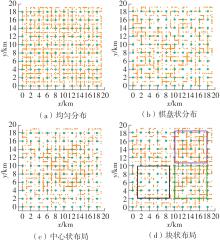
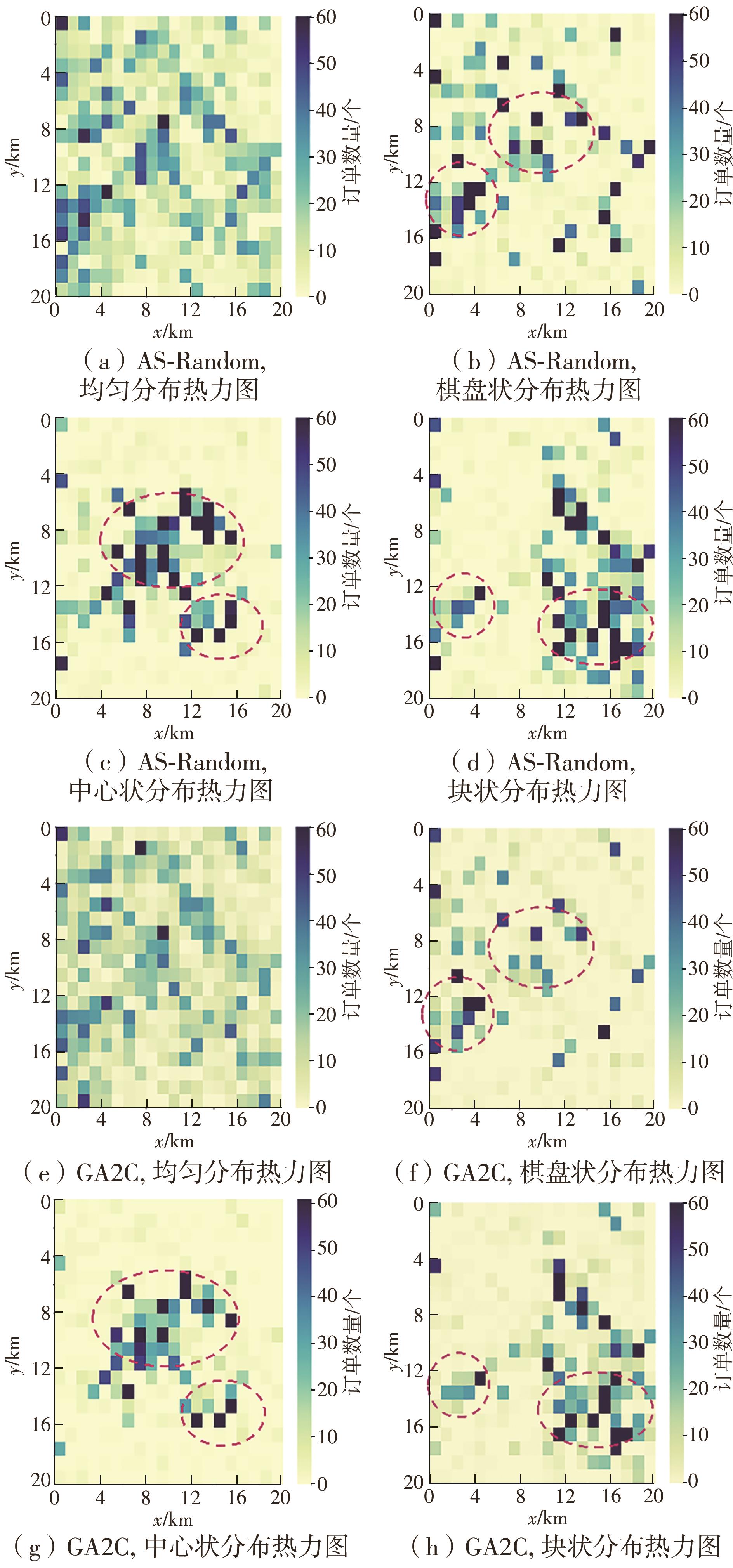
| 1 |
XU Z T, YIN Y F, CHAO X L,et al .A generalized fluid model of ride-hailing systems[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2021,150:587-605.
