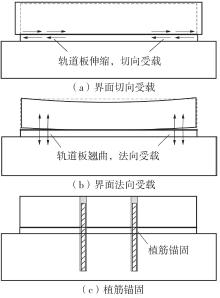
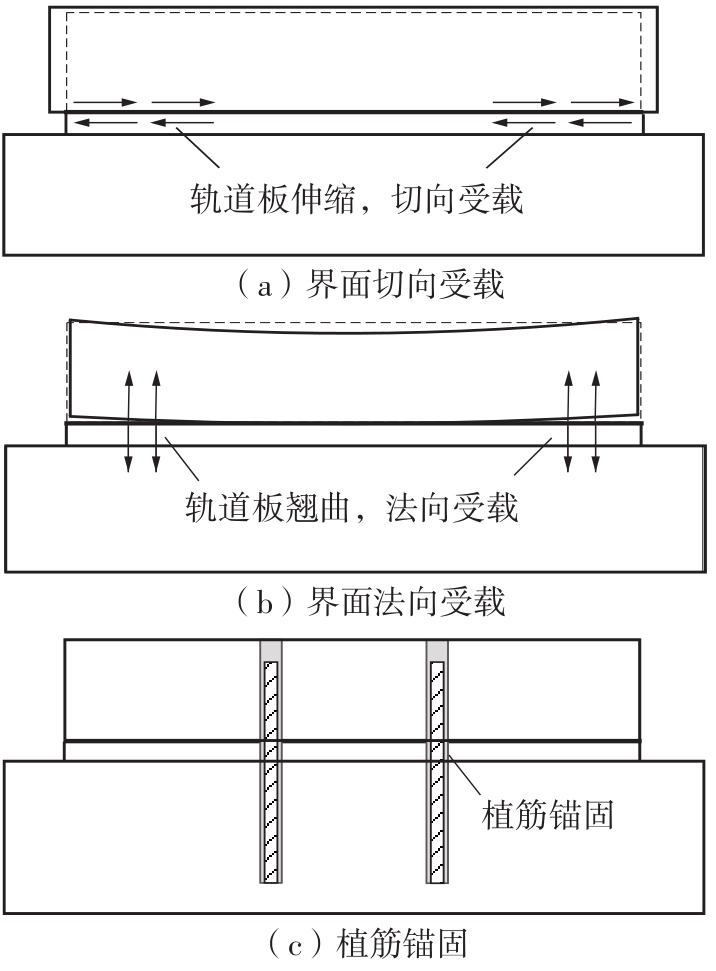
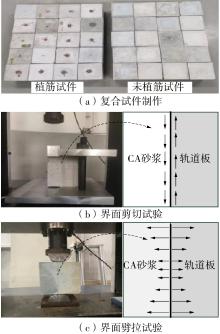
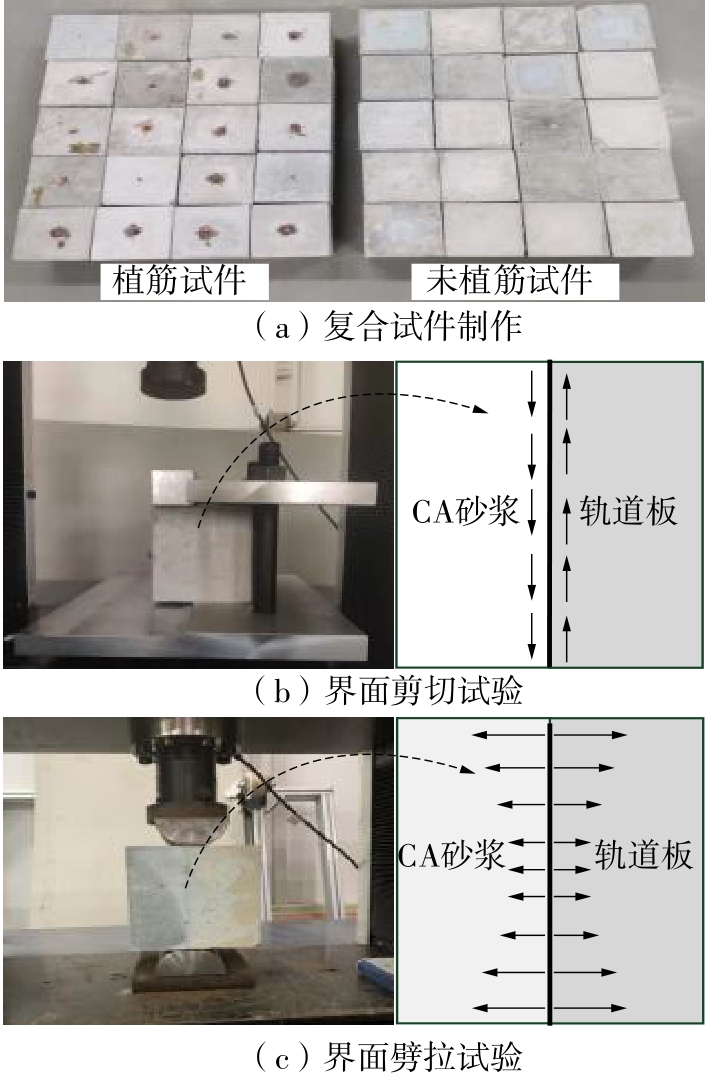
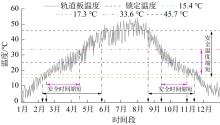
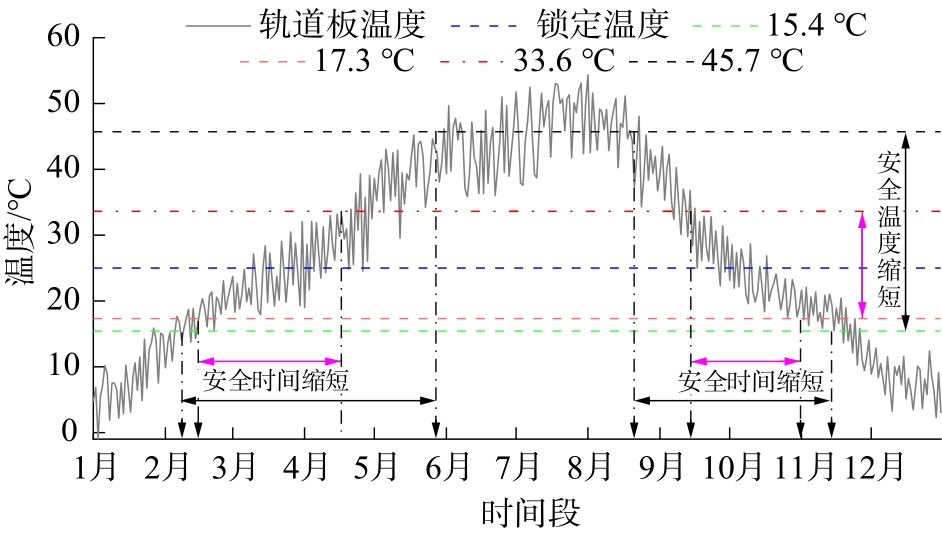
| 1 |
赵国堂,刘钰 .CRTSⅡ型板式无砟轨道结构层间离缝机理研究[J].铁道学报,2020,42(7):117-126.
|
|
ZHAO Guotang, LIU Yu .Mechanism analysis of delamination of CRTSⅡ slab ballastless track structure[J].Journal of the China Railway Society,2020,42(7):117-126.
|
| 2 |
CAI X P, LUO B C, ZHONG Y L,et al .Arching mechanism of the slab joints in CRTSII slab track under high temperature conditions[J].Engineering Failure Analysis,2019,98:95-108.
|
| 3 |
许玉德,缪雯颖,严道斌,等 .离缝修复条件下无砟轨道板温度翘曲变形特征[J].同济大学学报(自然科学版),2021,49(3):400-410.
|
|
XU Yude, MIAO Wenying, YAN Daobin,et al .War-ping features of ballastless track-slab under debonding-repaired condition[J].Journal of Tongji University(Natural Science),2021,49(3):400-410.
|
| 4 |
SONG L, LIU H B, CUI C X,et al .Thermal deformation and interfacial separation of a CRTS II slab ballastless track multilayer structure used in high-speed railways based on meteorological data[J].Construction and Buil-ding Materials,2020,237:117528/1-16.
|
| 5 |
HUANG Y C, GAO L, ZHONG Y L,et al .Study on the damage evolution of the joint and the arching deformation of CRTS-II ballastless slab track under complex temperature loading[J].Construction and Building Materials,2021,309:125083/1-12.
|
| 6 |
粟淼,朱琦治,戴公连,等 .考虑界面起始黏结缺陷的CRTS Ⅱ型板式无砟轨道温度变形[J].交通运输工程学报,2020,20(5):73-81.
|
|
SU Miao, ZHU Qizhi, DAI Gonglian,et al .Temperature deformation of CRTS II slab ballastless track conside-ring interfacial initial bond defects[J].Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2020,20(5):73-81.
|
| 7 |
钟阳龙,高亮,侯博文 .不同植筋方案纵连板轨道砂浆层抗剪性能分析[J].西南交通大学学报,2018,53(1):38-45,63.
|
|
ZHONG Yanglong, GAO Liang, HOU Bowen .Shear behavior of mortar layer in continuous slab track with different arrangement schemes of embedded steel bars[J].Journal of Southwest Jiaotong University,2018,53(1):38-45,63.
|
| 8 |
杨俊,陈瑞,张中亚,等 .植筋参数对UHPC-石材界面抗剪性能的影响研究[J].土木工程学报,2022,55(6):62-78.
|
|
YANG Jun, CHEN Rui, ZHANG Zhongya,et al .Effects of planting bar parameters on the shear resistance of UHPC-Stone interface[J].China Civil Engineering Journal,2022,55(6):62-78.
|
| 9 |
闫斌,刘施,戴公连,等 .我国典型地区无砟轨道非线性温度梯度及温度荷载模式[J].铁道学报,2016,38(8):81-86.
|
|
YAN Bin, LIU Shi, DAI Gonglian,et al .Vertical nonlinear temperature distribution and temperature mode of unballasted track in typical areas of China[J].Journal of the China Railway Society,2016,38(8):81-86.
|
| 10 |
刘昊旻,路宏遥,何越磊,等 .基于优化气象参数的轨道板内部温度试验研究与预测分析[J].铁道科学与工程学报,2019,16(5):1120-1128.
|
|
LIU Haomin, LU Hongyao, HE Yuelei,et al .Experimental study and prediction analysis of internal temperature of track slab based on optimized meteorological parameters[J].Journal of Railway Science and Enginee-ring,2019,16(5):1120-1128.
|
| 11 |
ZHOU R, ZHU X, REN W X,et al .Thermal evolution of CRTS Ⅱ slab track under various environmental temperatures:experimental study[J].Construction and Building Materials,2022,325:126699/1-17.
|
| 12 |
何越磊,黄自鹏,路宏遥,等 .温度荷载作用下高铁无砟轨道界面性能演变规律研究[J].铁道标准设计,2023,67(4):47-53.
|
|
HE Yuelei, HUANG Zipeng, LU Hongyao,et al .Study on the evolution law of interface performance of high-speed railway ballastless track under temperature load[J].Railway Standard Design,2023,67(4):47-53.
|
| 13 |
REN J J, WANG J, LI X,et al .Influence of cement asphalt mortar debonding on the damage distribution and mechanical responses of CRTS I prefabricated slab[J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,230:116995/1-12.
|
| 14 |
ZHU W F, CHEN X J, LI Z W,et al .A SAFT method for the detection of void defect inside a ballastless track structure using ultrasonic array sensors[J].Sensors,2019,19(21):4677/1-12.
|
| 15 |
LI Z W, LIU X Z, LU H Y,et al .Surface crack detection in precasted slab track in high-speed rail via infrared thermography[J].Materials,2020,13(21):4837/1-16.
|
| 16 |
田冬梅,邓德华,彭建伟,等 .温度对水泥乳化沥青砂浆层与混凝土层间界面黏结影响[J].铁道学报,2013,35(11):78-85.
|
|
TIAN Dongmei, DENG Dehua, PENG Jianwei,et al .Influence of temperature on interfacial bongding between cement emulsified asphalt mortar layer and concrete layer[J].Journal of the China Railway Society,2013,35(11):78-85.
|
| 17 |
赵春发,刘建超,毛海和,等 .温度梯度荷载作用下CRTS Ⅱ型板式无砟轨道砂浆层界面损伤分析[J].中国科学:技术科学,2018,48(1):79 -86.
|
|
ZHAO Chunfa, LIU Jianchao, MAO Haihe,et al .Interface damage analysis of CA mortar layer of the CRTS II ballastless slab track under temperature gradient loads[J].Scientia Sinica(Technologica),2018,48(1):79 -86.
|
| 18 |
勾红叶,刘畅,班新林,等 .高速铁路桥梁-轨道体系检测监测与行车安全研究进展[J].交通运输工程学报,2022,22(1):1-23.
|
|
GOU Hongye, LIU Chang, BAN Xinlin,et al .Research progress of detection,monitoring and running safety of bridge-track system for high-speed railway[J].Journal of Traffic and Transportation Engineering,2022,22(1):1-23.
|
| 19 |
许玉德,缪雯颖,严道斌,等 .基于改进混合模式内聚力模型的无砟轨道层间损伤分析[J].铁道学报,2021,43(4):125-135.
|
|
XU Yude, MIAO Wenying, YAN Daobin,et al .Analysis of interlayer interface damage in ballastless track based on improved mixed-mode cohesive zone model[J].Journal of the China Railway Society,2021,43(4):125-135.
|
| 20 |
XU Y D, YAN D B, ZHU W J,et al .Study on the mechanical performance and interface damage of CRTS II slab track with debonding repairment[J].Construction and Building Materials,2020,257:119600/1-16.
|
| 21 |
OINONEN A, MARQUIS G .A constitutive model for interface problems with frictional contact and cohesion[J].European Journal of Mechanics - A/Solids,2015,49:205-213.
|