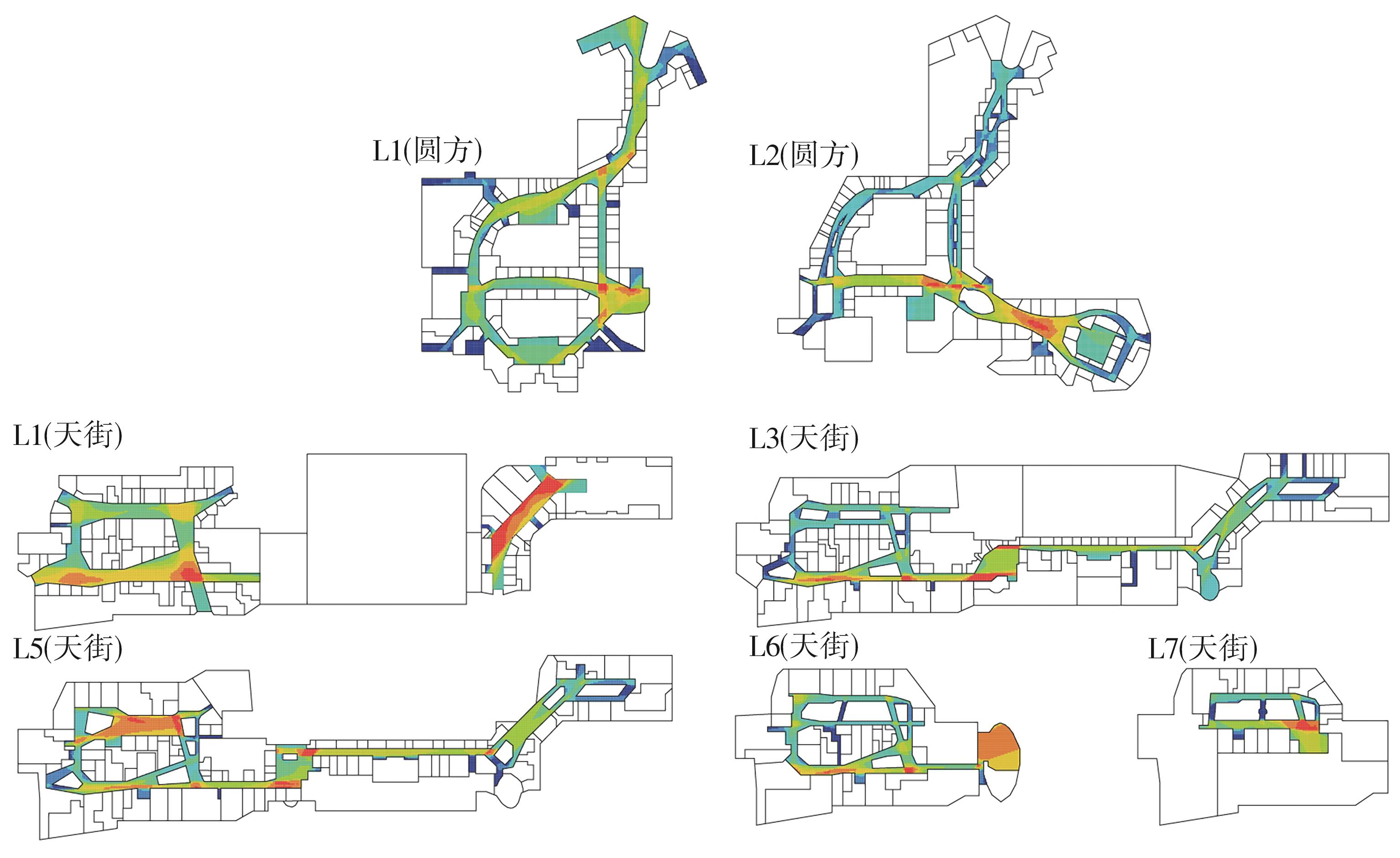
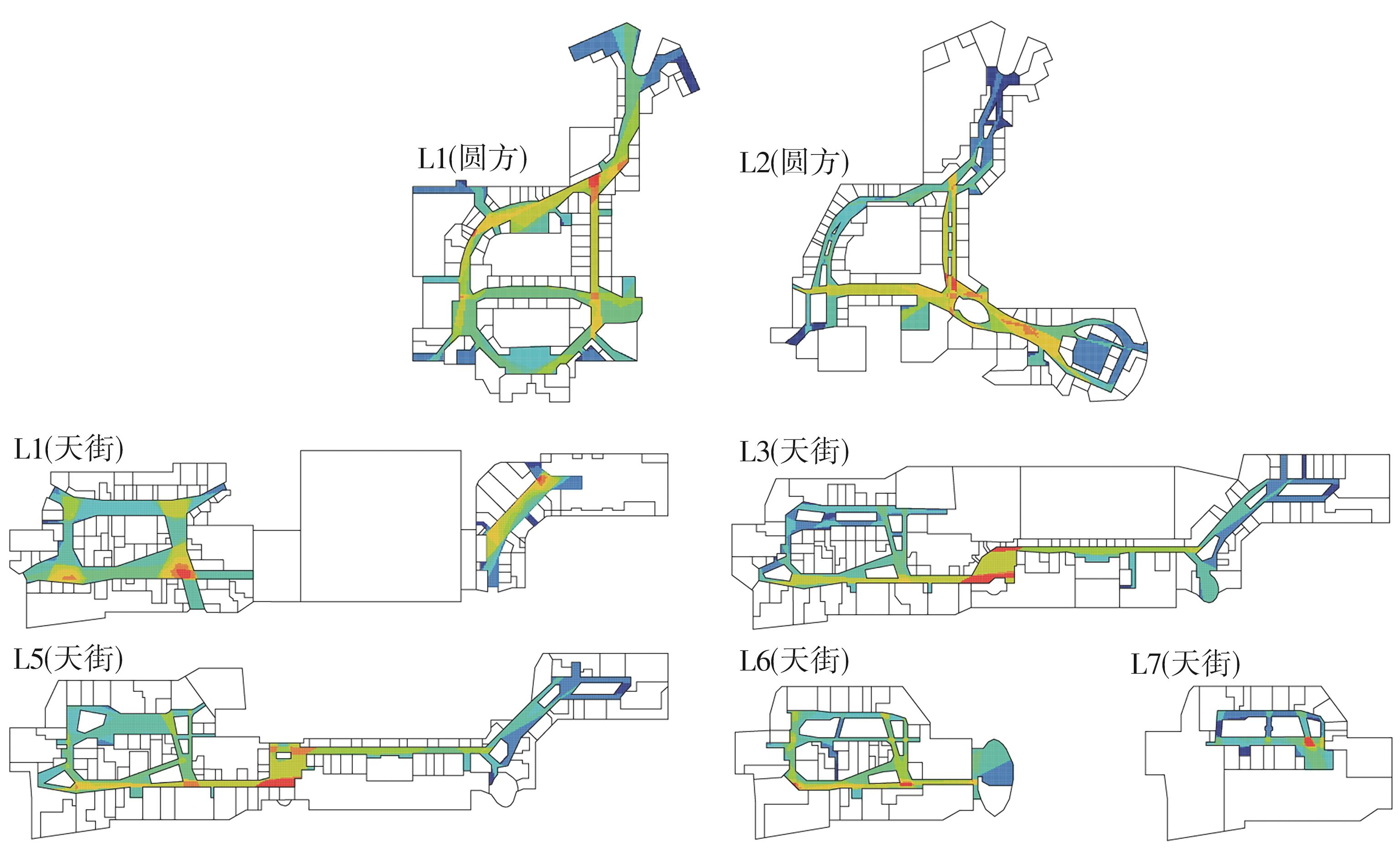
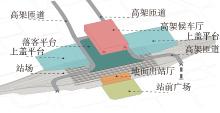
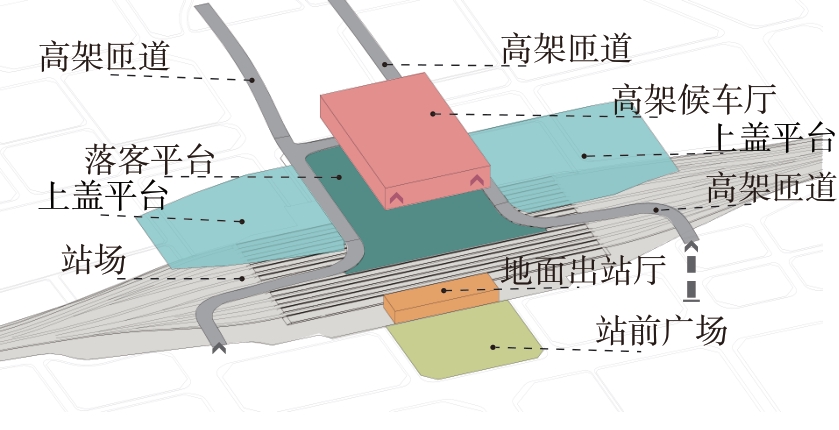
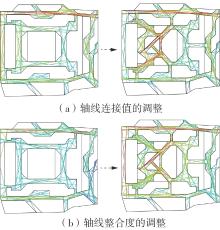
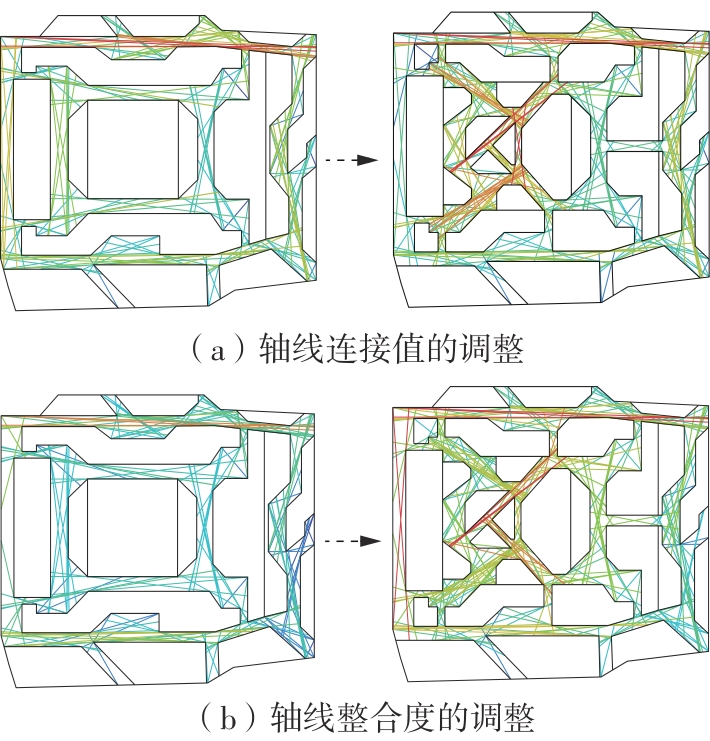