|
| 2 |
CHENG S F, JHA S S, RAJENDRAM R .Taxis strike back:a field trial of the driver guidance system[C]∥Proceedings of the 17th International Conference on Autonomous Agents and Multi-Agent Systems.Richland:ACM,2018:577-584.
|
| 3 |
LEI D C, WU Y S .Order-dispatching strategy induced by optimal transport plan for an online ride-hailing system[J].Transportation Research Record,2022,2676:156-169.
|
| 4 |
ODA T, CARLEE J W .MOVI:a model-free approach to dynamic fleet management[C]∥Proceedings of the IEEE INFOCOM 2018-IEEE Conference on Computer Communications.New York:IEEE,2018:2708-2716.
|
| 5 |
温惠英,林译峰,吴昊书,等 .基于城市道路交通环境演变的ECEA路径规划算法[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(10):1-10.
|
|
WEN Huiying, LIN Yifeng, WU Haoshu,et al .Extended co-evolutionary algorithm for path planning based on the urban traffic environment evolution[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2021,49(10):1-10.
|
| 6 |
XU J, ROUHOLLAH R, LADISLAU B,et al .A taxi dispatch system based on prediction of demand and destination[J].Journal of Parallel and Distributed Computing,2021,157(11):269-279.
|
| 7 |
ZHANG L Y, TAO H, MIN Y,et al .A taxi order dispatch model based on combinatorial optimization[C]∥Proceedings of the 23rd ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.New York:ACM,2017:2151-2159.
|
| 8 |
罗瑞发,郝慧君,徐桃让,等 .考虑时延的网联车混合交通流基本图模型[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(1):106-113.
|
|
LUO Ruifa, HAO Huijun, XU Taorang,et al .Fundamental diagram model of mixed traffic flow of connected vehicles considering time delay[J].Journal of South China University of Technology(Natural Science Edition),2023,51(1):106-113.
|
| 9 |
FEI M, HAN S, LIN S,et al .Data-driven robust taxi dispatch under demand uncertainties[J].IEEE Transactions on Control Systems Technology,2019,27(1):175-191.
|
| 10 |
SUTTON R, BARTO A .Reinforcement learning:an introduction[J].IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks,2015,16:285-286.
|
| 11 |
WEN J, ZHAO J, JAILLET P .Rebalancing shared mobility-on-demand systems:a reinforcement learning approach[C]∥2017 IEEE 20th International Conference on Intelligent Transportation Systems (ITSC).Yokohama:IEEE,2017:220-225.
|
| 12 |
LIU Z D, LI J Z, WU K S .Context-aware taxi dispatching at city-scale using deep reinforcement learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2022,23:1996-2009.
|
| 13 |
RONG H G, ZHOU X, YANG C,et al .The rich and the poor:a Markov decision process approach to optimizing taxi driver revenue efficiency[C]∥Proceedings of the 25th ACM International on Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.New York:ACM,2016:2329-2334.
|
| 14 |
FENG J K, GLUZMAN M O, DAI J G .Scalable deep reinforcement learning for ride-hailing[J].IEEE Control Systems Letters,2021,5:2060-2065.
|
| 15 |
LIU Z D, LI J Z and WU K .Context-aware taxi dispatching at city-scale using deep reinforcement learning[J].IEEE Transactions on Intelligent Transportation Systems,2020,23(3):1996-2009.
|
| 16 |
LIN K X, ZHAO R Y, XU Z,et al .Efficient large-scale fleet management via multi-agent deep reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.New York:ACM,2018:1774-1783.
|
| 17 |
SHOU Z Y, DI X, YE J P,et al .Optimal passenger-seeking policies on e-hailing platforms using aarkov decision process and imitation learning[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2020,111(2):91-113.
|
| 18 |
王福建,程慧玲,马东方,等 .基于深度逆向强化学习的城市车辆路径链重构[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2023,51(7):120-128.
|
|
WANG Fujian, CHENG Huiling, MA Dongfang,et al .Urban vehicle path chain reconstruction based on deep inverse reinforcement learning[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2023,51(7):120-128.
