华南理工大学学报(自然科学版) ›› 2024, Vol. 52 ›› Issue (1): 147-156.doi: 10.12141/j.issn.1000-565X.220835
• 物理学 • 上一篇
微纳挠曲电结构力电耦合响应的数值模拟方法
- 华南理工大学 土木与交通学院,广东 广州 510640
Numerical Simulation of Electromechanical Coupling Response of Nano Flexoelectric Structures
- School of Civil Engineering and Transportation,South China University of Technology,Guangzhou 510640,Guangdong,China
摘要:
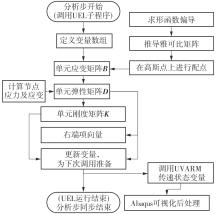
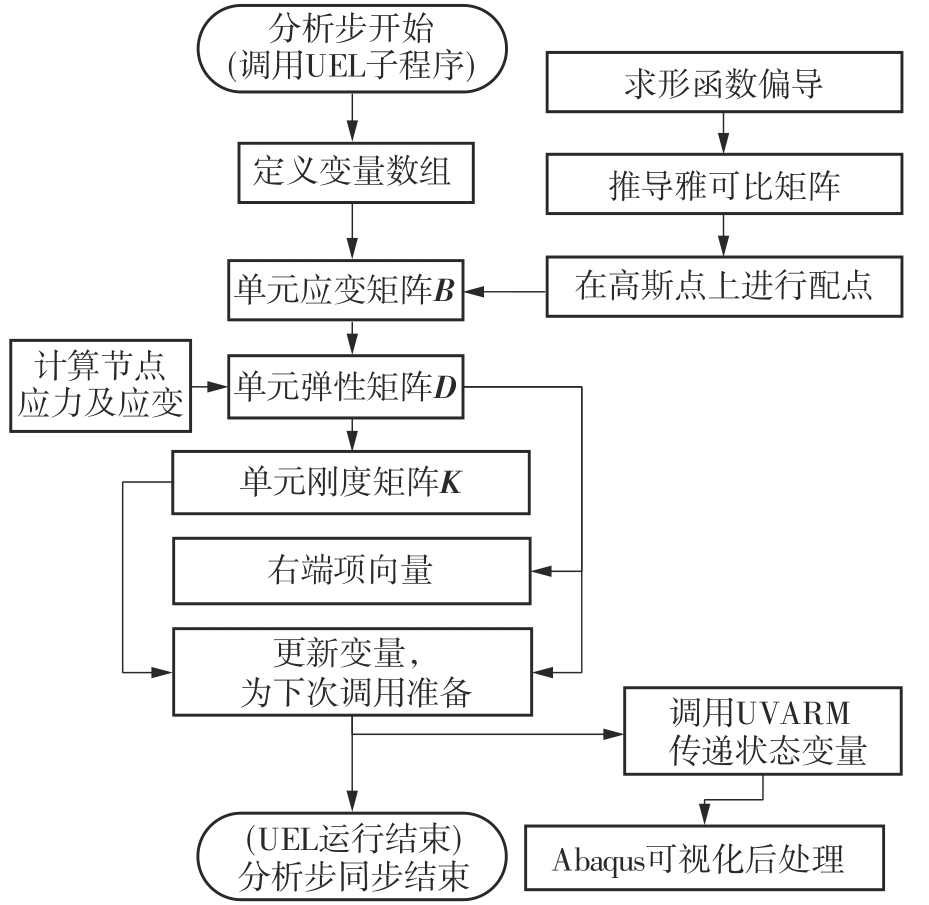
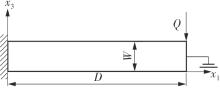
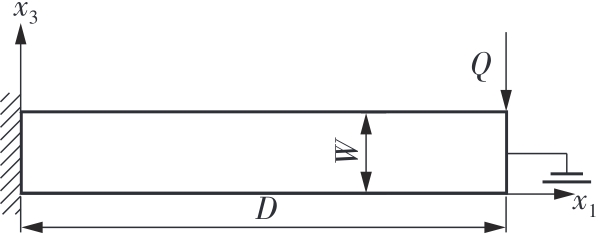