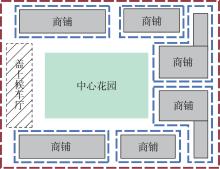
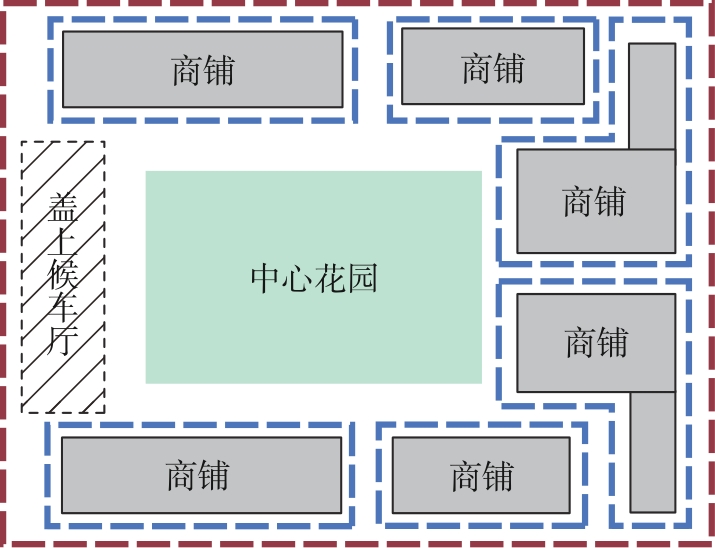
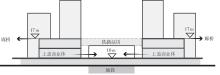
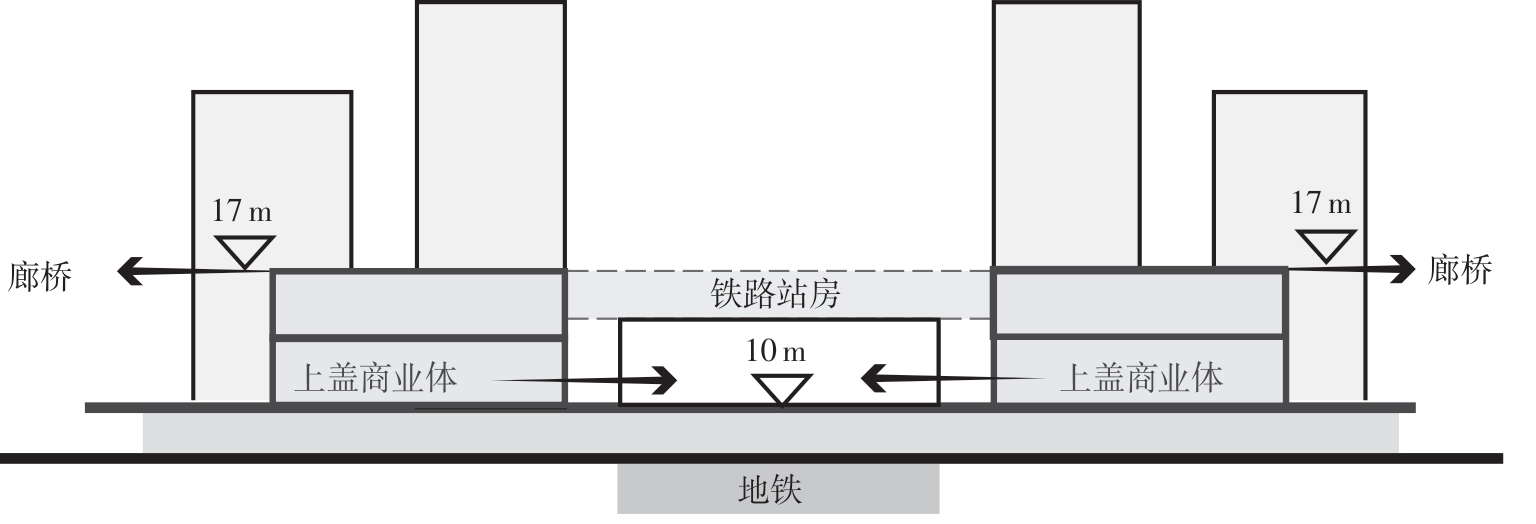
轨道交通枢纽具有天然的人流优势,在其上方进行立体化、复合化的上盖商业开发,已经成为新的建设模式,轨道交通枢纽上盖商业空间成为了旅客、通勤者及市民进行消费与社交活动的重要场所。