|
| 19 |
ZHOU M, JIN J R, ZHANG W N,et al .Multi-agent reinforcement learning for order-dispatching via order-vehicle distribution matching[C]∥Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.New York:ACM,2019:2645-2653.
|
| 20 |
TAN M .Multi-agent reinforcement learning:independent vs.cooperative agents[C]∥Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Machine Learning.Amherst:Morgan Kaufmann Publishers Inc,1993:330-337.
|
| 21 |
JIAO Y, TANG X C, QIN Z W,et al .Real-world ride-hailing vehicle repositioning using deep reinforcement learning[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2021,130:103289.
|
| 22 |
YANG Y D, LUO R, LI M,et al .Mean field multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the 35th International Conference on Machine Learning.Stockholm:JMLR,2018,80:5571-5580.
|
| 23 |
LI M, QIN Z W, JIAO Y,et al .Efficient ridesharing order dispatching with mean field multi-agent reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceeding of the World Wide Web Conference.New York:ACM,2019:983-994.
|
| 24 |
ZHU Z, KE J, WANG H,et al .A mean-field markov decision process model for spatial-temporal subsidies in ride-sourcing markets[J].Transportation Research Part B:Methodological,2021,150:540-565.
|
| 25 |
SHOU Z Y, DI X .Reward design for driver repositioning using multi-agent reinforcement learning[J].Transportation Research Part C:Emerging Technologies,2020,119:102738.
|
| 26 |
LOWE R, WU Y, TAMAR A,et al .Multi-agent actor-critic for mixed cooperative competitive environments[C]∥Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.New York:Curran Associates Inc,2017:6382-6393.
|
| 27 |
JIN J, ZHOU M, ZHANG W N,et al .Coride:joint order dispatching and fleet management for multi-scale ride-hailing platforms[C]∥Proceedings of the 28th ACM International Conference on Information and Knowledge Management.New York:ACM,2019:1983-1992.
|
| 28 |
XU Z, LI Z X, GUAN Q W,et al .Large-scale order dispatch in on-demand ride-hailing platforms:a learning and planning approach[C]∥Proceedings of the 24th ACM SIGKDD International Conference on Knowledge Discovery and Data Mining.New York:ACM,2018:905-913.
|
| 29 |
DAI H J, KHAKIK E, ZAHNG Y Y,et al .Learning combinatorial optimization algorithms over graphs[C]∥Proceedings of the 31st International Conference on Neural Information Processing Systems.New York:ACM,2017:6351-6361.
|
| 30 |
闫军威,黄琪,周璇 .基于Double-DQN的中央空调系统节能优化运行[J].华南理工大学学报(自然科学版),2019,47(1):135-144.
|
|
YAN Junwei, HUANG Qi, ZHOU Xuan .Energy-saving optimization operation of central air-conditioning system based on double-DQN algorithm[J].Journal of South China University of Technology (Natural Science Edition),2019,47(1):135-144.
|
| 31 |
BELLO I, PHAM H, LE Q,et al .Neural combinatorial optimization with reinforcement learning[J].Learning,2016,18:487-494.
|
| 32 |
YAN C W, ZHU H L, KOROLKO N,et al .Dynamic pricing and matching in ride-hailing platforms[J].Naval Research Logistics(NRL),2020,67(8):705-724.
|
| 33 |
ZHOU J, CUI G Q, HU S D,et al .Graph neural networks:a review of methods and applications[J].AI Open,2020,1:57-81.
|
| 34 |
WANG Y, SUN Y B, LIU Z W,et al .Dynamic graph CNN for learning on point clouds[J].ACM Transactions on Graphics,2019,38(5):1-12.
|
| 35 |
TOMAR M, EFRONI Y, GHAVAMZADEH M .Multi-step greedy reinforcement learning algorithms[C]∥Proceedings of the 37th International Conference on Machine Learning.Vienna:PMLR,2020:9504-9513.
|
| 36 |
YE D H, LIU Z, SUN M F,et al .Mastering complex control in MOBA games with deep reinforcement learning[C]∥Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence.Menlo Park:AAAI,2020:6672-6667.
|