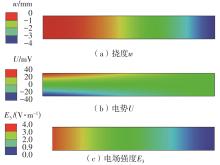
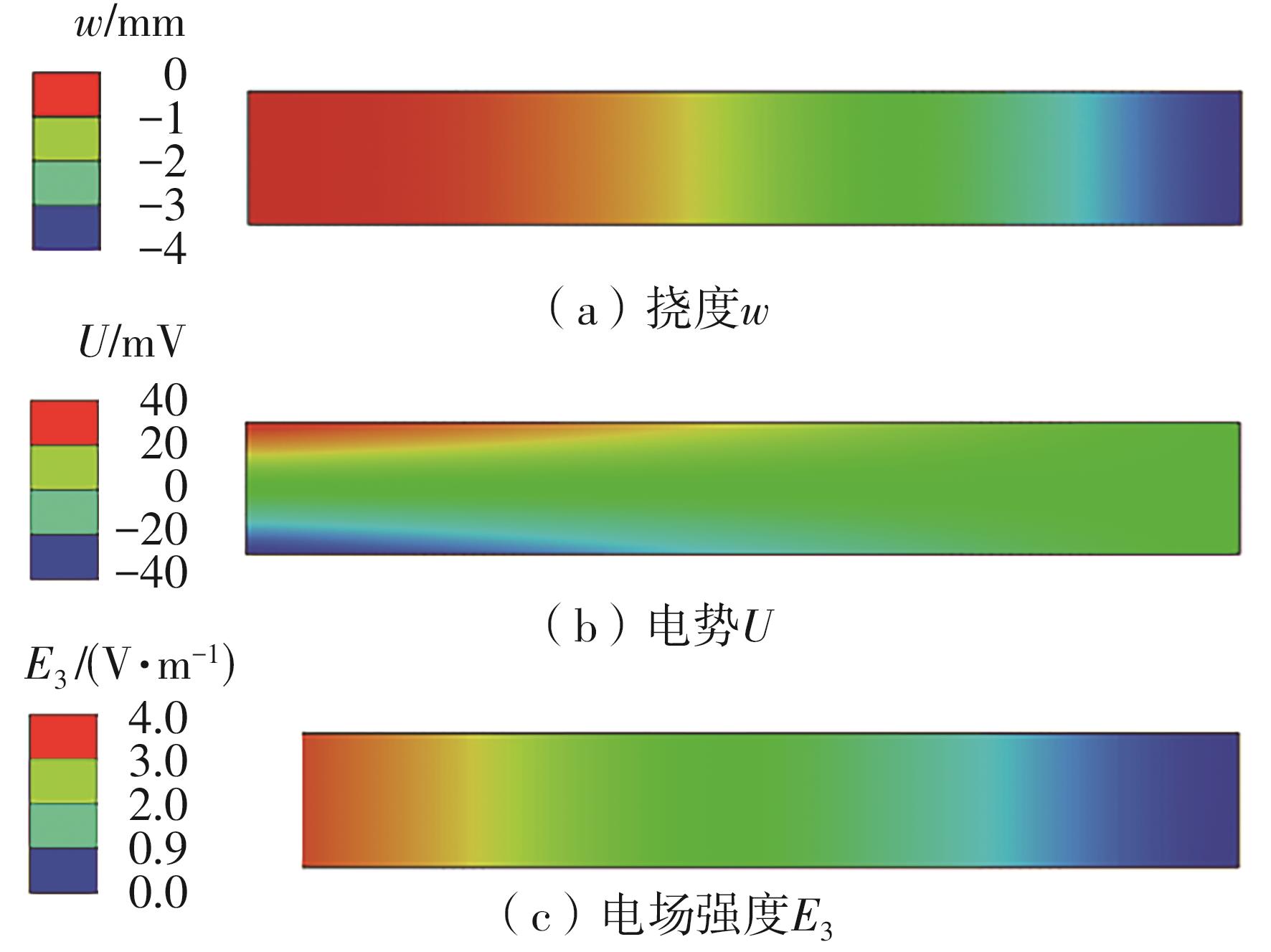
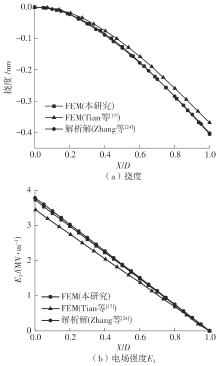
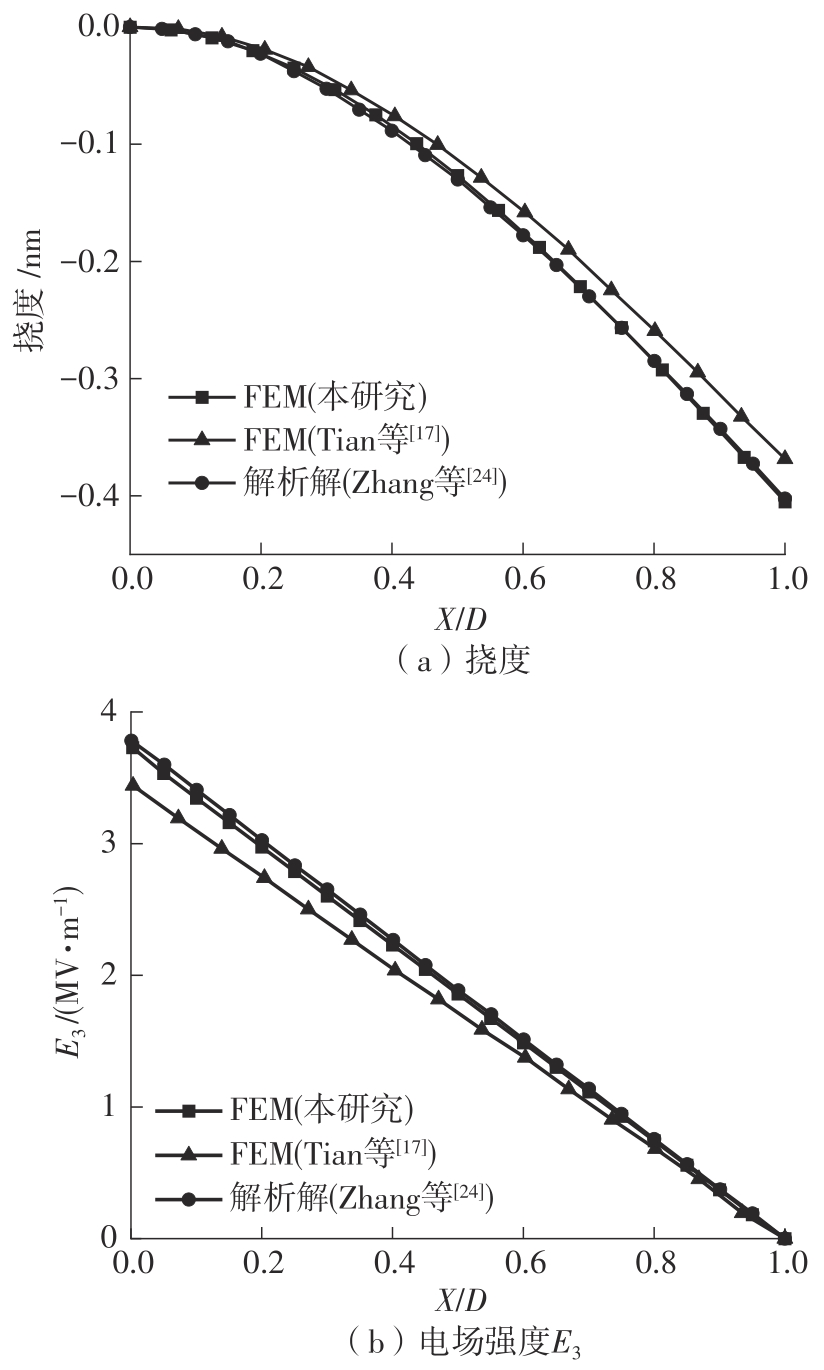
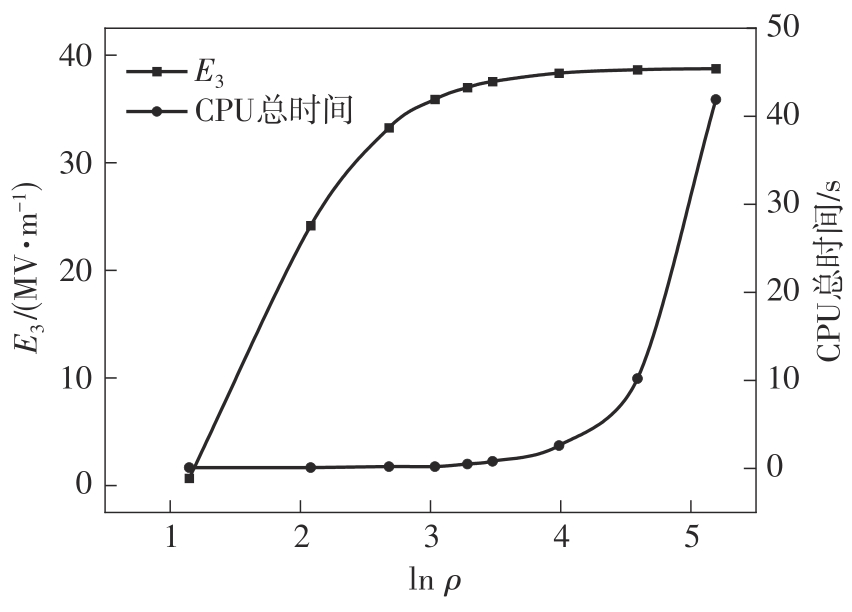
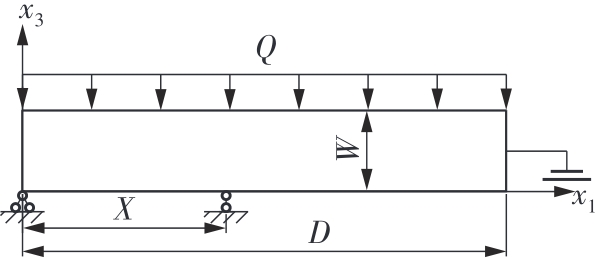