大多数轨道交通枢纽上盖商业空间的开发量都较大,空间组织关系复杂,容易出现功能需求不匹配、服务设施供给不足、动线组织混乱、换乘效率低下、空间品质不佳等问题,导致人流未得到充分引导、空间利用率低,影响到商业空间活力,进而影响商业空间的良性运营。因此,该文从轨道交通枢纽上盖商业空间活力研究入手,首先对轨道交通枢纽上盖商业空间构成要素进行分类研究,从功能组织、动线组织以及空间建构3个维度进行界定。然后选取国内已建成的2个轨道交通枢纽上盖商业空间进行实例分析,结合实地调研对样本空间进行筛选,梳理出对应3个维度的15个指标,采用空间句法理论及SPSS相关性分析等数据分析方法对指标进行量化研究。结果表明,空间活力与功能密度没有直接呈现出相关性,与动线组织的绝大部分指标呈现出较强的相关性,与空间建构的各项指标均呈现出较强的相关性。总结出的影响空间活力的关键指标,主要包括功能密度、空间可达性及可视性、出入口、垂直交通以及休憩空间的位置等。最后,结合成都站上盖商业开发项目提出设计策略的具体操作。该研究可为轨道交通枢纽上盖商业空间的相关设计提供了设计参考,并对相关理论探索带来新启示。
中图分类号: