| 1 |
YANG J, SAWAN M .From seizure detection to smart and fully embedded seizure prediction engine:a review[J].IEEE Transactions on Biomedical Circuits and Systems,2020,14(5):1008-1023.
|
| 2 |
ABDENNADHER M, SAXENA A, PAVLOVA M K .Evaluation and management of first-time seizure in adults [J].Semin Neurol,2021,41(5):477-482.
|
| 3 |
LIU J M, LIU Z L, MENG F X .The economic burden of epilepsy in a sample of people with epilepsy in China [J].Epilepsy Research,2013,103(2):288-293.
|
| 4 |
HAROWITZ J, CRANDALL L, McGUONE D,et al .Seizure-related deaths in children:the expanding spectrum[J].Epilepsia,2021,62(3):570-582.
|
| 5 |
KALEEM M, GURVE D, GUERGACHI A,et al .Patient-specific seizure detection in long-term EEG using signal-derived empirical mode decomposition (EMD)-based dictionary approach[J].IEEE Biomedical Signal Process Control,2018,15(5):157-165.
|
| 6 |
YAO X H, CHENG Q, ZHANG G Q .Automated classification of seizures against nonseizures:a deep learning approach[EB/OL].(2019-06-05)[2023-09-14]..
|
| 7 |
WEI Z C, ZOU J Z, ZHANG J,et al .Automatic epileptic EEG detection using convolutional neural network with improvements in time domain[J].IEEE Biomedical Signal Process Control,2019,53:101551/1-11.
|
| 8 |
HUANG C B, CHEN W T, CAO G T .Automatic epileptic seizure detection via attention-based CNN-BiRNN[C]∥ Proceedings of 2019 IEEE International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedicine.San Diego:IEEE,2019:660-663.
|
| 9 |
DUAN L J, WANG Z Y, QIAO Y H,et al .An automatic method for epileptic seizure detection based on deep metric learning[J].IEEE Journal of Biomedical and Health Informatics,2021,26(5):2147-2157.
|
| 10 |
YAO X H, LI X J, YE Q,et al .A robust deep learning approach for automatic classification of seizures against non-seizures[J].IEEE Biomedical Signal Processing and Control,2021,64:102215/1-20.
|
| 11 |
杨涌,秦小林,林小光,等 .基于数据增强和深度学习的特定患者癫痫检测分析方法[J].生物医学工程学杂志,2022,39(2):293-300.
|
|
YANG Yong, QIN Xiaolin, LIN Xiaoguang,et al .Epilepsy detection and analysis method for specific patient based on data augmentation and deep learning[J].Journal of Biomedical Engineering,2022,39(2):293-300.
|
| 12 |
ZHAO S, YANG J, XU Y,et al .Binary single-dimensional convolutional neural network for seizure prediction[EB/OL].(2022-06-08)[2023-09-14]..
|
| 13 |
GODOY R V, REIS T J, POLEGATO P H,et al .EEG-based epileptic seizure prediction using temporal multi-channel transformers[EB/OL].(2022-09-18)[2023-09-14]..
|
| 14 |
BASTANY Z, ASKARI S, DUMONT G A,et al .Association of cortical spreading depression and seizures in patients with medically intractable epilepsy[J].Clinical Neurophysiology,2020,131(12):2861-2874.
|
| 15 |
REDDY G, RAO R .Automated identification system for seizure EEG signals using tunable-Q wavelet transform[J].Engineering Science and Technology,an International Journal,2017,20(5):1486-1493.
|
| 16 |
HUANG Z, YANG X, HUANG S,et al .SECP-Net:SE-connection pyramid network for segmentation of organs at risk with nasopharyngeal carcinoma[J].Bioengineering,2023,10(10):1119/1-14.
|
| 17 |
GUO L, CHEN D, JIA K .Knowledge transferred adaptive filter pruning for CNN compression and acceleration[J].Science China Information Sciences,2022,65(12):229101/1-2.
|
| 18 |
赵荣超,吴百礼,陈祝云,等 .多尺度时空信息融合驱动的图神经网络故障诊断方法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(12):42-52.
|
|
ZHAO Rongchao, WU Baili, CHEN Zhuyun,et al .Graph neural network for fault diagnosis with multi-scale time-spatial information fusion mechanism[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,51(12):42-52.
|
| 19 |
CHEVYREV I, KORMILITZIN A .A primer on the signature method in machine learning[EB/OL].(2022-06-29)[2023-09-14]..
|
| 20 |
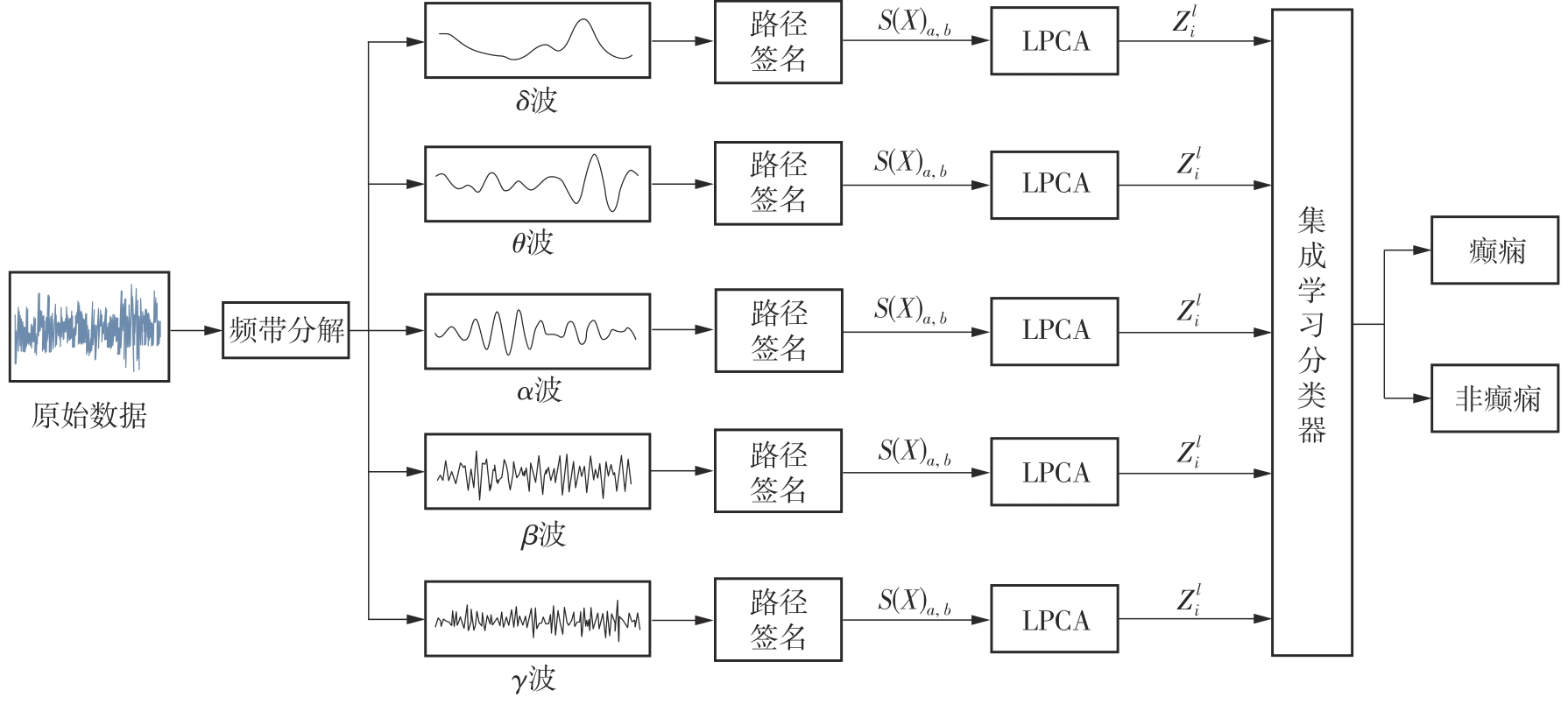
TANG Y, WU Q, MAO H,et al .Epileptic seizure detection based on path signature and Bi-LSTM network with attention mechanism[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Systems and Rehabilitation Engineering,2024,32(1):304-313.
|
| 21 |
ALUJA-BANET T, NONELL-TORRENT R .Local principal components analysis[J].Qüestiió,1991,15(3):267-278.
|
| 22 |
WU X, ZHOU J L, HE J X .Maximum likelihood estimation image denoising using non-local principle component analysis[J].Acta Photonica Sinica,2011,40(12):1827-1832.
|
| 23 |
KAMBHATLA N, LEEN T K .Dimension reduction by local principal component analysis[J].Neural Computation,1997,9(7):1493-1516.
|
| 24 |
AKYOL K .Stacking ensemble based deep neural networks modeling for effective epileptic seizure detection [J].Expert Systems with Applications,2020,148(15):249-258.
|
| 25 |
MURSALIN M, ZHANG Y, CHEN Y,et al .Automated epileptic seizure detection using improved correlation-based feature selection with random forest classifier[J].Neurocomputing,2017,241(7):204-214.
|
 ), YANG Hui1, WU Qianyi2, MAO Haifeng3
), YANG Hui1, WU Qianyi2, MAO Haifeng3