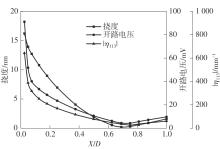
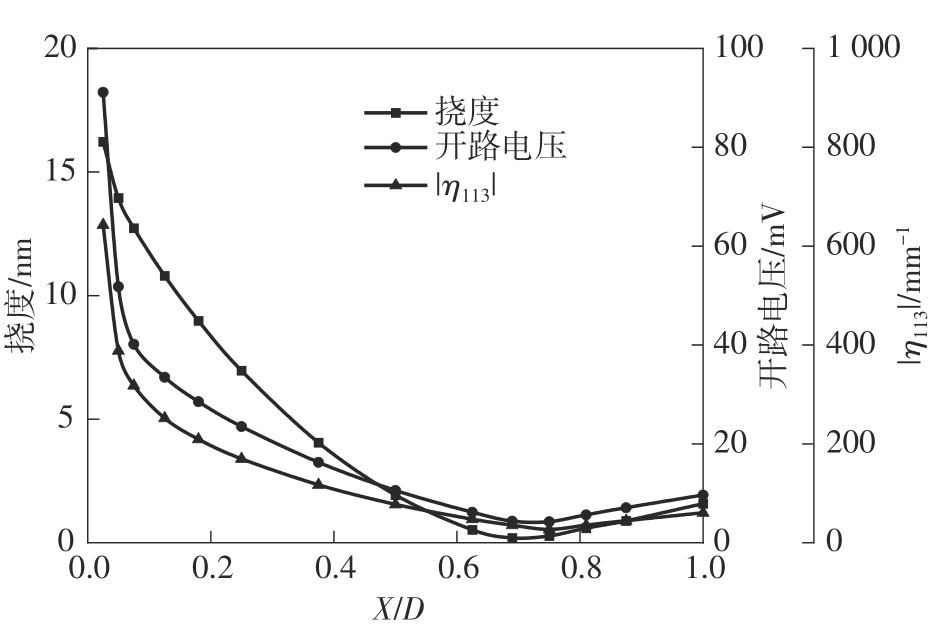
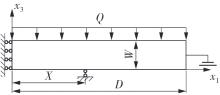
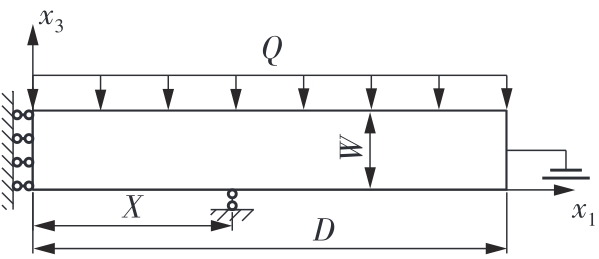
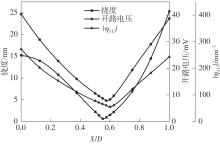
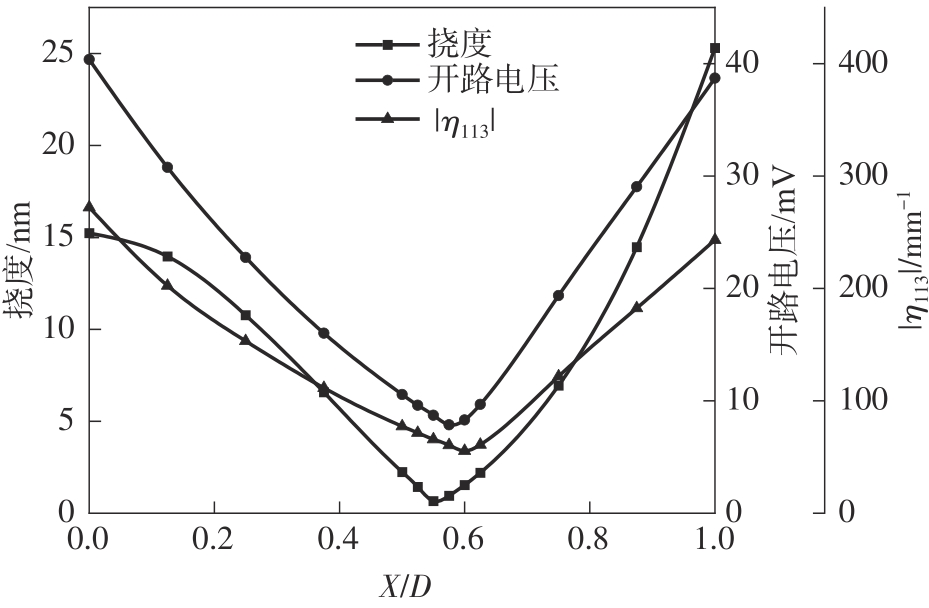
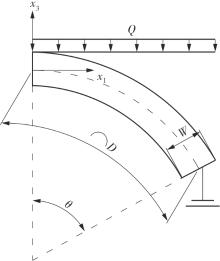
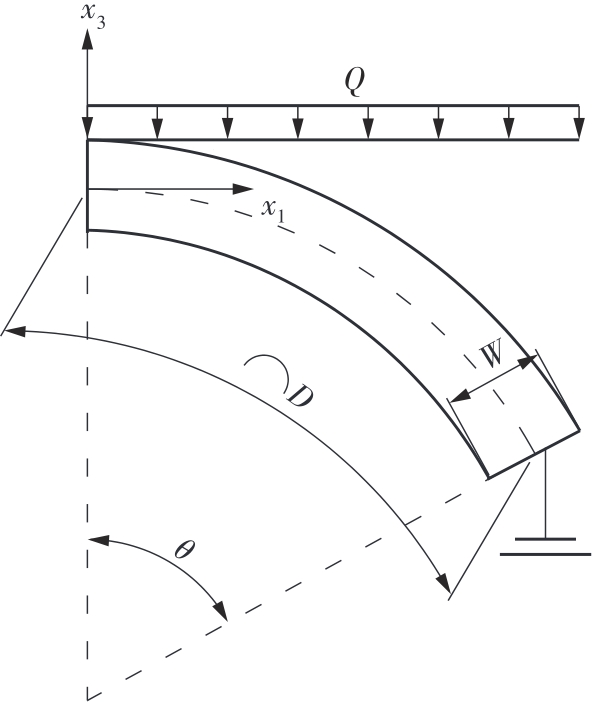
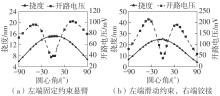
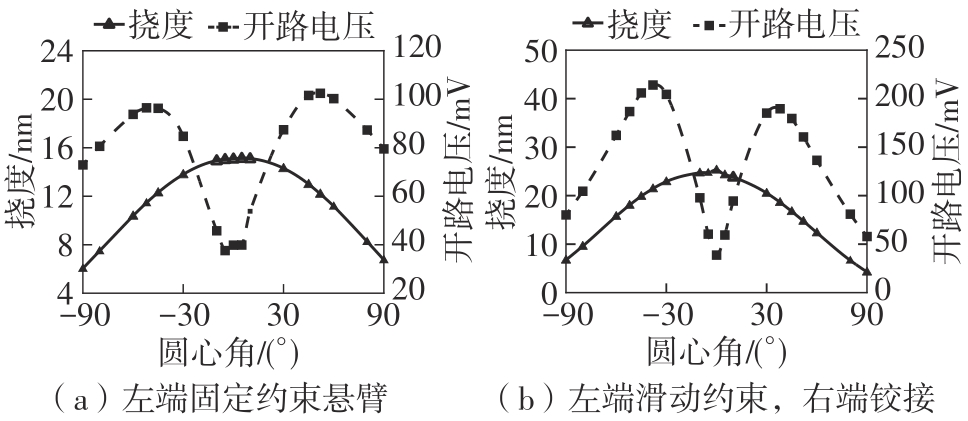
微纳米尺度下挠曲电效应相对于传统压电效应具有较高的机电耦合转换效率,其在传感、致动和俘能领域极具应用前景。然而目前多数商用有限元软件未包含挠曲电本构模型,无法对挠曲电结构进行有效的数值模拟。本研究基于Abaqus用户自定义单元(UEL)子程序进行二次开发,将挠曲电效应内化到计算模型。首先,结合配点混合有限元法(CMFEM),推导了挠曲电结构的力电耦合方程,并在Abaqus中开发了挠曲电单元,提供了挠曲电结构响应分析的数值模拟技术。与传统的混合有限元法(MFEM)相比,该方法的优点是易于建模,降低了计算自由度,提高了计算效率,节省了运算成本,并且挠度与电场强度指标都比其他方法更接近解析解。然后,通过上述数值模拟方法,建立了挠曲电结构响应分析数值模型,开展了矩形梁及弧形梁在不同边界条件下的力电耦合响应计算与分析。分析结果展示了梁的几何参数影响结构应变梯度
中图分类号: